2000 TOYOTA CAMRY turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 1175 of 4770
![TOYOTA CAMRY 2000 Service Repair Manual G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[1MZ±FE]
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Press TOYOTA CAMRY 2000 Service Repair Manual G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[1MZ±FE]
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Press](/manual-img/14/57447/w960_57447-1174.png)
G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[1MZ±FE]
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Pressure SW)
A 4 ABS Actuator
A 5 ABS Actuator
A 6 ABS Actuator and ECU
A 7 ABS and Traction Actuator
A 8 ABS and Traction Actuator
A 9 ABS Speed Sensor Front LH
A 10 ABS Speed Sensor Front RH
A 28 Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
A 29 Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
A 30 A/C Ambient Temp. Sensor
A 31 Airbag Sensor Front LH
A 32 Airbag Sensor Front RH
B 1 Back±Up Light SW
B 2 Brake Fluid Level Warning SW
C 1 Camshaft Position Sensor
C 2 Crankshaft Position Sensor
C 3 Cruise Control Actuator
D 1 Data Link Connector 1
D 2 Daytime Running Light Resistor
D 3 Diode (A/C)E 1 EGR Gas Temp. Sensor
E 2 EGR Valve Position Sensor
E 3 Electronically Controlled Transmission Solenoid
E 5 Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
E 6 Engine Hood Courtesy SW
F 1 Front Turn Signal Light and Parking Light LH
F 2 Front Turn Signal Light and Parking Light RH
F 3 Front Wiper Motor
F 4 Fusible Link Block
F 5 Fusible Link Block
F 6 Fusible Link Block
F 7 Fusible Link Block
F 8 Fusible Link Block
F 9 Fusible Link Block
G 1 Generator
G 2 Generator
H 1 Headlight LH
H 2 Headlight RH
H 3 Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
H 4 Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
H 5 Horn (High)
H 6 Horn (Low)
Page 1177 of 4770
![TOYOTA CAMRY 2000 Service Repair Manual G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[5S±FE]
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Pressu TOYOTA CAMRY 2000 Service Repair Manual G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[5S±FE]
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Pressu](/manual-img/14/57447/w960_57447-1176.png)
G ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING
Position of Parts in Engine Compartment
[5S±FE]
A 1 A/C Condenser Fan Motor
A 2 A/C Magnetic Clutch and Lock Sensor
A 3 A/C Triple Pressure SW
(A/C Dual and Single Pressure SW)
A 4 ABS Actuator
A 5 ABS Actuator
A 6 ABS Actuator and ECU
A 9 ABS Speed Sensor Front LH
A 10 ABS Speed Sensor Front RH
A 11 Air Fuel Ratio Sensor
A 31 Airbag Sensor Front LH
A 32 Airbag Sensor Front RH
B 1 Back±Up Light SW
B 2 Brake Fluid Level Warning SW
C 1 Camshaft Position Sensor
C 2 Crankshaft Position Sensor
C 3 Cruise Control Actuator
D 1 Data Link Connector 1
D 2 Daytime Running Light ResistorE 3 Electronically Controlled Transmission Solenoid
E 4 Electronically Controlled Transmission Solenoid
E 5 Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
E 6 Engine Hood Courtesy SW
F 1 Front Turn Signal Light and Parking Light LH
