Page 278 of 4770
A/C IDLE± UP VALVE INSPECTION
1. REMOVE IDLE±UP VALVE
(a) Disconnect the following connector and hoses:
(1) Idle±up valve connector
(2) Air hose from air intake chamber
(3) Air hose from air tube
(b) Remove the 2 bolts and idle±up valve together with
the 2 air hoses.
(c) Disconnect the 2 air hoses from the idle±up valve.
2. INSPECT IDLE±UP VALVE
A. Inspect idle±up valve for open circuit
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is continuity
between the terminals.
Resistance (Cold):
30±34�
If there is no continuity, replace the idle±up valve.
B. Inspect idle±up valve for ground
Using an ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity
between each terminal and the body.
If there is continuity, replace the idle±up valve.
A±C IDLE±UP VALVE
± 5S±FE ENGINEMFI/SFI SYSTEMEG1±228
Page 279 of 4770
(b) Apply battery voltage across the terminals.
(c) Check that air flows from port E to port F.
If operation is not as specified, replace the idle±up
valve. C. Inspect idle±up valve operation
(a) Check that air does not flow from port E to port F.
3. REINSTALL IDLE± UP VALVE
± 5S±FE ENGINEMFI/SFI SYSTEMEG1±229
Page 281 of 4770
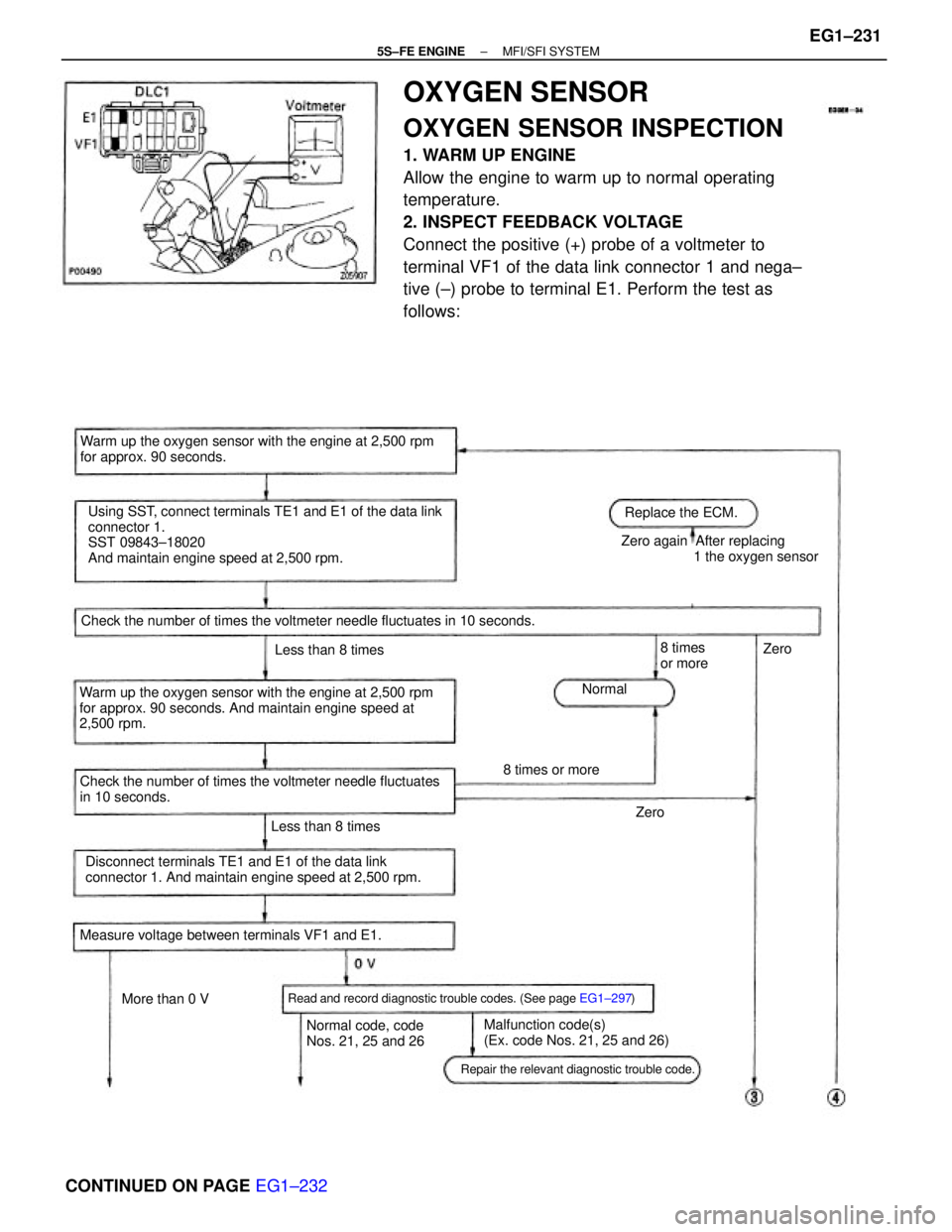
OXYGEN SENSOR
OXYGEN SENSOR INSPECTION
1. WARM UP ENGINE
Allow the engine to warm up to normal operating
temperature.
