2007 TOYOTA SIENNA Thermostat
[x] Cancel search: ThermostatPage 58 of 3000

INTRODUCTION – TERMSIN–51
IN
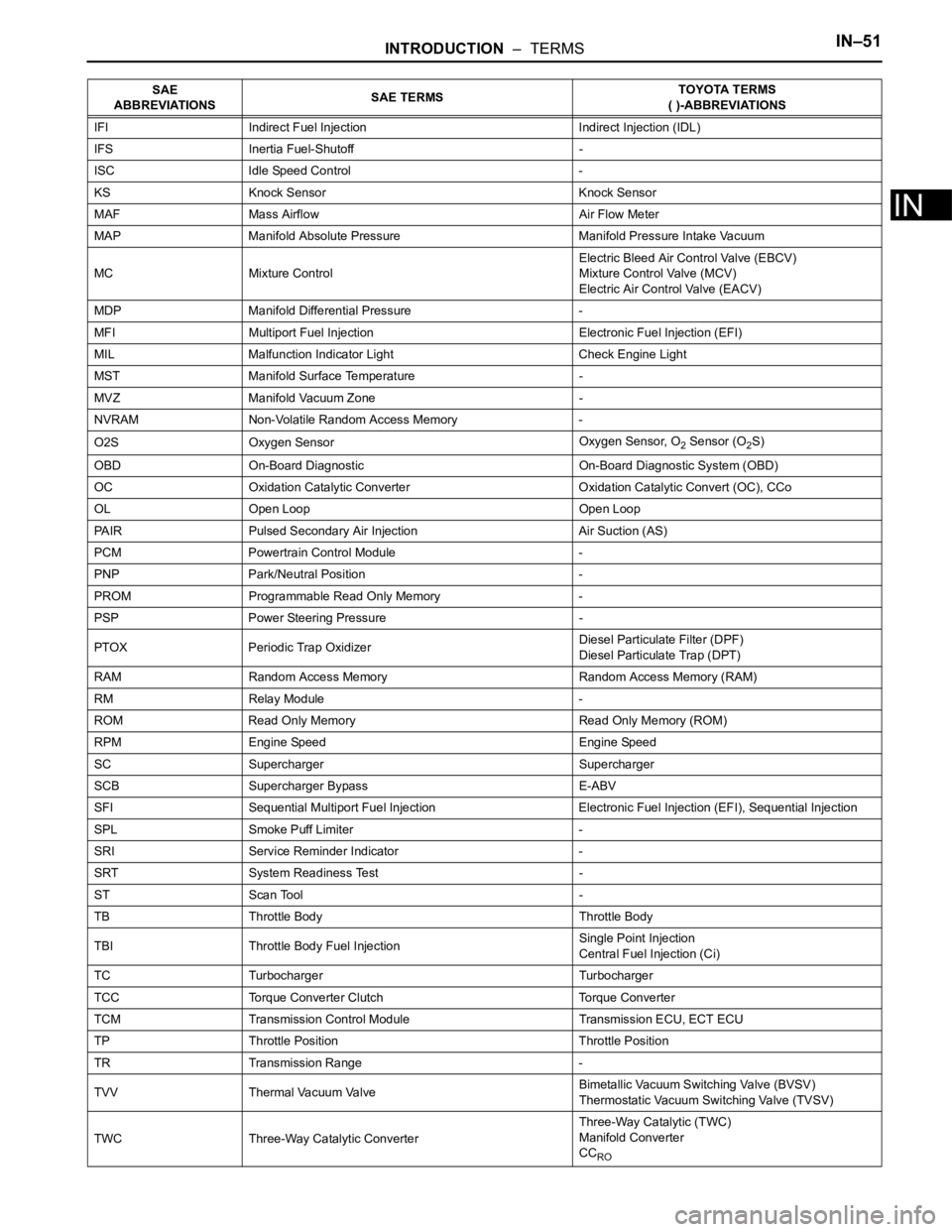
IFI Indirect Fuel Injection Indirect Injection (IDL)
IFS Inertia Fuel-Shutoff -
ISC Idle Speed Control -
KS Knock Sensor Knock Sensor
MAF Mass Airflow Air Flow Meter
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure Manifold Pressure Intake Vacuum
MC Mixture ControlElectric Bleed Air Control Valve (EBCV)
Mixture Control Valve (MCV)
Electric Air Control Valve (EACV)
MDP Manifold Differential Pressure -
MFI Multiport Fuel Injection Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
MIL Malfunction Indicator Light Check Engine Light
MST Manifold Surface Temperature -
MVZ Manifold Vacuum Zone -
NVRAM Non-Volatile Random Access Memory -
O2S Oxygen SensorOxygen Sensor, O
2 Sensor (O2S)
OBD On-Board Diagnostic On-Board Diagnostic System (OBD)
OC Oxidation Catalytic Converter Oxidation Catalytic Convert (OC), CCo
OL Open Loop Open Loop
PAIR Pulsed Secondary Air Injection Air Suction (AS)
PCM Powertrain Control Module -
PNP Park/Neutral Position -
PROM Programmable Read Only Memory -
PSP Power Steering Pressure -
PTOX Periodic Trap OxidizerDiesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
Diesel Particulate Trap (DPT)
RAM Random Access Memory Random Access Memory (RAM)
RM Relay Module -
ROM Read Only Memory Read Only Memory (ROM)
RPM Engine Speed Engine Speed
SC Supercharger Supercharger
SCB Supercharger Bypass E-ABV
SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI), Sequential Injection
SPL Smoke Puff Limiter -
SRI Service Reminder Indicator -
SRT System Readiness Test -
ST Scan Tool -
TB Throttle Body Throttle Body
TBI Throttle Body Fuel InjectionSingle Point Injection
Central Fuel Injection (Ci)
TC Turbocharger Turbocharger
TCC Torque Converter Clutch Torque Converter
TCM Transmission Control Module Transmission ECU, ECT ECU
TP Throttle Position Throttle Position
TR Transmission Range -
TVV Thermal Vacuum ValveBimetallic Vacuum Switching Valve (BVSV)
Thermostatic Vacuum Switching Valve (TVSV)
TWC Three-Way Catalytic ConverterThree-Way Catalytic (TWC)
Manifold Converter
CC
RO
SAE
ABBREVIATIONSSAE TERMSTOYOTA TERMS
( )-ABBREVIATIONS
Page 348 of 3000

ES–222GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
