2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 384 of 2305

Symptom:
SOLENOID RELAY
When Monitored and Set Condition:
SOLENOID RELAY
When Monitored: Ignition On - Continuously.
Set Condition: When there is a voltage deviation from the expected result of a CAB
internal self check.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
INTERMITTENT SOLENOID RELAY DTC
DAMAGED CAB/CAB HARNESS CONNECTOR
FUSED OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT RELAY OUTPUT CIRCUIT OPEN
FUSED B(+) CIRCUIT OPEN
GROUND CIRCUIT OPEN
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE CONTROLLER
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, read DTCs.
With the DRBIIIt, erase DTCs.
Turn the ignition off.
Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, read DTCs.
Does the DRBIIItdisplay SOLENOID RELAY?All
Ye s!Go To 2
No!Go To 6
2 Turn the ignition off.
Disconnect the CAB harness connector.
Inspect the CAB/CAB harness connector for damage.
Is there any broken, bent, pushed out, corroded or spread terminals?All
Ye s!Repair as necessary.
Perform ABS VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1.
No!Go To 3
63
BRAKES (CAB)
Page 388 of 2305

TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
3 The condition that set this DTC is not present at this time.
Monitor the DRBIIItwhile wiggle testing the related harness and connectors. Look
for any related parameters to change or for the DTC to reset.
Inspect the related harness and connectors.
Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched, or partially broken wires.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded terminals.
Inspect the tires and wheels to make sure that they are the correct size. All tires must
be the same size.
Inspect the steering column and Steering Angle Sensor for correct mounting and
installation.
Inspect the front end and steering components for damage or misalignment.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s!Repair as necessary.
No!Test Complete.
67
BRAKES (CAB)
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR GREATER THAN 720 DEGREES ÐContinued
Page 390 of 2305

TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
3 Turn the ignition off.
Disconnect the Steering Angle Sensor harness connector.
Inspect the harness and connectors related to this circuit. If any problems are found,
repair as necessary.
If no problems are found, replace the Steering Angle Sensor in accordance with the
Service Information.
Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, clear DTCs.
Using the DRBIIIt, perform the road test procedure.
With the DRBIIIt, read DTCs.
Does this DTC reset?All
Ye s!Replace the CAB in accordance with the Service Information.
No!Test Complete.
4 The condition that set this DTC is not present at this time.
Monitor the DRBIIItwhile wiggle testing the related harness and connectors. Look
for any related parameters to change or for the DTC to reset.
Inspect the related harness and connectors.
Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched, or partially broken wires.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded terminals.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s!Repair as necessary.
No!Test Complete.
69
BRAKES (CAB)
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR IMPLAUSIBLE CAN SIGNAL ÐContinued
Page 392 of 2305

TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
3 The condition that set this DTC is not present at this time.
Monitor the DRBIIItwhile wiggle testing the related harness and connectors. Look
for any related parameters to change or for the DTC to reset.
Inspect the related harness and connectors.
Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched, or partially broken wires.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded terminals.
Inspect the tires and wheels to make sure that they are the correct size. All tires must
be the same size.
Inspect the steering column and Steering Angle Sensor for correct mounting and
installation.
Inspect the front end and steering components for damage or misalignment.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s!Repair as necessary.
No!Test Complete.
71
BRAKES (CAB)
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR IMPLAUSIBLE VALUE ÐContinued
Page 394 of 2305

TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
3 The condition that set this DTC is not present at this time.
Monitor the DRBIIItwhile wiggle testing the related harness and connectors. Look
for any related parameters to change or for the DTC to reset.
Inspect the related harness and connectors.
Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched, or partially broken wires.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded terminals.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s!Repair as necessary.
No!Test Complete.
73
BRAKES (CAB)
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR IMPLAUSIBLE WHEEL SPEED ÐContinued
Page 395 of 2305

