Page 640 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-108
Item
No.Reference
page Inspection
procedure
No. Normal condition Inspection contents Drive contents Inspection
item
21Fan
controllerRadiator fan
motor is
driven.Ignition switch: “ON”Fan motor rotates
at high speed.Procedure
No. 2413A-87
36Secondary
air control
solenoid
valveSolenoid valve
turns from
OFF to ON.Ignition switch: “ON”Sound of opera-
tion can be heard
when solenoid
valve is driven.Procedure
No. 2913A-96
37Condenser
fan (HI)Condensor
fan motor is
driven.Ignition switch: “ON”Fan motor rotates
at high speed.Procedure
No. 2513A-89
38Condenser
fan (LOW)Second air
control
solenoid valveIgnition switch: “ON”Fan motor rotates
at low speed.
CHECK AT THE ENGINE-ECU TERMINALS
TERMINAL VOLTAGE CHECK CHART
1. Connect a needle-nosed wire probe (test harness:
MB991223 or paper clip) to a voltmeter probe.
2. Insert the needle-nosed wire probe into each of the
engine-ECU connector terminals from the wire side, and
measure the voltage while referring to the check chart.
NOTE
(1) Make the voltage measurement with the engine-ECU
connectors connected.
(2) You may find it convenient to pull out the engine-ECU
to make it easier to reach the connector terminals.
(3) The checks can be carried out off the order given
in the chart.
Caution
Short-circuiting the positive (+) probe between a
connector terminal and earth could damage the
vehicle wiring, the sensor, engine-ECU or all of them.
Be careful to prevent this!
3. If voltmeter shows any division from standard value, check
the corresponding sensor, actuator and related electrical
wiring, then repair or replace.
4. After repair or replacement, recheck with the voltmeter
to confirm that the repair has corrected the problem.
Needle-nosed wire probe
Page 646 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-114
CHECK CHART FOR RESISTANCE AND CONTINUITY
BETWEEN TERMINALS
1. Turn the ignition switch to “LOCK” (OFF) position.
2. Disconnect the engine-ECU connector.
3. Measure the resistance and check for continuity between
the terminals of the engine-ECU harness-side connector
while referring to the check chart.
NOTE
(1) When measuring resistance and checking continuity,
a harness for checking contact pin pressure should
be used instead of inserting a test probe.
(2) Checking need not be carried out in the order given
in the chart.
Caution
If the terminals that should be checked are mistaken,
or if connector terminals are not correctly shorted
to earth, damage may be caused to the vehicle wiring,
sensors, engine-ECU and/or ohmmeter.
Be careful to prevent this!
4. If the ohmmeter shows any deviation from the standard
value, check the corresponding sensor, actuator and
related electrical wiring, and then repair or replace.
5. After repair or replacement, recheck with the ohmmeter
to confirm that the repair or replacement has corrected
the problem.
Engine-ECU Harness Side Connector Terminal Arrangement
Terminal No.Inspection itemNormal condition (Check condition)
1-12No. 1 injector2-3Ω(at 20_C)
14 - 12No. 2 injector
2-12No. 3 injector
15 - 12No. 4 injector
Page 653 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-121
IDLE SPEED CONTROL SERVO (STEPPER MOTOR)
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the idle speed control servo connector, and
connect the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in
between.
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to the idle
speed control servo-side connector terminal No. 1,
terminal No. 3, terminal No. 4 and terminal No. 6
respectively.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 4, connection terminal No. 5,
connection terminal No. 17, and connection terminal No.
18 respectively.
