2007 TOYOTA SIENNA Fuel System
[x] Cancel search: Fuel SystemPage 472 of 3000

ES–1662GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was
warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of
a malfunction.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Turn the tester on.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(e) Read the DTCs.
Required Sensors / Components (Related)Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor, Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor,
Vehicle speed sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration 900 seconds
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0010, P0020 (VVT VSV 1, 2), P0011, P0012 (VVT System 1-Advance, Retard),
P0021, P0022 (VVT System 2-Adavance, Retard), P0031, P0032, P0051, P0052 (A/
F Sensor Heater Sensor 1), P0100, P0101, P0102, P0103 (MAF Sensor), P0110,
P0112, P0113 (IAT Sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117, P0118 (ECT Sensor), P0125
(Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop), P0136, P0156 (O2 Sensor 2), P0171, P0172
(Fuel System), P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306 (Misfire),
P0335 (CKP Sensor), P0340 (CMP sensor), P0345 (VVT sensor), P0351, P0352,
P0353, P0354, P0355, P0356 (Ignitor), P0500 (VSS), P2196, P2198(A/F Sensor
(Rationality)), P2A00, P2A03 (A/F Sensor (Slow Response))
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Either of following conditions is met: Condition 1 or 2
1. All of following conditions are met: Conditions (a), (b) and (c)
(a) ECT at engine start - IAT at engine start -15 to 7
C (5 to 45F)
(b) ECT at engine start -10 to 56
C (14 to 133F)
(c) IAT at engine start -10 to 56
C (14 to 133F)
2. All of following conditions are met: Conditions (d), (e) and (f)
(d) ECT at engine start - IAT at engine start More than 7
C (45F)
(e) ECT at engine start 56
C (133F) or less
(f) IAT at engine start -10
C (14F) or more
Accumulated time that vehicle speed is 80 mph (128
km/h) or moreLess than 20 seconds
Duration that all of the following conditions 1 and 2 are
met5 seconds or more
1. Estimated ECT 75
C (167F) or more
2. ECT sensor output Less than 75
C (167F)
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0128)
Page 474 of 3000

ES–1682GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HINT:
Sensor 2 refers to the sensor mounted behind the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and located far
from the engine assembly.
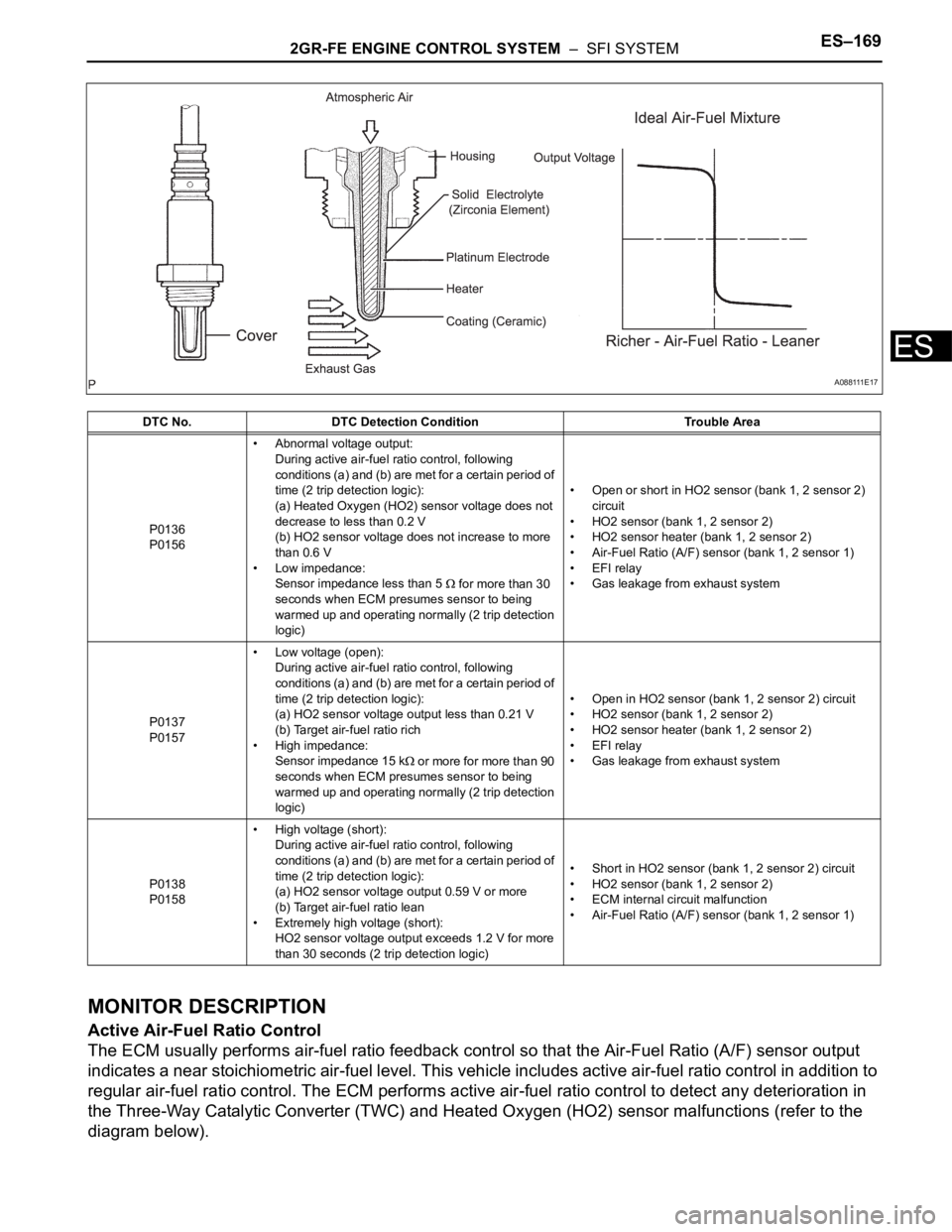
DESCRIPTION
A three-way catalytic converter (TWC) is used in order to convert the carbon monoxide (CO), hydro
