Page 421 of 2000
STEERING COLUMN – STEERING SYSTEMSR–3
SR
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
(2006/01- )
HINT:
Use the table below to help determine the cause of the
problem symptom. The potential causes of the symptoms are
listed in order of probability in the "Suspected Area" column
of the table. Check each symptom by checking the suspected
areas in the order they are listed. Replace parts as
necessary.
Steering system
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
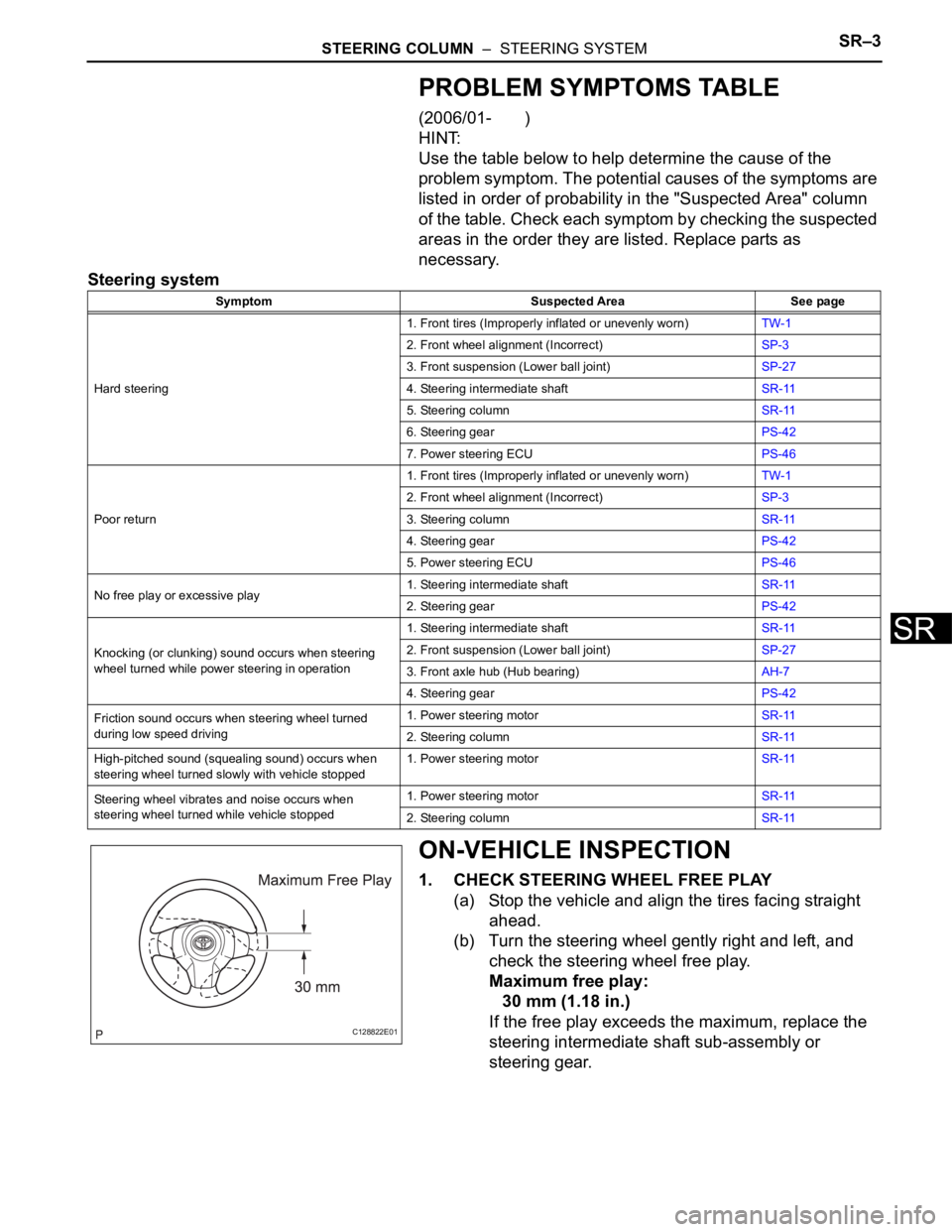
1. CHECK STEERING WHEEL FREE PLAY
(a) Stop the vehicle and align the tires facing straight
ahead.
(b) Turn the steering wheel gently right and left, and
check the steering wheel free play.
Maximum free play:
30 mm (1.18 in.)
