Page 555 of 4770

76CHASSISÐBRAKES
b. During Vehicle Acceleration (TRAC System Activated)
When a front wheel slips during acceleration, the TRAC system controls the engine output and braking of the front
wheels to help preventing wheel slippage.
The brake fluid pressure applied to the right and left front wheels is controlled separately accordingly to 3 control
modes ( pressure increase, holding, and pressure reduction) as explained below.
i) Pressure Increase Mode
During sudden acceleration or driving on a slippery surface, if the front wheels start to slip, a control signal from the
ABS & TRAC ECU causes the ABS & TRAC actuator to control the valves and pumps as described below, to effect
the pressure increase mode.
When the master cut and reservoir cut solenoid valves turn ON, port B is closed, port H is open and the pump operates
at the same time.
Accordingly, the brake fluid will be suctioned up from the master cylinder through parts G and H.
Then the brake fluid that is pressurized by the pump will be applied to the wheel cylinder through C and D.
Also, the brake fluid that pressurized by the pump is regulated to a constant pressure by the pressure regulator valve.
�Hydraulic Circuit�
�Condition of Each Valve and Pump Motor�
Part Name
Signal from
ABS & TRAC ECUOperation
Master Cut Solenoid ValveONPort BClosed
Reservoir Cut Solenoid ValveONPort HOpen
Pressure Holding ValveOFFPort COpen
Page 557 of 4770
78 CHASSISÐBRAKES
ii) Pressure Holding Mode
When the fluid pressure in the wheel cylinder is increased or decreased to attain the required pressure, the ABS &
TRAC ECU sends a control signal to turn ON the pressure holding valve.
Then, the fluid pressure that is applied to the wheel cylinder is cut off to hold the fluid pressure in the wheel cylinder.
�Hydraulic Circuit�
�Condition of Each Valve and Pump Motor�
Part Name
Signal from
ABS & TRAC ECUOperation
Master Cut Solenoid ValveONPort BClosed
Reservoir Cut Solenoid ValveOFFPort HClosed
Pressure Holding ValveONPort CClosed
Pressure Reduction ValveOFFPort FClosed
PumpONRotating
Page 558 of 4770
79CHASSISÐBRAKES
iii) Pressure Reduction Mode
When the fluid pressure in the wheel cylinder needs to be decreased, the ABS & TRAC ECU sends a control signal
to turn the pressure reduction valve ON, causing port F to open
Accordingly, the brake fluid in the wheel cylinder flows to ports E and F, reservoir, and pump, to reduce the fluid
pressure in the wheel cylinder.
The fluid pressure reduction rate is controlled by repetition of the pressure reduction and holding mode.
�Hydraulic Circuit�
�Condition of Each Valve and Pump Motor�
Part Name
Signal from
ABS & TRAC ECUOperation
Master Cut Solenoid ValveONPort BClosed
Reservoir Cut Solenoid ValveOFFPort HClosed
Pressure Holding ValveONPort CClosed
Pressure Reduction ValveONPort FOpen
PumpONRotating
Page 559 of 4770

80 CHASSISÐBRAKES
ABS & TRAC ECU
1) Wheel Speed Control
The ABS & TRAC ECU constantly receives signals from 4 speed sensors and calculates the speed of each wheel and
vehicle speed.
During sudden acceleration or driving on a slippery surface, if the drive wheels (front wheels) start to slip, the
difference in speed between the drive wheels are slipping.
Then, the ABS & TRAC ECU executes the right and left independent control of the front wheel brakes, the engine
torque control through fuel cutoff, and shift timing control according to the extent of the slip.
TRAC operation processes are described below.
1. The vehicle speed is determined by way of the rear wheel speed. This speed is then compared to the speed of the
front wheels, which are the drive wheels, to determine the slip condition of the drive wheels (front wheels).
2. The target control speed for the drive wheels is set based on the estimated vehicle speed.
3. If the speed of the front wheels, which are the drive wheels, exceeds the control starting speed, the ABS & TRAC
ECU determines that a slip has occurred and cuts off fuel according to the number of cylinders. By executing
engine torque control and brake control in this manner, the system regulates the speed
so that front wheels attain the target control speed. In addition, the system executes control to
prohibit the shifting of the automatic transaxle at this
time.
4. TRAC control ends when the drive wheels move to non±slippery surface or when the driver releases the
accelerator pedal.
Page 563 of 4770
88CHASSISÐSTEERING
2. Energy Absorbing Mechanism
Construction
The energy absorbing mechanism of the steering
column consists of a lower bracket, breakaway
bracket, and energy absorbing plate.
The breakaway bracket is attached to the instrument
panel reinforcement vial the capsule and energy
absorbing plate.
The steering column and the steering gear box are
connected with an elastic intermediate shaft.
Operation
The collision is transmitted to the steering wheel, and the lower bracket and the breakaway breacket will become
detached from each other, thus moving the entire unit forward. At the same time, the energy absorbingt plate becomes
deformed to absorb the energy of the impact.
�Energy Absorbing Plate�
Page 570 of 4770
95 BODYÐRUST±RESISTANT BODY
� WAX AND SEALER
Wax and sealer are applied to the hemmed portions fo the hood, door panels and luggage compartment door to
improve rust±resistant performance.
� UNDER COAT
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) coating is applied to the under side of the body. Athick coating to improve rust resistant
performane is applied to the bottome side of the cowl panel, the fender apron and other parts which are subject to
damage by flying stones, etc.
� ANTI±CHIPPING APPLICATION
Anti±chipping paint and PVC chipping primer are applied to the lower door panel area, front and rear wheel arches
and the rocker panel area to protect them from flying stones. In addition, soft±chip primer is applied to the hood.
