2007 TOYOTA SIENNA ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 37 of 3000
EM–382GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE ASSEMBLY
EM
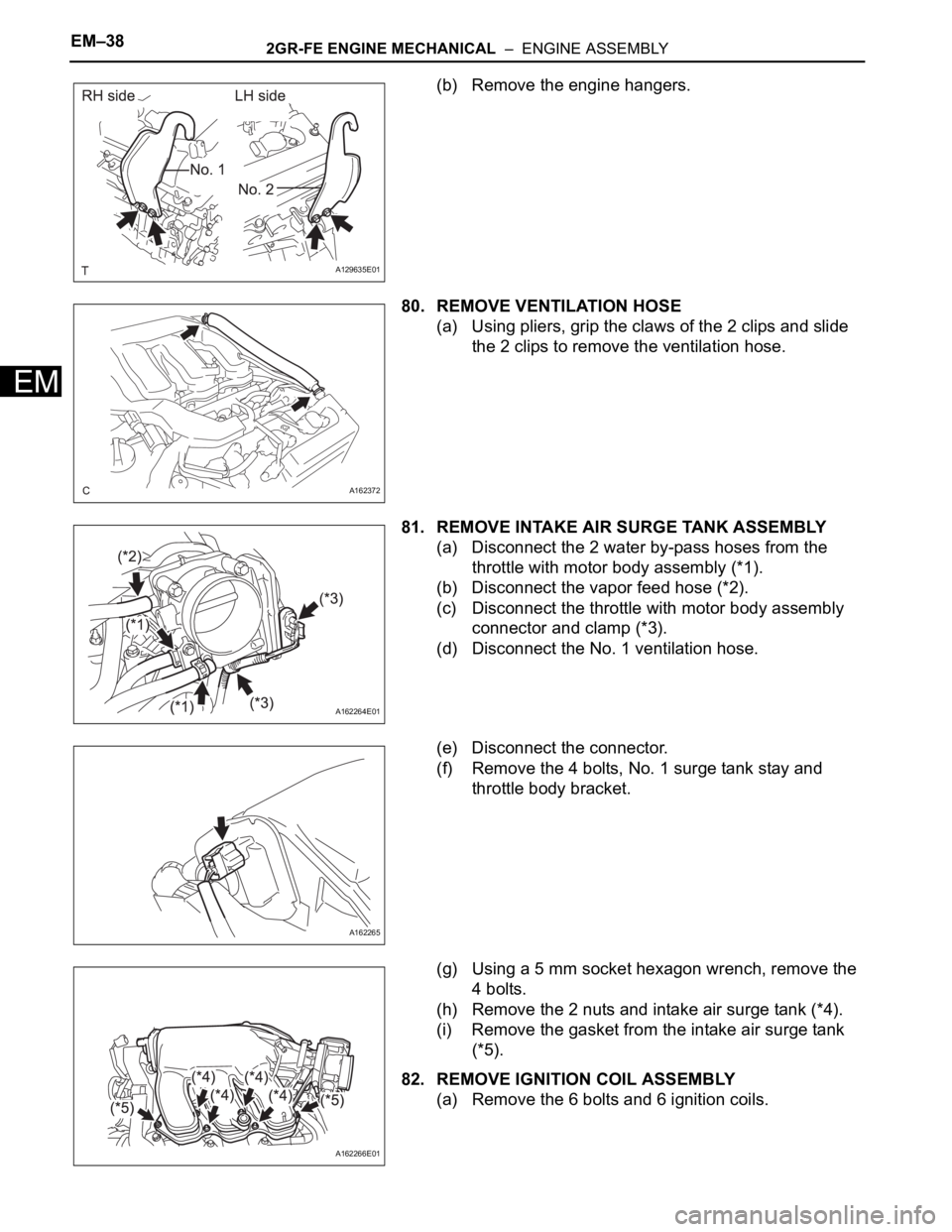
(b) Remove the engine hangers.
80. REMOVE VENTILATION HOSE
(a) Using pliers, grip the claws of the 2 clips and slide
the 2 clips to remove the ventilation hose.
81. REMOVE INTAKE AIR SURGE TANK ASSEMBLY
(a) Disconnect the 2 water by-pass hoses from the
throttle with motor body assembly (*1).
(b) Disconnect the vapor feed hose (*2).
(c) Disconnect the throttle with motor body assembly
connector and clamp (*3).
(d) Disconnect the No. 1 ventilation hose.
(e) Disconnect the connector.
(f) Remove the 4 bolts, No. 1 surge tank stay and
throttle body bracket.
(g) Using a 5 mm socket hexagon wrench, remove the
4 bolts.
(h) Remove the 2 nuts and intake air surge tank (*4).
(i) Remove the gasket from the intake air surge tank
(*5).
82. REMOVE IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the 6 bolts and 6 ignition coils.
A129635E01
A162372
A162264E01
A162265
A162266E01
Page 57 of 3000