2. INSPECT FEEDBACK VOLTAGE
Connect the positive (+) probe of a voltmeter to
terminal VF1 of the data link connector 1 and nega±
tive (±) probe to terminal E1. Perform the test as
follows:
Using SST, connect terminals TE1 and E1 of the data link
connector 1.
SST 09843±18020
And maintain engine speed at 2,500 rpm.
Warm up the oxygen sensor with the engine at 2,500 rpm
for approx. 90 seconds. And maintain engine speed at
2,500 rpm.Warm up the oxygen sensor with the engine at 2,500 rpm
for approx. 90 seconds.
CONTINUED ON PAGE EG1±232
Disconnect terminals TE1 and E1 of the data link
connector 1. And maintain engine speed at 2,500 rpm. Check the number of times the voltmeter needle fluctuates
in 10 seconds.Zero again After replacing
1 the oxygen sensor
Check the number of times the voltmeter needle fluctuates in 10 seconds.
Read and record diagnostic trouble codes. (See page EG1±297)
Malfunction code(s)
(Ex. code Nos. 21, 25 and 26) Measure voltage between terminals VF1 and E1.
Repair the relevant diagnostic trouble code.
Normal code, code
Nos. 21, 25 and 26Replace the ECM.
Less than 8 timesLess than 8 times
8 times or more
More than 0 V8 times
or more
NormalZero
Zero
± 5S±FE ENGINEMFI/SFI SYSTEMEG1±231
Page 283 of 4770
SUB OXYGEN SENSOR
SUB OXYGEN SENSOR INSPECTION
INSPECT SUB OXYGEN SENSOR
HINT: Inspect only when code No. 27 is displayed.
(a) Cancel the diagnostic trouble code. (See page EG1±299)
(b) Warm up the engine until it reaches normal operating
temperature.
(c) M/T:
Drive for 5 minutes or more at a speed less than 80
km/h (50 mph) in 4th or 5th gear.
A/T:
Drive for 5 minutes or more at a speed less than 80
km/h (50 mph) in ªDº position.
(d) Following the conditions in step (c), fully depress on
the accelerator pedal for 2 seconds or more.
(e) Stop the vehicle and turn the ignition switch OFF.
(f) Carry out steps (b), (c) and (d) again to test accelera±
tion. If code No.27 appears again, check the sub oxygen
sensor circuit. If the circuit is normal, replace the sub
oxygen sensor.
± 5S±FE ENGINEMFI/SFI SYSTEMEG1±233
Page 285 of 4770
2. CONNECT TACHOMETER TO ENGINE
Connect the test probe of a tachometer to terminal IG
(±) of the data link connector 1.
NOTICE:
wNEVER allow the tachometer terminal to touch
ground as it could result in damage to the igniter
and/or ignition coil.
wAs some tachometers are not compatible with this
ignition system, we recommend that you confirm
the compatibility of yours before use.
3. INSPECT FUEL CUT RPM
(a) Increase the engine speed to at least 2,500 rpm.
(b) Use a sound scope to check for injector operating
noise.
(c) Check that when the throttle lever is released, injector
operation noise stops momentarily and then resumes.
HINT: Measure with the A/C OFF.
Fuel return speed:
1,500 rpm
4. DISCONNECT TACHOMETER
FUEL CUT RPM
FUEL CUT RPM INSPECTION
1. WARM UP ENGINE
Allow the engine to warm up to normal operating
temperature.
± 5S±FE ENGINEMFI/SFI SYSTEMEG1±235
Page 289 of 4770

RADIATOR
The radiator performs the function of cooling the coolant which has passed through the water
jacket and become hot, and it is mounted in the front of the vehicle. The radiator consists of an
upper tank and lower tank, and a core which connects the two tanks. The upper tank contains the
inlet for coolant from the water jacket and the filler inlet. It also has a hose attached through
which excess coolant or steam can flow. The lower tank has an outlet and drain cock for the
coolant. The core contains many tubes through which coolant flows from the upper tank to the
lower tank as well as to cooling fins which radiate heat away from the coolant in the tubes. The
air sucked through the radiator by the electric fan, as well as the wind generated by the vehicle's
travel, passes through the radiator, cooling the coolant. Models with automatic transmission
include an automatic transmission fluid cooler built into the lower tank of the radiator. A fan with
an electric motor is mounted behind the radiator to assist the flow of air through the radiator. The
fan operates when the engine coolant temperature becomes high in order to prevent it from be-
coming too high.