CHECKING MONITOR STATUS
The purpose of the monitor result (mode 06) is to allow
access to the results for on-board diagnostic monitoring tests
of specific components/systems that are not continuously
monitored. Examples are catalyst, evaporative emission
(EVAP) and thermostat.
The monitor result allows the OBD II scan tool to display the
monitor status, test value, minimum test limit and maximum
test limit. These data are displayed after the vehicle has been
driven to run the monitor.
When the test value is not between the minimum test limit
and maximum test limit, the ECM (PCM) interprets this as a
malfunction. When the component is not malfunctioning, if the
difference of the test value and test limit is very small, the
component will malfunction in the near future.
Perform the following instructions to view the monitor status.
Although the Lexus diagnostic tester is used in the following
instructions, it can be checked using a generic OBD II scan
tool. Refer to your scan tool operator's manual for specific
procedures.
1. PERFORM MONITOR DRIVE PATTERN
The monitor results and test values can be checked with
the OBD II scan tool or the intelligent tester. The engine
control module (ECM) monitors the emissions-related
components such as the thermostat, catalyst converter
and evaporative emissions (EVAP), and determines
whether they are functioning normally or not. When
monitoring is finished, the ECM stores the monitor
results and the test values. The monitor result indicates
whether the component is functioning normally or not.
The test value is the value that was used to determine
the monitor result. If the test value is outside of the test
limit (malfunction criterion), the ECM determines the
component is malfunctioning. Some emissions-related
components have multiple test values to determine
monitor result. If one of these test values is outside of the
test limit, the ECM determines the component is
malfunctioning.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Start the engine and turn the tester on.
(c) Clear the DTCs.
(d) Run the vehicle in accordance with the applicable
drive pattern described in READINESS MONITOR
DRIVE PATTERN (See page ES-22). DO NOT turn
the ignition switch off.
NOTICE:
The test results will be lost if the ignition switch
is turned off.
