2000 TOYOTA CAMRY relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 1214 of 4770
2K 7
2F 42C10 23 15
E 4E3E2E1DD5 B BBB A BAB
A 16 A1
EB15A
EFI FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (
SEE PAGE 50)
II3 9
B±Y B±Y B±Y
B±Y B±W
B±R
G
R±L
W
Y
R
LB±Y
B±YB±YB±R W± B
R±L
W
Y
R
L W± B
EFI RELAY
B±Y
+B BATT
ENGINE CONTROL MODULEB E 7 E 8ACE 9 FC
#60 #50 #40 #30 #20 #10 2C 5
W± B
B 16NEO
BR±W
A 14EFI+
W
A 21EFI±
B
A 13TRC+
LG
A 20TRC±
L
FROM ABS AND
TRACTI ON ECU 2J8
A EAE
B±Y
, , ,
A2
B±R
W± B B±W B±W
2
2J
B±W
B±Y B±Y
B(
*1)
B(
*1)
B±Y
B± Y
D E10 EE11 , 3
A G±R
G IGSWMRELA BB C
A 7P
N5 B±W B
JUNCTION
CONNECTORB J 7 J 8A
PARK/NEUTRAL
POSITION SW
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR
P 1
J29
STAB 20 B
B± W
, B
II2 11
10
II2 2 1
GR(
*4 A/T)B±W
B±W
B±O
GR
* 1 : CALIFORNIA
* 4 : TMC MADE
* 3 : W/ ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM6
B± O
GR
B±W(
A/T)(
M/T)
(
*5)
(
*4)
(
*5 A/T)C 7
CLUTCH START
SW
(
A/T)
A 8B±W
* 2 : W/ TRACTION CONTROLC 10TXCT
L±Y
C 5RXCK
R±L
C 4CODE
G±W
TO TRANSPONDER
KEY AMPLIFIER
(
*3)
(
*3)
(
*3)
6
(
*1)
(
*2)
(
*2)
(
*2)
(
*2)
(
*2)(
A/T)
B C
B±O(
*5 M/T) GR(
*4 M/T)
B B
NSW A 9ID1 1
VV
ID1 10
B±Y
2 1VSV (
VAPOR
PRESSURE SENSOR) V 7
B± Y
J27
JUNCTION
CONNECTORB A, J28
TPC
* 5 : TMMK MADE
Page 1216 of 4770
I 2
I 2 I 2
I 2 I 21 2
1 2D 3
D 18 D23 D2D13 D14 A17 E 22D 9
1 II1 2
13 213 1 3 1
3 1 A
2312 34 2 4 2 2 B±Y
BR(
*1) BR
BR Y BR E2 VTA1 VC THG THW PTNKEGLSPS RSO RSC HTS OXS HAFR
B±LW± G
P BR
YY
BR BR
G±B G±Y YL BR BR
