Page 1961 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–73
ES
DESCRIPTION
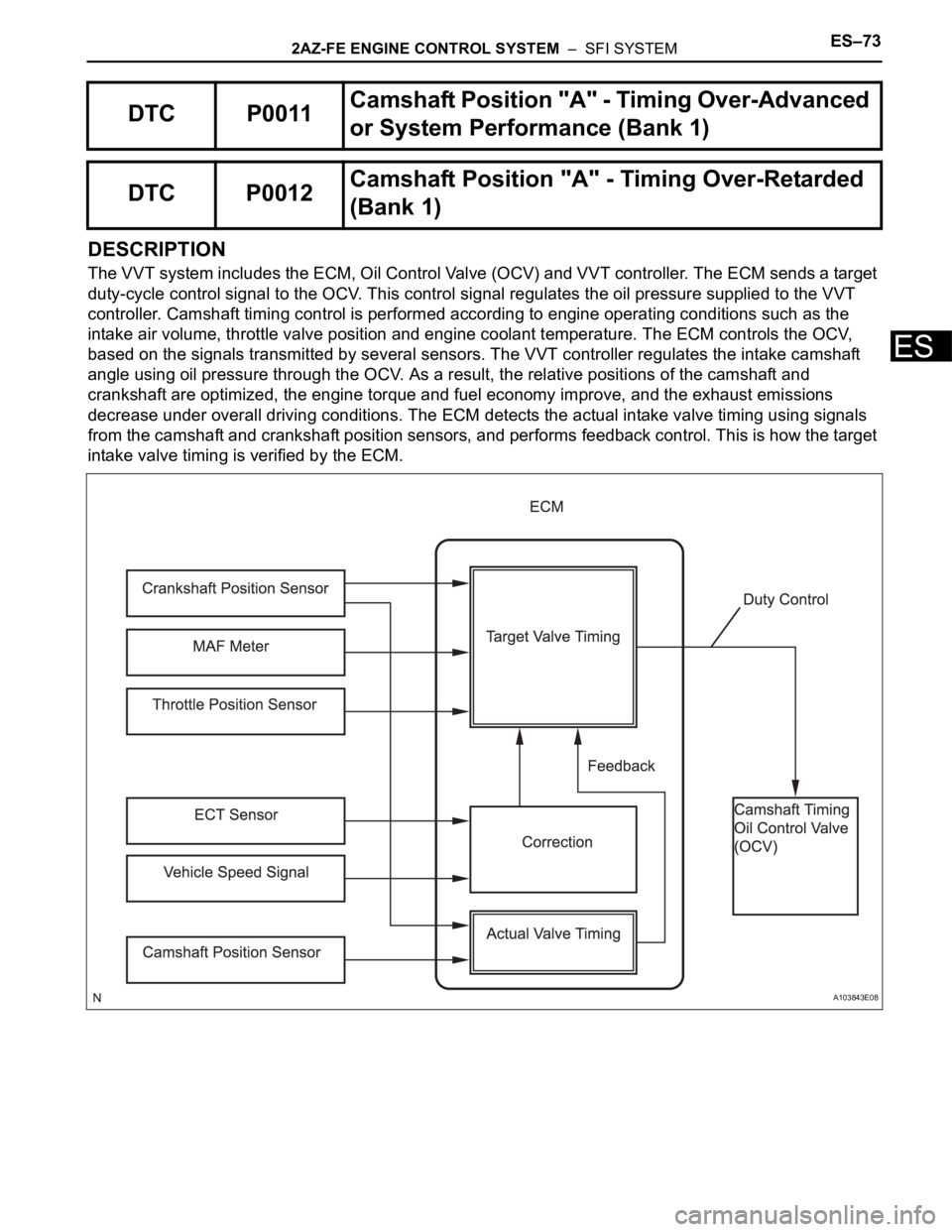
The VVT system includes the ECM, Oil Control Valve (OCV) and VVT controller. The ECM sends a target
duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil pressure supplied to the VVT
controller. Camshaft timing control is performed according to engine operating conditions such as the
intake air volume, throttle valve position and engine coolant temperature. The ECM controls the OCV,
based on the signals transmitted by several sensors. The VVT controller regulates the intake camshaft
angle using oil pressure through the OCV. As a result, the relative positions of the camshaft and
crankshaft are optimized, the engine torque and fuel economy improve, and the exhaust emissions
decrease under overall driving conditions. The ECM detects the actual intake valve timing using signals
from the camshaft and crankshaft position sensors, and performs feedback control. This is how the target
intake valve timing is verified by the ECM.
