2003 DODGE RAM oil change
[x] Cancel search: oil changePage 1340 of 2895
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
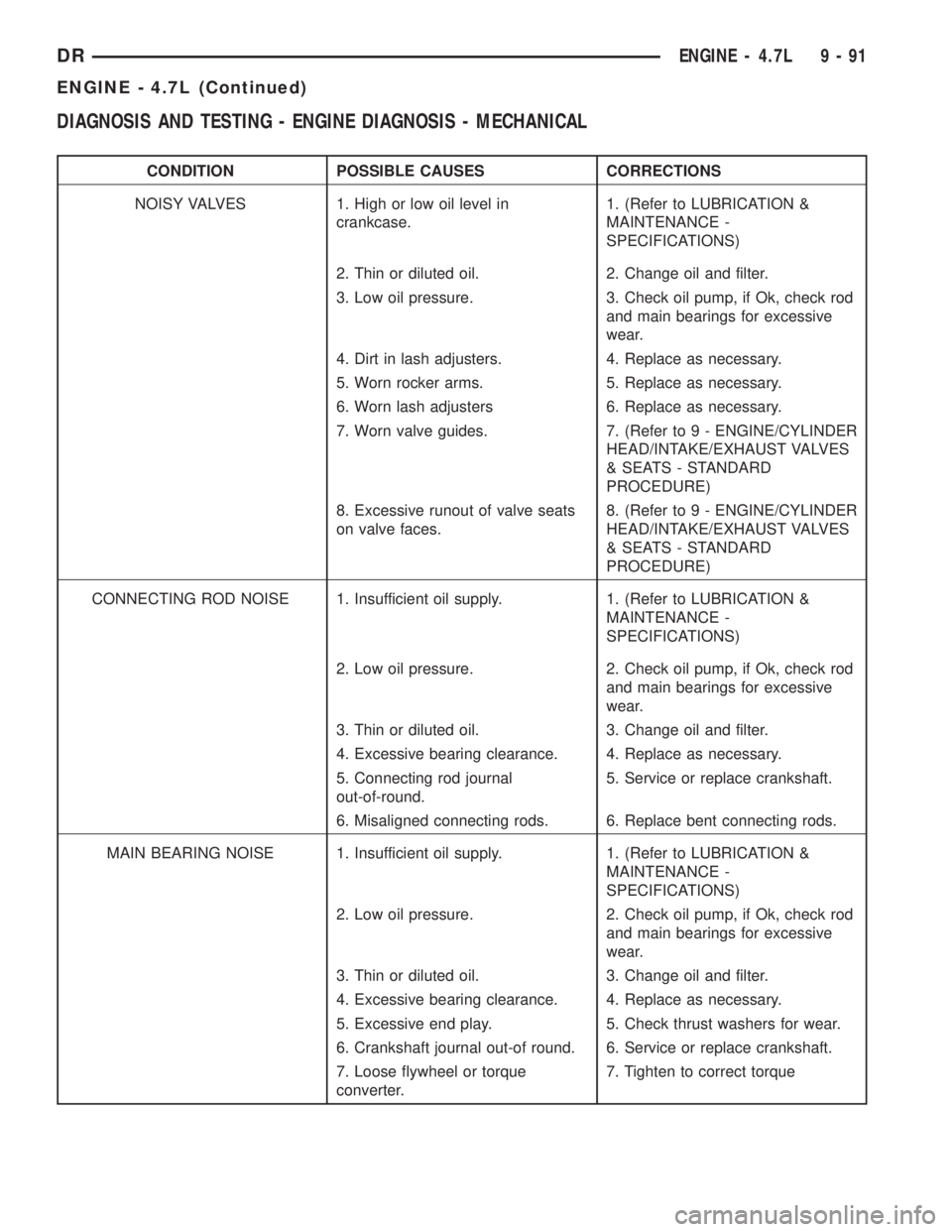
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 91
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1370 of 2895

CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of die cast mag-
nesium, and are not interchangeable from side-to-
side. It is imperative that nothing rest on the
cylinder head covers. Prolonged contact with other
items may wear a hole in the cylinder head cover.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RIGHT SIDE
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly, resonator assem-
bly and air inlet hose.