F 2 Front Turn Signal Light and Parking Light RH
F 3 Front Wiper Motor
F 4 Fusible Link Block
F 5 Fusible Link Block
F 6 Fusible Link Block
F 7 Fusible Link Block
F 8 Fusible Link Block
F 9 Fusible Link Block
G 1 Generator
G 2 Generator
H 1 Headlight LH
H 2 Headlight RH
H 3 Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
H 5 Horn (High)
H 6 Horn (Low)
Page 1180 of 4770
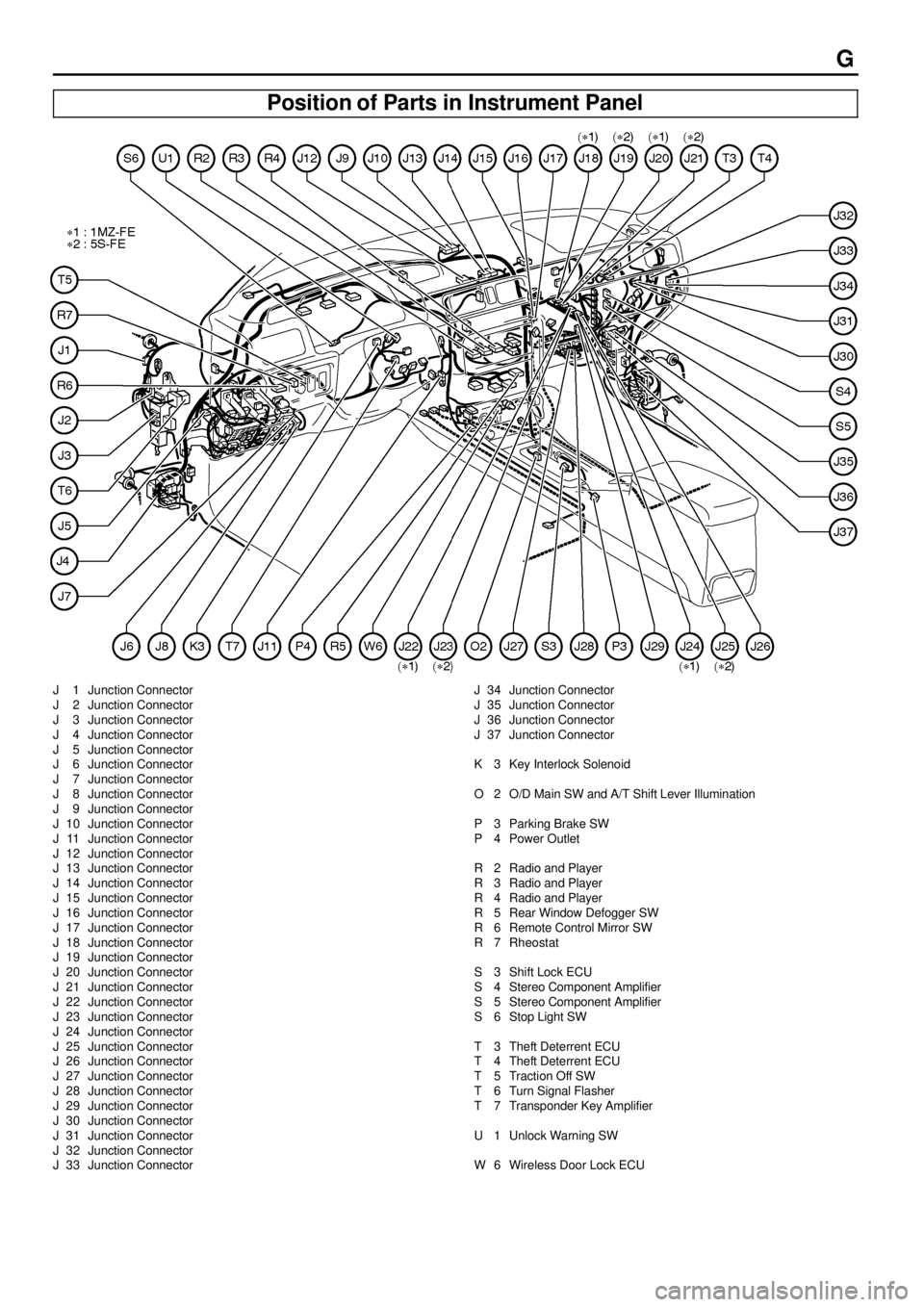
G
Position of Parts in Instrument Panel
J 1 Junction Connector
J 2 Junction Connector
J 3 Junction Connector
J 4 Junction Connector
J 5 Junction Connector
J 6 Junction Connector
J 7 Junction Connector
J 8 Junction Connector
J 9 Junction Connector
J 10 Junction Connector
J 11 Junction Connector
J 12 Junction Connector
J 13 Junction Connector
J 14 Junction Connector
J 15 Junction Connector
J 16 Junction Connector
J 17 Junction Connector
J 18 Junction Connector
J 19 Junction Connector
J 20 Junction Connector
J 21 Junction Connector
J 22 Junction Connector
J 23 Junction Connector
J 24 Junction Connector
J 25 Junction Connector
J 26 Junction Connector
J 27 Junction Connector
J 28 Junction Connector
J 29 Junction Connector
J 30 Junction Connector
J 31 Junction Connector
J 32 Junction Connector
J 33 Junction ConnectorJ 34 Junction Connector
J 35 Junction Connector
J 36 Junction Connector
J 37 Junction Connector
K 3 Key Interlock Solenoid
O 2 O/D Main SW and A/T Shift Lever Illumination
P 3 Parking Brake SW
P 4 Power Outlet
R 2 Radio and Player
R 3 Radio and Player
R 4 Radio and Player
R 5 Rear Window Defogger SW
R 6 Remote Control Mirror SW
R 7 Rheostat
S 3 Shift Lock ECU
S 4 Stereo Component Amplifier
S 5 Stereo Component Amplifier
S 6 Stop Light SW
T 3 Theft Deterrent ECU
T 4 Theft Deterrent ECU
T 5 Traction Off SW
T 6 Turn Signal Flasher
T 7 Transponder Key Amplifier
U 1 Unlock Warning SW
W 6 Wireless Door Lock ECU
Page 1220 of 4770

This system utilizes an engine control module and maintains overall control of the engine, transmission and so on. An outline
of the engine control is explained here.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) Engine coolant temp. signal circuit
The engine coolant temp. sensor detects the engine coolant temp. and has a built±in thermistor with a resistance which
varies according to the water temp. is input into TERMINAL THW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(2) Intake air temp. signal circuit
The intake air temp. sensor is installed in the mass air flow meter and detects the intake air temp., which is input as a
control signal into TERMINAL THA of the engine control module.
(3) Oxygen sensor signal circuit
The oxygen density in the exhaust gases is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINALS OXL1, OXR1
(Except California) and OXS of the engine control module. To maintain stable detection performance by the heated
oxygen sensor, a heater is used for warming the sensor. The heater is also controlled by the engine control module
(HTL, HTR (Except California) and HTS).
(4) RPM signal circuit
Camshaft position and crankshaft position are detected by the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor.