Symptom:
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR INTERNAL FAULT
POSSIBLE CAUSES
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR INTERMITTENT DTC
STEERING ANGLE SENSOR
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1NOTE: If a system undervoltage or overvoltage DTC is set along with this
DTC, diagnose the system voltage DTC first.
NOTE: Electromagnetic (radio) interference can cause an intermittent
system malfunction by interrupting communication between the sensor
and the CAB.
Turn the ignition on.
With the DRBIIIt, erase DTCs.
Move the Steering Wheel from stop to stop several times.
With the DRBIIIt, perform the road test procedure.
With the DRBIIIt, read DTCs.
NOTE: The Steering Angle Sensor is very sensitive to changes due to
alignment problems. The sensor must be recalculated using the DRBIIItif
alignment has been changed by more than 5 degrees.
Does this DTC reset?All
Ye s!Inspect the Steering Angle Sensor for proper installation. Inspect
the wiring and connectors. Repair as necessary. If no other
problems are found, replace the Steering Angle Sensor in accor-
dance with the Service Information.
No!Go To 2
2 The condition that set this DTC is not present at this time.
Monitor the DRBIIItwhile wiggle testing the related harness and connectors. Look
for any related parameters to change or for the DTC to reset.
Inspect the related harness and connectors.
Look for any chafed, pierced, pinched, or partially broken wires.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded terminals.
Inspect the tires and wheels to make sure that they are the correct size. All tires must
be the same size.
Inspect the steering column and Steering Angle Sensor for correct mounting and
installation.
Inspect the front end and steering components for damage or misalignment.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s!Repair as necessary.
No!Test Complete.
74
BRAKES (CAB)
Page 401 of 2305
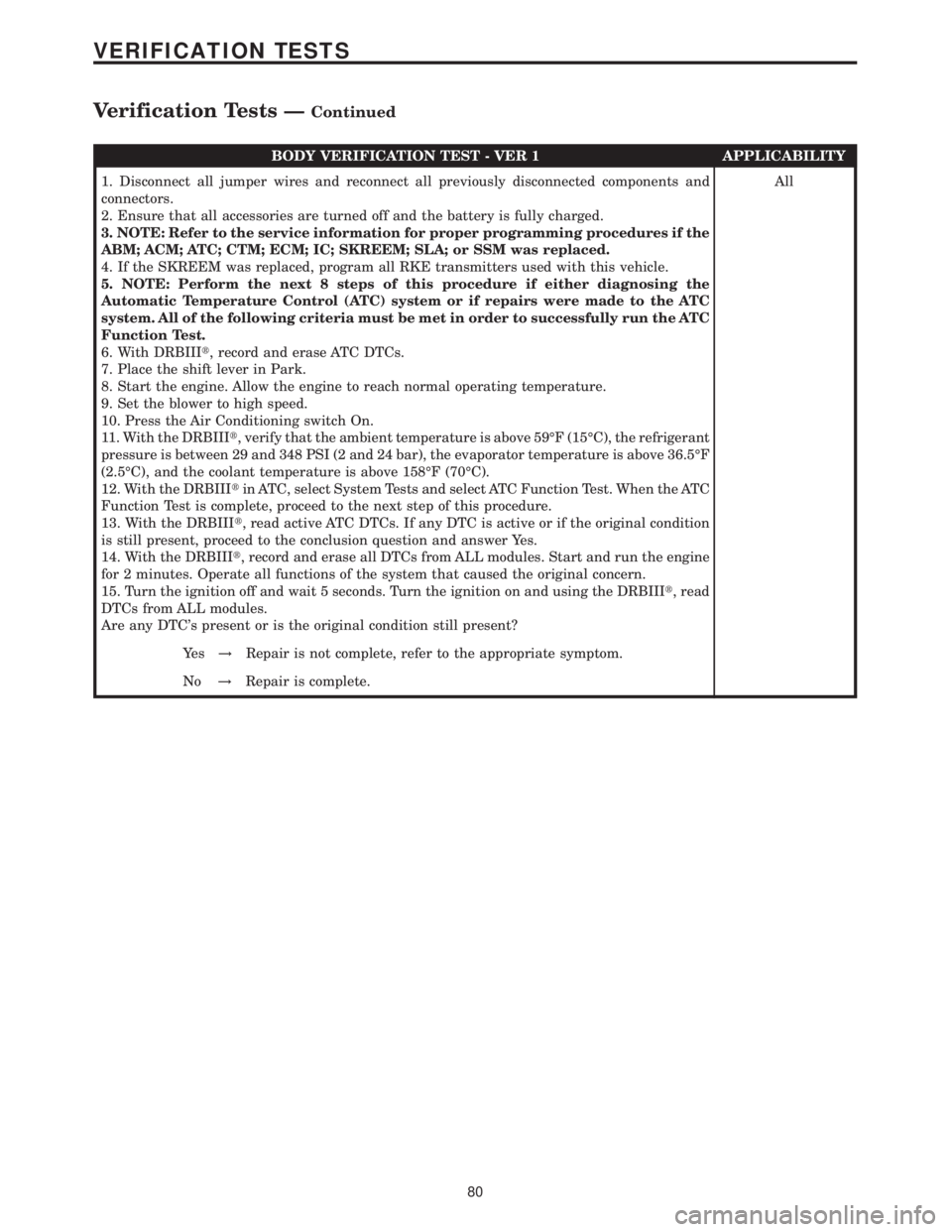
BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1 APPLICABILITY
