Page 648 of 1449

MPI -Troubleshooting13A-116
INSPECTION PROCEDURE USING AN
ANALYZER
AIR FLOW SENSOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the air flow sensor connector, and connect
the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in between.
(All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to air flow
sensor connector terminal No. 3.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 65.
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightLow
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minIdle speed
Standard wave pattern
(V)
10
0The time (cycle time) T is reduced when
the amount of intake air increases.
Times T1 and T2 are equal.
Time T
T1 T2
Observation conditions (from conditions above engine speed is increased by racing.)
Time (V)
10
0T
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Check that cycle time T becomes shorter and the frequency increases when the engine speed is increased.
Analyzer
Special
patterns
pickup
Page 649 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-117
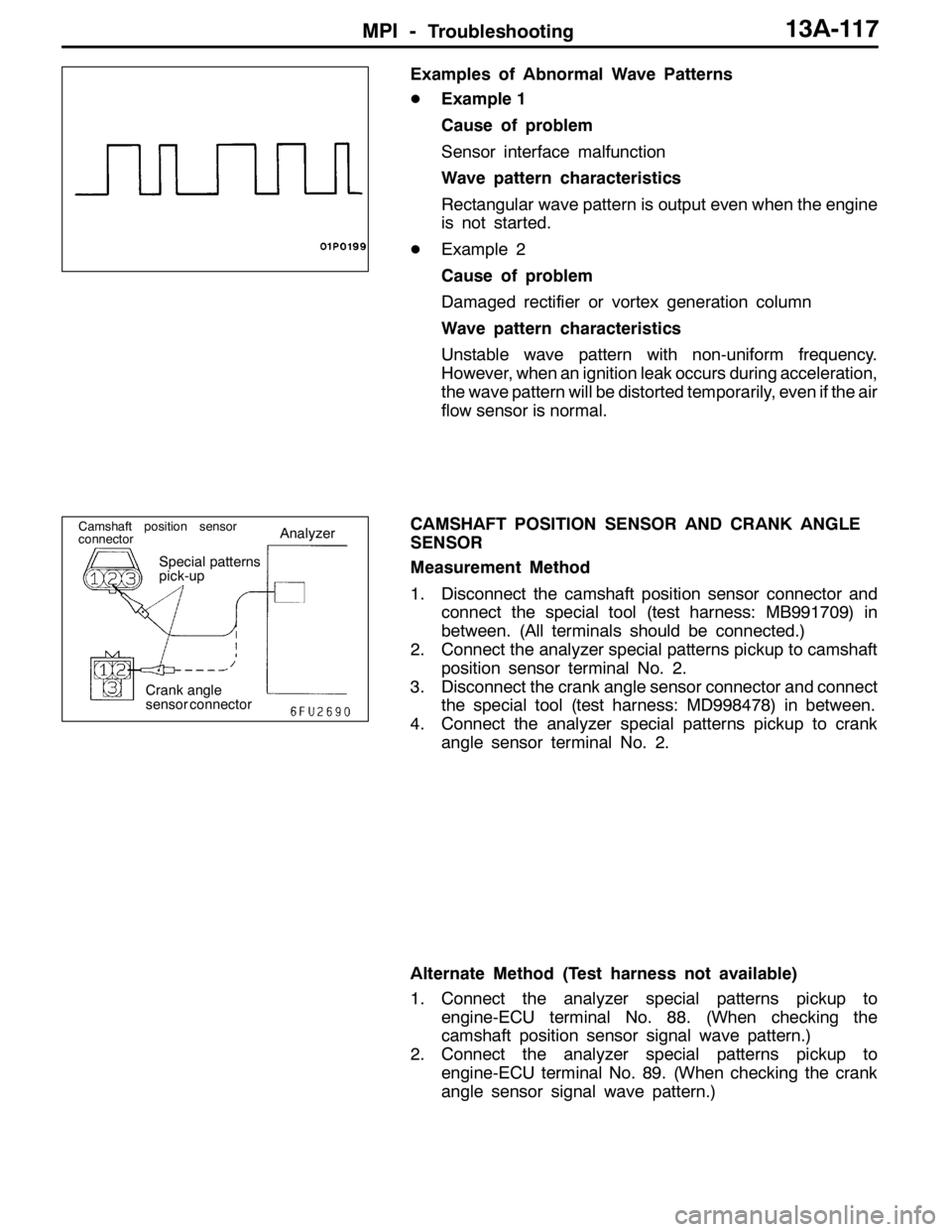
Examples of Abnormal Wave Patterns
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Sensor interface malfunction
Wave pattern characteristics
Rectangular wave pattern is output even when the engine
is not started.
