2007 ISUZU KB P190 length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 2732 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–253
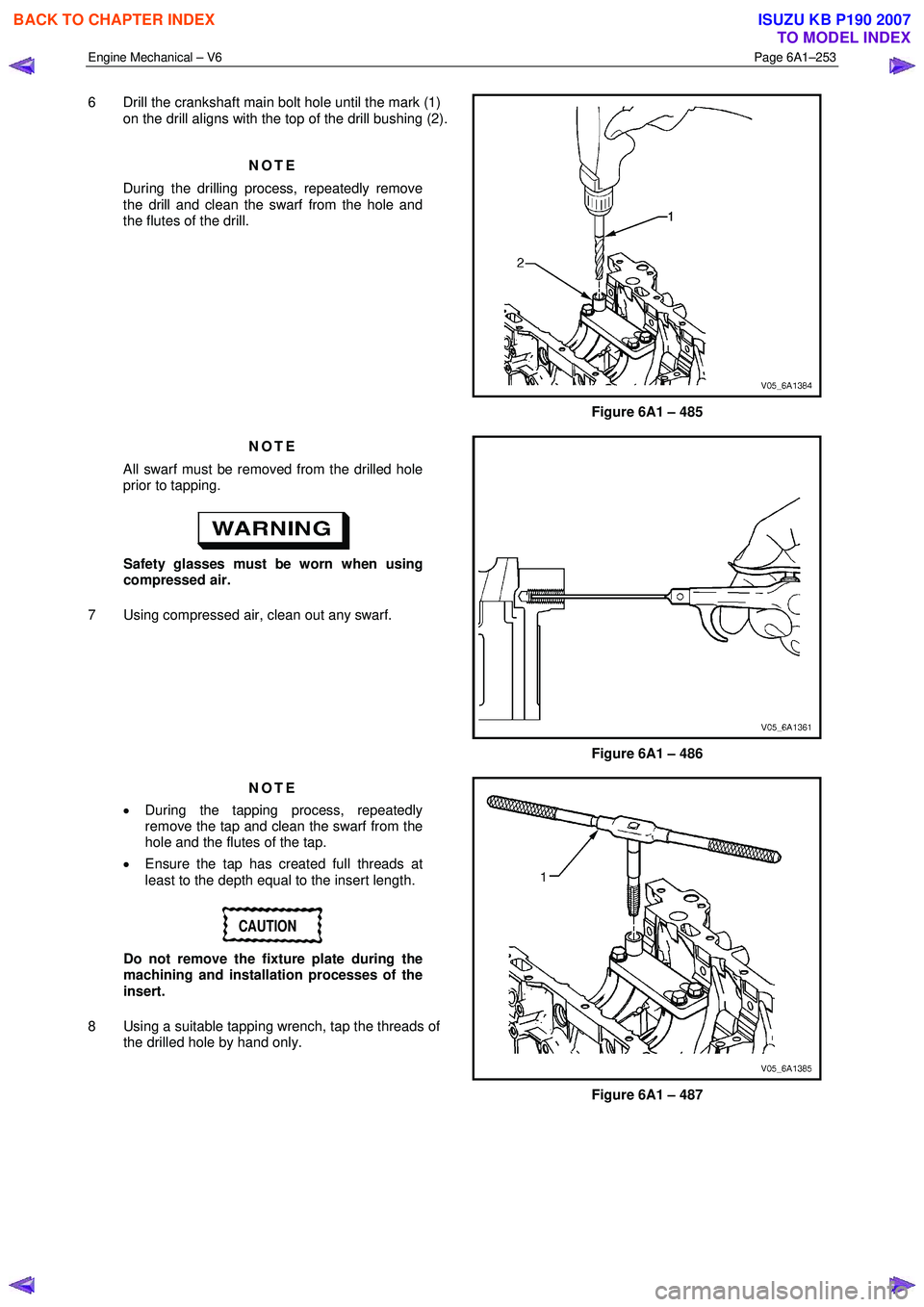
6 Drill the crankshaft main bolt hole until the mark (1)
on the drill aligns with the top of the drill bushing (2).
NOTE
During the drilling process, repeatedly remove
the drill and clean the swarf from the hole and
the flutes of the drill.
Figure 6A1 – 485
NOTE
All swarf must be removed from the drilled hole
prior to tapping.
Safety glasses must be worn when using
compressed air.