Y
R±W
Y±B
P±B
B
B± R(
*1)
BR(
*1)BBR BRB±Y B±Y
B±Y
(
SHIELDED)
(
SHIELDED)(
SHIELDED) Y
A
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(
BANK 1 SENSOR 2)
AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
(
BANK 1 SENSOR 1) I 1
H 8
A28
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J20
T 2
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
EGR GAS TEMP. SENSOR
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR
VAPOR PRESSURE SENSOREGR VAL VE
POSITION SENSOR
POWER STEERING
OIL PRESSURE SWE 1
E 5
V 1E 2
P 2
ENGINE CONTROL MODULEB E 7 E 8ACE 9 DE10+B E1
HT OX
PTNK
E2 VCC
E2 VTA VC BRI 2ID1 6IG34II2 1 C 16
6
IND
P
R±Y R±Y R±Y
G± W G±W
E 29
FROM FAN NO. 1 RELAYCF
IMLD , , , EE1 1 , B B
B JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J2 4
B(
*1)
THEFT
DETERRENT
ECU T 3 BR B(
*1)
AFR± AFR+
B D
B D
B J10
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR E 16 E15 B9B8D11 D20
G(
*1 *4)
BR(
*1 *5)
R(
*1 *4)
B±R(
*1 *5)
B(
*1) B±Y
D 12 D4 I 2 BR
I 2
I 2 42
31A
OX HTBR
B
Y±RBR
B±Y (
SHIELDED)
(
*6)(
*6)
(
*6)
(
*6) (
*6) (
*6)
OXL1 HTLE1 +B
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(
BANK 2 SENSOR 1) H 4
(
SHIELDED)BR(
*6)
BR(
*6)BR(
*6) BR(
*6)
II13
ID15 II1 4ID12
BRBR
YBR(
*6)
* 1 : CALIFORNIA
* 4 : TMC MADE
* 5 : TMMK MADE
* 6 : EXCEPT CALIFORNIA
(
*1)
Page 1220 of 4770

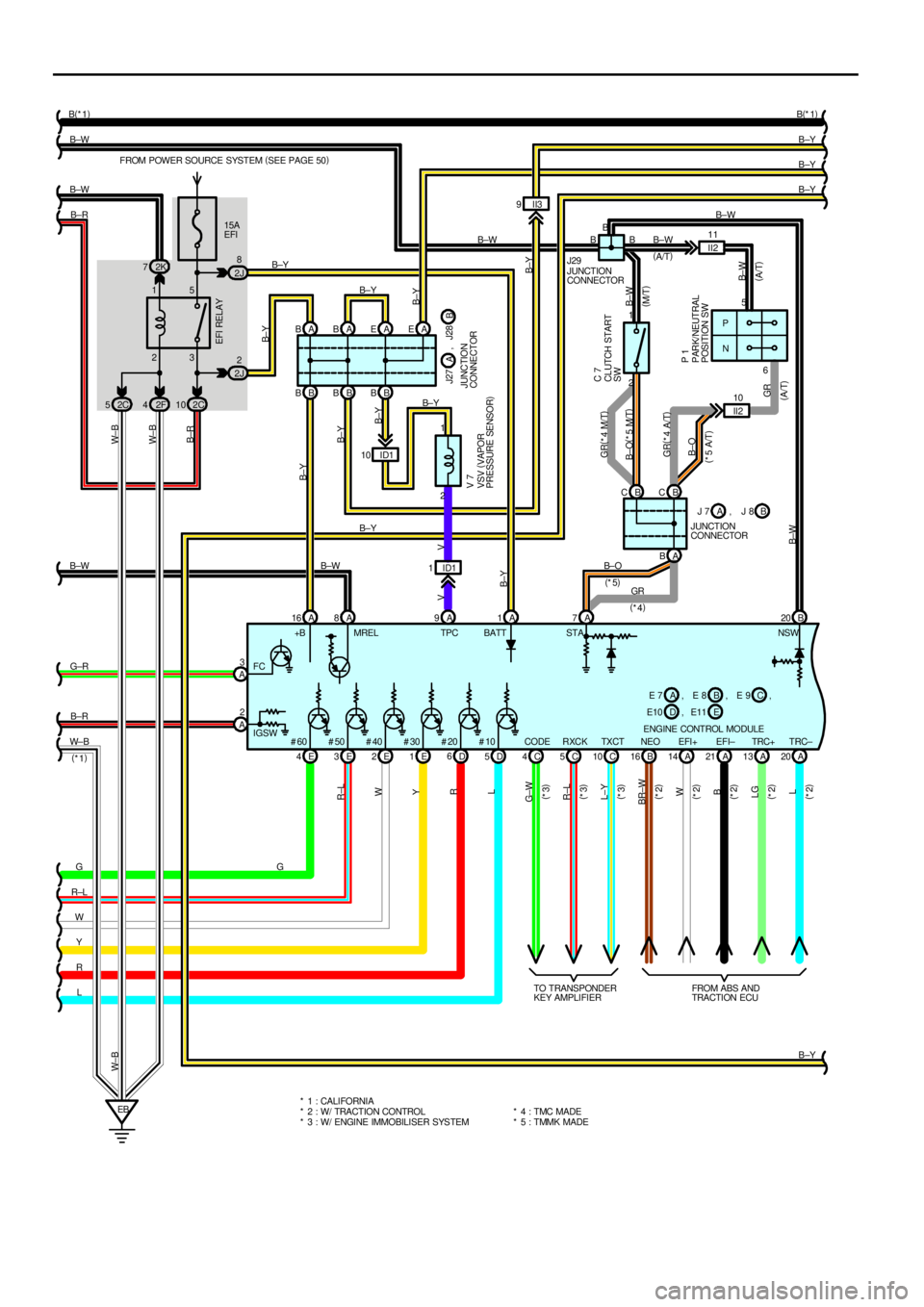
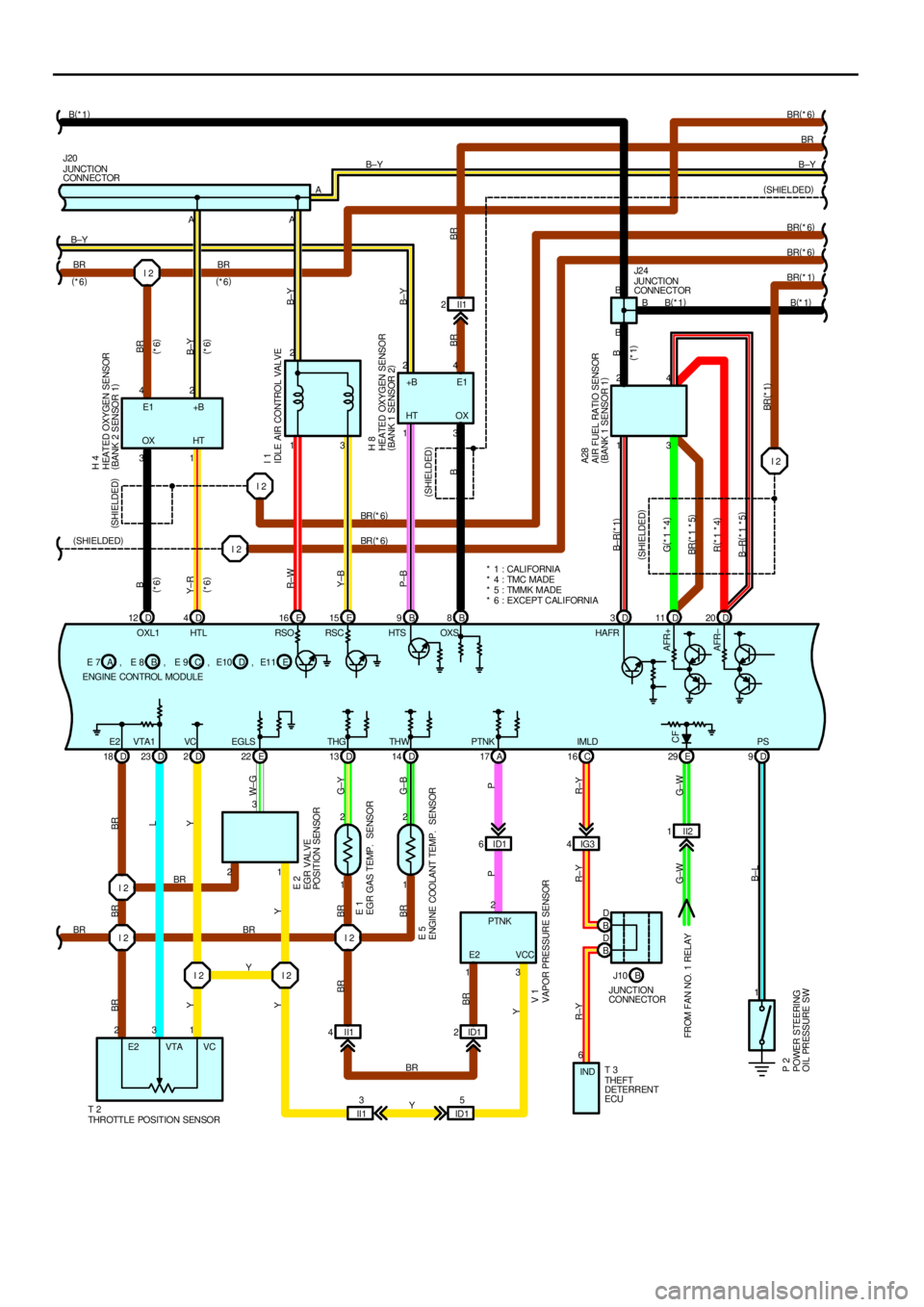
This system utilizes an engine control module and maintains overall control of the engine, transmission and so on. An outline
of the engine control is explained here.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) Engine coolant temp. signal circuit
The engine coolant temp. sensor detects the engine coolant temp. and has a built±in thermistor with a resistance which
varies according to the water temp. is input into TERMINAL THW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(2) Intake air temp. signal circuit
The intake air temp. sensor is installed in the mass air flow meter and detects the intake air temp., which is input as a
control signal into TERMINAL THA of the engine control module.
(3) Oxygen sensor signal circuit
The oxygen density in the exhaust gases is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINALS OXL1, OXR1
(Except California) and OXS of the engine control module. To maintain stable detection performance by the heated
oxygen sensor, a heater is used for warming the sensor. The heater is also controlled by the engine control module
(HTL, HTR (Except California) and HTS).
(4) RPM signal circuit
Camshaft position and crankshaft position are detected by the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor.
The camshaft position is input as a control signal to TERMINAL G22+ of the engine control module, and the engine
RPM is input into TERMINAL NE+.
(5) Throttle signal circuit
The throttle position sensor detects the throttle valve opening angle as a control signal, which is input into TERMINAL
VTA1 of the engine control module.