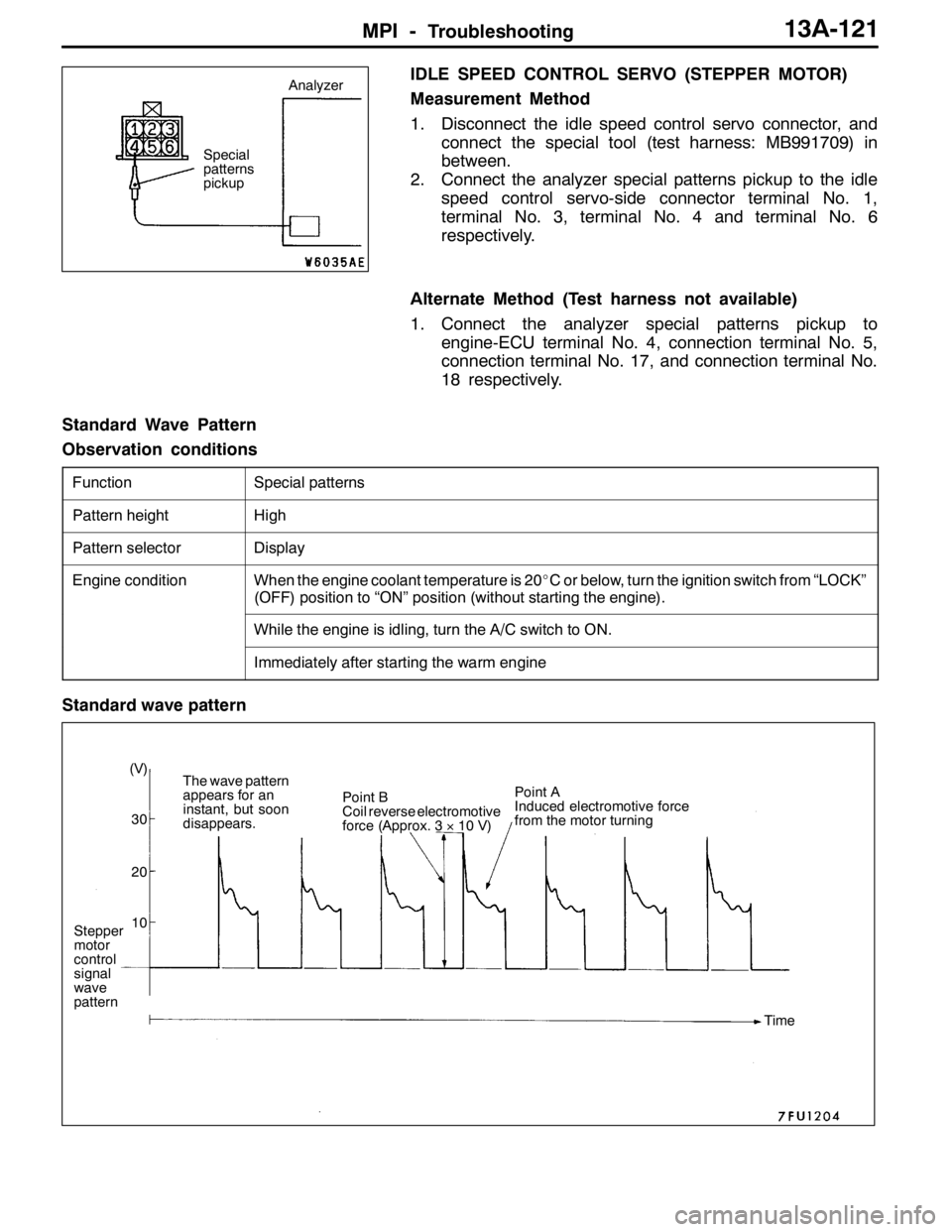
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightHigh
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine conditionWhen the engine coolant temperature is 20_C or below, turn the ignition switch from “LOCK”
(OFF) position to “ON” position (without starting the engine).
While the engine is idling, turn the A/C switch to ON.
Immediately after starting the warm engine
Standard wave pattern
Stepper
motor
control
signal
wave
pattern(V)
30
20
10The wave pattern
appears for an
instant, but soon
disappears.Point B
Coil reverse electromotive
force (Approx. 3×10 V)Point A
Induced electromotive force
from the motor turning
Time
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 655 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-123
IGNITION COIL AND POWER TRANSISTOR
DIgnition coil primary signal
Refer to GROUP 16 - Ignition system.
DPower transistor control signal
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the ignition coil connector, and connect the
special tool (test harness: MB991658) in between. (All
terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to terminal
No. 3 of each ignition coil connector in turn.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 10 (No. 1 - No. 4), terminal
No. 23 (No. 2 - No. 3) respectively.