carbon (HC), and nitrogen oxides (HOx) into less harmful substances. To allow the TWC to function
effectively, it is necessary to keep the air-fuel ratio of the engine near the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. For
helping the ECM to deliver accurate air-fuel ratio control, a Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor becomes used.
The HO2 sensor is located behind the TWC, and detects the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.
Since the sensor is integrated with the heater that heats the sensing portion, it is possible to detect the
oxygen concentration even when the intake air volume is low (the exhaust gas temperature is low).
When the air-fuel ratio becomes lean, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas becomes rich. The
HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is lean (low voltage, i.e. less than 0.45 V).
Conversely, when the air-fuel ratio is richer than the stoichiometric air-fuel level, the oxygen concentration
in the exhaust gas becomes lean. The HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is
rich (high voltage, i.e. more than 0.45 V). The HO2 sensor has the property of changing its output voltage
drastically when the air-fuel ratio is close to the stoichiometric level.
The ECM uses the supplementary information from the HO2 sensor to determine whether the air-fuel ratio
after the TWC is rich or lean, and adjusts the fuel injection time accordingly. Thus, if the HO2 sensor is
working improperly due to internal malfunctions, the ECM is unable to compensate for deviations in the
primary air-fuel ratio control.
DTC P0136Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
DTC P0137Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
DTC P0138Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
DTC P0156Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2
Sensor 2)
DTC P0157Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2
Sensor 2)
DTC P0158Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2
Sensor 2)
Page 475 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–169
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
Active Air-Fuel Ratio Control
The ECM usually performs air-fuel ratio feedback control so that the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor output
indicates a near stoichiometric air-fuel level. This vehicle includes active air-fuel ratio control in addition to
regular air-fuel ratio control. The ECM performs active air-fuel ratio control to detect any deterioration in
the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor malfunctions (refer to the
diagram below).