7 Using compressed air, clean out any swarf.
Figure 6A1 – 486
NOTE
• During the tapping process, repeatedly
remove the tap and clean the swarf from the
hole and the flutes of the tap.
• Ensure the tap has created full threads at
least to the depth equal to the insert length.
CAUTION
Do not remove the fixture plate during the
machining and installation processes of the
insert.
8 Using a suitable tapping wrench, tap the threads of the drilled hole by hand only.
Figure 6A1 – 487
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2738 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–259
NOTE
All swarf must be removed from the drilled hole
prior to tapping.
Safety glasses must be worn when using
compressed air.
7 Using compressed air, clean out any swarf.
Figure 6A1 – 502
CAUTION
Do not remove the fixture plate during the
machining and installation processes of the
insert.
NOTE
• During the tapping process, repeatedly
remove the tap and clean swarf from the
hole and the flutes of the tap.
• Ensure the tap has created full threads at
least to the depth equal to the insert length.
8 Using a suitable tapping wrench, tap the threads of the drilled hole by hand only.
Figure 6A1 – 503
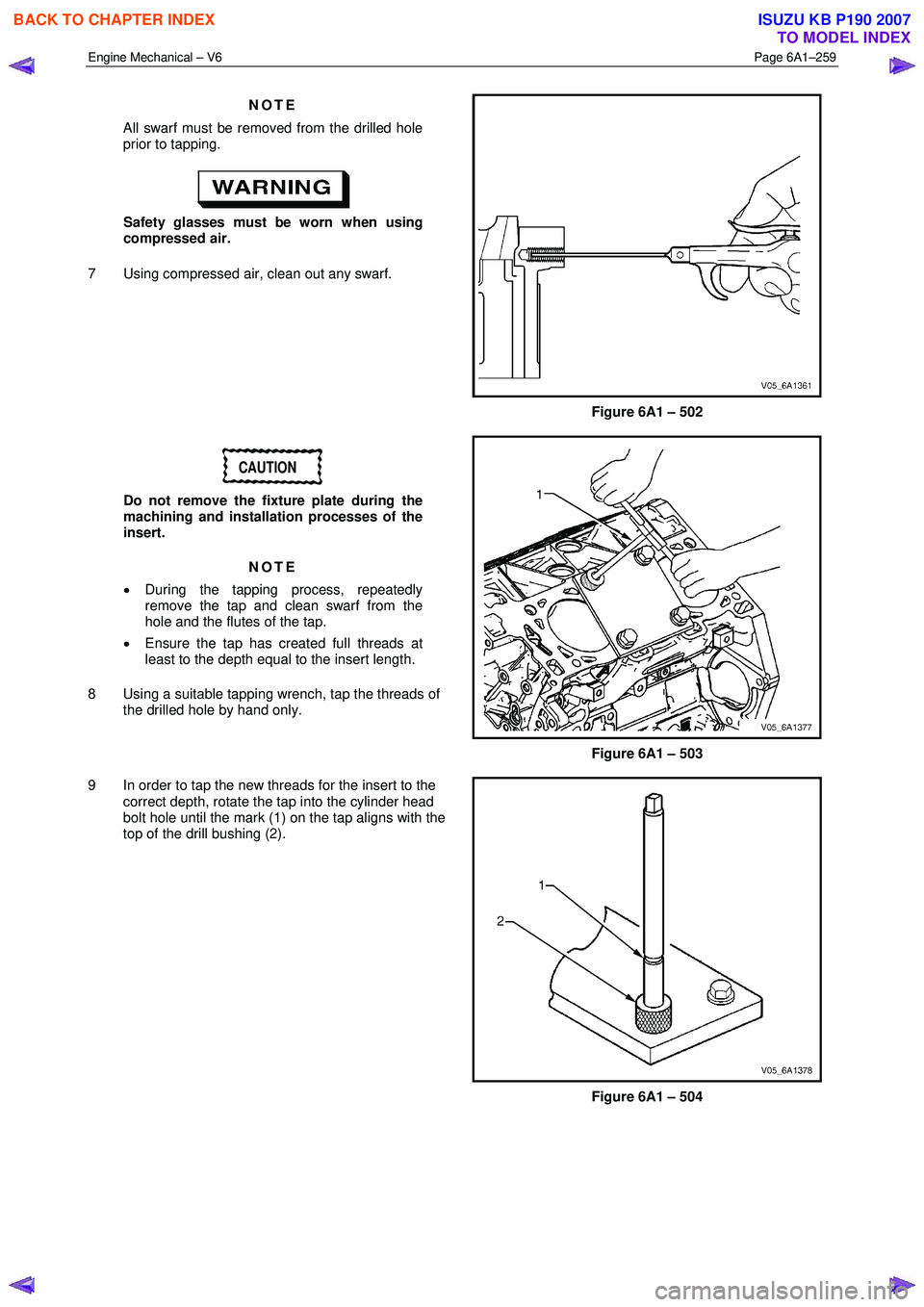
9 In order to tap the new threads for the insert to the correct depth, rotate the tap into the cylinder head
bolt hole until the mark (1) on the tap aligns with the
top of the drill bushing (2).
