2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 water pump
[x] Cancel search: water pumpPage 2343 of 5267

Fuel enters the system from the electric fuel transfer (lift) pump, which is located inside of the fuel tank and attached
to the fuel tank module (the fuel transfer pump is no longer attached to the engine). Fuel is forced through the fuel
filter element and then enters the Fuel Pump/Gear Pump, which is attached to the rear of the fuel injection pump.
The Fuel Pump/Gear Pump is a low-pressure pump and produce pressures ranging from 551.5 kpa (80 psi) to 1241
kpa (180) psi. Fuel then enters the fuel injection pump. Low pressure fuel is then supplied to the FCA (Fuel Control
Actuator).
The FCA is an electronically controlled solenoid valve. The ECM controls the amount of fuel that enters the high-
pressure pumping chambers by opening and closing the FCA based on a demanded fuel pressure. The FPS (Fuel
Pressure Sensor) on the fuel rail monitors the actual fuel pressure and provides it as an input to the ECM. When
the actuator is opened, the maximum amount of fuel is being supplied to the fuel injection pump. Any fuel that does
not enter the injection pump is directed to the overflow valve. The overflow valve regulates how much excess fuel
is used for lubrication of the pump and how much is returned to the tank through the drain manifold.
Fuel entering the injection pump is pressurized to between 300-1600 bar (4351-23,206 psi) by three radial pumping
chambers. The pressurized fuel is then supplied to the fuel rail.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
WATER DRAINING AT FUEL FILTER
Refer to Fuel Filter/Water Separatorremoval/installation for procedures.
CLEANING FUEL SYSTEM PARTS
CAUTION: Cleanliness cannot be overemphasized when handling or replacingdieselfuelsystemcompo-
nents. This especially includes the fuel injectors, high-pressure fuel lines and fuel injection pump. Very tight
tolerances are used with these parts. Dirt contamination could cause rapid part wear and possible plugging
of fuel injector nozzle tip holes. This in turn could lead to possible engine misfire. Always wash/clean any
fuel system component thoroughly before disassembly and then air dry. Capor cover any open part after
disassembly. Before assembly, examine each part for dirt, grease or othercontaminants and clean if nec-
essary. When installing new parts, lubricate them with clean engine oil orclean diesel fuel only.
FUEL SYSTEM PRIMING
A certain amount of air becomes trappedin the fuel system when fuel system components on the supply and/or
high-pressure side are serviced or replaced. Fuel system priming is accomplished using the electric fuel transfer (lift)
pump.
Servicing or replacing fuel system components will not require fuel systempriming.
The fuel transfer (lift) pump is self-priming: When the key is first turnedon (without cranking engine), the pump
operates for approximately 1 to 2 second and then shuts off (Note: When ambient temperatures are cold enough to
cause the intake air heaters to operate, the fuel lift pump will operate during the entire intake air pre-heat cycle).
The pump will also operate for up to 25 seconds after the starter is quickly engaged, and then disengaged without
allowing the engine to start. The pump shuts off immediately if the key is onand the engine stops running.
1. Turn key to CRANK position and quickly release key to ON position before engine starts. This will operate fuel
transfer pump for approximately 25 seconds.
2. Crank engine. If the engine does not start after 25 seconds, turn key to OFF position, and leave it off for at least
5 seconds. Repeat previous step until engine starts.
3. Fuel system priming is now completed.
4. Attempt to start engine. If engine will not start, proceed to following steps.When engine does start, it may run
erratically and be noisy for a few minutes. This is a normal condition.
CAUTION: Do not engage the starter motor for more than 30 seconds at a time. Allow two minutes between
cranking intervals.