(6) Vehicle speed signal circuit
The vehicle speed sensor, installed inside the transmission, detects the vehicle speed and inputs a control signal into
TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module.
(7) Park/Neutral position SW signal circuit
The Park/Neutral position SW detects whether the shift position is in neutral, parking or not, and inputs a control signal
into TERMINAL STA of the engine control module.
(8) A/C SW signal circuit
The A/C control assembly (Automatic A/C) or A/C Amplifier (Manual A/C) inputs the A/C operations into TERMINAL A/C
of the engine control module as a control signal.
(9) Battery signal circuit
(California or w/ engine immobiliser and/or traction control)
Voltage is always supplies to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module.
If you turn on the ignition SW, the current goes from TERMINAL MREL of the engine control module to the EFI relay and
put on the relay, and the voltage related to the engine control module operation is supplied to TERMINAL +B of the
engine control module through the EFI relay.
(Except California or w/ engine immobiliser and/or traction control)
Voltage is constantly applied to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module. When the ignition SW is turned on,
voltage for engine control module start±up power supply is applied to TERMINAL +B of engine control module via EFI
relay.
(10) Intake air volume signal circuit
Intake air volume is detected by the mass air flow meter and a signal is input into TERMINAL VG of the engine control
module as a control signal.
(11) NSW signal circuit
To confirm whether the engine is cranking, the voltage applied to the starter motor during cranking is detected and the
signal is input into TERMINAL NSW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(12) Engine knock signal circuit
Engine knocking is detected by the knock sensor 1 and 2, then the signals are input into TERMINALS KNKR and KNKL
of the engine control module as a control signal.
(13) Air fuel ratio signal circuit (California)
The air fuel ratio is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINALS AFL+, AFR+ of the engine control module.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1223 of 4770