Figure 6A1 – 504
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2767 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–288
5 Specifications
General
Engine Type.................................................................................................................... ..... V6
Bank Angle ..................................................................................................................... .... 60°
Displacement ............................................................................................ 3.6 litre (3,565 cm3)
Bore ........................................................................................................................... .... 94 mm
Stroke ......................................................................................................................... 85.6 mm
Compression Ratio ......................................................................................................... 10.2: 1
Cranking Speed at 40 °C .............................................................................................80 r.p.m.
Spark Plug Gap ............................................................................................................ 1.1 m m
Firing Order............................................................................................................. 1-2-3- 4-5-6
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter ........................................................................... 93.992 – 94.008 mm
Cylinder Out-of-Round – Production Maximum ........................................................ 0.013 mm
Crankshaft Main bearing bore Diameter .................................................. 72.867 – 72.881 mm
Cylinder Head Deck Surface Flatness ........................................................................ 0.05 mm
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal Diameter ........................................................... 55.992 – 56.008 mm
Connecting Rod Journal Out-of-Round..................................................................... 0.005 mm
Connecting Rod Journal Taper ................................................................................ .0.005 mm
Connecting Rod Journal Width (Production)........................................................... 22.000 mm
Connecting Rod Journal Width (Service limit).......................................... 21.920 – 22.080 mm
Crankshaft End Play .................................................................................... 0.100 – 0.330 mm
Crankshaft Main Bearing Clearance ............................................................ 0.010 – 0.060 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Diameter ......................................................... .67.992 – 68.008 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Out-of-Round .................................................................... 0.005 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Taper................................................................................ .0.005 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #2, 4 (Production) ....................................................... 24 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #2, 4 (Service)....................................... 23.900 – 24.100 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #3 (Production) .................................................... 24.400 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Width, #3 (Service) .......................................... 24.360 – 24.440 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Thrust Wall Runout .............................................. 0.000 – 0.040 mm
Crankshaft Main Journal Thrust Wall Square .............................................. 0.000 – 0.010 mm
Crankshaft Rear Flange Runout ............................................................................... 0.025 mm
Crankshaft Reluctor Ring Runout - Maximum........................................................... 1.500 mm
Crankshaft Thrust Bearing Clearance.......................................................... 0.076 – 0.305 mm
Crankshaft Thrust Surface Runout ........................................................................... 0.040 mm
Crankshaft Thrust Surface – Height Diameter ........................................................ 95.000 mm
Connecting Rod
Connecting Rod Length - Bore Centre-to-Centre.................................................. 150.400 mm
Connecting Rod Bore Diameter - Bearing End ........................................ 59.620 – 59.636 mm
Connecting Rod Bore Diameter - Pin End ............................................... 24.007 – 24.021 mm
Connecting Rod Width ........................................................................................... 21.775 mm
Connecting Rod Side Clearance.................................................................. 0.095 – 0.355 mm
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance ............................................................ 0.010 – 0.070 mm
Piston
Piston Diameter ....................................................................................... 93.956 – 93.974 mm
Piston Pin Bore Diameter ........................................................................ 24.005 – 24.009 mm
Piston Ring Groove Width - First (Top) Compression Ring ......................... 1.220 – 1.240 mm
Piston Ring Groove Width - Second Compression Ring .............................. 1.510 – 1.530 mm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2768 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–289