Page 373 of 3000
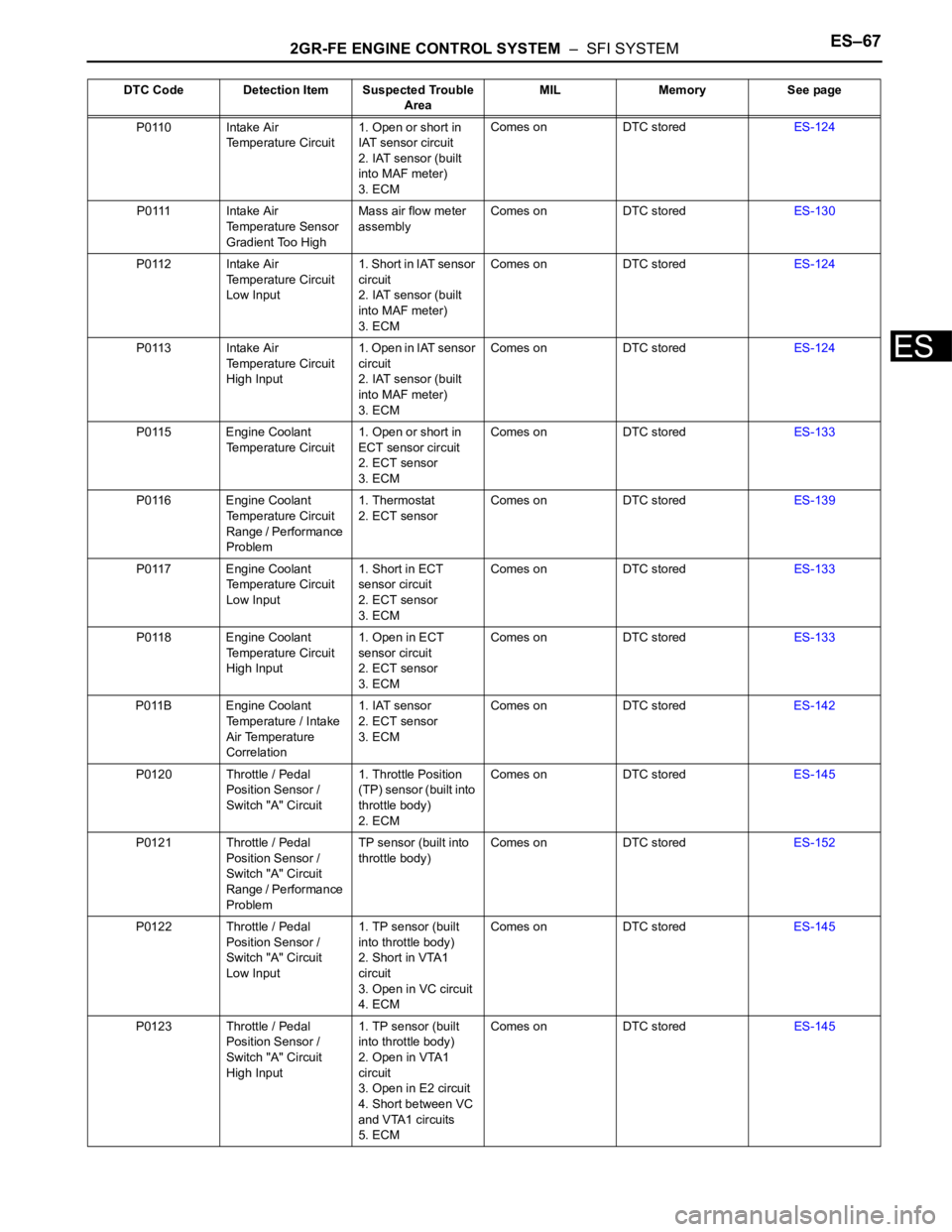
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–67
ES
P0110 Intake Air
Temperature Circuit1. Open or short in
IAT sensor circuit
2. IAT sensor (built
into MAF meter)
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-124
P0111 Intake Air
Temperature Sensor
Gradient Too HighMass air flow meter
assemblyComes on DTC storedES-130
P0112 Intake Air
Temperature Circuit
Low Input1. Short in IAT sensor
circuit
2. IAT sensor (built
into MAF meter)
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-124
P0113 Intake Air
Temperature Circuit
High Input1 . O p e n i n I AT s e n s o r
circuit
2. IAT sensor (built
into MAF meter)
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-124
P0115 Engine Coolant
Temperature Circuit1. Open or short in
ECT sensor circuit
2. ECT sensor
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-133
P0116 Engine Coolant
Temperature Circuit
Range / Performance
Problem1. Thermostat
2. ECT sensorComes on DTC storedES-139
P0117 Engine Coolant
Temperature Circuit
Low Input1. Short in ECT
sensor circuit
2. ECT sensor
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-133
P0118 Engine Coolant
Temperature Circuit
High Input1. Open in ECT
sensor circuit
2. ECT sensor
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-133
P011B Engine Coolant
Temperature / Intake
Air Temperature
Correlation1. IAT sensor
2. ECT sensor
3. ECMComes on DTC storedES-142
P0120 Throttle / Pedal
Position Sensor /
Switch "A" Circuit1. Throttle Position
(TP) sensor (built into
throttle body)
2. ECMComes on DTC storedES-145
P0121 Throttle / Pedal
Position Sensor /
Switch "A" Circuit
Range / Performance
ProblemTP sensor (built into
throttle body)Comes on DTC storedES-152
P0122 Throttle / Pedal
Position Sensor /
Switch "A" Circuit
Low Input1. TP sensor (built
into throttle body)
2. Short in VTA1
circuit
3. Open in VC circuit
4. ECMComes on DTC storedES-145
P0123 Throttle / Pedal
Position Sensor /
Switch "A" Circuit
High Input1. TP sensor (built
into throttle body)
2. Open in VTA1
circuit
3. Open in E2 circuit
4. Short between VC
and VTA1 circuits
5. ECMComes on DTC storedES-145 DTC Code Detection Item Suspected Trouble
AreaMIL Memory See page
Page 374 of 3000

ES–682GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
P0125 Insufficient Coolant
Temperature for
Closed Loop Fuel
Control1. Cooling system
2. Engine coolant
temperature sensor