(3) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove air conditioning compressor retaining
bolts and move compressor to the left.
(6) Remove heater hoses.
(7) Disconnect injector and ignition coil connectors.
(8) Disconnect and remove positive crankcase ven-
tilation (PCV) hose.
(9) Remove oil fill tube.
(10) Un-clip injector and ignition coil harness and
move away from cylinder head cover.
(11) Remove right rear breather tube and filter
assembly.
(12) Remove cylinder head cover retaining bolts.
(13) Remove cylinder head cover.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
REMOVAL - LEFT SIDE
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the resonator assemble and air inlet
hose.
(3) Disconnect injector connectors and un-clip the
injector harness.
(4) Route injector harness in front of cylinder head
cover.
(5) Disconnect the left side breather tube and
remove the breather tube.
(6) Remove the cylinder head cover mounting
bolts.
(7) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder head cover gasket surface.
Clean head rail, if necessary.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RIGHT SIDE
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
CAUTION: DO NOT allow other components includ-
ing the wire harness to rest on or against the
engine cylinder head cover. Prolonged contact with
other objects may wear a hole in the cylinder head
cover.
(1) Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.
(2) Install cylinder head cover and hand start all
fasteners. Verify that all double ended studs are in
the correct location shown in (Fig. 39).
(3) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs).
(4) Install right rear breather tube and filter
assembly.
(5) Connect injector, ignition coil electrical connec-
tors and harness retaining clips.
(6) Install the oil fill tube.
(7) Install PCV hose.
(8) Install heater hoses.
(9) Install air conditioning compressor retaining
bolts.
(10) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 39 Cylinder Head CoverÐRight
ITEM DESCRIPTION TORQUE
1 Cover Fasteners 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 121
Page 1388 of 2895

Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the piston for scoring, or scraping marks in
the piston skirts. Check the ring lands for cracks
and/or deterioration.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing piston and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, install the piston rings.
(2) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings. Tighten ring compressor.Ensure posi-
tion of rings do not change during this opera-
tion.
(3) Position bearing onto connecting rod. Ensure
that hole in bearing shell aligns with hole in connect-
ing rod. Lubricate bearing surface with clean engine
oil.
(4) Install Special Tool 8507 Connecting Rod
Guides into connecting rod bolt threads (Fig. 74).(5) The pistons are marked on the piston pin bore
surface with an raised ªFº indicating installation
position. This mark must be pointing toward the
front of engine on both cylinder banks. The connect-
ing rod oil slinger slot faces the front of the engine
(Fig. 75).
(6) Wipe cylinder bore clean and lubricate with
engine oil.
(7) Rotate crankshaft until connecting rod journal
is on the center of cylinder bore. Insert rod and pis-
ton into cylinder bore and carefully position connect-
ing rod guides over crankshaft journal.
(8) Tap piston down in cylinder bore using a ham-
mer handle. While at the same time, guide connect-
ing rod into position on rod journal.
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Lubricate rod bolts and bearing surfaces with
engine oil. Install connecting rod cap and bearing.
Tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus 90É.
(10) Install the following components:
²Cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
²Timing chain and cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- INSTALLATION).
Fig. 74 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
INSTALLATION
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 75 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
ORIENTATION
1 - MAJOR THRUST SIDE OF PISTON
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 139
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1401 of 2895

Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800
kilometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhib-
ited loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about five
minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug if
damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil described in this sec-
tion.
(8) Install oil fill cap.
(9) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(10) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used
engine oil after it has been drained from a vehicle
engine. Refer to the WARNING at beginning of this
section.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise (Fig. 97)to
remove it from the cylinder block oil filter boss.