Piston Ring Groove Width - Oil Control Ring ............................................... 2.510 – 2.530 mm
Piston to Bore Clearance ............................................................................. 0.026 – 0.052 mm
Piston Pin
Piston Pin Diameter ..................................................................................23.997 - 24.000 mm
Piston Pin Length..................................................................................... 60.600 – 61.100 mm
Piston Pin Clearance to Connecting Rod Bore ............................................. 0.007 – 0.024mm
Piston Pin Clearance to Piston Pin Bore....................................................... 0.004 – 0.012mm
Piston Rings
Piston Ring to Groove Clearance:
• First (Top) Compression Ring............................................................... 0.030 – 0.065 mm
• Second Compression Ring ................................................................... 0.015 – 0.060 mm
• Oil Control Ring .................................................................................... 0.030 – 0.170 mm
Piston Ring End Gap:
• First (Top) Compression Ring............................................................... 0.150 – 0.300 mm
• Second Compression Ring ................................................................... 0.280 – 0.480 mm
• Oil Control Ring .................................................................................... 0.150 – 0.600 mm
Cylinder Head
Combustion Chamber Volume.................................................................................. 53.600 cc
Valve Guide Bore Diameter – Intake ........................................................... 6.000 – 6.020 mm
Valve Guide Bore Diameter – Exhaust ........................................................ 6.000 – 6.020 mm
Valve Guide Installed Height.................................................................... 14.050 – 14.550 mm
Stationary Hydraulic Lash Adjuster (SHLA) Bore Diameter ..................... 12.008 – 12.030 mm
Valve Seat Angle – Seating Surface ................................................................................... 45 °
Valve Seat Angle – Relief Surface ...................................................................................... 30 °
Valve Seat Angle – Undercut Surface ................................................................................ 60 °
Valve Seat Runout – Maximum ................................................................................ 0.050 mm
Valve Seat Width – Exhaust Seating Surface .............................................. 1.400 – 1.800 mm
Valve Seat Width – Exhaust Relief Surface ................................................. 0.700 – 0.900 mm
Valve Seat Width – Intake Seating Surface ................................................. 1.000 – 1.400 mm
Valve Seat Width – Intake Relief Surface .................................................... 0.500 – 0.700 mm
Engine Block Deck Surface Flatness .......................................................................... 0.05 mm
Exhaust Manifold Deck Surface Flatness ................................................................... 0.25 mm
Intake Manifold Deck Surface Flatness ...................................................................... 0.05 mm
Valve System
Face Angle..................................................................................................................... 44.25°
Face Runout ............................................................................................................. 0.038 m m
Valve Face Width – Exhaust..................................................................................... 2.750 mm
Valve Face Width – Intake ........................................................................................ 2.180 mm
Valve Head Diameter – Exhaust .............................................................. 30.470 – 30.730 mm
Valve Head Diameter – Intake ................................................................. 36.830 – 37.090 mm
Valve Installed Height .................................................................................. 35.26 – 36.69 mm
Valve Length – Exhaust .......................................................................................... 97.110 mm
Valve Length – Intake ........................................................................................... 101.230 mm
Valve Stem Diameter (standard).................................................................. 5.955 – 5.975 mm
Valve Stem Diameter (oversize) .................................................................. 6.013 – 6.033 mm
Valve Stem to Guide Clearance................................................................... 0.025 – 0.065 mm
Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Diameter ........................................................... 11.986 – 12.000 mm
Hydraulic Lash Adjuster to Bore Clearance ................................................. 0.037 – 0.041 mm
Rocker Arm/Camshaft Follower Ratio............................................................................. 1.68:1
Rocker Arm/Camshaft Follower Roller Diameter ..................................... 17.740 – 17.800 mm
Valve Spring Free Length ........................................................................ 42.500 – 45.500 mm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2785 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–8
Page 6A1–8
1 General Information
The HFV6 engine features a closed vee, deep skirt die cast aluminium cylinder block with cast iron cylinder liners,
internally balanced crankcase, full length wa ter jackets and six bolt main bearing caps.