![TOYOTA CAMRY 2000 Service Repair Manual ENGINE CONTROL (1MZ±FE)
I8, I9, I10, I11, I12, I13 INJECTOR
2±1 : Approx. 13.8 W
CIR OPN RELAY [R/B NO.1]
3±5 : Closed with starter running
EFI RELAY [ENGINE ROOM J/B NO.2]
3±5 : Closed with igni TOYOTA CAMRY 2000 Service Repair Manual ENGINE CONTROL (1MZ±FE)
I8, I9, I10, I11, I12, I13 INJECTOR
2±1 : Approx. 13.8 W
CIR OPN RELAY [R/B NO.1]
3±5 : Closed with starter running
EFI RELAY [ENGINE ROOM J/B NO.2]
3±5 : Closed with igni](/manual-img/14/57447/w960_57447-1222.png)
ENGINE CONTROL (1MZ±FE)
I8, I9, I10, I11, I12, I13 INJECTOR
2±1 : Approx. 13.8 W
CIR OPN RELAY [R/B NO.1]
3±5 : Closed with starter running
EFI RELAY [ENGINE ROOM J/B NO.2]
3±5 : Closed with ignition SW at ON or ST position
: PARTS LOCATION
CodeSee PageCodeSee PageCodeSee Page
A12C30H830J2431
A2826 (1MZ±FE)H326 (1MZ±FE) J2631
A2926 (1MZ±FE)H426 (1MZ±FE)J27A31
A34A30I127 (1MZ±FE)J28B31
A35B30I827 (1MZ±FE) J2931
C126 (1MZ±FE)I927 (1MZ±FE)J35A31
C226 (1MZ±FE) I1027 (1MZ±FE)J26B31
C730I1127 (1MZ±FE)J4032
C9B30I1227 (1MZ±FE)K127 (1MZ±FE)
C10C30I1327 (1MZ±FE)K227 (1MZ±FE)
D126 (1MZ±FE) I1630M227 (1MZ±FE)
D530J331P127 (1MZ±FE)
E126 (1MZ±FE) J431P227 (1MZ±FE)
E226 (1MZ±FE) J7A31S631
E526 (1MZ±FE)J8B31T227 (1MZ±FE)
E7A30J9A31T331
E8B30J10B31U131
E9C30J1131V127 (1MZ±FE)
E10D30J1231V227 (1MZ±FE)
E11E30J1531V427 (1MZ±FE)
F4A26 (1MZ±FE)J1831V527 (1MZ±FE)
F6C26 (1MZ±FE)J2031V627 (1MZ±FE)
F1432 J2231V727 (1MZ±FE)
: RELAY BLOCKS
CodeSee PageRelay Blocks (Relay Block Location)
124Engine Room R/B No.1 (Engine Compartment Left)
224Engine Room R/B No.2 (Near the Battery)
Page 1229 of 4770
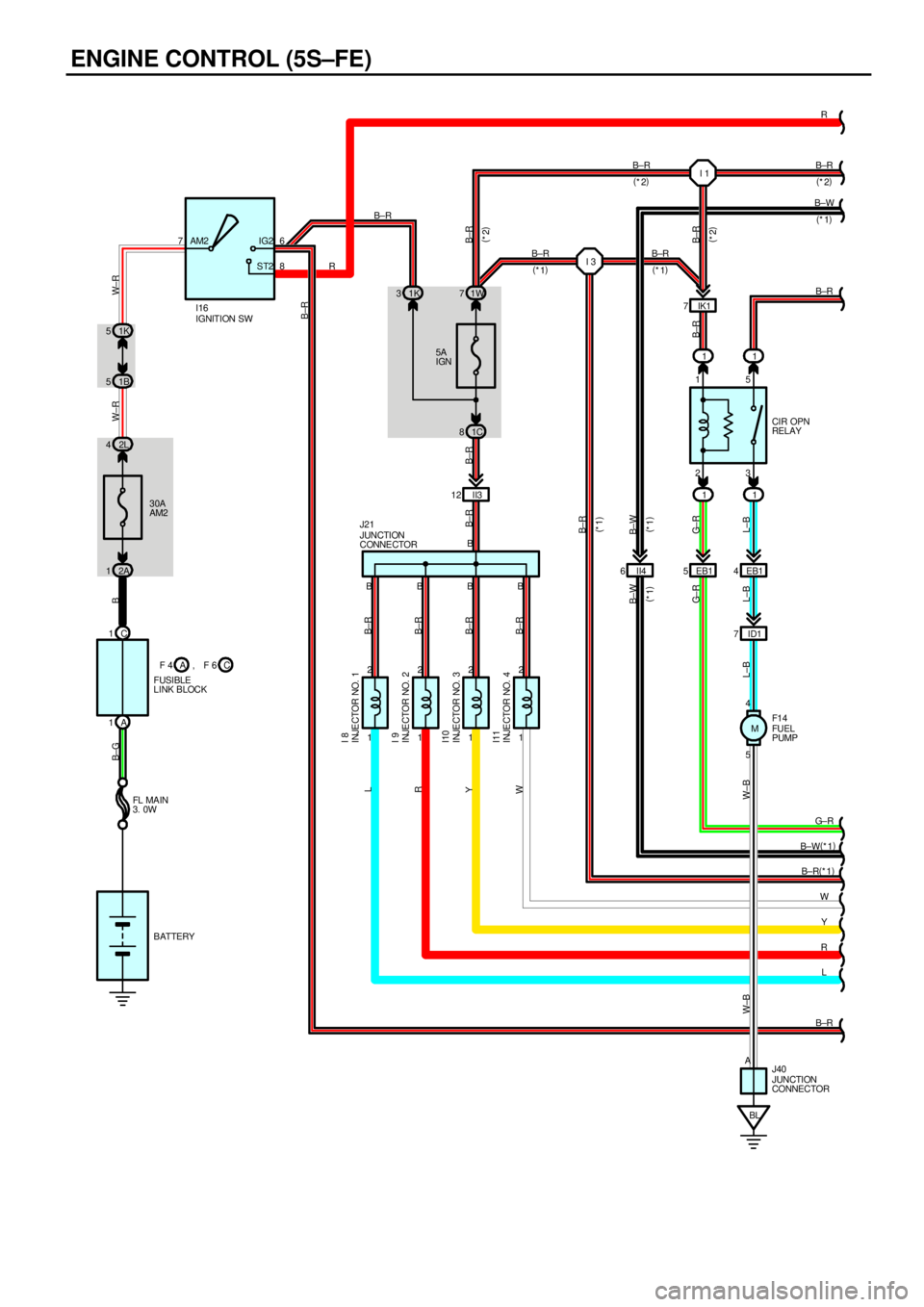
ENGINE CONTROL (5S±FE)
11
11 23 15
CIR OPN
RELAY 5A
IGN
30A
AM2 1K 5
2L 41K 31W7
1C 8 1B 5
2A 1
BL ID1 7EB1 4 EB1 5 II3 12
1 2
1 2
1 2
1 2 C 1
A 176
8 AM2 IG2
ST2
B B B B
5 4 B
G± R
B±W(
*1)
B±R(
*1)
W
Y B±R B±RR
B±R
R
L±B L±B L±B W±B W±BG± RB±R B±R B±RW± R W±R B B±G
B±R B±R B±R B±R
WY RL
IGNITION SW
JUNCTION
CONNE CTOR
FUEL
PUMP
INJE CTOR NO. 1
INJE CTOR NO. 2
INJE CTOR NO. 3
INJE CTOR NO. 4
I16
J21
F1 4
I 8
I 9
I10
I11
BATTERY FL MA IN