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Damaged rectifier or vortex generation column
Wave pattern characteristics
Unstable wave pattern with non-uniform frequency.
However, when an ignition leak occurs during acceleration,
the wave pattern will be distorted temporarily, even if the air
flow sensor is normal.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR AND CRANK ANGLE
SENSOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the camshaft position sensor connector and
connect the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in
between. (All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to camshaft
position sensor terminal No. 2.
3. Disconnect the crank angle sensor connector and connect
the special tool (test harness: MD998478) in between.
4. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to crank
angle sensor terminal No. 2.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 88. (When checking the
camshaft position sensor signal wave pattern.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 89. (When checking the crank
angle sensor signal wave pattern.)
Crank angle
sensor connector
Camshaft position sensor
connectorAnalyzer
Special patterns
pick-up
Page 651 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-119
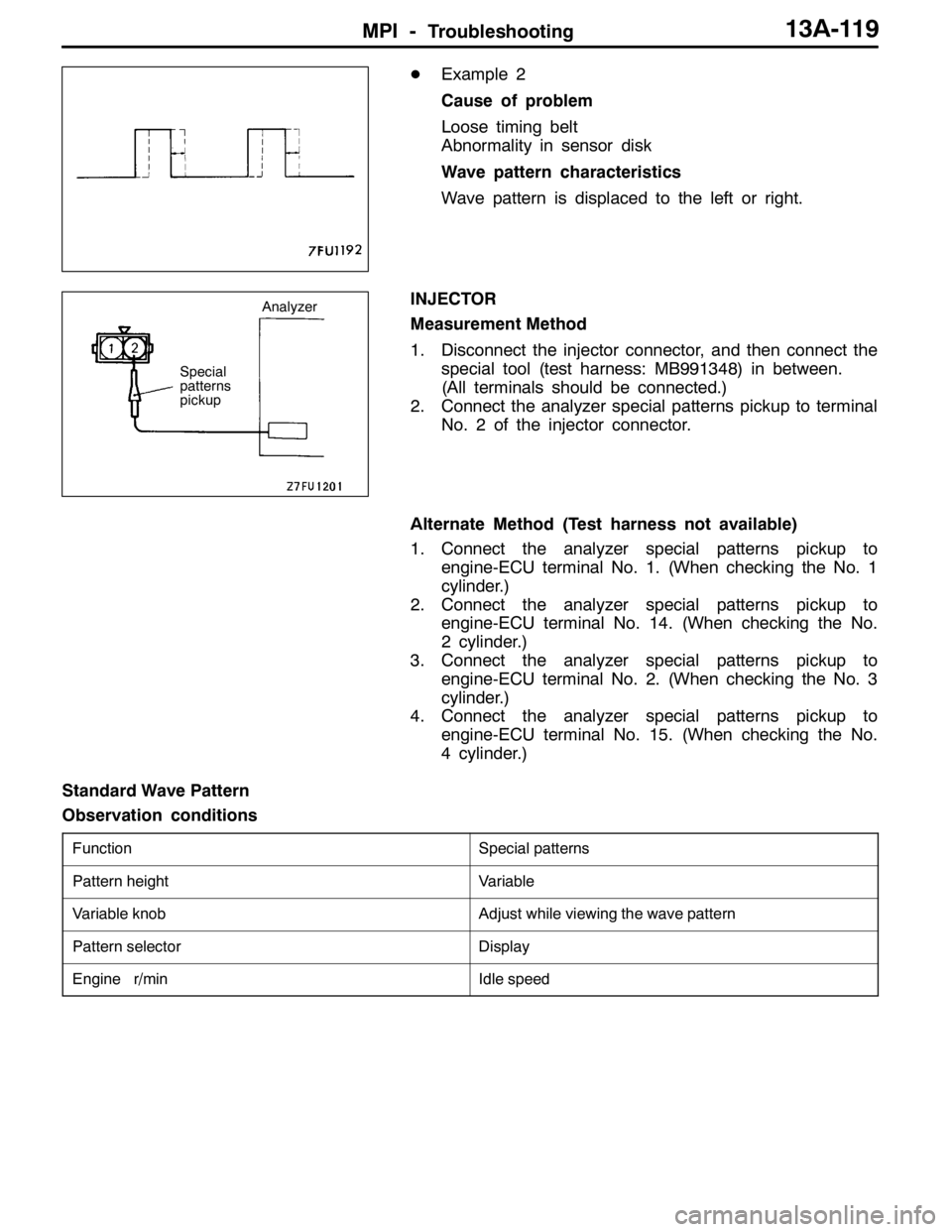
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Loose timing belt
Abnormality in sensor disk
Wave pattern characteristics
Wave pattern is displaced to the left or right.