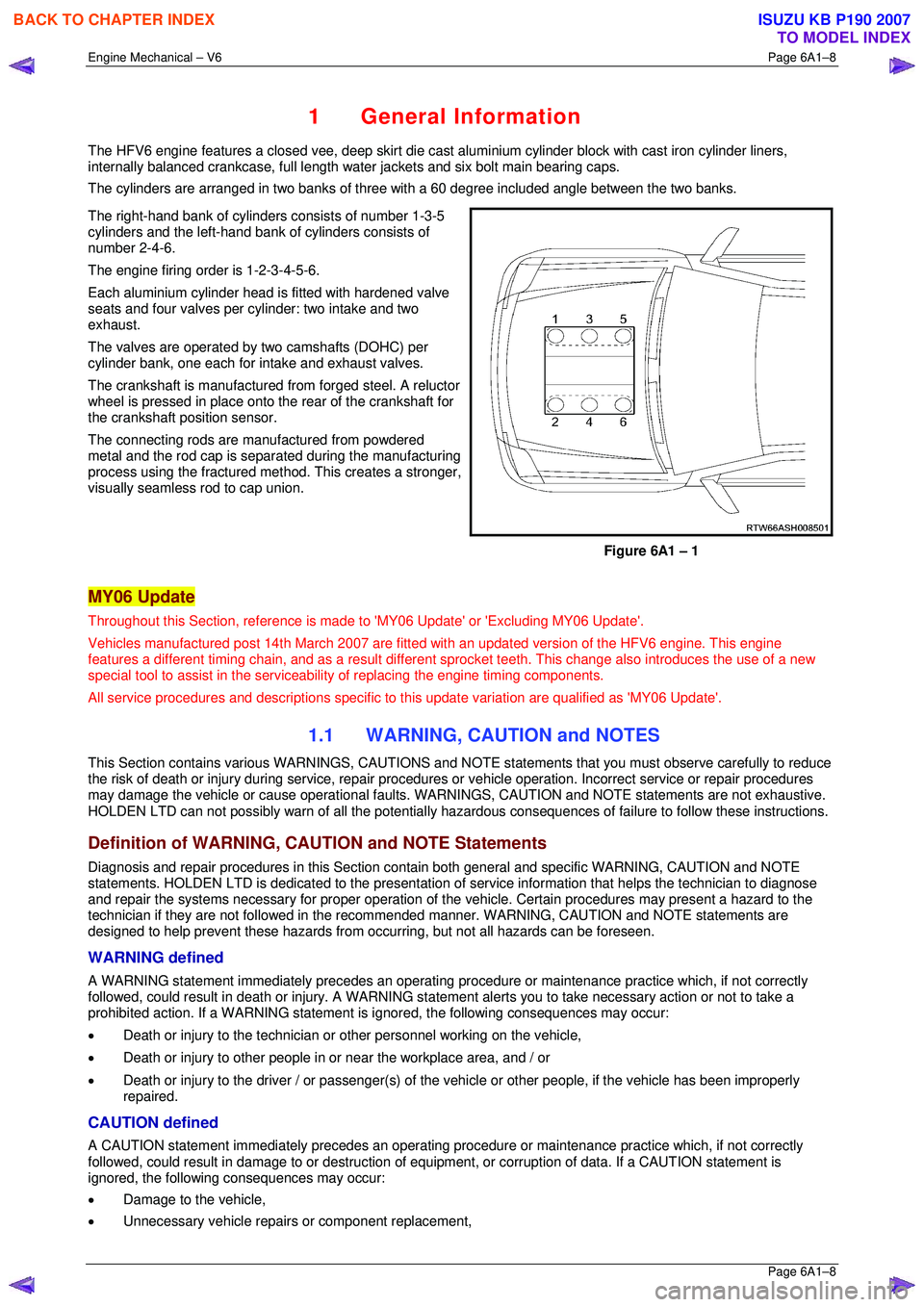
The cylinders are arranged in two banks of three with a 60 degree included angle between the two banks.
The right-hand bank of cylinders consists of number 1-3-5
cylinders and the left-hand bank of cylinders consists of
number 2-4-6.
The engine firing order is 1-2-3-4-5-6.
Each aluminium cylinder head is fitted with hardened valve
seats and four valves per cylinder: two intake and two
exhaust.
The valves are operated by two camshafts (DOHC) per
cylinder bank, one each for intake and exhaust valves.
The crankshaft is manufactured from forged steel. A reluctor
wheel is pressed in place onto the rear of the crankshaft for
the crankshaft position sensor.
The connecting rods are m anufactured from powdered
metal and the rod cap is separ ated during the manufacturing
process using the fractured me thod. This creates a stronger,
visually seamless rod to cap union.
Figure 6A1 – 1
MY06 Update
Throughout this Section, reference is made to 'MY06 Update' or 'Excluding MY06 Update'.
Vehicles manufactured post 14th Marc h 2007 are fitted with an updated version of the HFV6 engine. This engine
features a different timing chain, and as a result different sprocket teeth. This change also introduces the use of a new
special tool to assist in the serviceab ility of replacing the engine timing components.