3. ThermostatComes on DTC storedES-154
P0128 Coolant Thermostat
(Coolant
Temperature Below
Thermostat
Regulating
Temperature)1. Thermostat
2. Cooling system
3. ECT sensor
4. ECMComes on DTC storedES-157
P0136 Oxygen Sensor
Circuit Malfunction
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)1. Open or short in
HO2 sensor (bank 1,
2 sensor 2) circuit
2. HO2 sensor (bank
1, 2 sensor 2)
3. HO2 sensor heater
(bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
4. Air-Fuel Ratio (A/
F) sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 1)
5. EFI relay
6. Gas leakage from
exhaust systemComes on DTC storedES-160
P0137 Oxygen Sensor
Circuit Low Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)1. Open in HO2
sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 2) circuit
2. HO2 sensor (bank
1, 2 sensor 2)
3. HO2 sensor heater
(bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
4. EFI relay
5. Gas leakage from
exhaust systemComes on DTC storedES-160
P0138 Oxygen Sensor
Circuit High Voltage
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)1. Short in HO2
sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 2) circuit
2. HO2 sensor (bank
1, 2 sensor 2)
3. ECM internal
circuit malfunction
4. Air-Fuel ratio (A/F)
sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 1)Comes on DTC storedES-160
P0141 Oxygen Sensor
Heater Circuit
Malfunction (Bank 1
Sensor 2)1. HO2 sensor
2. ECMComes on DTC storedES-109
P0156 Oxygen Sensor
Circuit Malfunction
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)1. Open or short in
HO2 sensor (bank 1,
2 sensor 2) circuit
2. HO2 sensor (bank
1, 2 sensor 2)
3. HO2 sensor heater
(bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
4. Air-Fuel Ratio (A/
F) sensor (bank 1, 2
sensor 1)
5. EFI relay
6. Gas leakage from
exhaust systemComes on DTC storedES-160 DTC Code Detection Item Suspected Trouble
AreaMIL Memory See page
Page 453 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–147
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0115 (See page ES-133).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECT sensor is used to monitor the ECT. The ECT sensor has a built-in thermistor with a resistance
that varies according to the temperature of the engine coolant. When the ECT becomes low, the
resistance of the thermistor increases. When the temperature becomes high, the resistance drops. These
variations in the resistance are reflected in the voltage output from the ECT sensor.