INJECTOR
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the injector connector, and then connect the
special tool (test harness: MB991348) in between.
(All terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to terminal
No. 2 of the injector connector.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 1. (When checking the No. 1
cylinder.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 14. (When checking the No.
2 cylinder.)
3. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 2. (When checking the No. 3
cylinder.)
4. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 15. (When checking the No.
4 cylinder.)
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightVariable
Variable knobAdjust while viewing the wave pattern
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minIdle speed
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 653 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-121
IDLE SPEED CONTROL SERVO (STEPPER MOTOR)
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the idle speed control servo connector, and
connect the special tool (test harness: MB991709) in
between.
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to the idle
speed control servo-side connector terminal No. 1,
terminal No. 3, terminal No. 4 and terminal No. 6
respectively.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 4, connection terminal No. 5,
connection terminal No. 17, and connection terminal No.
18 respectively.
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation conditions
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightHigh
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine conditionWhen the engine coolant temperature is 20_C or below, turn the ignition switch from “LOCK”
(OFF) position to “ON” position (without starting the engine).
While the engine is idling, turn the A/C switch to ON.
Immediately after starting the warm engine
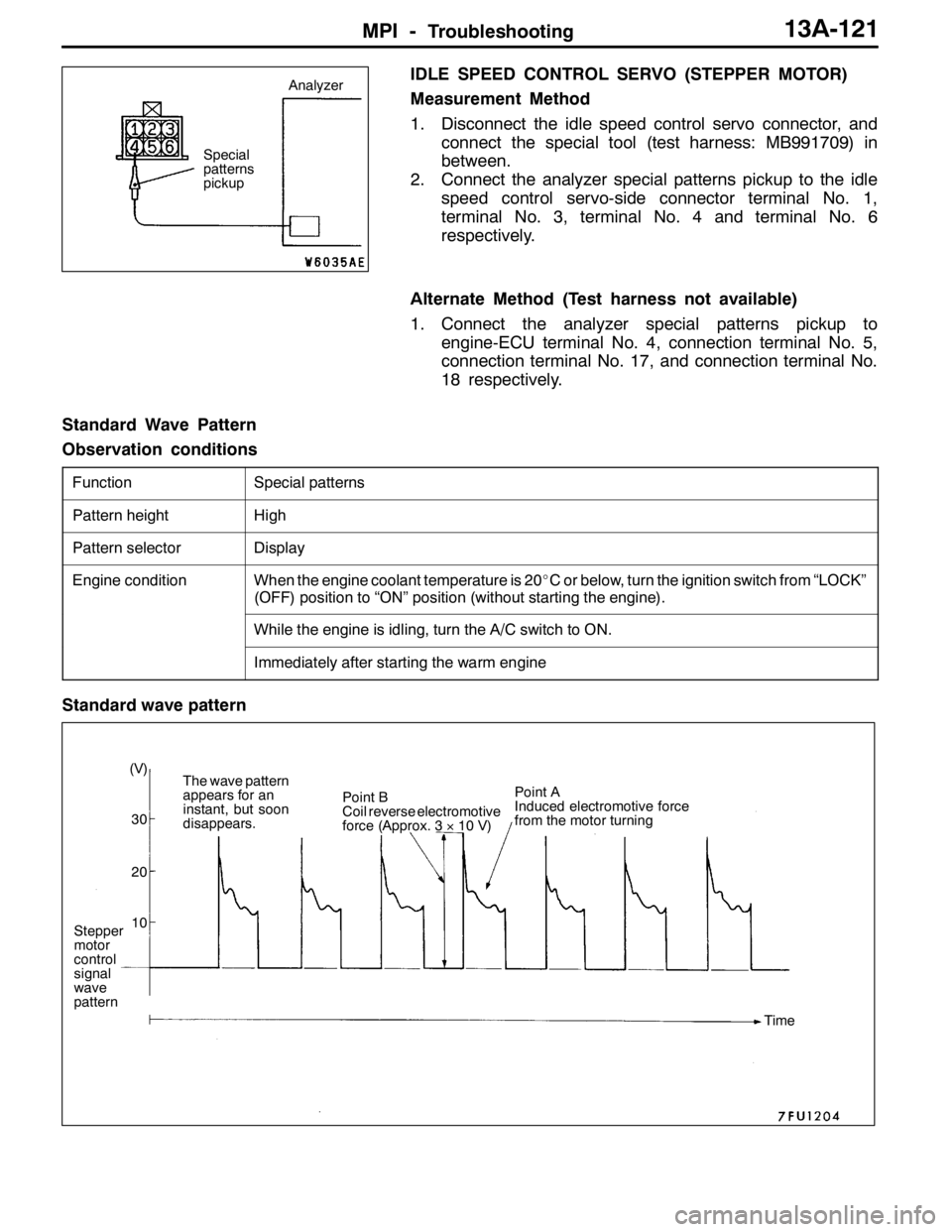
Standard wave pattern
Stepper
motor
control
signal
wave
pattern(V)
30
20
10The wave pattern
appears for an
instant, but soon
disappears.Point B
Coil reverse electromotive
force (Approx. 3×10 V)Point A
Induced electromotive force
from the motor turning
Time
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 654 of 1449
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-122
Wave Pattern Observation Points
Check that the standard wave pattern appears when the stepper motor is operating.
Point A: Presence or absence of induced electromotive force from the motor turning. (Refer to the abnormal
wave pattern.)
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Induced electromotive force does not appear or is extremely small.Motor is malfunctioning