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0136
P0156• Abnormal voltage output:
During active air-fuel ratio control, following
conditions (a) and (b) are met for a certain period of
time (2 trip detection logic):
(a) Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor voltage does not
decrease to less than 0.2 V
(b) HO2 sensor voltage does not increase to more
than 0.6 V
• Low impedance:
Sensor impedance less than 5
for more than 30
seconds when ECM presumes sensor to being
warmed up and operating normally (2 trip detection
logic)• Open or short in HO2 sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
circuit
• HO2 sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
• HO2 sensor heater (bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
• Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
• EFI relay
• Gas leakage from exhaust system
P0137
P0157• Low voltage (open):
During active air-fuel ratio control, following
conditions (a) and (b) are met for a certain period of
time (2 trip detection logic):
(a) HO2 sensor voltage output less than 0.21 V
(b) Target air-fuel ratio rich
• High impedance:
Sensor impedance 15 k
or more for more than 90
seconds when ECM presumes sensor to being
warmed up and operating normally (2 trip detection
logic)• Open in HO2 sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 2) circuit
• HO2 sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
• HO2 sensor heater (bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
• EFI relay
• Gas leakage from exhaust system
P0138
P0158• High voltage (short):
During active air-fuel ratio control, following
conditions (a) and (b) are met for a certain period of
time (2 trip detection logic):
(a) HO2 sensor voltage output 0.59 V or more
(b) Target air-fuel ratio lean
• Extremely high voltage (short):
HO2 sensor voltage output exceeds 1.2 V for more
than 30 seconds (2 trip detection logic)• Short in HO2 sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 2) circuit
• HO2 sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 2)
• ECM internal circuit malfunction
• Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
A 0 8 8 111 E 1 7
Page 476 of 3000
ES–1702GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
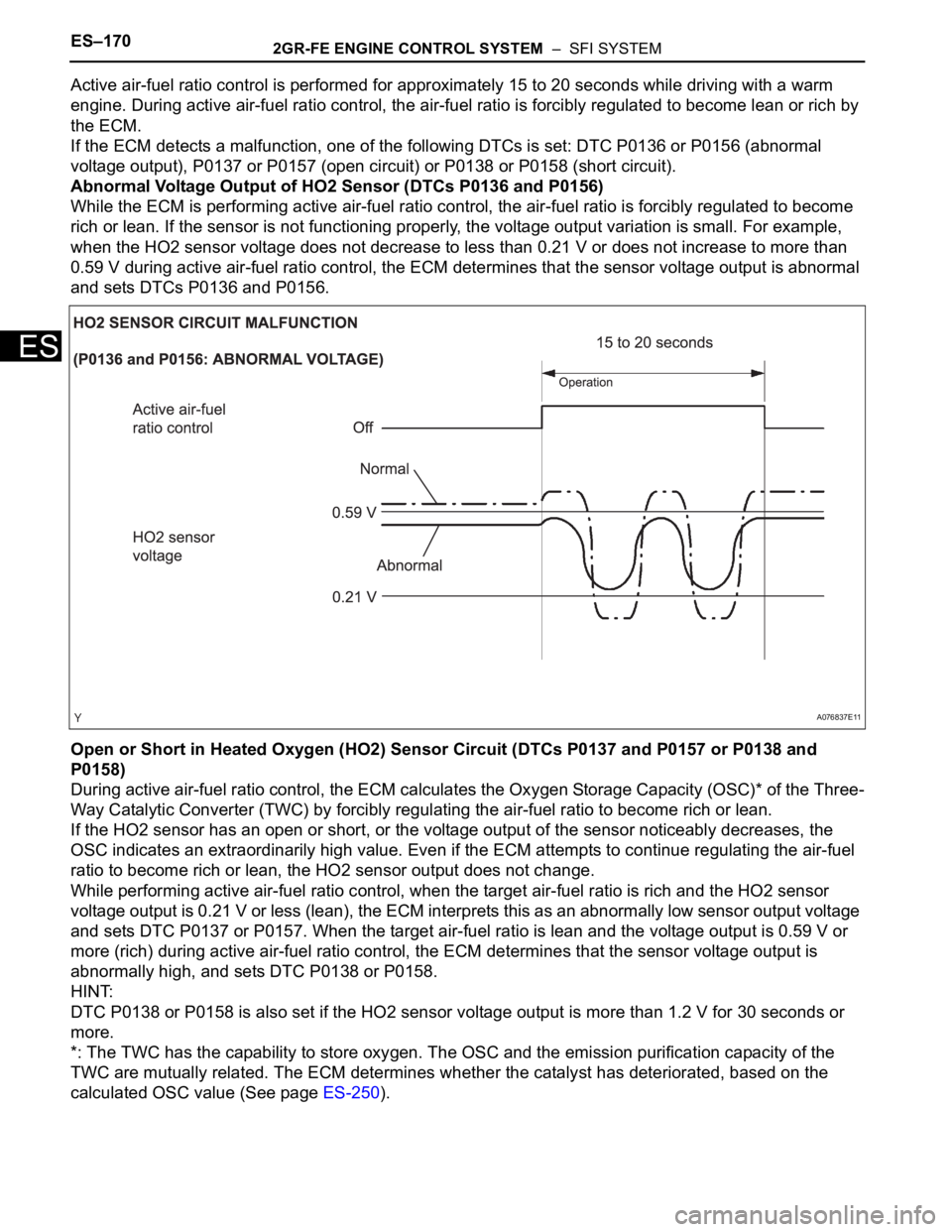
Active air-fuel ratio control is performed for approximately 15 to 20 seconds while driving with a warm
engine. During active air-fuel ratio control, the air-fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become lean or rich by
the ECM.