The camshaft position is input as a control signal to TERMINAL G22+ of the engine control module, and the engine
RPM is input into TERMINAL NE+.
(5) Throttle signal circuit
The throttle position sensor detects the throttle valve opening angle as a control signal, which is input into TERMINAL
VTA1 of the engine control module.
(6) Vehicle speed signal circuit
The vehicle speed sensor, installed inside the transmission, detects the vehicle speed and inputs a control signal into
TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module.
(7) Park/Neutral position SW signal circuit
The Park/Neutral position SW detects whether the shift position is in neutral, parking or not, and inputs a control signal
into TERMINAL STA of the engine control module.
(8) A/C SW signal circuit
The A/C control assembly (Automatic A/C) or A/C Amplifier (Manual A/C) inputs the A/C operations into TERMINAL A/C
of the engine control module as a control signal.
(9) Battery signal circuit
(California or w/ engine immobiliser and/or traction control)
Voltage is always supplies to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module.
If you turn on the ignition SW, the current goes from TERMINAL MREL of the engine control module to the EFI relay and
put on the relay, and the voltage related to the engine control module operation is supplied to TERMINAL +B of the
engine control module through the EFI relay.
(Except California or w/ engine immobiliser and/or traction control)
Voltage is constantly applied to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module. When the ignition SW is turned on,
voltage for engine control module start±up power supply is applied to TERMINAL +B of engine control module via EFI
relay.
(10) Intake air volume signal circuit
Intake air volume is detected by the mass air flow meter and a signal is input into TERMINAL VG of the engine control
module as a control signal.
(11) NSW signal circuit
To confirm whether the engine is cranking, the voltage applied to the starter motor during cranking is detected and the
signal is input into TERMINAL NSW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(12) Engine knock signal circuit
Engine knocking is detected by the knock sensor 1 and 2, then the signals are input into TERMINALS KNKR and KNKL
of the engine control module as a control signal.
(13) Air fuel ratio signal circuit (California)
The air fuel ratio is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINALS AFL+, AFR+ of the engine control module.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1221 of 4770

ENGINE CONTROL (1MZ±FE)
2. CONTROL SYSTEM
*SFI system
The SFI system monitors the engine condition through the signals, which are input from each sensor (Input signals (1) to
(12) ). The best fuel injection volume is decided based on this data and the program memorized by the engine control
module, and the control signal is output to TERMINALS #10, #20, #30, #40, #50 and #60 of the engine control module
to operate the injector (Inject the fuel). The SFI system produces control of fuel injection operation by the engine control
module in response to the driving conditions.