Point B: Height of coil reverse electromotive force
Contrast with standard wave patternProbable cause
Coil reverse electromotive force does not appear or is extremely small.Short in the coil
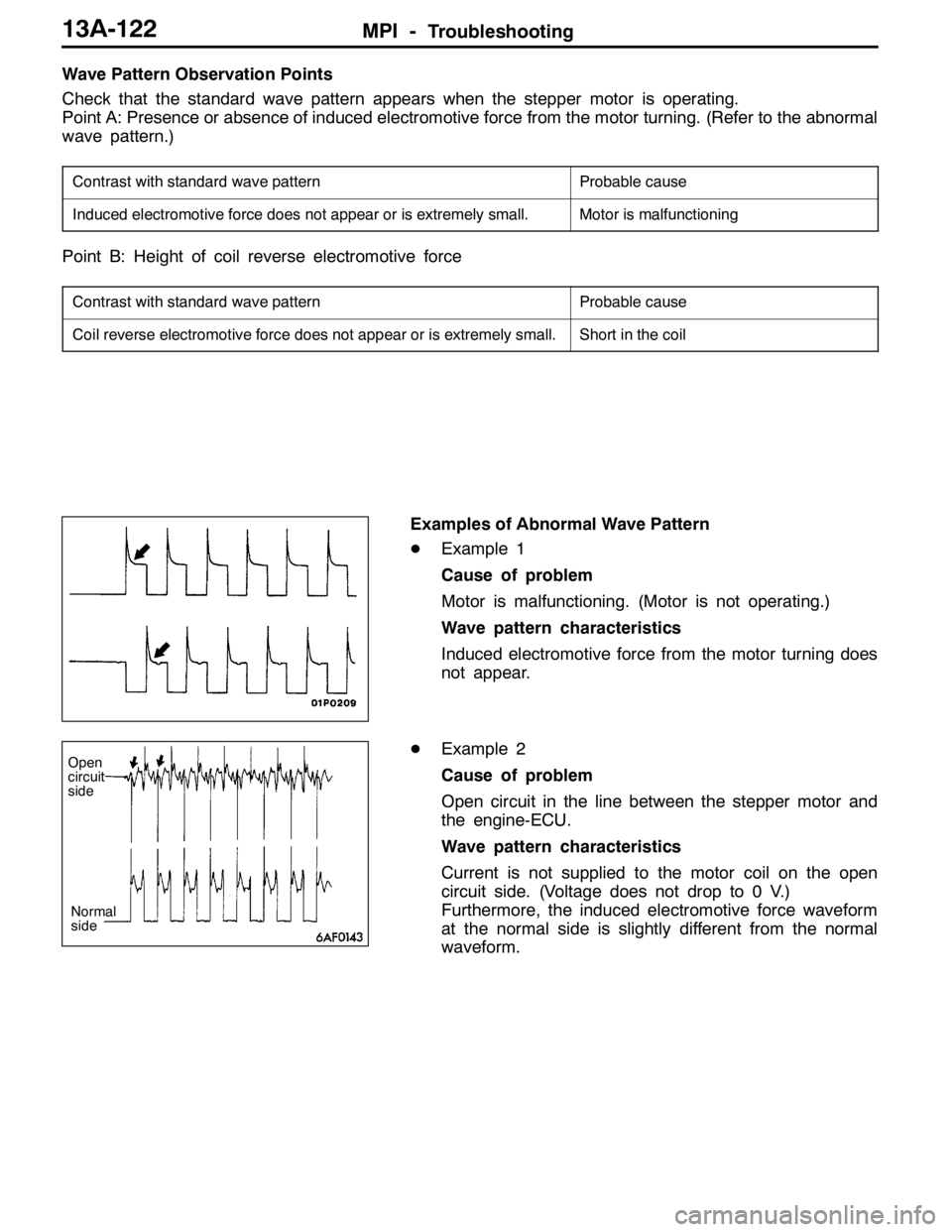
Examples of Abnormal Wave Pattern
DExample 1
Cause of problem
Motor is malfunctioning. (Motor is not operating.)
Wave pattern characteristics
Induced electromotive force from the motor turning does
not appear.
DExample 2
Cause of problem
Open circuit in the line between the stepper motor and
the engine-ECU.
Wave pattern characteristics
Current is not supplied to the motor coil on the open
circuit side. (Voltage does not drop to 0 V.)
Furthermore, the induced electromotive force waveform
at the normal side is slightly different from the normal
waveform.
Open
circuit
side
Normal
side
Page 655 of 1449
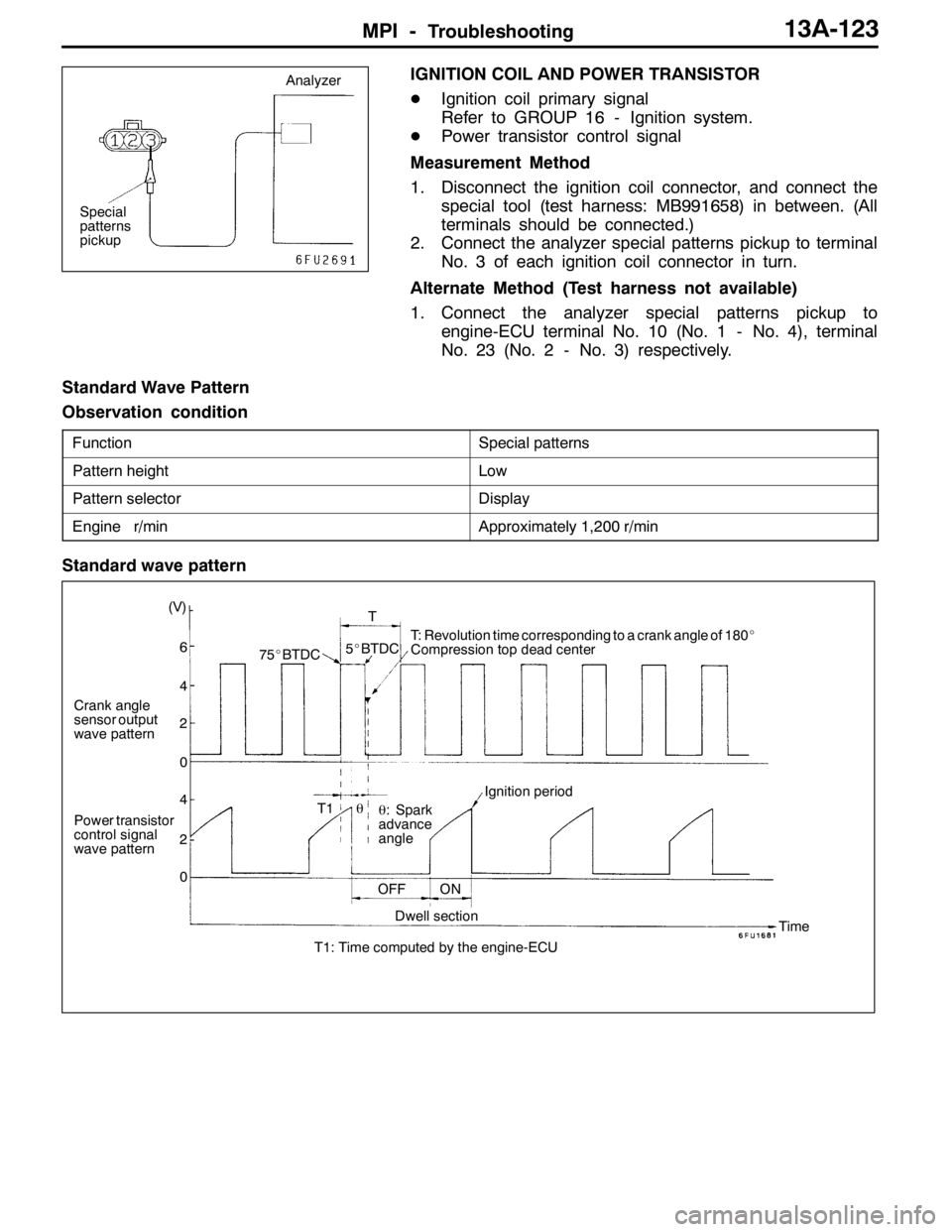
MPI -Troubleshooting13A-123
IGNITION COIL AND POWER TRANSISTOR
DIgnition coil primary signal
Refer to GROUP 16 - Ignition system.
DPower transistor control signal
Measurement Method
1. Disconnect the ignition coil connector, and connect the
special tool (test harness: MB991658) in between. (All
terminals should be connected.)
2. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to terminal