1. Disconnect all jumper wires and reconnect all previously disconnected components and
connectors.
2. Ensure that all accessories are turned off and the battery is fully charged.
3. NOTE: Refer to the service information for proper programming procedures if the
ABM; ACM; ATC; CTM; ECM; IC; SKREEM; SLA; or SSM was replaced.
4. If the SKREEM was replaced, program all RKE transmitters used with this vehicle.
5. NOTE: Perform the next 8 steps of this procedure if either diagnosing the
Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) system or if repairs were made to the ATC
system. All of the following criteria must be met in order to successfully run the ATC
Function Test.
6. With DRBIIIt, record and erase ATC DTCs.
7. Place the shift lever in Park.
8. Start the engine. Allow the engine to reach normal operating temperature.
9. Set the blower to high speed.
10. Press the Air Conditioning switch On.
11. With the DRBIIIt, verify that the ambient temperature is above 59ÉF (15ÉC), the refrigerant
pressure is between 29 and 348 PSI (2 and 24 bar), the evaporator temperature is above 36.5ÉF
(2.5ÉC), and the coolant temperature is above 158ÉF (70ÉC).
12. With the DRBIIItin ATC, select System Tests and select ATC Function Test. When the ATC
Function Test is complete, proceed to the next step of this procedure.
13. With the DRBIIIt, read active ATC DTCs. If any DTC is active or if the original condition
is still present, proceed to the conclusion question and answer Yes.
14. With the DRBIIIt, record and erase all DTCs from ALL modules. Start and run the engine
for 2 minutes. Operate all functions of the system that caused the original concern.
15. Turn the ignition off and wait 5 seconds. Turn the ignition on and using the DRBIIIt, read
DTCs from ALL modules.
Are any DTC's present or is the original condition still present?All
Ye s!Repair is not complete, refer to the appropriate symptom.
No!Repair is complete.
80
VERIFICATION TESTS
Verification Tests ÐContinued
Page 425 of 2305