*ESA system
The ESA system monitors the engine condition through the signals, which are input to the engine control module from
each sensor (Input signals from 1, 3, 4, 12). The best ignition timing is decided according to this data and the memorized
data in the engine control module and the control signal is output to TERMINALS IGT1, IGT2 and IGT3. This signal
controls the igniter to provide the best ignition timing for the driving conditions.
*Heated oxygen sensor heater control system
The heated oxygen sensor heater control system turns the heater on when the intake air volume is low (Temp. of
exhaust emissions is low), and warms up the heated oxygen sensor to improve detection performance of the sensor.
The engine control module evaluates the signals from each sensor (Input signals from 1, 4, 9, 10), current is output to
TERMINALS HTL, HTR and HTS, controlling the heater.
*Idle air control system
The idle air control system (Rotary solenoid type) increases the RPM and provides idle stability for fast idle±up when the
engine is cold, and when the idle speed has dropped due to electrical load and so on, the engine control module
evaluates the signals from each sensor (Input signals from 1, 4, 5, 8, 9), current is output to TERMINALS RSO and RSC
to control idle air control valve.
*EGR control system
The EGR control system detects the signal from each sensor (Input signals from 1, 4, 9, 10), and outputs current to
TERMINAL EGR to control the VSV (EGR).
The EGR valve position sensor is mounted on the EGR valve. this sensor converts the EGR valve opening height into a
voltage and sends it to the engine control module as the EGR valve position signal.
*ACIS
ACIS includes a valve in the bulkhead separating the surge tank into two parts. This valve is opened and closed in
accordance with the driving conditions to control the intake manifold length in two stages for increased engine output in
all ranges from low to high speeds.
The engine control module judges the engine speed by the signals ( (4), (5) ) from each sensor and outputs signals to
the TERMINAL ACIS to control the VSV (Intake air control).
3. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
With the diagnosis system, when there is a malfunction in the engine control module signal system, the malfunctioning
system is recorded in the memory.
4. FAIL±SAFE SYSTEM
When a malfunction occurs in any systems, if there is a possibility of engine trouble being caused by continued control
based on the signals from that system, the fail±safe system either controls the system by using data (Standard values)
recorded in the engine control module memory or else stops the engine.
Page 1235 of 4770

ENGINE CONTROL (5S±FE)
This system utilizes an engine control module and maintains overall control of the engine, transmission and so on. An outline
of the engine control is explained here.
1. INPUT SIGNALS
(1) Engine coolant temp. signal circuit
The engine coolant temp. sensor detects the engine coolant temp. and has a built±in thermistor with a resistance which
varies according to the engine coolant temp. thus the engine coolant temp. is input in the form of a control signal into
TERMINAL THW of the engine control module.
(2) Intake air temp. signal circuit
The intake air temp. sensor detects the intake air temp., which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL THA of the
engine control module.
(3) Oxygen sensor signal circuit
The oxygen density in the exhaust gases is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL OX1 (except
California) and OX2 of the engine control module.
(4) RPM signal circuit
Camshaft position and crankshaft position are detected by the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor.
Camshaft position is input as a control signal to TERMINAL G+ of the engine control module, and engine RPM is input
into TERMINAL NE+.
(5) Throttle signal circuit
The throttle position sensor detects the throttle valve opening angle, which is input as a control signal into TERMINAL
VTA of the engine control module.
(6) Vehicle speed signal circuit
The vehicle speed sensor, installed inside the transmission, detects the vehicle speed and inputs a control signal into
TERMINAL SPD of the engine control module.
(7) Park/Neutral position SW signal circuit (A/T)
The Park/Neutral position SW detects whether the shift position are in neutral, parking or not, and inputs a control signal
into TERMINAL STA of the engine control module.
(8) A/C SW signal circuit
The A/C amplifier function is built in the engine control module. The A/C SW signal inputs into the TERMINAL A/C SW of
the engine control module.
