Page 377 of 4770

MATRIX CHART OF PROBLEM SYMPTOMS
When the malfunction code is not confirmed in the diagnostic trouble code check and the problem still can
not be confirmed in the basic inspection, then proceed to this step and perform troubleshooting according
to the numbered order given in the table below.
*: Except California specification vehicles.
Park/Neutral position switch circuitManifold absolute pressure sensor circuit
VSV circuit for fuel pressure control
Ignition signal circuit (Spark test)
After acceleration pedal depressed
After acceleration pedal released
Switch condition signal circuit
Muffler explosion (after fire)No initial combustion
Back up power source circuit
Hesitation/Poor accelerationNo complete combustion
ECM power source circuit
Starter and Starter relay
Engine control module
High engine idle speed
Low engine idle speedUnder normal condition
During A/C operationEngine does not crank
A/C cut control circuit Starter signal circuit
Soon after starting
Fuel system circuit
When N to D shiftIncorrect first idle
Poor
Driveability
IAC valve circuit Difficult to
start
Injector circuit
Rough idling
Does not
start
Compression
Suspect area
Cold engine
Ignition coil Engine Stall
EG R system
Hot engine
Poor Idling
Spark plug
A/T faultylG±10,30*
IG±11,30 Distributor
Symptom
ST±19,21
See page
IG±8,28* IG±6,26*
Hunting
Surging
EG1±400
EG1±410 EG1±390
EG1±403
EG1±408
EG1±415
EG1±419EG1±383EG1±372
EG1±428EG1±396
EG1 ±424
AX1±68 EG1±23
IN±36
± 5S±FE ENGINEMATRIX CHART OF PROBLEM SYMPTOMSEG1±327
Page 433 of 4770

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the engine is cranked, the intake air flow is slow, so fuel vaporization is poor. A rich mixture
is therefore necessary in order to achieve good startability. While the engine is being cranked, the
battery positive voltage is applied to terminal STA of the ECM. The starter signal is mainly used to
increase the fuel injection volume for the starting injection control and after±start injection control.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
HINT: This diagnostic chart is based on the premise that the engine is cranked normally. If the
engine is not cranked, proceed to the matrix chart of problem symptoms on page EG1±327, w
Open or short in starter signal circuit.
wOpen or short in ignition switch or starter
relay circuit.
wECM
Check for open in harness and connector
between ECM and relay.Proceed to next circuit inspection
shown on matrix chart (See page
E±G±327). Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition
Repair or replace harness or
connector.
WIRING DIAGRAM
No starter signal to ECM.
Check and replace ECM.Check for the test mode.Trouble Area
DTC 43 Starter Signal Circuit
DTC No.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±383
Page 434 of 4770
Setting the test mode.
(1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
(2) Connect terminals TE2 and E1 of DLC2.
(3) Turn ignition switch ON.
(Don't start the engine)
(4) Connect terminals TE1 and E1 of DLC2.
Check for open in harness and connector between engine control
module and starter relay (See page IN±31). Check output condition of diagnostic trouble code 43.
Proceed to next circuit inspection shown on
matrix chart (See page EG1±327).
Check and replace engine control module.Repair or replace harness or connector.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Check if code ª43º is output by the malfunc-
tion indicator lamp.
Code ª43º is output.
Start the engine.
Check if the code ª43º disappear.
Code ª43º is not output.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±384
Page 442 of 4770
Check for open and short in harness and
connector between EFI main relay and ECM.
Check for open in harness and connector
between EGR gas temp. sensor and ECM. Check voltage of VSV for EGR Power source.
Repair or replace harness or
connector.
Repair or replace harness or
connector. Check resistance of EGR gas temp. sensor. Check EGR system (See page EG1±153) .
WIRING DIAGRAM
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Check resistance of VSV for EG R.
Replace EGR gas temp. sensor.
Check and replace ECM.Check and replace ECM.Replace VSV for EG R.
Repair EGR system.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±392
Page 444 of 4770
Remove VSV for EGR. (See page EG1±154, 155*).
Measure resistance between terminals of VSV for
EG R.
Check for open and short in harness and connector between EFI
main relay and VSV for EGR, VSV and engine control module. (See page IN±31). Check resistance between terminals of VSV for EGR.
Check EGR system (See page EG1±153).
Check and replace engine control module.Repair or replace harness or connector. Replace VSV for EGR.