All service procedures and descriptions specific to this update variation are qualified as 'MY06 Update'.
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various WARNING S, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that y ou must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during servic e, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operat ional faults. WARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of a ll the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the reco mmended manner. WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from o ccurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A WARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maint enance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury . A WARNING statement alerts you to ta ke necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a WARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately prec edes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equi pment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2833 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–56
Page 6A1–56
Step Action Yes No
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the squealing noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK.
Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis
of the noise Go to Step 4
4
Inspect the accessory drive components for a seized bearing and
general malfunctions.
Did you find and correct any seized bearings or general malfunctions
in the accessory drive system? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5
Test the accessory drive belt tensi oner for correct operation, refer to
Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner Diagnosis.
Did you find and repair any problems with t he tensioner? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
6
Inspect the accessory drive belt is the correct length, refer to 3.5
Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you find and repair any problems with the drive belt length? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 7
7 Inspect the accessory drive pulleys for misalignment.
Did you find and correct any misaligned accessory drive pulleys? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8 Check the accessory drive pulleys are the correct size.
Did you find and replace any incorrect pulleys? Go to Step 9 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
9 Reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm
the repair.
Did you correct the squeal noise? Accessory drive
system OK Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2839 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–62
Page 6A1–62
Drive Belt Falls Off
Definition
The drive belt falls off during normal operation or does not ride correctly on the accessory drive pulleys.
Diagnostic Aids
If the accessory drive belt repeatedly falls off the drive pulleys, this is most likely due to pulley misalignment.
An extra load that is quickly applied and released by an a ccessory drive component (e.g. A/C compressor) may cause
the accessory drive belt to fall off. In th is circumstance, confirm the fault by operating the accessory drive components in
turn, noting which one caused the belt to fall off.
Lack of drive belt tension may also cause the belt to fall o ff the pulleys. Low drive belt tension could be caused by one of
the following:
• an incorrect drive belt length,
• a faulty drive belt tensioner, or
• a stretched or faulty drive belt.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the condition of t he drive belt. Damage may have occurred to the dr ive belt when it first fell off or it may
have been damaged which caused the belt to fall off.
4 Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused by:
• the incorrect installation or mount ing of an accessory drive component,
• the incorrect installation of an a ccessory drive component pulley, or
• a damaged or bent accessory drive pulley.
Test for a misaligned pulley using a suitable straight edge in the pulley grooves across two or more pulleys. If a
misaligned pulley is found, refer to the service informa tion for the particular component, for the correct pulley
replacement procedures.
5 Inspecting the pulleys should include an inspection for dents or other damage that would prevent the drive belt from
seating correctly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface of a pulley when the back side of the belt is
used.
6 Accessory drive component mounting brackets that are bent will cause the drive belt to fall off.
7 Inspection of the fasteners can eliminat e the possibility that an incorrect fastener was installed. Missing, loose or
incorrect fasteners may cause pulley misalignment from the fasteners moving under load. Over-tightening of the
fasteners may cause deflection of mounting brackets and result in misaligned accessory drive pulleys.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Inspect for a damaged accessory drive belt.
Did you find any damage on the drive belt? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Install a new accessory drive belt, re
fer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Does the drive belt continue to fall off? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 12
4 Inspect the accessory drive system pulleys for misalignment
Did you find and repair any misaligned drive system pulleys? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 5
5 Inspect for a dented or cracked accessory drive system pulley.
Did you find and repair any dented or cracked drive system? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 6
6 Inspect for bent accessory drive component mounting brackets.
Did you find and repair any bent mounting brackets? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 7