The ECM monitors the sensor voltage and uses this value to calculate the ECT. If the sensor voltage
output deviates from the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this deviation as a malfunction in the
ECT sensor and sets the DTC.
Examples:
• Upon starting the engine, the ECT is between 35
C and 60C (95F and 140F). If the ECT remains
within 3
C (5.4F) of the stating temperature after driving for 250 seconds, the DTC is set (2 trip
detection logic).
• Upon starting the engine, the ECT is over 60
C (140F). If the ECT remains within 1C (1.8F) of the
starting temperature after driving for 250 seconds, the DTC is set (6 trip detection logic).
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC P0116Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range /
Performance Problem
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0116ECTs as listed below are nearly same (2 trip detection
logic):
– ECT when engine is started at lower than 60
C
(140
F) of ECT
– ECT when engine is warmed up
•Thermostat
• ECT sensor ECTs as listed below are nearly same when engine is
started at higher than 60
C (140F) of ECT (2 trip
detection logic)
– ECT when engine is stopped after driving
– ECT when engine is started at lower than 60
C
(140F) of ECT
When either of following conditions is met (2 trip
detection logic):
• When cold engine started and engine warmed up,
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor value
does not change
• After engine is warmed up, ECT sensor value does
not change when engine stopped and then next
cold engine start is performed
Related DTCsP0116: Engine coolant temperature sensor output stuck at low engine coolant
temperature
P0116: Engine coolant temperature sensor output stuck at high engine coolant
temperature
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related) Crankshaft position sensor, intake air temperature sensor and mass air flow meter
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration 5 hours
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Page 455 of 3000
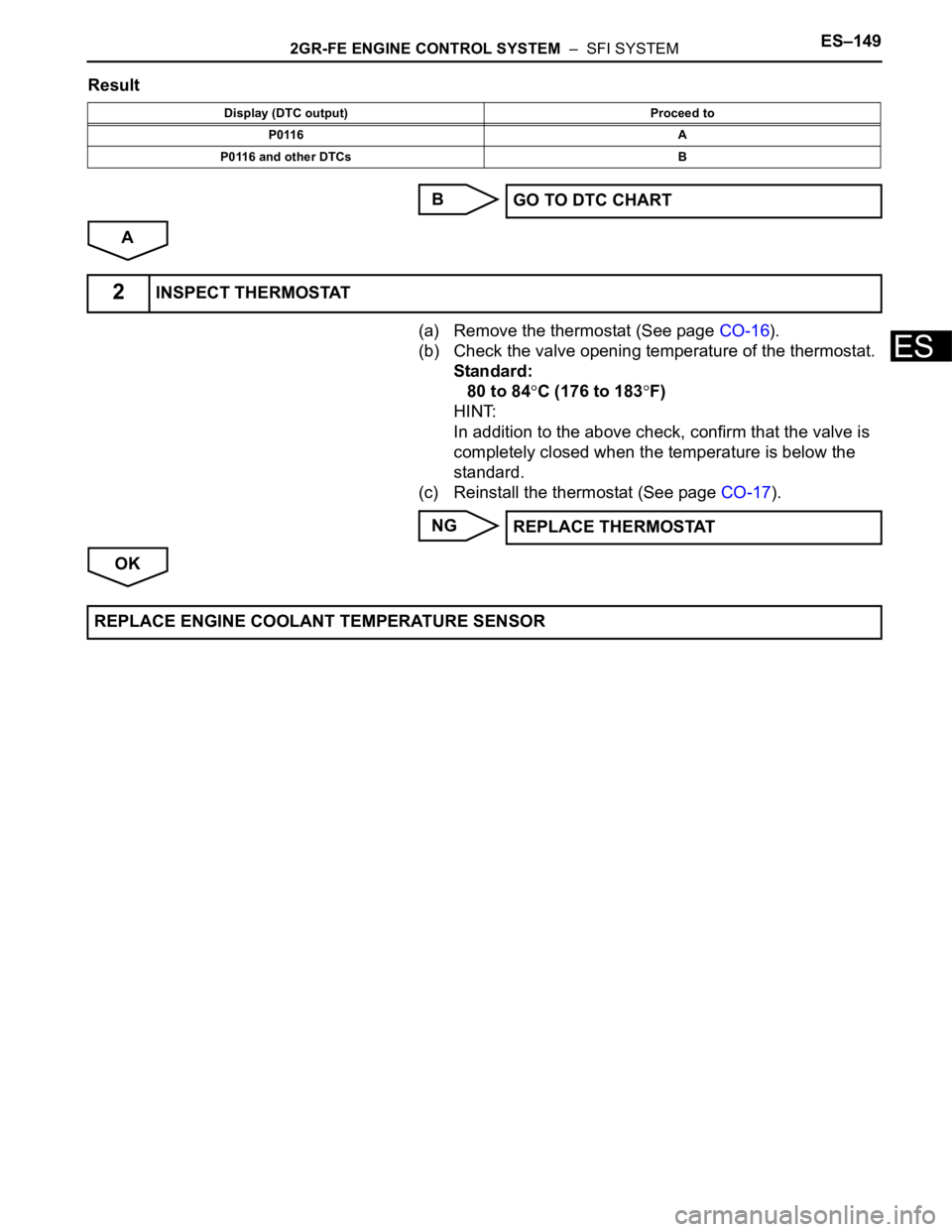
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–149
ES
Result
B
A
(a) Remove the thermostat (See page CO-16).