(9) Battery signal circuit
Voltage is constantly applied to TERMINAL BATT of the engine control module. When the ignition SW is turned on, the
voltage for engine control module start±up power supply is applied to TERMINAL +B of engine control module via EFI
relay.
(10) Intake air volume signal circuit
Intake air volume is detected by the manifold absolute pressure sensor (for manifold pressure) and is input as a control
signal into TERMINAL PIN of the engine control module.
(11) Starter signal circuit
To confirm whether the engine is cranking, the voltage applied to the starter motor during cranking is detected and the
signal is input into TERMINAL NSW of the engine control module as a control signal.
(12) Engine knock signal circuit
Engine knocking is detected by knock sensor 1 and the signal is input into TERMINAL KNK as a control signal.
(13) Electrical load signal circuit
The signal when systems such as the rear window defogger, headlights, etc. Which cause a high electrical burden are
on is input to TERMINAL ELS as a control signal.
(14) Air fuel ratio signal circuit (California)
The air fuel ratio is detected and input as a control signal into TERMINAL AF+ of the engine control module.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1251 of 4770

HEADLIGHT (w/ DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT)
The current from the FL MAIN is always flowing from the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Coil side) to TERMINAL H±LP of the
daytime running light relay (Main), from DOME fuse to TERMINAL +B of the daytime running light relay (Main) and from the
ALT fuse to Taillight relay (Coil side) to TERMINAL TAIL (TMMK Made) of the daytime running light relay (Main).
When the ignition SW is turned on, the current flowing through the GAUGE fuse flows to TERMINAL IG of the daytime
running light relay (Main).
1. DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT OPERATION
When the engine is started, voltage generated at TERMINAL L of the generator is applied to TERMINAL CHG± of the
daytime running light relay (Main). If the parking brake lever is pulled up (Parking brake SW on) at this time, the relay is not
activated so the daytime running light system does not operate. If the parking brake lever is then released (Parking brake
SW off), a signal is input to TERMINAL PKB of the relay.
This activates the daytime running light relay (Main) and the HEAD relay is turned to on, so the current flows from the MAIN
fuse to the HEAD relay (Point side) to TERMINAL 1 of the DIM relay to TERMINAL 4 to H±LP LH (LWR), H±LP RH (LWR)
fuses to TERMINAL 1 of the headlights to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of the daytime running light resistor to TERMINAL 2
to GROUND, causing the headlights to light up (Headlights light up dimmer than normal brightness.). Once the daytime
running light system operates and the headlights light up, the headlights remain on even if the parking brake lever is pulled
up (Parking brake SW on).
If the engine stalls and the ignition SW remains on, the headlights remain light up even through current is no longer output
from TERMINAL L of the generator. If the ignition SW is then turned off, the headlights go off.
If the engine is started with the parking brake lever released (Parking brake SW off), the daytime running light system
operates and headlights light up when the engine starts.
2. HEADLIGHT OPERATION
When the light control SW is switched to HEAD position and the dimmer SW is set to LOW position, causing the daytime
running light relay (Main) and the HEAD relay to turn on, so the current flows from the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Point side)
to DRL NO.2 fuse to TERMINAL 3 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 4 to TERMINAL H±ON of the daytime running light
relay (Main) to TERMINAL H to TERMINAL 3 of the integration relay to TERMINAL 4 to TERMINAL 13 of the light control
SW to TERMINAL 16 to GROUND, activating the DRL. NO.4 relay. The current to HEAD relay (Point side) then flows to
TERMINAL 1 of the DIM relay to TERMINAL 4 to H±LP LH (LWR), H±LP RH (LWR) fuses to TERMINAL 1 of the headlights
to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 2 to GROUND, causing the headlights to light up at
normal intensity.
When the light control SW is switched to HEAD position and the dimmer SW is set to HIGH position, the signal from the
dimmer SW is input to the daytime running light relay (Main). This activates the daytime running light relay (Main) and the
HEAD relay is turned on, so the current flows from the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Point side) to TERMINAL 1 of the DIM
relay to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL DIM of the daytime running light relay (Main), activating the DIM relay. This causes
current to flow from TERMINAL 1 of the DIM relay to TERMINAL 2 to HEAD LH (UPR), HEAD RH (UPR) fuses to TERMINAL
2 of the headlights to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 2 to GROUND, causing the
headlights to light up at high beam and the high beam indicator light to light up.