If the free play exceeds the maximum, replace the
steering intermediate shaft sub-assembly or
steering gear.
Symptom Suspected Area See page
Hard steering1. Front tires (Improperly inflated or unevenly worn)TW-1
2. Front wheel alignment (Incorrect)SP-3
3. Front suspension (Lower ball joint)SP-27
4. Steering intermediate shaftSR-11
5. Steering columnSR-11
6. Steering gearPS-42
7. Power steering ECUPS-46
Poor return1. Front tires (Improperly inflated or unevenly worn)TW-1
2. Front wheel alignment (Incorrect)SP-3
3. Steering columnSR-11
4. Steering gearPS-42
5. Power steering ECUPS-46
No free play or excessive play1. Steering intermediate shaftSR-11
2. Steering gearPS-42
Knocking (or clunking) sound occurs when steering
wheel turned while power steering in operation1. Steering intermediate shaftSR-11
2. Front suspension (Lower ball joint)SP-27
3. Front axle hub (Hub bearing)AH-7
4. Steering gearPS-42
Friction sound occurs when steering wheel turned
during low speed driving1. Power steering motorSR-11
2. Steering columnSR-11
High-pitched sound (squealing sound) occurs when
steering wheel turned slowly with vehicle stopped1. Power steering motorSR-11
Steering wheel vibrates and noise occurs when
steering wheel turned while vehicle stopped1. Power steering motorSR-11
2. Steering columnSR-11
C128822E01
Page 1580 of 2000
BRAKE – BRAKE MASTER CYLINDERBR–27
BR
INSPECTION
NOTICE:
• The master cylinder and piston are designed so that
the piston can easily fall out. Prevent this by making
sure that the tip of the master cylinder points
downward when handling the master cylinder.
• Make sure foreign matter does not attach to the
master cylinder's piston. If foreign matter attaches,
clean it off with a cloth. Then apply lithium soap base
glycol grease to the entire outer circumference
contact surface area of the piston.
1. INSPECT AND ADJUST BRAKE BOOSTER PUSH
ROD
HINT:
Adjust the booster push rod when the master cylinder is
replaced with a new one. Adjustment is not necessary
when the master cylinder is reinstalled and the booster is
replaced with a new one.
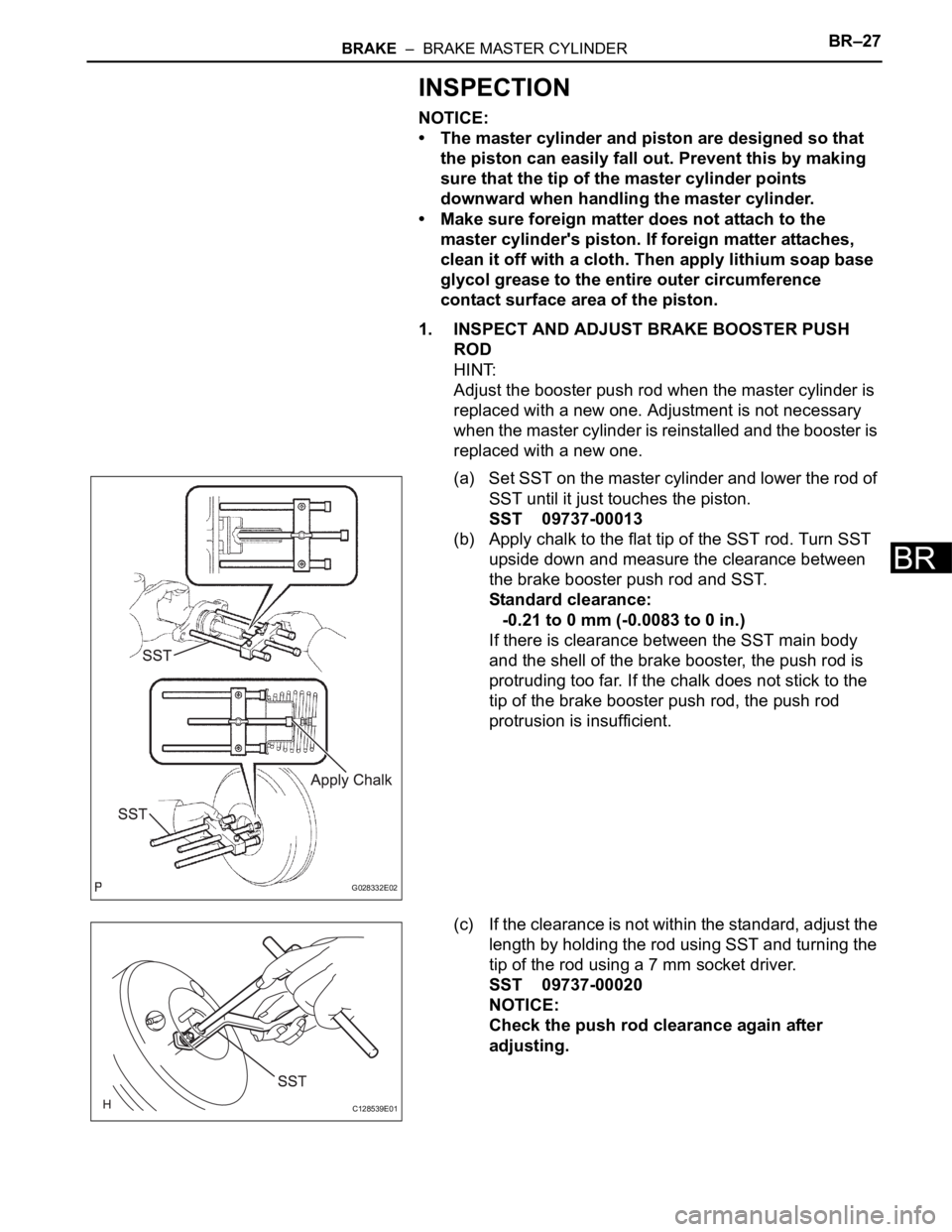
(a) Set SST on the master cylinder and lower the rod of
SST until it just touches the piston.
SST 09737-00013
(b) Apply chalk to the flat tip of the SST rod. Turn SST
upside down and measure the clearance between
the brake booster push rod and SST.
Standard clearance:
-0.21 to 0 mm (-0.0083 to 0 in.)
If there is clearance between the SST main body
and the shell of the brake booster, the push rod is