No. 3 of each ignition coil connector in turn.
Alternate Method (Test harness not available)
1. Connect the analyzer special patterns pickup to
engine-ECU terminal No. 10 (No. 1 - No. 4), terminal
No. 23 (No. 2 - No. 3) respectively.
Standard Wave Pattern
Observation condition
FunctionSpecial patterns
Pattern heightLow
Pattern selectorDisplay
Engine r/minApproximately 1,200 r/min
Standard wave pattern
Crank angle
sensor output
wave pattern
Power transistor
control signal
wave pattern(V)
75_BTDC5_BTDCT: Revolution time corresponding to a crank angle of 180_
Compression top dead center
θ: Spark
advance
angleIgnition period
OFF ON
Dwell section
T1: Time computed by the engine-ECUTime θ T1T
6
4
2
0
4
2
0
Special
patterns
pickupAnalyzer
Page 663 of 1449
MPI -On-vehicle Service13A-131
COMPONENT LOCATION
NameSymbolNameSymbol
A/C relayJFuel pump relay 1, 2Q
A/C switchTFuel pump relay 3H
Air flow sensor (integrated intake air tempera-
ture sensor and barometric pressure sensor)OFuel pump resistorH
Camshaft position sensorNIdle speed control servo (stepper motor)G
Crank angle sensorKIgnition coil (integrated power transister)M
Detonation sensorEInjectorC
Diagnosis connectorSOxygen sensor (front)L
EGR control solenoid valveDOxygen sensor (rear)X
Engine control relayIPower steering fluid pressure switchA