If the ECM detects a malfunction, one of the following DTCs is set: DTC P0136 or P0156 (abnormal
voltage output), P0137 or P0157 (open circuit) or P0138 or P0158 (short circuit).
Abnormal Voltage Output of HO2 Sensor (DTCs P0136 and P0156)
While the ECM is performing active air-fuel ratio control, the air-fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become
rich or lean. If the sensor is not functioning properly, the voltage output variation is small. For example,
when the HO2 sensor voltage does not decrease to less than 0.21 V or does not increase to more than
0.59 V during active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM determines that the sensor voltage output is abnormal
and sets DTCs P0136 and P0156.
Open or Short in Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor Circuit (DTCs P0137 and P0157 or P0138 and
P0158)
During active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM calculates the Oxygen Storage Capacity (OSC)* of the Three-
Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) by forcibly regulating the air-fuel ratio to become rich or lean.
If the HO2 sensor has an open or short, or the voltage output of the sensor noticeably decreases, the
OSC indicates an extraordinarily high value. Even if the ECM attempts to continue regulating the air-fuel
ratio to become rich or lean, the HO2 sensor output does not change.
While performing active air-fuel ratio control, when the target air-fuel ratio is rich and the HO2 sensor
voltage output is 0.21 V or less (lean), the ECM interprets this as an abnormally low sensor output voltage
and sets DTC P0137 or P0157. When the target air-fuel ratio is lean and the voltage output is 0.59 V or
more (rich) during active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM determines that the sensor voltage output is
abnormally high, and sets DTC P0138 or P0158.
HINT:
DTC P0138 or P0158 is also set if the HO2 sensor voltage output is more than 1.2 V for 30 seconds or
more.
*: The TWC has the capability to store oxygen. The OSC and the emission purification capacity of the
TWC are mutually related. The ECM determines whether the catalyst has deteriorated, based on the
calculated OSC value (See page ES-250).
A076837E11
Page 478 of 3000
ES–1722GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
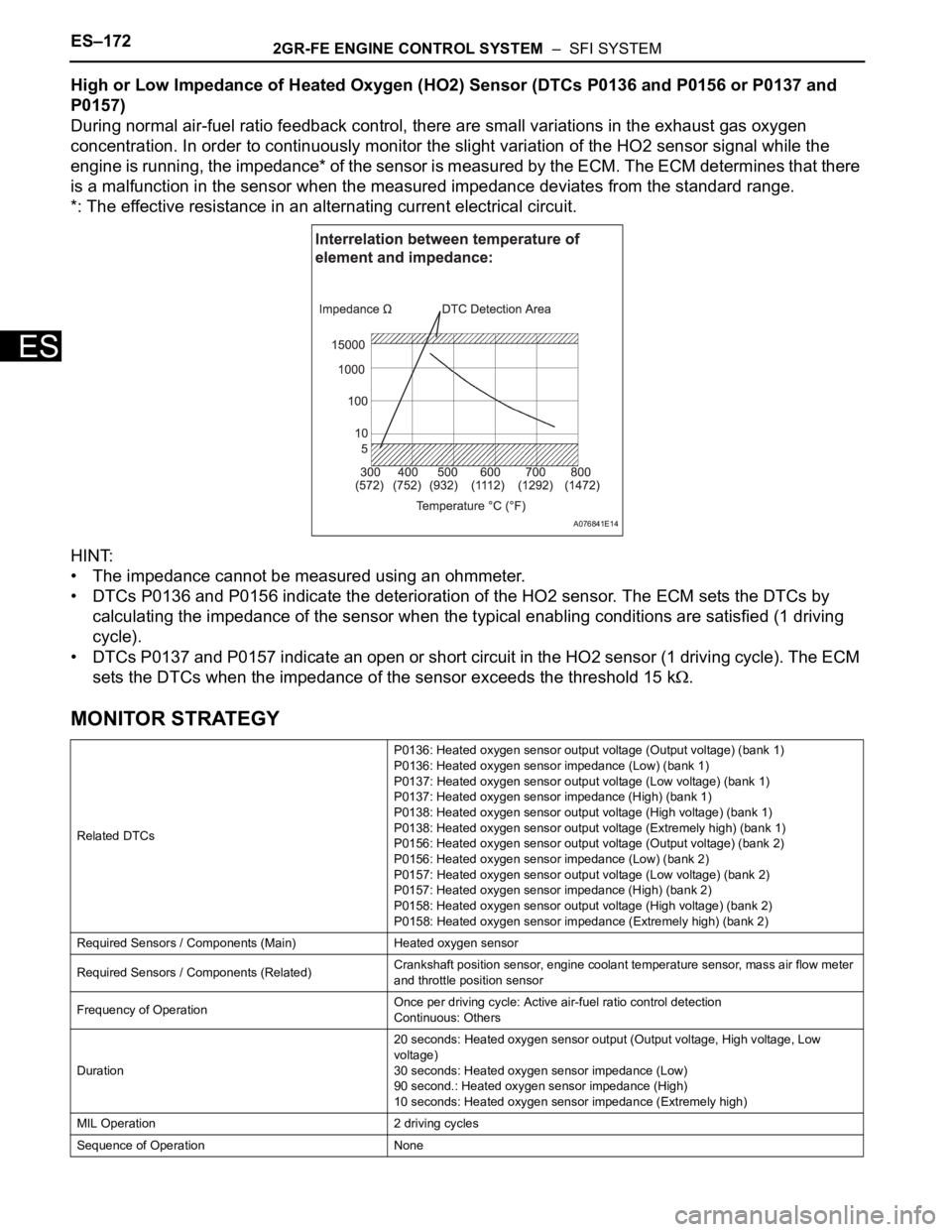
High or Low Impedance of Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor (DTCs P0136 and P0156 or P0137 and
P0157)
During normal air-fuel ratio feedback control, there are small variations in the exhaust gas oxygen
concentration. In order to continuously monitor the slight variation of the HO2 sensor signal while the
engine is running, the impedance* of the sensor is measured by the ECM. The ECM determines that there
is a malfunction in the sensor when the measured impedance deviates from the standard range.
*: The effective resistance in an alternating current electrical circuit.
HINT:
• The impedance cannot be measured using an ohmmeter.
• DTCs P0136 and P0156 indicate the deterioration of the HO2 sensor. The ECM sets the DTCs by
calculating the impedance of the sensor when the typical enabling conditions are satisfied (1 driving
cycle).
• DTCs P0137 and P0157 indicate an open or short circuit in the HO2 sensor (1 driving cycle). The ECM
sets the DTCs when the impedance of the sensor exceeds the threshold 15 k
.
MONITOR STRATEGY
Related DTCsP0136: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (Output voltage) (bank 1)