protruding too far. If the chalk does not stick to the
tip of the brake booster push rod, the push rod
protrusion is insufficient.
(c) If the clearance is not within the standard, adjust the
length by holding the rod using SST and turning the
tip of the rod using a 7 mm socket driver.
SST 09737-00020
NOTICE:
Check the push rod clearance again after
adjusting.
G028332E02
C128539E01
Page 1608 of 2000

PS–8POWER STEERING – ELECTRONIC POWER STEERING SYSTEM
PS
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
HINT:
Use the table below to help determine the cause of the
problem symptom. The potential causes of the symptoms are
listed in order of probability in the "Suspected area" column of
the table. Check each symptom by checking the suspected
areas in the order they are listed. Replace parts as
necessary.
Electronic power steering system
Symptom Suspected area See page
Heavy steering1. Front tires (improperly inflated, unevenly worn)TW-1
2. Front wheel alignment (incorrect)SP-3
3. Front suspension (lower ball joint)SP-27
4. Steering gear assemblyPS-42
5. Power steering motor PS-25
6. Power source voltage of power steering ECUPS-37
7. Power steering ECUPS-46
Steering effort differs between turning right and left, or
steering effort uneven1. Front tires (improperly inflated, unevenly worn)TW-1
2. Front wheel alignment (incorrect)SP-3
3. Front suspension (lower ball joint)SP-27
4. Steering gear assemblyPS-42
5. Torque sensor (built into steering column) PS-22
6. Steering column assemblySR-11
7. Power steering motor PS-25
8. Power steering ECUPS-46
While driving, steering effort does not change in
accordance with vehicle speed or steering wheel does
not return properly1. Front suspension (lower ball joint)SP-27
2. Speed sensorBC-28
3. Skid control ECUBC-41
4. Torque sensor (built into steering column) PS-22
5. Power steering motor PS-25
6. Power steering ECUPS-46
7. Controlling CAN communication systemCA-8
Friction occurs when turning steering wheel during low
speed driving1. Power steering motor PS-25
2. Steering column assemblySR-11
High-pitched sound (squeaking) occurs when turning
steering wheel slowly with vehicle stopped1. Power steering motor PS-25
Steering wheel vibrates and noise occurs when turning
steering wheel with vehicle stopped1. Power steering motor PS-25
2. Steering column assemblySR-11
P/S warning always indicated on combination meter1. Power source voltage of power steering ECUPS-37
2. Combination meterME-53
3. Power steering ECUPS-46