(b) Check the valve opening temperature of the thermostat.
Standard:
80 to 84
C (176 to 183F)
HINT:
In addition to the above check, confirm that the valve is
completely closed when the temperature is below the
standard.
(c) Reinstall the thermostat (See page CO-17).
NG
OK
Display (DTC output) Proceed to
P0116 A
P0116 and other DTCs B
GO TO DTC CHART
2INSPECT THERMOSTAT
REPLACE THERMOSTAT
REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Page 468 of 3000

ES–1622GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P0115 (See page ES-133).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The resistance of the ECT sensor varies in proportion to the actual ECT. The ECM supplies a constant
voltage to the sensor and monitors the signal output voltage of the sensor. The signal voltage output
varies according to the changing resistance of the sensor. After the engine is started, the ECT is
monitored through this signal. If the ECT sensor indicates that the engine is not yet warm enough for
closed-loop fuel control, despite a specified period of time having elapsed since the engine was started,
the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor or cooling system and sets the DTC.
Example:
The ECT is 0
C (32F) at engine start. After 5 minutes running time, the ECT sensor still indicates that the
engine is not warm enough to begin closed-loop fuel (air-fuel ratio feedback) control. The ECM interprets
this as a malfunction in the sensor or cooling system and sets the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0115 (See page ES-134).
DTC P0125Insufficient Coolant Temperature for Closed
Loop Fuel Control
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0125Engine coolant temperature (ECT) does not reach
closed-loop enabling temperature for 20 minutes (this
period varies with engine start ECT)• Cooling system
• Engine coolant temperature sensor
• Thermostat
Related DTCs P0125: Insufficient engine coolant temperature for closed-loop fuel control
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Thermostat, cooling system
Required Sensors / Components (Related) Engine coolant temperature sensor and mass air flow meter