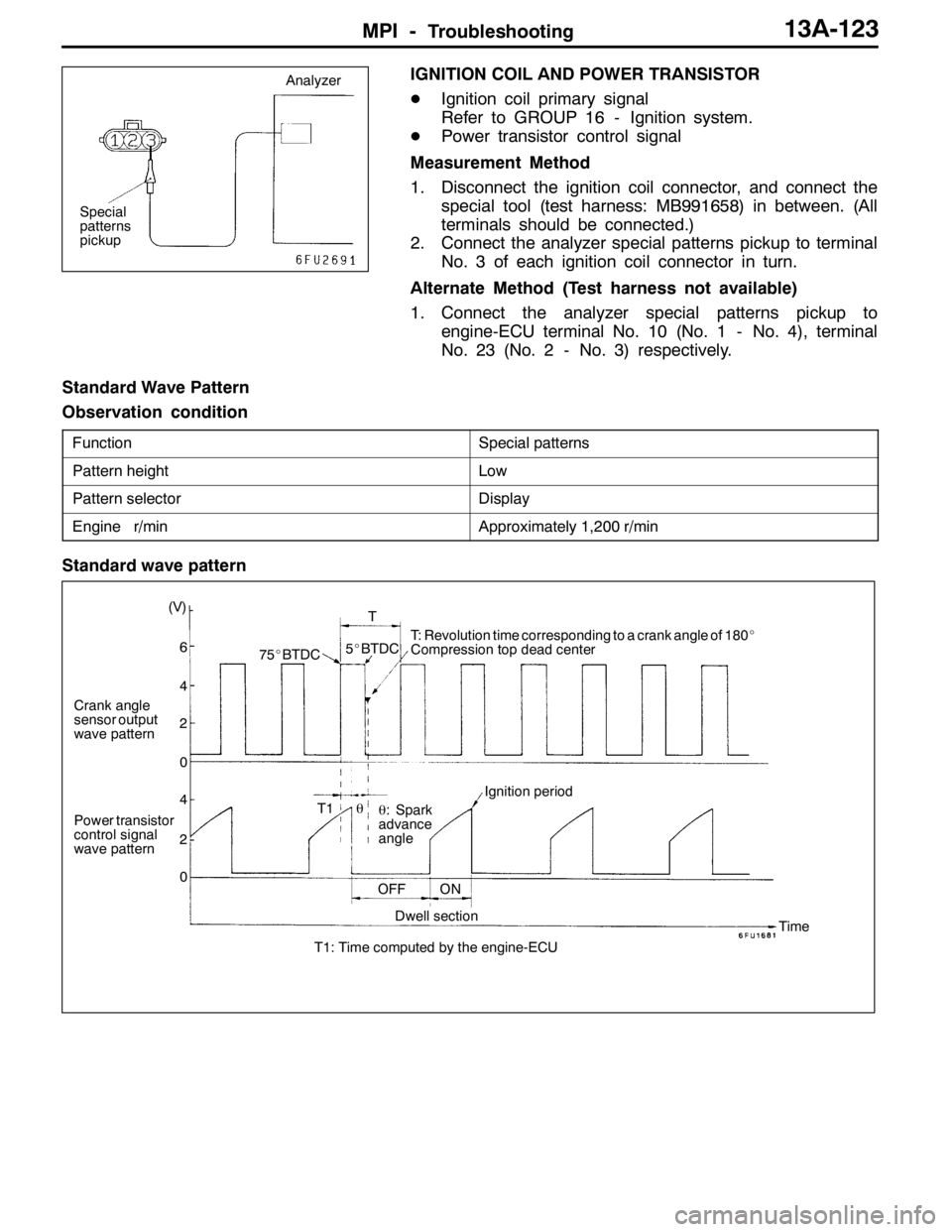
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation condition
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightLow
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minApproximately 1,200 r/min
Standard wave pattern
Crank angle
sensor output
wave pattern
Power transistor
control signal
wave pattern(V)
75_BTDC5_BTDCT: Revolution time corresponding to a crank angle of 180_
Compression top dead center
θ: Spark
advance
angleIgnition period
OFF ON
Dwell section
T1: Time computed by the engine-ECUTime θ T1T
6
4
2
0
4
2
0
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 682 of 1449

FUEL SUPPLY - General Information/On-vehicle Service13B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
DThe steel fuel tank is located under the floor of the rear seats to provide increased safety and increase
the amount of luggage compartment space.
DThe fuel tank has been equipped with a valve assembly which incorporates a fuel cut-off valve to
prevent fuel from leaking out in the event of a collision for adjusting the pressure inside the fuel
tank.
DThe fuel pump module contains a fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel pressure regulator.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
FUEL PUMP AND GAUGE ASSEMBLY (FUEL
PUMP)
1. FUEL PUMP OPERATION CHECK
Refer to GROUP 13A - On-vehicle service
2. FUEL PUMP REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the rear seat cushion assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
(2) Remove the service hole cover.