3.2.2 ECM OPERATING MODES
As input signals to the ECM change, the ECM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For
example, the ECM must calculate a different fuel
quantity and fuel timing for engine idle condition
than it would for a wide open throttle condition.
There are several different modes of operation that
determine how the ECM responds to the various
input signals.
Ignition Switch On (Engine Off)
When the ignition is turned on the ECM activates
the glow plug relay for a time period that is deter-
mined by engine coolant temperature, intake air
temperature and battery voltage.
Engine Start-Up Mode
The ECM uses the intake air temperature sensor,
engine temperature sensor and the crankshaft po-
sition sensor (engine speed) inputs to determine
fuel injection quantity.
Normal Driving Modes
Engine idle, warm-up, acceleration, deceleration
and wide open throttle modes are controlled based
on all of the sensor inputs to the ECM. The ECM
uses these sensor inputs to adjust fuel quantity and
fuel injector timing. EGR valve control is performed
using feedback from the oxygen sensor. An oxygen
sensor is located in the exhaust manifold to sample
oxygen content exiting the engine cylinders. The
ECM uses the O2 sensor, along with other sensor
inputs, to govern the amount of exhaust gas recir-
culation to reduce HC (HydroCarbons) and CO
(Carbon Monoxide). Engine coolant is routed
through the base of the EGR valve to provide
additional cooling of the exhaust gas, which further
helps the reductions of emissions. The EGR valve
has a self-cleaning function. When the engine is
shut off, the EGR valve rotates twice to reduce
carbon deposits at the valve seat.
Overheat Production Mode
If the engine temperature is above 105ÉC (221ÉF)
and vehicle speed is above 40 km/h (25 MPH) the
ECM will limit fuel quantity for engine protection.
Limp-In Mode
The ECM utilizes different degrees of engine
limp-in. The ECM is able to limit engine rpm,
engine power output (turbo boost reduction), acti-
vate engine cooling fan or all of these functions
based on the type of fault that is detected. Critical
engine performance faults such as accelerator pedal
position sensor fault will result in a fixed idle speed
of approximately 680 rpm regardless of actual pedalposition. Other less critical faults will result in
power reduction throughout the full range of driv-
ing conditions.
Overspeed Detection Mode
If the ECM detects engine RPM that exceeds
5200 RPM, the ECM will set a DTC in memory,
limit engine RPM to no more than 2500 RPM, and
illuminate the MIL until the DTC is cleared.
After-Run Mode
The ECM transfers RAM information to ROM
and performs an Input/Output state check.
3.2.3 MONITORED CIRCUITS
The ECM is able to monitor and identify most
driveability related trouble conditions. Some cir-
cuits are directly monitored through ECM feedback
circuitry. In addition, the ECM monitors the voltage
state of some circuits and compares those states
with expected values. Other systems are monitored
indirectly when the ECM conducts a rationality test
to identify problems.
Although most subsystems of the engine control
module are either directly or indirectly monitored,
there may be occasions when diagnostic trouble
codes are not immediately identified. For a trouble
code to set, a specific set of conditions must occur
and unless these conditions occur, a DTC will not
set.
3.2.4 SKREEM OVERVIEW
The sentry key remote entry module system
(SKREEM) is designed to prevent unauthorized
vehicle operation. The system consists of a sentry
key remote entry module (SKREEM), ignition
key(s) equipped with a transponder chip and the
ECM. When the ignition switch is turned on, the
SKREEM interrogates the ignition key. If the igni-
tion key is Valid or Invalid, the SKREEM sends a
message to the ECM indicating ignition key status.
Upon receiving this message the ECM will termi-
nate engine operation or allow the engine to con-
tinue to operate.
3.2.5 SKREEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The SKREEM has been programmed to transmit
and monitor many different coded messages as well
as CAN Bus messages. This monitoring is called
On-Board Diagnostics. Certain criteria must be met
for a DTC to be entered into SKREEM memory. The
criteria may be a range of; input voltage, CAN Bus
message or coded messages to the SKREEM. If all
the criteria for monitoring a circuit or function are
met and a fault is detected, a DTC will be stored in
the SKREEM memory and the START ERROR indi-
cator will be turned on in the instrument cluster.
2
GENERAL INFORMATION