When the dimmer SW is switched to FLASH position, the signal from the dimmer SW is input to the daytime running light
relay (Main). This activates the daytime running light relay (Main) and the HEAD relay is turned on, so the current flows from
the MAIN fuse to HEAD relay (Point side) to DRL NO.2 fuse to TERMINAL 3 of the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 4 to
TERMINAL H±ON of the daytime running light relay (Main) to TERMINAL H to TERMINAL 8 of the dimmer SW to
TERMINAL 16 to GROUND, activating the DRL NO.4 relay. At the same time, the current flows from the TERMINAL 1 of the
DIM relay to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL DIM of the daytime running light relay (Main), activating the DIM relay, and also
flows from the HEAD LH (UPR), HEAD RH (UPR) fuses to TERMINAL 2 of the headlights to TERMINAL 3 to TERMINAL 1 of
the DRL NO.4 relay to TERMINAL 2 to GROUND, causing the headlights to light up at high beam and the high beam
indicator light to light up.
SYSTEM OUTLINE
Page 1258 of 4770

With the ignition SW turned on, the current flows to TERMINAL 7 of the integration relay through GAUGE fuse.
Voltage is applied at all times to TERMINAL (C) 2 of the integration relay through the taillight relay coil side, and to
TERMINAL (C) 3 through the HEAD relay coil side (w/o daytime running light) or through the daytime running light relay
(Main) (w/ daytime running light).
1. NORMAL LIGHTING OPERATION
With the light control SW turned to TAIL position, a signal is input into TERMINAL (C) 1 of the integration relay. Due to this
signal, the current flowing to TERMINAL (C) 2 of the relay flows to TERMINAL (C) 1 to TERMINAL 14 of the light control SW
to TERMINAL 16 to GROUND, and taillight relay causes taillights to turn on.
With the light control SW turned to HEAD position, a signal is input into TERMINALS (C) 1 and (C) 4 of the integration relay.
Due to this signal, the current flowing to TERMINAL (C) 3 of the relay flows to TERMINAL (C) 4 to TERMINAL 13 of the light
control SW to TERMINAL 16 to GROUND in the headlight circuit, and causes taillight and HEAD relay to turn the lights on.
The taillight circuit is same as above.
2. LIGHT AUTO TURN OFF OPERATION
With light on and ignition SW turned off (Input signal goes to TERMINAL 7 of the relay), when the driver's door is opened
(Input signal goes to TERMINAL 6 of the relay), the relay operates and the current is cut off which flows from TERMINAL (C)
2 of the relay to TERMINAL (C) 1 In taillight circuit and from TERMINAL (C) 3 to TERMINAL (C) 4 in headlight circuit.
As a result, all lights are turned off automatically.
HEAD RELAY [ENGINE ROOM J/B NO.2]
2±1 : Closed with the light control SW at HEAD position or the dimmer SW at FLASH position
Closed with the engine running and the parking brake lever released (w/ daytime running light)
TAILLIGHT RELAY [INSTRUMENT PANEL J/B]
3±5 : Closed with the light control SW at TAIL or HEAD position
D12 DOOR COURTESY SW FRONT LH
1±GROUND : Continuity with the front LH door open
I17 (C)
INTEGRATION RELAY
7±GROUND : Approx. 12 volts with the ignition SW at ON position
6±GROUND : Continuity with the front LH door open
1±GROUND : Always approx. 12 volts
10±GROUND : Always continuity
(C) 2±GROUND : Always approx. 12 volts
(C) 3±GROUND : Always approx. 12 volts
(C) 4±GROUND : Continuity with the light control SW at HEAD position
(C) 1±GROUND : Continuity with the light control SW at TAIL or HEAD position
: PARTS LOCATION
CodeSee PageCodeSee PageCodeSee Page
C1330F6C26 (1MZ±FE)J231
D6A30F6C28 (5S±FE)J731D6B30F9F26 (1MZ±FE)J1131
D1232F9F28 (5S±FE)J3231
F4A26 (1MZ±FE)I17C30F4A28 (5S±FE)J131
SYSTEM OUTLINE
SERVICE HINTS