3. 0W
JUNCTION
CONNECTOR J40 A
G± R
B±RR
L
B±R
B±W
(
*1)
II4 6
B±W
(
*1)B±W
(
*1)
B±R
(
*1)(
*2)
(
*2)
F 4
FUSIBLE
LINK BLOCKC A, F 6IK1 7I 1
I 3B±R
B±R
B±R B±R B±R
(
*2)
(
*2)
(
*1)
(
*1)
M
Page 1232 of 4770
FROM POWER SOURCE SYSTEM (
SEE PAGE 50)
1C 91J11
1 2
2 1
IK2 7IK22
IK2 9II3 10 II21
1 I 2 I 2
A 10 A 20 A21 A19 C19 B11 C4 B 6C8B15 C4C17 C5A2
2 1 B8 1 3
2 A
B4 2123
A
1 3
2 5 1
BR
B±YBR BRB±Y(
*6) B±Y
BR
BR
BR
BR
BR
B±Y PS SW THR LOCK IN PRS MGC TE1
A/C SW LOCK
B±LL±R L±W BRW±L W±L W±LG L±Y
G L±YR±BR±B R±W
R±BW
L±Y
L±W
B±R
BR
L
B±W
G±O G±O
B±YB±Y
BR
B±Y
BR
OX1 HT1 TE1 NE+ NE± G+ E LSE1 +B
10A TAIL
10A
MIRROR±
HEATER (
SHIELDED)
(
SHIELDED) (
SHIELDED)
(
*6) (
*6)(
*6)
(
*6)
L
B±R
(
*6)
DIODE
(
IDLE±UP)
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
(
BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
DATA LINK
CONNECTOR 1
CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR
CAMSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR
JUNCTION
CONNECTORH 3
D 1
C 2
C 1
J12
D11
JUNCTION CONNECTOR
A/C SWHEATER CONTROL SW
A/C EVAPORATOR
TEMP. SENSOR
POWER STEERING OIL PRESSURE SWFROM MG
CLT RELAY
FROM
A/C DUAL
PRESSURE SW
FROM A/ C
MAGNETIC
CLUTCH AND
LOCK SENSORJ12
A13
P 2H 9
A14* 5 : CALIFORNIA
* 6 : EXCEPT CALIFORNIA
BR
ENGINE CONTROL MODULEB E 7 E 8ACE 9 +B E1
OX HT* 1 : W/ ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM
* 2 : W/O ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM
, , DE10 , B 5C1B7D12 D6D11 A13(
*1)
(
*2)
IG3 8D 4KSW
L±B L±B L±B
TO UNLOCK
WARN ING SW
A 10 A 15 A21 A13 C18 B10 B12
IG3 4II4 3D 1IMLD
R±Y R±Y R±Y
6
IND R±YTHEFT DETERRENT
ECU T 3
(
*1)
(
*2) D 3D8D9TXCT CODE RXCK
R±L
G± W
L±Y
TO TRANSPONDER
KEY AMPLIFIER
DD
J10
JUNCTION
CONNECTORII4 9 * 3 : TMC MADE
* 4 : TMMK MADE
Page 1235 of 4770

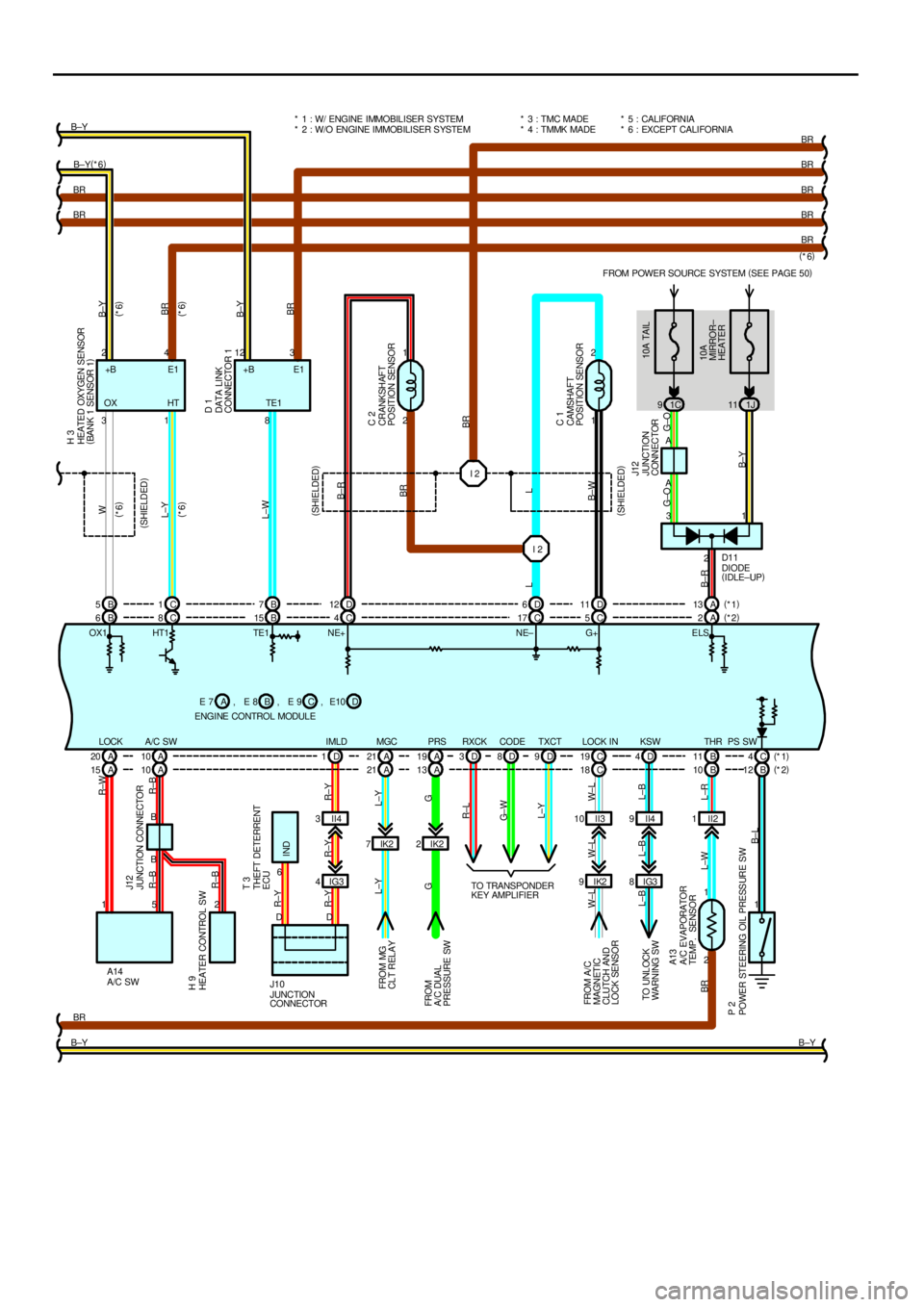
ENGINE CONTROL (5S±FE)
This system utilizes an engine control module and maintains overall control of the engine, transmission and so on. An outline
of the engine control is explained here.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) Engine coolant temp. signal circuit
The engine coolant temp. sensor detects the engine coolant temp. and has a built±in thermistor with a resistance which