IN–50INTRODUCTION – TERMS
IN
GLOSSARY OF SAE AND TOYOTA
TERMS
This glossary lists all SAE-J1930 terms and abbreviations
used in this manual in compliance with SAE
recommendations, as well as their TOYOTA equivalents.
SAE
ABBREVIATIONSSAE TERMSTOYOTA TERMS
( )-ABBREVIATIONS
A/C Air Conditioning Air Conditioner
ACL Air Cleaner Air Cleaner, A/CL
AIR Secondary Air Injection Air Injection (AI)
AP Accelerator Pedal -
B+ Battery Positive Voltage +B, Battery Voltage
BARO Barometric Pressure HAC
CAC Charge Air Cooler Intercooler
CARB Carburetor Carburetor
CFI Continuous Fuel Injection -
CKP Crankshaft Position Crank Angle
CL Closed Loop Closed Loop
CMP Camshaft Position Cam Angle
CPP Clutch Pedal Position -
CTOX Continuous Trap Oxidizer -
CTP Closed Throttle Position LL ON, Idle ON
DFI Direct Fuel Injection Direct Injection (DI./INJ)
DI Distributor Ignition -
DLC3 Data Link Connector 3 OBD II Diagnostic Connector
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code Diagnostic Trouble Code
DTM Diagnostic Test Mode -
ECL Engine Coolant Level -
ECM Engine Control Module Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature Coolant Temperature, Water Temperature (THW)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only MemoryElectrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM), Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EPROM)
EFE Early Fuel Evaporation Cold Mixture Heater (CMH), Heat Control Valve (HCV)
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
EI Electronic Ignition Distributorless Ignition (DLI)
EM Engine Modification Engine Modification (EM)
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM)
EVAP Evaporative Emission Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP)
FC Fan Control -
FEEPROMFlash Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory-
FEPROM Flash Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory -
FF Flexible Fuel -
FP Fuel Pump Fuel Pump
GEN Generator Alternator
GND Ground Ground (GND)
HO2S Heated Oxygen SensorHeated Oxygen Sensor (HO
2S)
IAC Idle Air Control Idle Speed Control (ISC)
IAT Intake Air Temperature Intake or Inlet Air Temperature
ICM Ignition Control Module -
Page 60 of 3000

IN–30INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU
CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
GENERAL INFORMATION
A large number of ECU controlled systems are used in the
SIENNA. In general, ECU controlled systems are considered
to be very intricate, requiring a high level of technical
knowledge to troubleshoot. However, most problem checking
procedures only involve inspecting the ECU controlled
system's circuits one by one. An adequate understanding of
the system and a basic knowledge of electricity is enough to
perform effective troubleshooting, accurate diagnoses and
necessary repairs.
FOR USING INTELLIGENT TESTER
– Before using the intelligent tester, read the tester
operator's manual thoroughly.
– If the tester cannot communicate with the ECU controlled
systems when the tester is connected to the DLC3 with the
ignition switch on and the tester turned on, there is a
problem on the vehicle side or tester side.
(1) If communication is normal when the tester is
connected to another vehicle, inspect the diagnosis
data link line (Bus (+) line) or ECU power circuit of the
vehicle.
(2) If communication is still not possible when the tester is
connected to another vehicle, the problem is probably
in the tester itself. Perform the Self Test procedures
outlined in the tester operator's manual.
Page 64 of 3000

IN–34INTRODUCTION – HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT ECU CONTROLLED SYSTEMS
IN
3. CHECK FOR SHORT CIRCUIT
(a) If the wire harness is ground shorted (Fig. 5), locate
the section by conducting a resistance check with
the body ground (below).
(b) Check the resistance with the body ground.
(1) Disconnect connectors A and C and measure
the resistance.
Standard resistance (Fig. 6)
HINT:
Measure the resistance while lightly shaking the
wire harness vertically and horizontally. If your
results match the examples above, an open
circuit exists between terminal 1 of connector A
and terminal 1 of connector C.
(2) Disconnect connector B and measure the
resistance.
Standard resistance (Fig. 7)
If the results match the examples above, a short
circuit exists between terminal 1 of connector B2
and terminal 1 of connector C.
4. CHECK AND REPLACE ECU
NOTICE:
• The connector should not be disconnected from
the ECU. Perform the inspection from the
backside of the connector on the wire harness
side.
• When no measuring condition is specified,
perform the inspection with the engine stopped
and the ignition switch on.
• Check that the connectors are fully seated. Check
for loose, corroded or broken wires.
Z017008E02
Z017009E02
Tester Connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Body
groundBelow 1
Connector A terminal 2 - Body
ground10 k or higher
Z017808E02
Tester Connection Specified Condition
Connector A terminal 1 - Body
ground10 k
or higher
Connector B2 terminal 2 - Body
ground Below 1
Page 76 of 3000