DTC P0011Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Over-Advanced
or System Performance (Bank 1)
DTC P0012Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Over-Retarded
(Bank 1)
A103843E08
Page 1962 of 2000

ES–742AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the intake valve timing using the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system to control the
intake camshaft. The VVT system includes the ECM, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) and the VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
If the difference between the target and actual intake valve timings is large, and changes in the actual
intake valve timing are small, the ECM interprets this as the VVT controller stuck malfunction and sets a
DTC.
Example:
A DTC is set when the following conditions 1, 2 and 3 are met:
1. The difference between the target and actual intake valve timing is more than 5
CA (Crankshaft
Angle) and the condition continues for more than 4.5 seconds.
2. It takes 5 seconds or more to change the valve timing by 5
CA.
3. After above conditions 1 and 2 are met, the OCV is forcibly activated 63 times or more.
DTC P0011 (Advanced Cam Timing) is subject to 1 trip detection logic.
DTC P0012 (Retarded Cam Timing) is subject to 2 trip detection logic.
These DTCs indicate that the VVT controller cannot operate properly due to OCV malfunctions or the
presence of foreign objects in the OCV.
The monitor will run if all of the following conditions are met:
– The engine is warm (the engine coolant temperature is 75
C [167F] or more).
– The vehicle has been driven at more than 64 km/h (40 mph) for 3 minutes.
– The engine has idled for 3 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0011Advanced camshaft timing:
With warm engine and engine speed of between 550 rpm and
4,000 rpm, all conditions (1), (2) and (3) met (1 trip detection
logic):
1. Difference between target and actual intake valve timings
more than 5
CA (Crankshaft Angle) for 4.5 seconds
2. Current intake valve timing fixed (timing changes less than
5
CA in 5 seconds)
3. Variations in VVT controller timing more than 19
CA of
maximum delayed timing (malfunction in advance timing)• Valve timing
•OCV
• OCV filter
• Camshaft timing gear assembly
•ECM
P0012Retarded camshaft timing:
With warm engine and engine speed of between 550 rpm and
4,000 rpm, all conditions (1), (2) and (3) met (2 trip detection
logic):
1. Difference between target and actual intake valve timings
more than 5
CA (Crankshaft Angle) for 4.5 seconds
2. Current intake valve timing fixed (timing changes less than
5
CA in 5 seconds)
3. Variations in VVT controller timing 19CA or less of
maximum delayed timing (malfunction in retarded timing)• Valve timing
•OCV
• OCV filter
• Camshaft timing gear assembly
•ECM
Related DTCsP0011: Advanced camshaft timing
P0012: Retarded camshaft timing
Required Sensors/Components (Main) VVT OCV and VVT Actuator
Required Sensors/Components (Related)Crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor and Engine
coolant temperature sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Within 10 seconds
MIL OperationAdvanced camshaft timing: Immediate
Retarded camshaft timing: 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Page 1967 of 2000

2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–79
ES
DESCRIPTION
In the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system, the appropriate intake valve open and close timing is
controlled by the ECM. The ECM performs intake valve control by performing the following: 1) controlling
the camshaft and camshaft timing oil control valve, and operating the camshaft timing gear; and 2)
changing the relative positions of the gaps between the camshaft and crankshaft.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the valve timing by using the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system to control the intake
camshaft. The VVT system includes the ECM, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) and the VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
The ECM calibrates the intake valve timing by setting the intake camshaft to the most retarded angle while
the engine is idling. The ECM closes the OCV to retard the cam. The ECM stores this value as the VVT
learning value. When the difference between the target and actual intake valve timings is 5
CA
(Crankshaft Angle) or less, the ECM stores it.
If the VVT learning value matches the following conditions, the ECM determines the existence of a
malfunction in the VVT system, and sets the DTC.
• VVT learning value: Less than 25
CA, or more than 51CA.
• Above condition continues for 18 seconds or more.
This DTC indicates that the angle between the intake camshaft and the crankshaft is incorrect due to
factors such as the timing chain having jumped a tooth.
This monitor begins to run after the engine has idled for 5 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
DTC P0016Crankshaft Position - Camshaft Position Corre-
lation (Bank 1 Sensor A)
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0016Deviation in crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals
(2 trip detection logic)• Mechanical system (Timing chain has jumped tooth or
chain stretched)
•ECM
Related DTCs P0016: Camshaft timing misalignment at idling
Required Sensors/Components VVT actuator
Required Sensors/Components Camshaft position sensor, Crankshaft position sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Within 1 minute
MIL Operation 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not presentP0011 (VVT system 1 - advance)
P0012 (VVT system 1 - retarded)
P0115 - P0118 (ECT sensor)
Engine RPM 550 to 1,000 rpm
One of following conditions met -
VVT learning value when camshaft maximum retarded Less than 27.8
CA
VVT learning value when camshaft maximum retarded More than 48
CA