5. Perform previous fuel priming procedure steps using fuel transfer pump. Be sure fuel is present at fuel tank.
6. Crank the engine for 30 seconds at a time to allow fuel system to prime.
Page 2345 of 5267
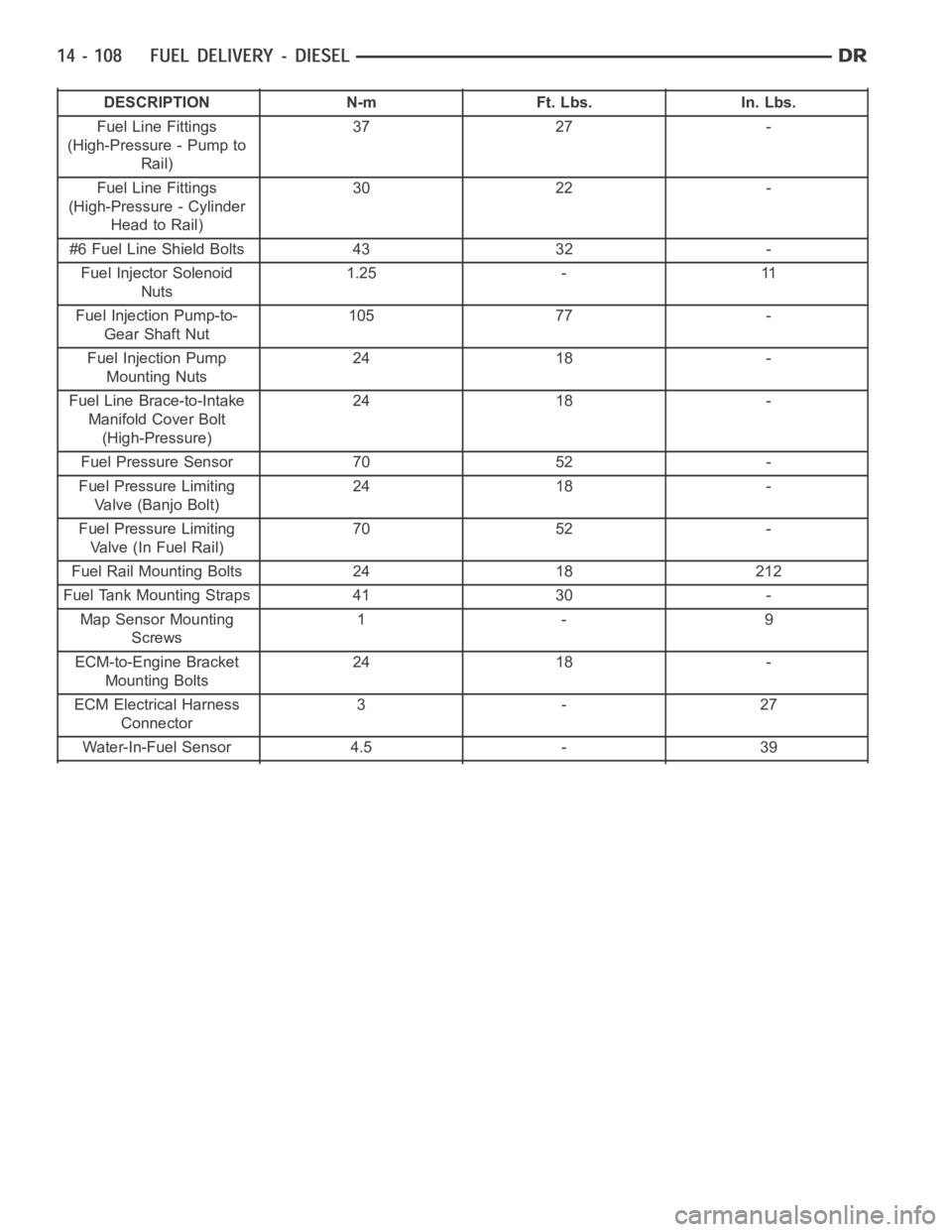
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Line Fittings
(High-Pressure - Pump to
Rail)37 27 -
Fuel Line Fittings
(High-Pressure - Cylinder
Head to Rail)30 22 -
#6 Fuel Line Shield Bolts 43 32 -
Fuel Injector Solenoid
Nuts1.25 - 11
Fuel Injection Pump-to-
Gear Shaft Nut105 77 -
Fuel Injection Pump
Mounting Nuts24 18 -
Fuel Line Brace-to-Intake
Manifold Cover Bolt
(High-Pressure)24 18 -
Fuel Pressure Sensor 70 52 -
Fuel Pressure Limiting
Valve(BanjoBolt)24 18 -
Fuel Pressure Limiting
Valve (In Fuel Rail)70 52 -
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts 24 18 212
Fuel Tank Mounting Straps 41 30 -
Map Sensor Mounting
Screws1- 9
ECM-to-Engine Bracket
Mounting Bolts24 18 -
ECM Electrical Harness
Connector3-27
Water-In-Fuel Sensor 4.5 - 39
Page 2348 of 5267

FILTER - FUEL / WATER SEPARATOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel filter/water separator assembly is located on left side of engineabove the starter motor. The assembly also
includes the fuel heater, Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor and a screened banjobolt attached at the bottom of the fuel
filter canister.