Repair EGR system. Resistance: 33 ± 39� (Cold)
*: Except California specification vehicle.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±394
Page 450 of 4770
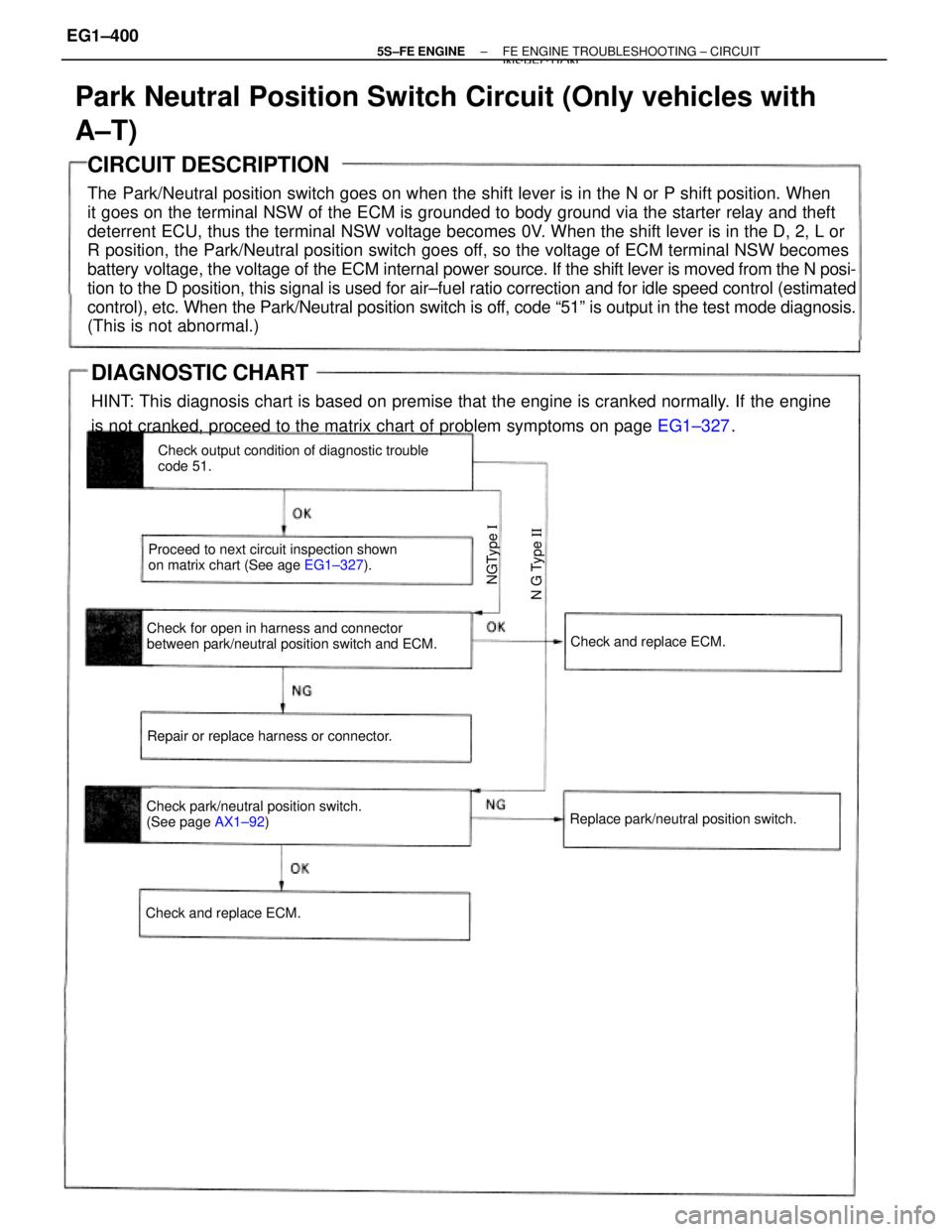
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The Park/Neutral position switch goes on when the shift lever is in the N or P shift position. When
it goes on the terminal NSW of the ECM is grounded to body ground via the starter relay and theft
deterrent ECU, thus the terminal NSW voltage becomes 0V. When the shift lever is in the D, 2, L or
R position, the Park/Neutral position switch goes off, so the voltage of ECM terminal NSW becomes
battery voltage, the voltage of the ECM internal power source. If the shift lever is moved from the N posi-
tion to the D position, this signal is used for air±fuel ratio correction and for idle speed control (estimated
control), etc. When the Park/Neutral position switch is off, code ª51º is output in the test mode diagnosis.
(This is not abnormal.)
Park Neutral Position Switch Circuit (Only vehicles with
A±T)
Check for open in harness and connector
between park/neutral position switch and ECM.Check output condition of diagnostic trouble
code 51.
Proceed to next circuit inspection shown
on matrix chart (See age EG1±327).
Check park/neutral position switch.
(See page AX1±92) Repair or replace harness or connector.
Replace park/neutral position switch.Check and replace ECM.
Check and replace ECM.
N G Type II NGType I
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
HINT: This diagnosis chart is based on premise that the engine is cranked normally. If the engine
is not cranked, proceed to the matrix chart of problem symptoms on page EG1±327.