Page 571 of 4770
96BODYÐLOW VIBRATION, LOW NOISE BODY
LOW VIBRATION, LOW NOISE BODY
Effective application of vibration damping and noide suppressant materials reduces engine and road noise.
� SOUND ABSORBING AND VIBRATION DAMPING MATERIALS
�Sandwich panels are ussed in the dash panel, cowl panel, front floor panel and rear wheel housings.
�Resin binding asphalt sheet and foamed asphalt sheet are optimally allocated to reduce engine and road noise for
quieter vehicle operation.
�Foamed material is applied onto the roof panel and pillars to reduce wind noise.
�Resin Binding Asphalt Sheet and Foamed Asphalt Sheet�
�Foamed Sponge Rubber�
Page 586 of 4770
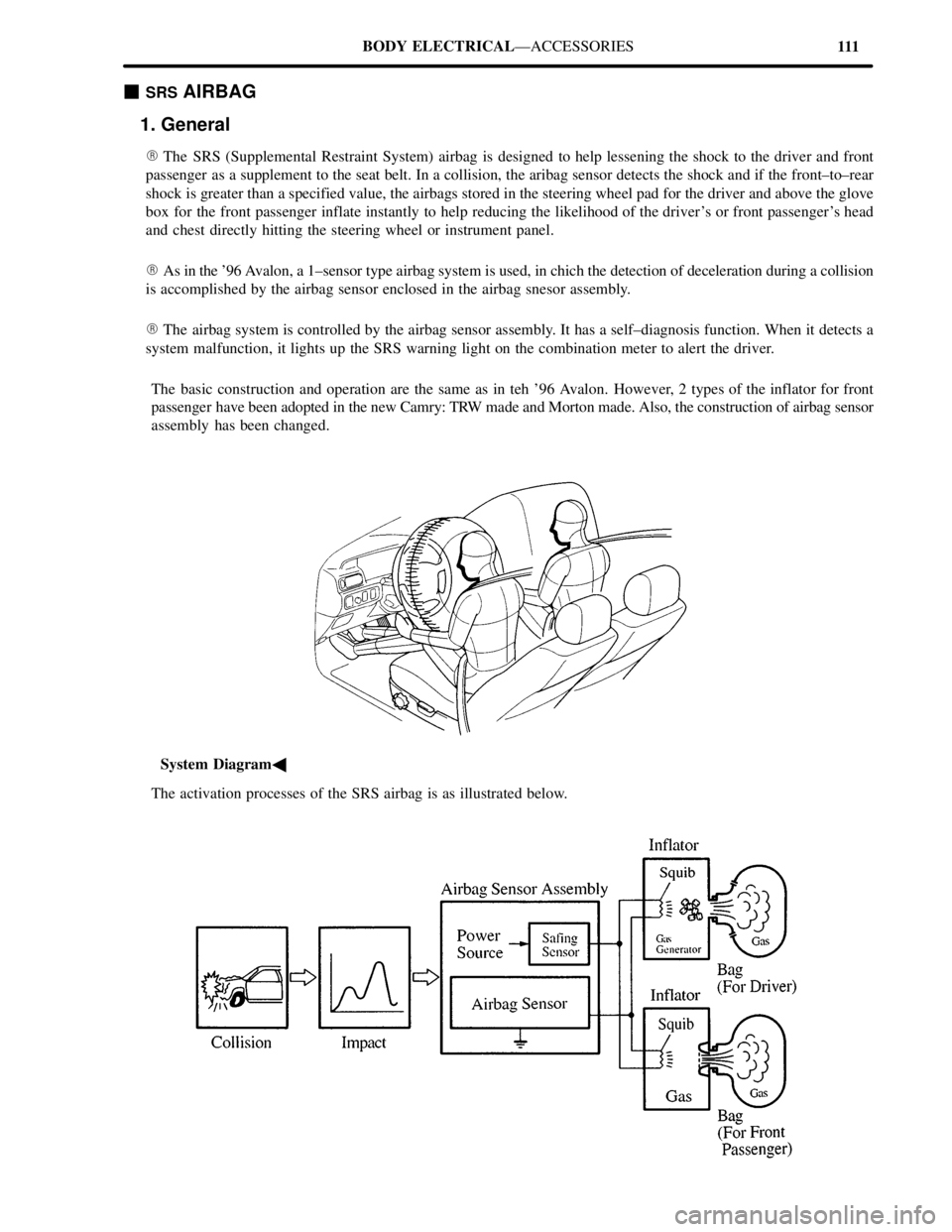
111 BODY ELECTRICALÐACCESSORIES
� SRS AIRBAG
1. General
�The SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) airbag is designed to help lessening the shock to the driver and front
passenger as a supplement to the seat belt. In a collision, the aribag sensor detects the shock and if the front±to±rear
shock is greater than a specified value, the airbags stored in the steering wheel pad for the driver and above the glove
box for the front passenger inflate instantly to help reducing the likelihood of the driver's or front passenger's head
and chest directly hitting the steering wheel or instrument panel.
�As in the '96 Avalon, a 1±sensor type airbag system is used, in chich the detection of deceleration during a collision
is accomplished by the airbag sensor enclosed in the airbag snesor assembly.
�The airbag system is controlled by the airbag sensor assembly. It has a self±diagnosis function. When it detects a
system malfunction, it lights up the SRS warning light on the combination meter to alert the driver.
The basic construction and operation are the same as in teh '96 Avalon. However, 2 types of the inflator for front
passenger have been adopted in the new Camry: TRW made and Morton made. Also, the construction of airbag sensor
assembly has been changed.
�System Diagram�
The activation processes of the SRS airbag is as illustrated below.