(3) Disconnect the harness connector, high-pressure fuel
tube, suction hose and return hose.
(4) Unscrew the mounting nuts to remove the fuel pump
and gauge assembly.
(5) Replace the fuel pump. (Refer to P.13B-7.)
(6) Install the fuel pump and gauge assembly. Tighten
the mounting nuts to the specified torque.
Specified torque: 2.5± 0.5 N·m
(7) Connect the harness connector, high-pressure fuel
tube, suction hose, and return hose.
Caution
1) Snap the high-pressure fuel hose or suction
hose one-touch joint into place, then pull back
slightly on the hose to assure it is securely
fitted. However, the connection should have
a play of approx. 3 mm.
2) Insert the return hose for 20 - 30 mm for
connection.
(8) Install the service hole cover.
(9) Install the rear seat cushion assembly.
(Refer to GROUP 52A.)
Harness
connectorHigh-pressurefuel tube
Suction hose
Return hose
3mm
Corresponding
sideHigh-pressure fuel tube
Page 686 of 1449
FUEL SUPPLY - Fuel Tank13B-6
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
"AAHIGH-PRESSURE FUEL HOSE/SUCTION HOSE
INSTALLATION
Caution
Snap the high-pressure fuel hose or suction hose
one-touch joint into place, then pull back slightly on the
hose to assure it is securely fitted. However, the
connection should have a play of approx. 3 mm.
"BAFUEL TANK RETURN HOSE INSTALLATION
Caution
Insert the return hose for 20 - 30 mm for connection.
3mm
Corresponding
sideHigh-pressure fuel tube
Page 708 of 1449
INTAKE AND EXHAUST -General Information15-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
SUPERCHARGING PRESSURE CONTROL
By controlling the duty of the waste gate solenoid valve, the waste gate actuator functions to control the supercharging
pressure. This allows a supercharged pressure matching the engine operation state to be attained. Control is carried
out to prevent excessive supercharging and thereby prevent engine damage.
SECONDARY AIR CONTROL
When decelerating during high-speed travel, the secondary air is introduced into the upstream of the turbocharger
to prevent the turbine speed from dropping and to increase the acceleration responsiveness after deceleration.
The secondary air is introduced into each cylinder of the exhaust manifold to maximize the effect.
Secondary air
control solenoid
valve
Air
inletSecondary
air valve
Waste gate
solenoid
valve
Waste gate
actuator
TurbochargerVacuum
tank
Page 758 of 1449

ENGINE ELECTRICAL -Ignition System16-26
IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
This system is equipped with two ignition coils (A
and B) with built-in power transistors for the No.
1 and No. 4 cylinders and the No. 2 and No. 3
cylinders respectively.
Interruption of the primary current flowing in the
primary side of ignition coil A generates a high
voltage in the secondary side of ignition coil A.
The high voltage thus generated is applied to the
spark plugs of No. 1 and No. 4 cylinders to generate
sparks. At the time that the sparks are generated
at both spark plugs, if one cylinder is at the
compression stroke, the other cylinder is at the
exhaust stroke, so that ignition of the compressed
air/fuel mixture occurs only for the cylinder which
is at the compression stroke.
In the same way, when the primary current flowing
in ignition coil B is interrupted, the high voltage
thus generated is applied to the spark plugs of
No. 2 and No. 3 cylinders.
The Engine-ECU turns the two power transistors
inside the ignition coils alternately on and off. Thiscauses the primary currents in the ignition coils
to be alternately interrupted and allowed to flow
to fire the cylinders in the order 1-3-4-2.
The Engine-ECU determines which ignition coil
should be controlled by means of the signals from
the camshaft position sensor which is incorporated
in the camshaft and from the crank angle sensor
which is incorporated in the crankshaft. It also
detects the crankshaft position in order to provide
ignition at the most appropriate timing in response
to the engine operation conditions. It also detects
the crankshaft position in order to provide ignition
at the most appropriate timing in response to the
engine operation conditions.
When the engine is cold or operated at high
altitudes, the ignition timing is slightly advanced
to provide optimum performance.
When the automatic transmission shifts gears, the
ignition timing is also retarded in order to reduce
output torque, thereby alleviating shifting shocks.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Crank angle sensor
Ignition switch - ST
Vehicle speed signalEngine-ECU
Ignition coil A
Ignition coil B Ignition switch
Spark plugBattery
To tachometerCylinder No. Air flow sensor
1 4
23
Detonation sensor