varies according to the engine coolant temp. thus the engine coolant temp. is input in the form of a control signal into
TERMINAL THW of the engine control module.
(2) Intake air temp. signal circuit
The intake air temp. sensor detects the intake air temp., which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL THA of the
engine control module.
(3) Oxygen sensor signal circuit
The oxygen density in the exhaust gases is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL OX1 (except
California) and OX2 of the engine control module.
(4) RPM signal circuit
Camshaft position and crankshaft position are detected by the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor.
Camshaft position is input as a control signal to TERMINAL G+ of the engine control module, and engine RPM is input
into TERMINAL NE+.
(5) Throttle signal circuit
The throttle position sensor detects the throttle valve opening angle, which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL
VTA of the engine control module.
(6) Vehicle speed signal circuit
The vehicle speed sensor, installed inside the transmission, detects the vehicle speed and inputs a control signal into
TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module.
(7) Park/Neutral position SW signal circuit (A/T)
The Park/Neutral position SW detects whether the shift position are in neutral, parking or not, and inputs a control signal
into TERMINAL STA of the engine control module.
(8) A/C SW signal circuit
The A/C amplifier function is built in the engine control module. The A/C SW signal inputs into the TERMINAL A/C SW of
the engine control module.
(9) Battery signal circuit
Voltage is constantly applied to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module. When the ignition SW is turned on, the
voltage for engine control module start±up power supply is applied to TERMINAL +B of engine control module via EFI
relay.
(10) Intake air volume signal circuit
Intake air volume is detected by the manifold absolute pressure sensor (for manifold pressure) and is input as a control
signal into TERMINAL PIN of the engine control module.