P0136: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (Low) (bank 1)
P0137: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (Low voltage) (bank 1)
P0137: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (High) (bank 1)
P0138: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (High voltage) (bank 1)
P0138: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (Extremely high) (bank 1)
P0156: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (Output voltage) (bank 2)
P0156: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (Low) (bank 2)
P0157: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (Low voltage) (bank 2)
P0157: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (High) (bank 2)
P0158: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage (High voltage) (bank 2)
P0158: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (Extremely high) (bank 2)
Required Sensors / Components (Main) Heated oxygen sensor
Required Sensors / Components (Related)Crankshaft position sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor, mass air flow meter
and throttle position sensor
Frequency of OperationOnce per driving cycle: Active air-fuel ratio control detection
Continuous: Others
Duration20 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor output (Output voltage, High voltage, Low
voltage)
30 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (Low)
90 second.: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (High)
10 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (Extremely high)
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
A076841E14
Page 479 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–173
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Output Voltage, High Voltage and Low Voltage):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (Low):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (High):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Extremely High):
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Output voltage):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Low output voltage):
The monitor will run whenever these DTCs are not
presentP0031, P0032, P0051, P0052 (A/F Sensor Heater Sensor 1), P0100, P0101, P0102,
P0103 (MAF Sensor), P0110, P0112, P0113 (IAT Sensor), P0115, P0116, P0117,
P0118 (ECT Sensor), P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222, P0223, P2135
(TP Sensor), P0125 (Insufficient ECT for Closed Loop), P0171, P0172 (Fuel
System), P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, P0306 (Misfire), P0335
(CKP Sensor), P0340 (CMP Sensor), P0500 (VSS), P2196, P2198 (A/F Sensor
(Rationality)), P2A00, P2A03 (A/F Sensor (Slow Response))
Active air-fuel ratio control Performing
Active air-fuel ratio control is performed when the
following conditions are met:-
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Engine coolant temperature 75
C (167F) or more
Idle OFF
Engine RPM Less than 3200 rpm
A/F sensor status Activated
Fuel system status Closed loop
Fuel-cut OFF
Engine load 10 to 70%
Shift position 4th or more
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Estimated HO2S temperature Less than 700
C (1292F)
ECM monitor Completed
DTC P0606 Not set
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Estimated HO2S temperature 450
C (842F) or more
DTC P0606 Not set
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Time after engine start 2 seconds or more
Either of the following conditions is met: 1 or 2
1. All of the following conditions (a), (b) and (c) are met -