OPERATION
The fuel filter/water separator protects the fuel injection pump by removing water and contaminants from the fuel.
The construction of the filter/separator allows fuel to pass through it, but helps prevent moisture (water) from doing
so. Moisture collects at the bottom of the canister.
Refer to the maintenance schedules in the owners manual for the recommended fuel filter replacement intervals.
For draining of water from canister, refer to Fuel Filter/Water SeparatorRemoval/Installation section.
There is a screened banjo bolt that is attached at the bottom of the fuel filter canister. It provides additional filtering
for the high pressure fuel system components.
A Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor is attached to the side of fuel filter housing. Refer to Water-In-Fuel Sensor Descrip-
tion/Operation.
The fuel heater is installed into the top of the filter/separator housing.Refer to Fuel Heater Description/Operation.
REMOVAL
Refer to maintenance schedules in this manual, or the
Owner’s Manual for recommended fuel filter replace-
ment intervals.
Draining water from fuel filter/water separator
housing:
The housing drain valve (9) serves two purposes. One
is topartiallydrain the filter housing of excess water.
The other is tocompletelydrain the housing for fuel
filter, drain valve, heater element or water-in-fuel sen-
sor replacement.
The filter housing should be partially drained when-
ever the water-in-fuel warning lamp remains illumi-
nated. (Note that lamp will be illuminated for
approximately two seconds when ignition key is ini-
tially placed in ON position for a bulb check).
1. A drain hose (7) is located at the bottom of drain
valve. Place drain pan under drain hose.
2.With engine not running,rotate drain valve han-
dle counter-clockwise (rearward) to OPEN (DRAIN)
position. Hold drain valve open until all water and
contaminants have been removed and clean fuel
exits.
3. If drain valve, fuel heater element or Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor is being replaced, drain housing completely.
Dispose of mixture in drain pan according to applicable regulations.
4. After draining operation, rotate valve handle clockwise (forward) to the CLOSE position.
Page 2350 of 5267

7.Fuel Heater Element Replacement:The heater
element (2) is located in the fuel filter housing.
a. Remove fuel filter. See previous steps.
b. Disconnect electrical connector.
c. Remove two T-15 Torx head mounting screws
(3) from fuel heater element.
d. Remove fuel heater.
8.Drain Valve Replacement:The drain valve
assembly (9) is located on the side of the fuel filter
housing.
a. Disconnect drain hose (7) from the fuel drain
valve.
b. Remove 4 drain valve mounting screws (T-15
Torx head) (8).
c. Remove drain valve from filter housing.
9. Remove the screened banjo bolt (9) that is located
on the bottom of the fuel filter housing. It attaches
the Injection Pump supply line to the fuel filter
housing.
INSTALLATION
Refer to maintenance schedules for recommended fuel filter replacement intervals.
1. Thoroughly clean inside of filter housing, filter cap and all related components.
2.Fuel Filter:
a.The engine has a self-priming low-pressure fuel system. Refer to StandardProcedures-Fuel System
Priming.
b. Install new O-ring to canister lid and lubricate O-ring with clean engine oil.
c. Position new element to canister lid. Place this assembly into canisterby rotating clockwise.
d. Tighten cap to 34 Nꞏm (25 ft. lbs.) torque. Do not overtighten cap.
3.Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor:
Page 2373 of 5267

PUMP - FUEL TRANSFER
DESCRIPTION
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is part of the fuel pump module. The fuel pump module is located in the fuel
tank. The 12–volt electric pump is operated and controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM controls
a relay in the Intelligent Power Module(IPM) for transfer pump operation.
OPERATION
The purpose of the fuel transfer pump is to supply (transfer) a low-pressure fuel source:fromthe fuel tank,through
the fuel filter/water separator andtothe fuel injection pump. Here, the low-pressure is raised to a high-pressure by
the fuel injection pump for operation of the high-pressure fuel injectors. Check valves within the pump, control direc-
tion of fuel flow and prevent fuel bleed-back during engine shut down.