Fig. 96 ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK 4.7L ENGINE
1 - TRANSMISSION DIPSTICK
2 - ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK
3 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP
Fig. 97 Oil Filter - 4.7L Engine
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
9 - 152 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
OIL (Continued)
Page 1406 of 2895

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the oil pump onto the crankshaft and
install one oil pump retaining bolts.
(2) Position the primary timing chain tensioner
and install three retaining bolts.
(3) Tighten the oil pump and primary timing chain
tensioner retaining bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
the sequence shown (Fig. 107).
(4) Install the secondary timing chain tensioners
and timing chains (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the pick-up tube and oil pan (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold is made of a composite mate-
rial and features long runners which maximizes low
end torque. The intake manifold uses single plane
sealing which consist of eight individual press in
place port gaskets to prevent leaks. Eight studs and
two bolts are used to fasten the intake to the head.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐINTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water at the suspected
leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM is observed the area of the
suspected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
(3) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors for the follow-
ing components:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
(5) Disconnect brake booster hose and positive
crankcase ventilation (PCV) hose.
(6) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(7) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(8) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(9) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
(11) Bleed fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(12) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove throttle body assembly and mounting
bracket.
(14) Drain cooling system below coolant tempera-
ture level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(15) Remove the heater hoses from the engine
front cover and the heater core.
Fig. 107 Oil Pump And Primary Timing Chain
Tensioner Tightening Sequence
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 157
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1413 of 2895

VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTIONÐTIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The timing drive system (Fig. 114) has been
designed to provide quiet performance and reliability
to support anon-free wheelingengine. Specifically
the intake valves are non-free wheeling and can be
easily damaged with forceful engine rotation if cam-
shaft-to-crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing
drive system consists of a primary chain and two sec-
ondary timing chain drives.
OPERATION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
type. The primary chain drives the large fifty tooth
idler sprocket directly from a 25 tooth crankshaft
sprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by a
pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed guide.
The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic wear
faces for low friction and long wear. The primarychain receives oil splash lubrication from the second-
ary chain drive and oil pump leakage. The idler
sprocket assembly connects the primary and second-
ary chain drives. The idler sprocket assembly con-
sists of two integral thirty tooth sprockets and a fifty
tooth sprocket that is splined to the assembly. The
spline joint is a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle
type. The idler sprocket assembly spins on a station-
ary idler shaft. The idler shaft is press-fit into the
cylinder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
inverted tooth type, one to drive the camshaft in each
SOHC cylinder head. There are no shaft speed
changes in the secondary chain drive system. Each
secondary chain drives a thirty tooth cam sprocket