± 5S±FE ENGINEFE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING ± CIRCUITINSPECTION
EG1±400
Page 453 of 4770
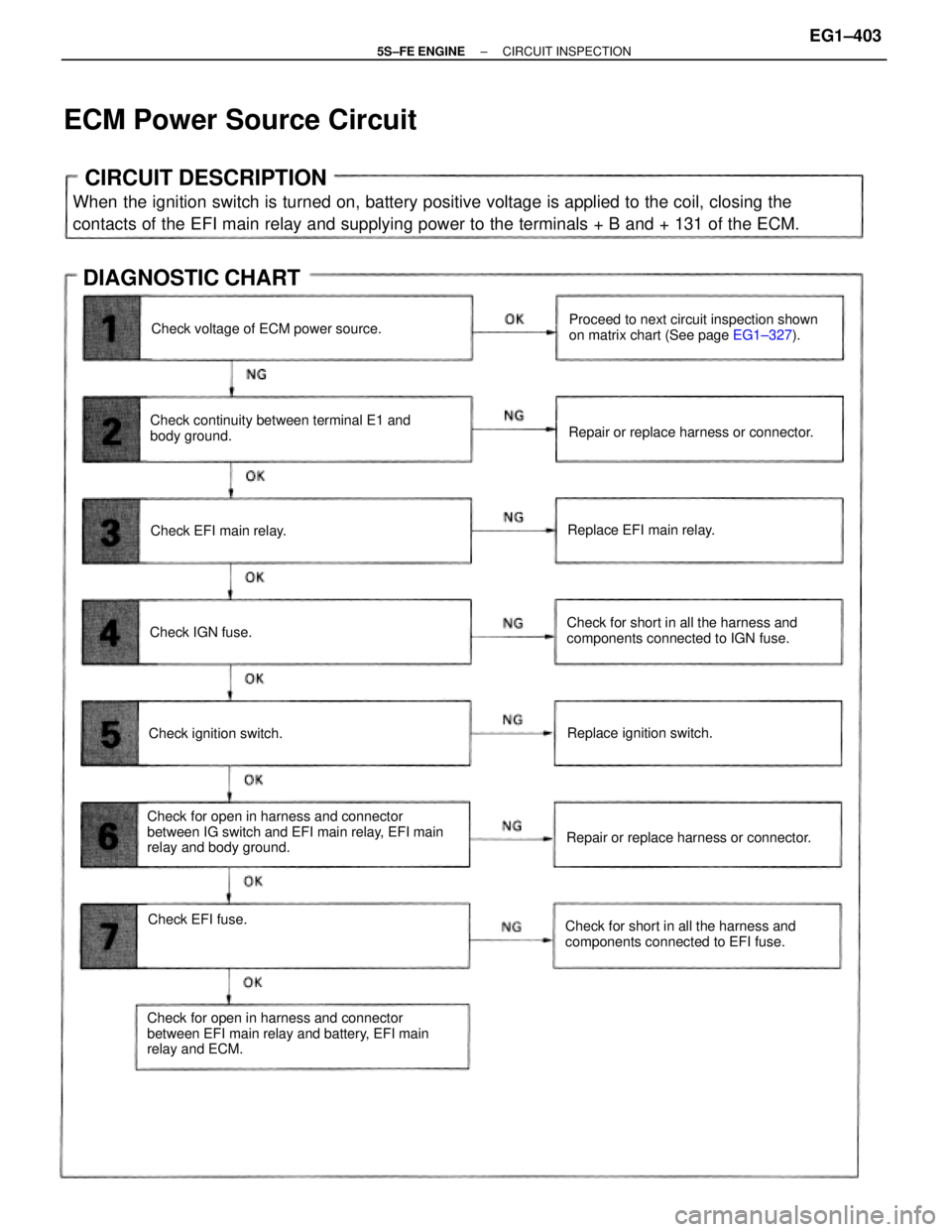
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the ignition switch is turned on, battery positive voltage is applied to the coil, closing the
contacts of the EFI main relay and supplying power to the terminals + B and + 131 of the ECM.
Check for open in harness and connector
between IG switch and EFI main relay, EFI main
relay and body ground.
Check for open in harness and connector
between EFI main relay and battery, EFI main
relay and ECM.Check continuity between terminal E1 and
body ground.Proceed to next circuit inspection shown
on matrix chart (See page EG1±327).
Check for short in all the harness and
components connected to IGN fuse.
Check for short in all the harness and
components connected to EFI fuse.
ECM Power Source Circuit
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Repair or replace harness or connector. Check voltage of ECM power source.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Replace ignition switch.
Check EFI fuse.Replace EFI main relay.
Check ignition switch.Check EFI main relay.
Check IGN fuse.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±403
Page 456 of 4770
Remove EFI main relay from J/B No±2.
Check continuity between terminals of EFI main
relay shown below.
Remove IGN fuse from J/B No.1.
Check continuity of IGN fuse.(1) Apply battery voltage between terminals 1
and 2.
(2) Check continuity between terminals 3 and 5.
Check for short in all the harness and
components connected to IGN fuse (See
attached wiring diagram).
Check EFI main relay.
Continuity
(Reference value 72�)
Replace EFI main relay.
Check IGN fuse.
Terminals 3 and 5
Terminals 1 and 2
Terminals 3 and 5 ContinuityOpen
Continuity
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±406