Maximum current flow to the pump is 5 amperes.
With the engine running, the pump has a 100 percent duty-cycle.
The transfer pump is self-priming: When the key is first turned on (withoutcranking engine), the pump will operate
for approximately 2 seconds and then shut off (Note: When ambient temperatures are cold enough to cause the
intake air heaters to operate, the fuel lift pump will operate during the entire intake air pre-heat cycle). The pump will
also operate for up to 25 seconds after the starter is engaged, and then disengaged and the engine is not running.
The pump shuts off immediately if the key is on and the engine stops running.
The fuel volume of the transfer pump will always provide more fuel than the fuel injection pump requires. Excess
fuel is returned from the injection pump through an overflow valve, and then back to the fuel tank.
REMOVAL
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is a part of the fuel tank module. It is not serviced separately. Refer to Fuel
Tank Module Removal or Installation for procedures (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL TANK
MODULE - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is a part of the fuel tank module. It is not serviced separately (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL TANK MODULE - INSTALLATION).
Page 3000 of 5267
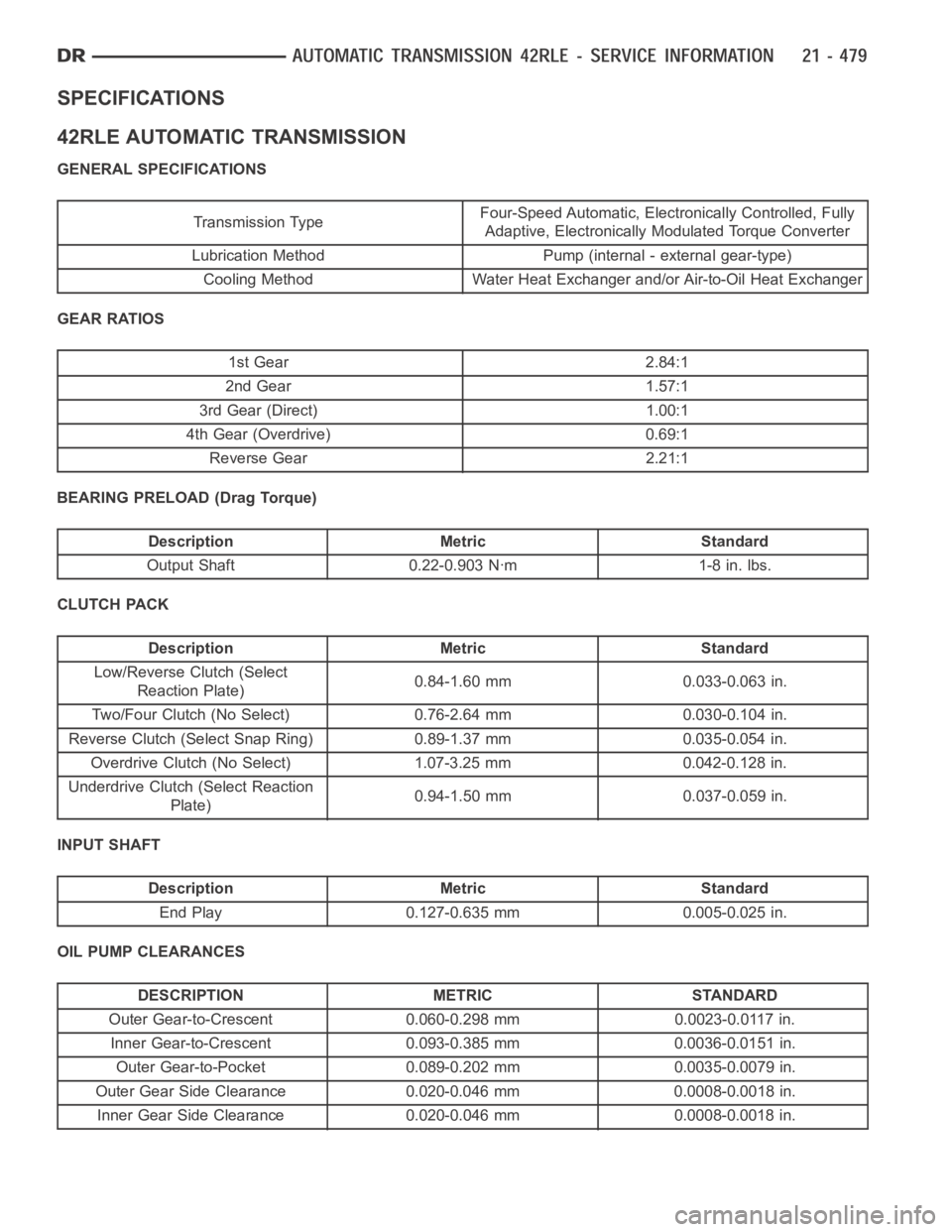
SPECIFICATIONS
42RLE AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Transmission TypeFour-Speed Automatic, Electronically Controlled, Fully
Adaptive, Electronically Modulated Torque Converter
Lubrication Method Pump (internal - external gear-type)
Cooling Method Water Heat Exchanger and/or Air-to-Oil Heat Exchanger
GEAR RATIOS
1st Gear 2.84:1
2nd Gear 1.57:1
3rd Gear (Direct) 1.00:1
4th Gear (Overdrive) 0.69:1
Reverse Gear 2.21:1
BEARING PRELOAD (Drag Torque)
Description Metric Standard
Output Shaft 0.22-0.903 Nꞏm 1-8 in. lbs.
CLUTCH PACK
Description Metric Standard
Low/Reverse Clutch (Select
Reaction Plate)0.84-1.60 mm 0.033-0.063 in.
Two/Four Clutch (No Select) 0.76-2.64 mm 0.030-0.104 in.
Reverse Clutch (Select Snap Ring) 0.89-1.37 mm 0.035-0.054 in.
Overdrive Clutch (No Select) 1.07-3.25 mm 0.042-0.128 in.
Underdrive Clutch (Select Reaction
Plate)0.94-1.50 mm 0.037-0.059 in.
INPUT SHAFT
Description Metric Standard
End Play 0.127-0.635 mm 0.005-0.025 in.
OIL PUMP CLEARANCES
DESCRIPTION METRIC STANDARD
Outer Gear-to-Crescent 0.060-0.298 mm 0.0023-0.0117 in.
Inner Gear-to-Crescent 0.093-0.385 mm 0.0036-0.0151 in.