Fig. 114 Timing Drive System
1 - RIGHT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
2 - SECONDARY TIMING CHAIN TENSIONER (LEFT AND RIGHT
SIDE NOT COMMON)
3 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
4 - LEFT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET AND SECONDARY CHAIN
5 - CHAIN GUIDE
6 - TWO PLATED LINKS ON RIGHT CAMSHAFT CHAIN7 - PRIMARY CHAIN
8 - IDLER SPROCKET
9 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
10 - PRIMARY CHAIN TENSIONER
11 - TWO PLATED LINKS ON LEFT CAMSHAFT CHAIN
12 - SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
9 - 164 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
Page 1430 of 2895
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
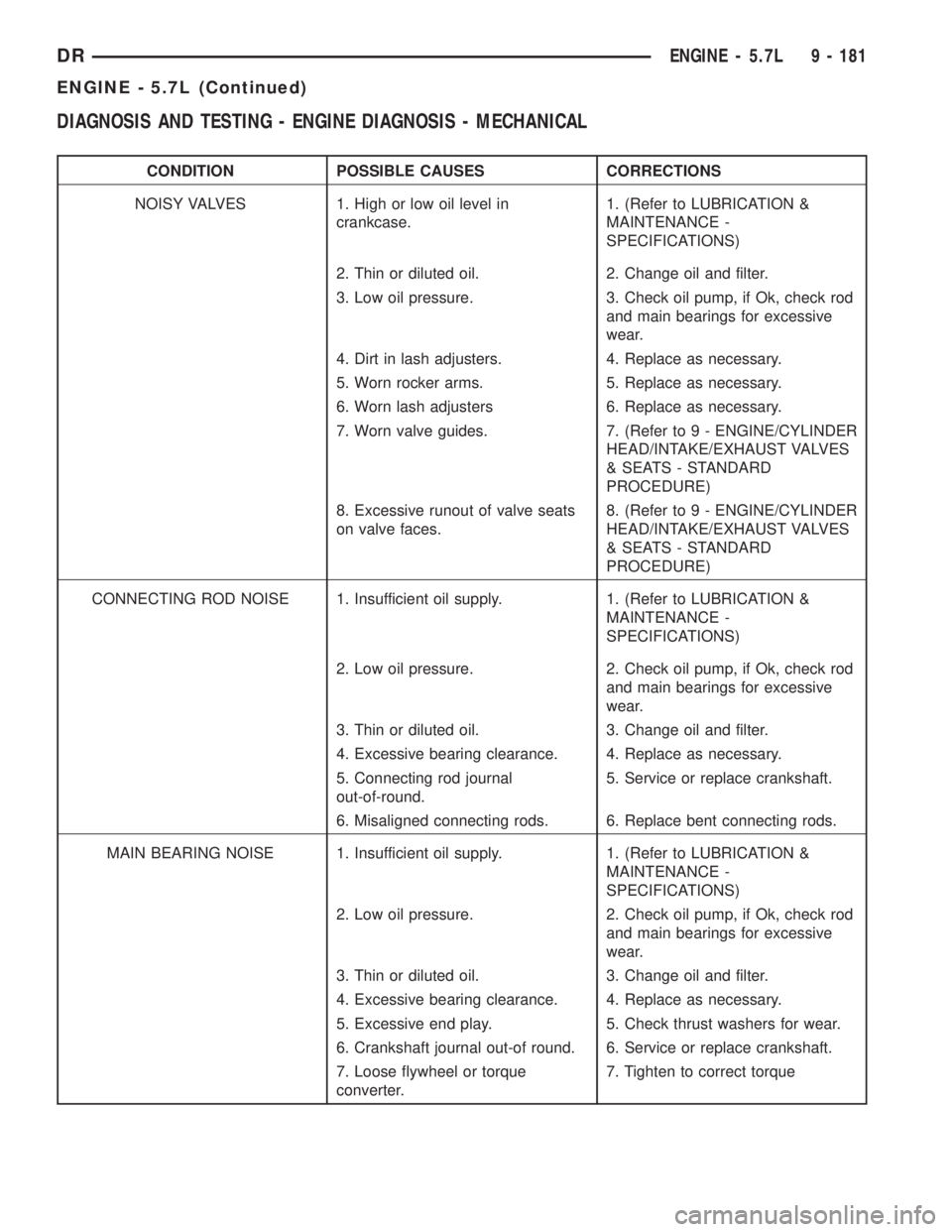
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 181
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1432 of 2895
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION
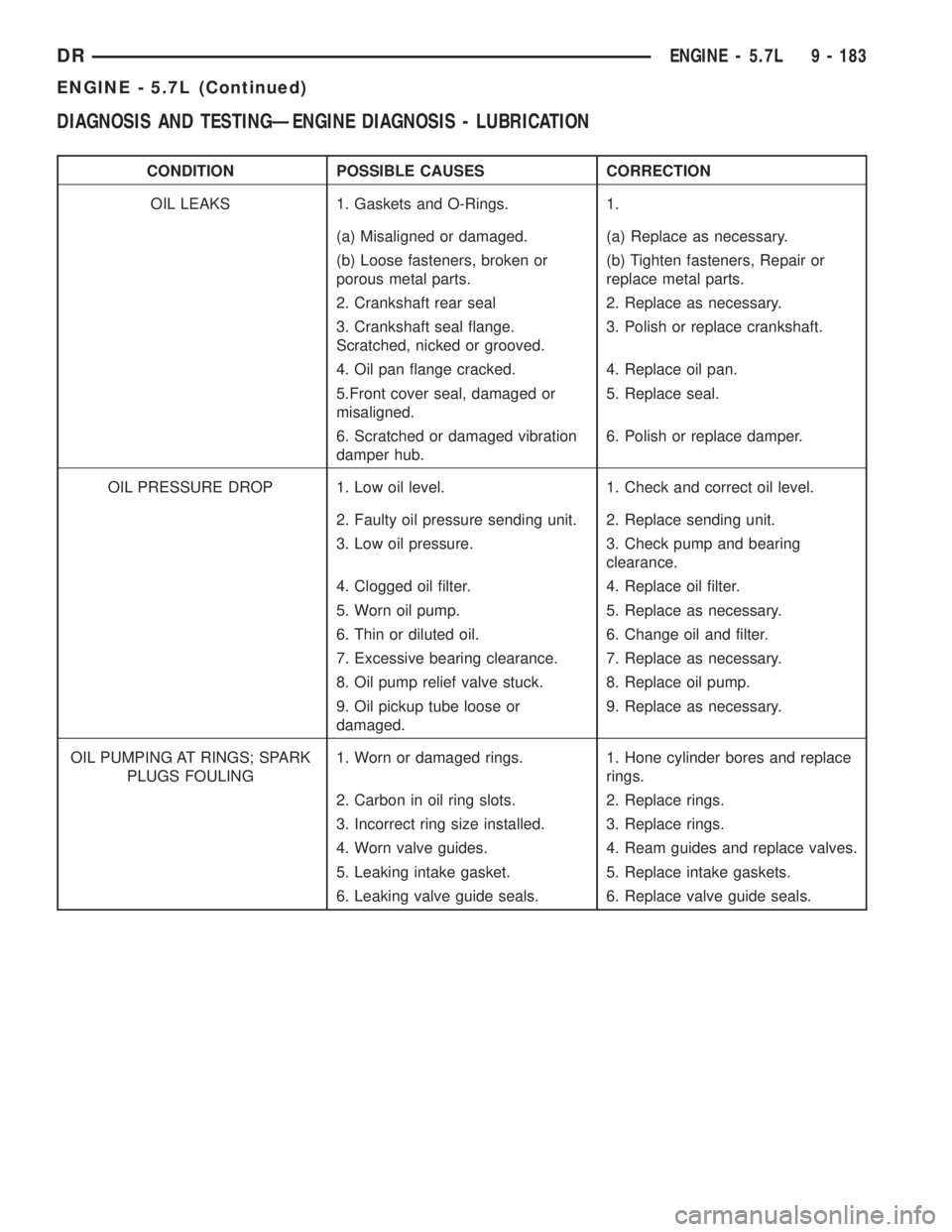
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS 1. Gaskets and O-Rings. 1.
(a) Misaligned or damaged. (a) Replace as necessary.
(b) Loose fasteners, broken or
porous metal parts.(b) Tighten fasteners, Repair or
replace metal parts.
2. Crankshaft rear seal 2. Replace as necessary.
3. Crankshaft seal flange.
Scratched, nicked or grooved.3. Polish or replace crankshaft.
4. Oil pan flange cracked. 4. Replace oil pan.
5.Front cover seal, damaged or
misaligned.5. Replace seal.
6. Scratched or damaged vibration
damper hub.6. Polish or replace damper.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter.
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump.
9. Oil pickup tube loose or
damaged.9. Replace as necessary.
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings.
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings.
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves.
5. Leaking intake gasket. 5. Replace intake gaskets.
6. Leaking valve guide seals. 6. Replace valve guide seals.
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 183
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)