Frequency of Operation Continuous
Duration78 seconds: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -8.34
C (17F) or more
131.3 seconds: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -19.45 to -8.34C (-3 to
17
F)
20 minutes: Engine coolant temperature at engine start less than -19.45
C (-3F)
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF) sensor, P0110, P0111, P0112, P0113 (IAT
sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT sensor)
Fuel cut OFF
Engine Running
Time until actual engine coolant temperature reaches
closed-loop fuel control enabling temperature78 seconds or more: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -8.34
C (17F) or
more
131.3 seconds or more: Engine coolant temperature at engine start -19.45 to -8.34
C
(-3 to 17
F)
20 minutes or more: Engine coolant temperature at engine start less than -19.45C (-
3
F)
Page 469 of 3000
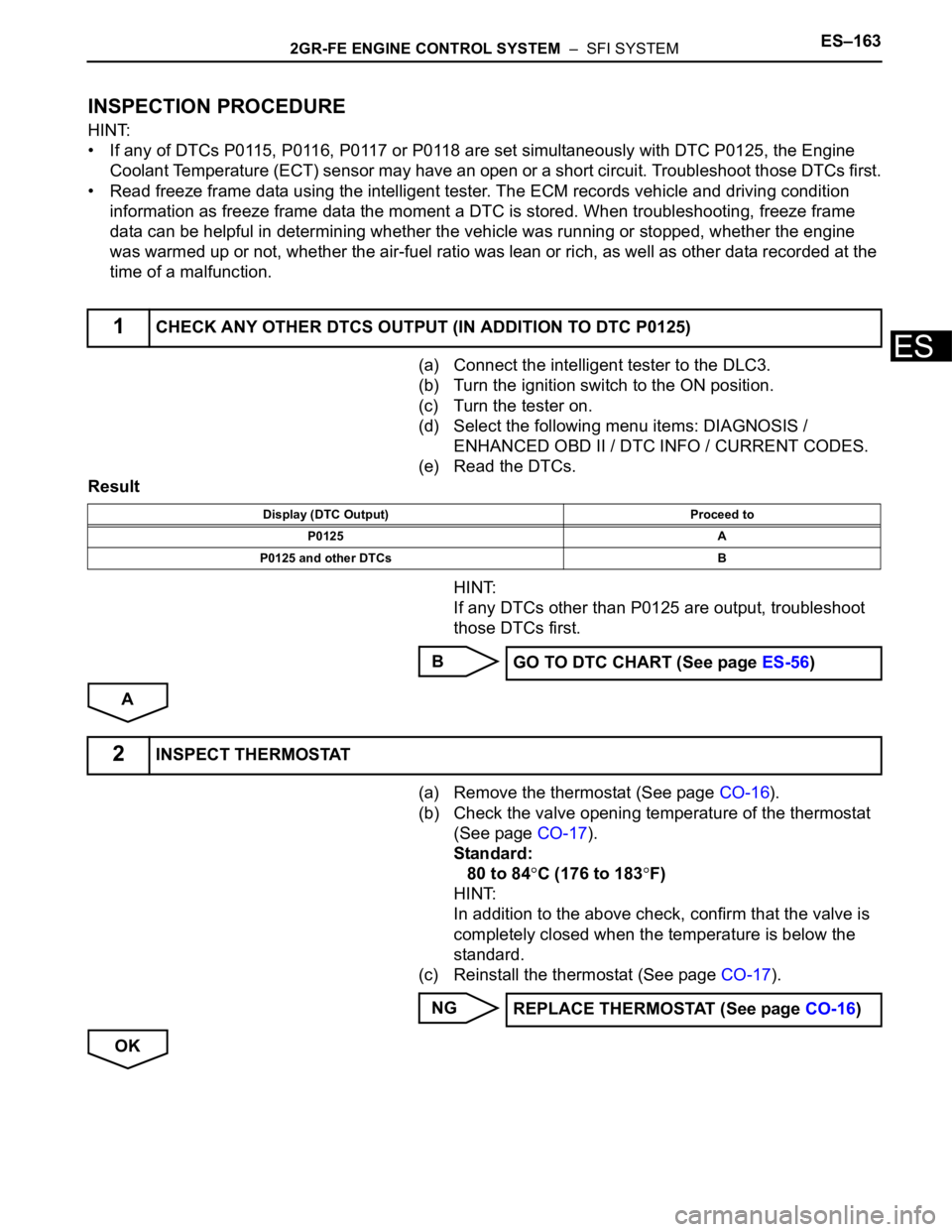
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–163
ES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
• If any of DTCs P0115, P0116, P0117 or P0118 are set simultaneously with DTC P0125, the Engine
Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor may have an open or a short circuit. Troubleshoot those DTCs first.
• Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame
data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine
was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the
time of a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Result
HINT:
If any DTCs other than P0125 are output, troubleshoot
those DTCs first.
B
A
(a) Remove the thermostat (See page CO-16).
(b) Check the valve opening temperature of the thermostat
(See page CO-17).
Standard:
80 to 84
C (176 to 183F)
HINT:
In addition to the above check, confirm that the valve is
completely closed when the temperature is below the
standard.
(c) Reinstall the thermostat (See page CO-17).
NG
OK
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0125)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to
P0125 A
P0125 and other DTCs B
GO TO DTC CHART (See page ES-56)
2INSPECT THERMOSTAT
REPLACE THERMOSTAT (See page CO-16)