Engine coolant temperature sensorNResistor (for injector)H
Engine warning lamp (check engine lamp)RSecondary air control solenoid valveD
Engine-ECUUThrottle position sensorG
Fan motor relayJVehicle speed sensorF
Fuel pressure control solenoid valveBWaste gate solenoid valveP
ABCDEFGHIJK
LMNOP
QRSTU
Page 668 of 1449
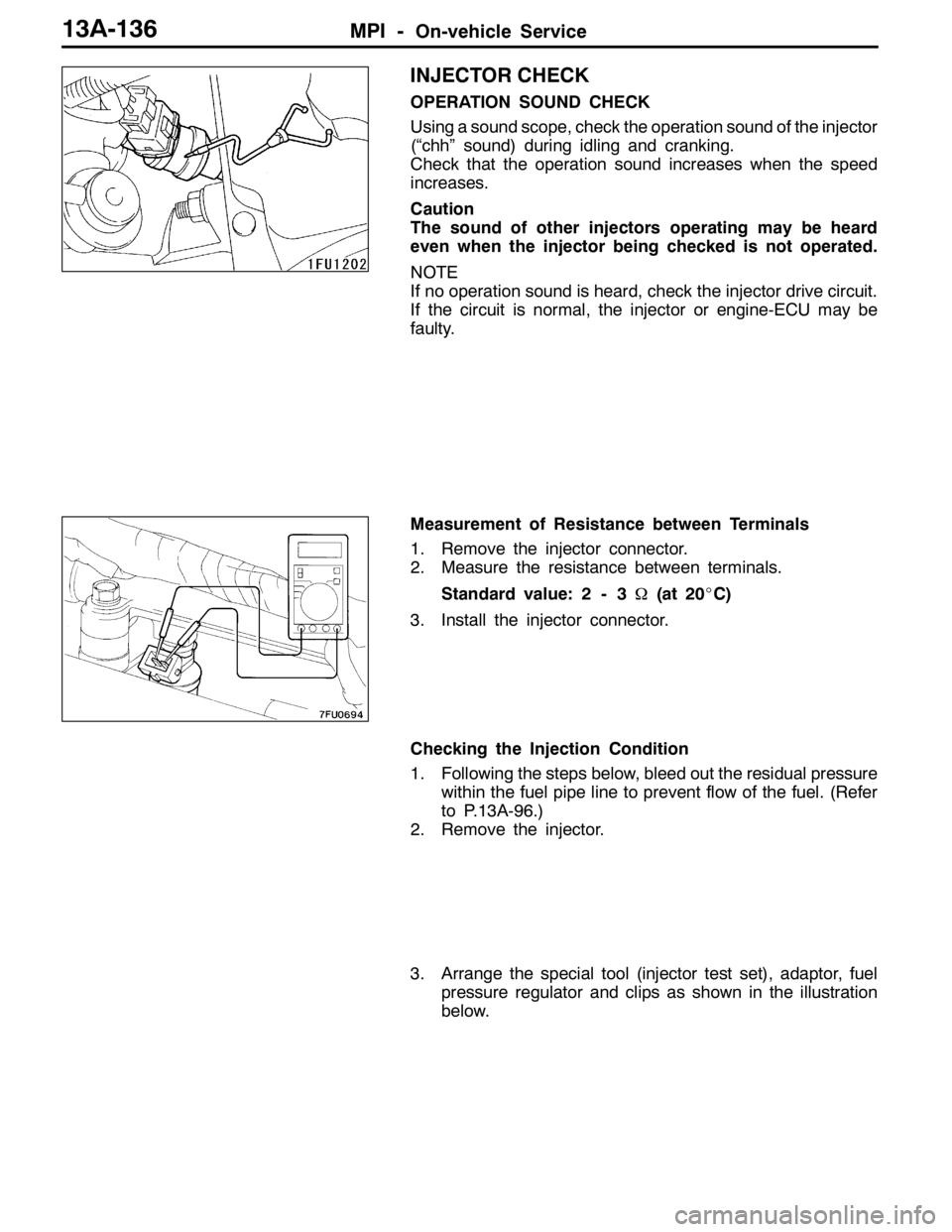
MPI -On-vehicle Service13A-136
INJECTOR CHECK
OPERATION SOUND CHECK
Using a sound scope, check the operation sound of the injector
(“chh” sound) during idling and cranking.
Check that the operation sound increases when the speed
increases.
Caution
The sound of other injectors operating may be heard
even when the injector being checked is not operated.
NOTE
If no operation sound is heard, check the injector drive circuit.
If the circuit is normal, the injector or engine-ECU may be
faulty.
Measurement of Resistance between Terminals
1. Remove the injector connector.
2. Measure the resistance between terminals.
Standard value: 2 - 3Ω(at 20_C)
3. Install the injector connector.
Checking the Injection Condition
1. Following the steps below, bleed out the residual pressure
within the fuel pipe line to prevent flow of the fuel. (Refer
to P.13A-96.)
2. Remove the injector.
3. Arrange the special tool (injector test set), adaptor, fuel
pressure regulator and clips as shown in the illustration
below.