2GR-FE COOLING – COOLING FAN SYSTEMCO–5
CO
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1. INSPECT COOLING FAN SYSTEM
(a) Put the vehicle in the following conditions:
(1) The engine switch is off.
(2) The coolant temperature is less than 95
C
(203
F).
(3) The battery voltage is between 9 and 14 V.
(4) The A/C switch is OFF.
(b) Clamp the 400 A probe of an ammeter over the M+
wire of each cooling fan motor.
(c) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and wait
for approximately 10 seconds. Check that the fan
stops.
(d) Start the engine. Check that the fan stops with the
engine idling.
HINT:
• Make sure that the radiator engine coolant
temperature is less than 95
C (203F).
• Turn the A/C switch OFF.
(e) Check that the fan operates when the A/C switch is
turned ON (MAX COOL and the magnetic clutch is
operating).
Standard current
HINT:
The coolant temperature is less than 95
C (203F).
(f) Check that the fan operates when the engine
coolant temperature sensor connector is
disconnected.
Standard current
Item Specified Condition
No. 1 cooling fan motor 5 to 14 A
No. 2 cooling fan motor 4 to 12 A
Item Specified Condition
No. 1 cooling fan motor 5 to 19 A
No. 2 cooling fan motor 4 to 16 A
Page 80 of 3000

IG–62GR-FE IGNITION – IGNITION COIL AND SPARK PLUG
IG
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
NOTICE:
In this section, the terms "cold" and "hot" refer to the
temperature of the coils. "Cold" means approximately -
10
C (14F) to 50C (122F). "Hot" means approximately
50
C (122F) to 100C (212F).
1. INSPECT IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY
(a) Check for DTCs.
NOTICE:
If any DTC is present, perform troubleshooting
in accordance with the procedures for that DTC.
(b) Remove the ignition coil assembly and spark plug.
(See page IG-8).
(c) Check that sparks occur.
(1) Disconnect the 6 fuel injector connectors.
(2) Install the spark plugs to each ignition coil, and
connect the ignition coil connectors.
(3) Ground the spark plugs.
(4) Check if a spark occurs at each spark plug
while the engine is being cranked.
NOTICE:
• Be sure to ground the spark plugs when
checking.
• Replace the ignition coil if it receives an
impact.
• Do not crank the engine for more than 2
seconds.
(d) Perform the spark test according to the flowchart
below.
(1) Check that the ignition coil connector is
securely connected.
Result
(2) Perform a spark test on each ignition coil.
1. Replace the ignition coil with a normal one.
2. Perform the spark test again.
Result
A133895
A133897
Result Proceed to
NG Connect securely
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NG Go to next step
OK Replace ignition coil
Page 81 of 3000

2GR-FE IGNITION – IGNITION COIL AND SPARK PLUGIG–7
IG
(3) Check the spark plug (See page EM-1).
Result
(4) Check the power supply to the ignition coil.
1. Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
2. Check that there is battery voltage at the
ignition coil positive (+) terminal.
Result
(5) Measure the resistance of the crankshaft
position sensor (See page ES-514).
Result
(6) Check the IGT signal from the ECM (See page
ES-233)
Result
(e) Using a 16 mm (0.63 in.) plug wrench, install the
spark plugs.
Torque: 18 N*m (184 kgf*cm, 13 ft.*lbf)
(f) Connect the 6 fuel injector connectors.
(g) Install the ignition coil assembly (See page IG-10).
2. INSPECT SPARK PLUG
NOTICE:
• Never use a wire brush for cleaning.
• Never attempt to adjust the electrode gap on a
used spark plug.
(a) Check the electrode.
(1) Using a megohmmeter, measure the insulation
resistance.
Standard insulation resistance:
10 M
or higher
HINT:
• If the result is 10 M
or less, clean the plug
and measure the resistance again.
• If a megohmmeter is not available, perform
the following simple inspection instead.
(b) Alternative inspection method:
(1) Quickly accelerate the engine to 4000 rpm 5
times.
Result Proceed to
NG Replace spark plug
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NGCheck wiring between ignition
switch and ignition coil
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NG Replace crankshaft position sensor
OK Go to next step
Result Proceed to
NG Check ECM
OKRepair wiring between ignition coil
and ECM
I039522E10
Page 82 of 3000

IG–82GR-FE IGNITION – IGNITION COIL AND SPARK PLUG
IG
(2) Remove the spark plugs.
(3) Visually check the spark plug.
If the electrode is dry, the spark plug is
functioning properly. If the electrode is damp,
proceed to the next step.
(c) Check the spark plug for any damage to its threads
and insulator. If there is damage, replace the spark
plug.
Recommended spark plug
NOTICE:
Use only the listed spark plug or equivalent to
ensure engine performance and smooth
driveability.
(d) Check the spark plug electrode gap.
Maximum electrode gap for used spark plug:
1.4 mm (0.055 in.)
If the gap is greater than the maximum, replace the
spark plug.
Electrode gap for new spark plug:
1.0 to 1.1 mm (0.039 to 0.043 in.)
(e) Clean the spark plugs.
If the electrode has traces of wet carbon, clean the
electrode with a spark plug cleaner and then dry it.
Standard air pressure:
588 kPa (6 kgf*cm
2, 85 psi)
Standard duration:
20 seconds or less
HINT:
Only use the spark plug cleaner when the electrode
is free of oil. If the electrode has traces of oil, use
gasoline to clean off the oil before using the spark
plug cleaner.
(f) Install the ignition coil assembly and spark plug.
(See page IG-10).
Manufacturer Spark Plug Type
DENSO FK20HR11
A163282E01
B062019