(a) Commanded air-fuel ratio 14.3 or less
(b) Rear HO2 sensor voltage 0.21 to 0.59 V
(c) OSC (Oxygen Storage Capacity of Catalyst) 2.0 g (0.0044 lb) or more
2. All of the following conditions (d), (f) and (g) are met. -
(d) Commanded air-fuel ratio 14.9 or more
(f) Rear HO2 sensor voltage 0.21 to 0.59 V
(g) OSC 2.0 g (0.0044 lb) or more
All of the following conditions (a), (b) and (c) are met. -
(a) Commanded air-fuel ratio 14.3 or less
Page 480 of 3000

ES–1742GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (High output voltage):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (Low):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (High):
Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (Extremely High):
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
MONITOR RESULT
Refer to CHECKING MONITOR STATUS (See page ES-19).
(b) Rear HO2 sensor voltage Less than 0.21 V
(c) OSC (Oxygen Storage Capacity of Catalyst) 2.0 g (0.0044 lb) or more
All of the following conditions (a), (b) and (c) are met. -
(a) Commanded air-fuel ratio 14.9 or more
(b) Rear HO2 sensor voltage More than 0.59 V
(c) OSC (Oxygen Storage Capacity of Catalyst) 2.0 g (0.0044 lb) or more
Duration that following condition is met 30 seconds or more
Rear heated oxygen sensor impedance Less than 5
Duration that following condition is met 90 seconds or more
Rear heated oxygen sensor impedance 15 k
or more
Duration that following condition is met 10 seconds or more
Rear heated oxygen sensor voltage 1.2 V or more
Duration that following condition is met 30 seconds or more
Heated oxygen sensor voltage Varies between 0.1 and 0.9 V
Page 483 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–177
ES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
For use of the intelligent tester only:
Malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing the A/F CONTROL function provided in the ACTIVE
TEST. The A/F CONTROL function can help to determine whether the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated
Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
The following instructions describe how to conduct the A/F CONTROL operation using the intelligent
tester.
1. Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
2. Start the engine and turn the tester on.
3. Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
4. Select the following menu items on the tester: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE TEST / A/F
CONTROL.
5. Perform the A/F CONTROL operation with the engine in an idling condition (press the RIGHT or LEFT
button to change the fuel injection volume).
6. Monitor the voltage outputs of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1S1 and O2S B1S2 or AFS B2S1 and
O2S B2S2) displayed on the tester.
HINT:
• The A/F CONTROL operation lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5% or increases the injection
volume by 25%.
• Each sensor reacts in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
Standard voltage
NOTICE:
The Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the Heated Oxygen
(HO2) sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
Tester Display (Sensor) Injection Volumes Status Voltages
AFS B1S1 or AFS B2S1 (A/F) +25% Rich Less than 3.0
AFS B1S1 or AFS B2S1 (A/F) -12.5% Lean More than 3.35
O2S B1S2 or O2S B2S2 (HO2) +25% Rich More than 0.55
O2S B1S2 or O2S B2S2 (HO2) -12.5% Lean Less than 0.4
CaseA/F Sensor (Sensor 1)
Output VoltageHO2 Sensor (Sensor 2)
Output VoltageMain Suspected
Trouble Area
1-