(11) Starter signal circuit
To confirm whether the engine is cranking, the voltage applied to the starter motor during cranking is detected and the
signal is input into TERMINAL NSW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(12) Engine knock signal circuit
Engine knocking is detected by knock sensor 1 and the signal is input into TERMINAL KNK as a control signal.
(13) Electrical load signal circuit
The signal when systems such as the rear window defogger, headlights, etc. Which cause a high electrical burden are
on is input to TERMINAL ELS as a control signal.
(14) Air fuel ratio signal circuit (California)
The air fuel ratio is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL AF+ of the engine control module.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1236 of 4770

2. CONTROL SYSTEM
*SFI system
The SFI system monitors the engine condition through the signals, which are input from each sensor (Input signals from
(1) to (14) etc.) to the engine control module. The best fuel injection volume is decided based on this data and the
program memorized by the engine control module, and the control signal is output to TERMINALS #10, #20, #30 and
#40 of the engine control module to operate the injector. (Inject the fuel). The SFI system produces control of fuel
injection operation by the engine control module in response to the driving conditions.
*ESA system
The ESA system monitors the engine condition through the signals, which are input to the engine control module from
each sensor (Input signals from (1), (2), (4) to (12) etc.) the best ignition timing is detected according to this data and the
memorized data in the engine control module, and the control signal is output to TERMINALS IGT1 and IGT2. This
signal controls the igniter to provide the best ignition timing for the driving conditions.
*Idle Air Control system
The IAC system (Step motor type) increases the RPM and provides idling stability for fast idle±up when the engine is
cold and when the idle speed has dropped due to electrical load, etc. The engine control module evaluates the signals
from each sensor (Input signals (1), (4) to (8), (13) etc.), outputs current to TERMINALS ISCO and ISCC, and controls
the idle air control valve.
*Fuel pump control system
The engine control module operation outputs to TERMINAL FC and controls the CIR OPN relay. Thus controls the fuel
pump drive speed in response to conditions.
*EGR control system
The EGR cut control system controls the VSV (EGR) by evaluating the signals from each sensor which are input to the
engine control module (Input signals (1), (5), (6), (9) etc.) and by sending output to TERMINAL EGR of the engine
control module.
*A/C conditioning operation system
In addition to the conventional A/C cut control, the engine control module performs the air conditioning operation as well
since the A/C amplifier function is built in it.
3. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
With the diagnosis system, when there is a malfunctioning in the engine control module signal system, the malfunction
system is recorded in the memory. The malfunctioning system can then be found by reading the display (Code) of the
malfunction indicator lamp.
4. FAIL±SAFE SYSTEM
When a malfunction occurs in any system, if there is a possibility of engine trouble being caused by continued control based
on the signals from that system, the fail±safe system either controls the system by using data (Standard values) recorded in
the engine control module memory or else stops the engine.
E7 (A), E8 (B), E9 (C), E10 (D) ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
Voltage at engine control module wiring connector
BATT±E1 : Always 9.0±14.0 volts
+B±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts (Ignition SW at ON position)
VC±E2 :4.5± 5.5 volts (Ignition SW at ON position)
VTA±E2 :0.3± 0.8 volts (Ignition SW on and throttle valve fully closed)
3.2±4.9 volts (Ignition SW on and throttle valve open)
PIM±E2 :3.3± 3.9 volts (Ignition SW at ON position)
THA±E2 :0.5±3.4 volts (Ignition SW on and intake air temp. 20°C, 68°F)
THW±E2 :0.2± 1.0 volts (Ignition SW on and coolant temp. 80°C, 176°F)
STA±E1 :6.0±14.0 volts (Engine cranking)
W±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts (No trouble and engine running)
TE1±E1 :9.0±14.0 volts (Ignition SW at ON position)
NSW±E1 :0± 3.0 volts (Ignition SW on and Park/Neutral position SW position P or N position)
9.0±14.0 volts (Ignition SW on and except Park/Neutral position SW position P or N position)
IGT1, IGT2±E1 : Pulse generation (Engine cranking or idling)
#10, #20, #30, #40±E01, E02 :9.0±14.0 volts (Ignition SW at ON position)
RESISTANCE AT ENGINE CONTROL MODULE WIRING CONNECTORS
(Disconnect wiring connector)
VC±E2 :2.5±5.0 kW
THA±E2 :2.21±2.69 kW (Intake air temp. 20°C, 68°F)
THW±E2 :0.29±0.354 kW (Coolant temp. 80°C, 176°F)
SERVICE HINTS