7 Inspect for incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners.
Did you find any incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3055 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–278
Page 6A1–278
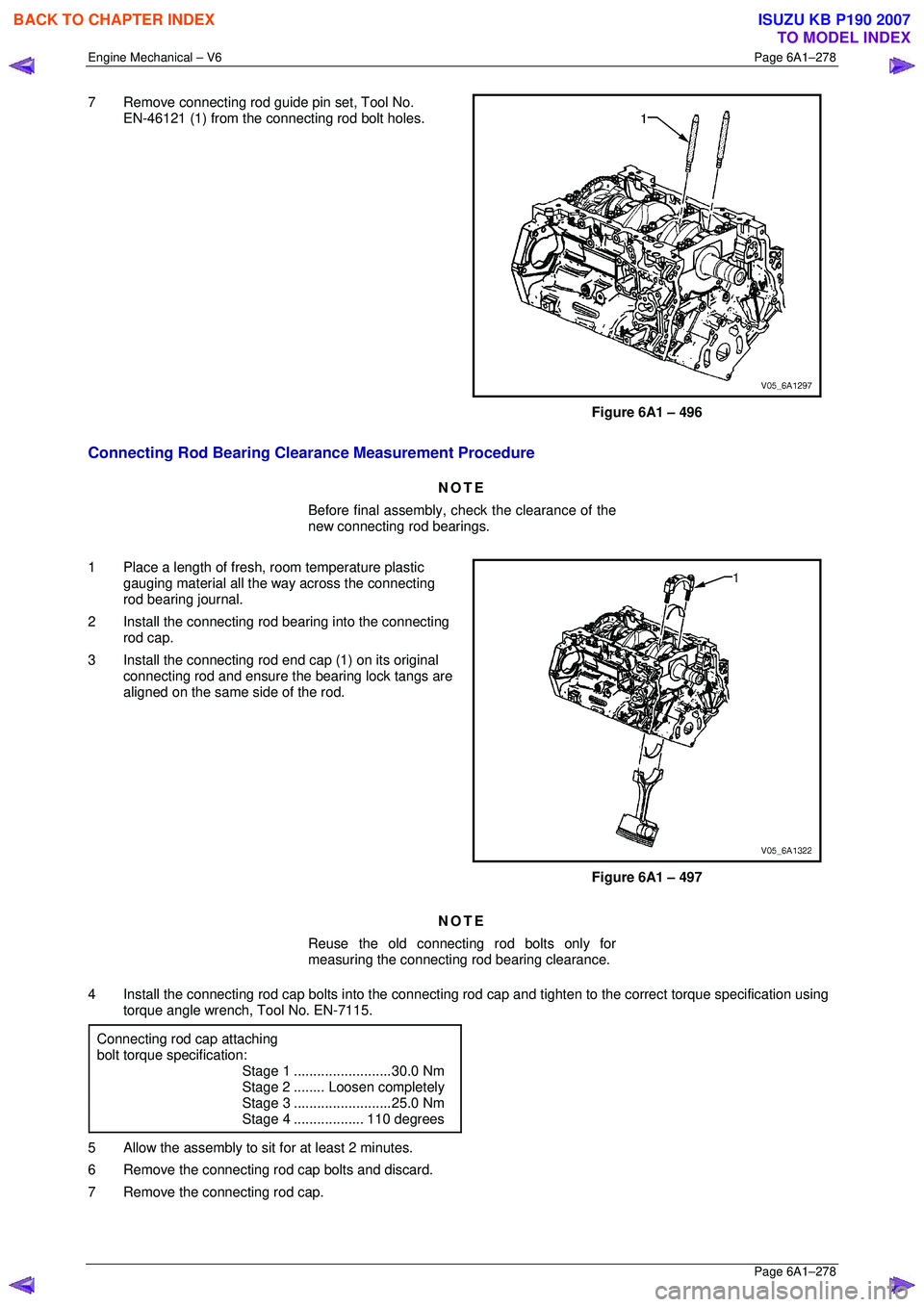
7 Remove connecting rod guide pin set, Tool No.
EN-46121 (1) from the connecting rod bolt holes.
Figure 6A1 – 496
Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance Measurement Procedure
NOTE
Before final assembly, check the clearance of the
new connecting rod bearings.
1 Place a length of fresh, room temperature plastic
gauging material all the way across the connecting
rod bearing journal.
2 Install the connecting rod bearing into the connecting
rod cap.
3 Install the connecting rod end cap (1) on its original
connecting rod and ensure t he bearing lock tangs are
aligned on the same side of the rod.
Figure 6A1 – 497
NOTE
Reuse the old connecting rod bolts only for
measuring the connecting rod bearing clearance.
4 Install the connecting rod cap bolts in to the connecting rod cap and tighten to the correct torque specification using
torque angle wrench, Tool No. EN-7115.
Connecting rod cap attaching
bolt torque specification:
Stage 1 .........................30.0 Nm
Stage 2 ........Loosen completely
Stage 3 .........................25.0 Nm
Stage 4 ..................110 degrees
5 Allow the assembly to sit for at least 2 minutes.
6 Remove the connecting rod cap bolts and discard.
7 Remove the connecting rod cap.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007