Outer Gear-to-Pocket 0.089-0.202 mm 0.0035-0.0079 in.
Outer Gear Side Clearance 0.020-0.046 mm 0.0008-0.0018 in.
Inner Gear Side Clearance 0.020-0.046 mm 0.0008-0.0018 in.
Page 5056 of 5267

Condition Possible Causes Correction
5. Engine overheating.5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace the
liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty A/C compressor.3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace the
compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice
tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace the
liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
HEATER PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Group 7 - Cooling for the procedures to check the engine coolant
level and flow, engine coolant reserve/recovery system operation, accessory drive belt condition and tension, radi-
ator air flow and the fan drive operation. Perform the HVAC System Test (refer to 24 - HVAC Electrical Diagnostics).
If any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are found in the A/C-heater control, powertrain control module (PCM) or
engine control module (ECM) (depending on engine application), gateway module or totally integrated power module
(TIPM), repair as necessary.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system through two heater hoses. With the engine idling at normal oper-
ating temperature, set the temperature control to maximum heat position,the mode control to the floor position, and
the blower motor control to the highest speed position. Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of the air
being discharged from the floor outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the Heater Temperature Refer-
ence chart.
HEATER TEMPERATURE REFERENCE
Ambient Air Temperature16° C
(60° F)21° C
(70° F)26° C
(80° F)32° C
(90° F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62° C
(144° F)64° C
(147° F)65° C
(150° F)67° C
(153° F)
If the heater outlet air temperature is below the minimum specification, refer to Group 7 - Cooling. Both of the heater
hoses should be hot to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should be slightly cooler than the coolant supply
heater hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the supply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. RefertoGroup7-Coolingformoreinformation.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW
Possible locations or causes of obstructed coolant flow are as follows:
Faulty water pump.
Faulty thermostat.
Pinched or kinked heater hoses.