RADIATOR CAP
The radiator cap is a pressure type cap which seals the radiator, resulting in pressurization of the
radiator as the coolant expands. The pressurization prevents the coolant from boiling even when
the engine coolant temperature exceeds 100°C (212°F). A relief valve (pressurization valve) and a
vacuum valve (negative pressure valve) are built into the radiator cap. The relief valve opens and
lets steam escape through the overflow pipe when the pressure generated inside the cooling sys-
tem exceeds the limit (coolant temperature: 110±120°C (230±248°F), pressure; 58.8103.0 kpa
(0.6±1.05 kgf/cm
2, 8.5±14.9 psi). The vacuum valve opens to alleviate the vacuum which develops
in the cooling system after the engine is stopped and the engine coolant temperature drops. The
valve's opening allows the coolant in the reservoir tank to return to the cooling system.
RESERVOIR TANK
The reservoir tank is used to catch coolant which overflows from the cooling system as a result
of volumetric expansion when the coolant is heated. The coolant in the reservoir tank returns to
the radiator when the coolant temperature drops, thus keeping the radiator full at all times and
avoiding needless coolant loss.
Check the reservoir tank level to learn if the coolant needs to be replenished.
WATER PUMP
The water pump is used for forced circulation of coolant through the cooling system. It is
mounted on the front of the cylinder block and driven by a timing belt.
THERMOSTAT
The thermostat has a wax type bypass valve and is mounted in the water inlet housing. The
thermostat includes a type of automatic valve operated by fluctuations in the engine coolant
temperature. This valve closes when the engine coolant temperature drops, preventing the
circulation of coolant through the engine and thus permitting the engine to warm up rapidly. The
valve opens when the engine coolant temperature has risen, allowing the circulation of coolant.
Wax inside the thermostat expands when heated and contracts when cooled. Heating the wax
thus generates pressure which overpowers the force of the spring which keeps the valve closed,
thus opening the valve. When the wax cools, its contraction allows the force of the spring to take
effect once more, closing the valve. The thermostat in this engine operates at a temperature of
82�C (180�F).
± 5S±FE ENGINECOOLING SYSTEMEG1±239
Page 291 of 4770

2. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT QUALITY
There should not be any excessive deposits of rust or
scales around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole,
and the engine coolant should be free from oil.
If excessively dirty, replace the engine coolant.
3. REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Remove the radiator cap.
CAUTION: To avoid the danger of being burned, do not
remove It while the engine and radiator are still hot, as
fluid and steam can be blown out under pressure.
(b) Drain the engine coolant from the radiator drain cock
and engine drain plug. (Engine drain plug at the right
rear of cylinder block.)
(c) Close the drain cock and plug.
Torque (Engine drain plug):
13 N±m (130 kgf±cm, 9 ft±lbf)
(d) Slowly fill the system with coolant.
Use a good brand of ethylene±glycol base
coolant and mix it according to the
manufacturer 's directions.
Using engine coolant which includes more than
5096 ethylene±glycol (but not more than 7096) is
recommended.
NOTICE:
wDo not use a alcohol type coolant.
wThe engine coolant should be mixed with demineral±
ized water or distilled water.
Capacity (w/ Heater):
8.3 liters (6.7 US qts, 5.5 Imp.qts)
(a) Reinstall the radiator cap.
(f) Warm up the engine and check for leaks.
(g) Recheck the engine coolant level and refill as neces±
sary.
COOLANT CHECK AND
REPLACEMENT
1. CHECK ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL AT RESERVOIR
TANK
The engine coolant level should be between the
ºLOWº and ªFULLº lines.
If low, check for leaks and add engine coolant up to
the ªFULLº line.
± 5S±FE ENGINECOOLING SYSTEMEG1±241
Page 294 of 4770
(See Components for Removal and Installation)
1. INSTALL THERMOSTAT AND WATER INLET TO
WATER PUMP COVER
(a) Install a new gasket to the thermostat.
(b) Align the jiggle valve of the thermostat with the upper
side of the stud bolt, and insert the thermostat in the
water pump.
HINT: The jiggle valve may be set within 5� of either
side of the prescribed position. 10. REMOVE WATER INLET AND THERMOSTAT FROM
WATER PUMP COVER
(a) Remove the 2 nuts and water inlet from the water
pump.
(b) Remove the thermostat.
(c) Remove the gasket from the thermostat.
WATER PUMP INSPECTION
INSPECT WATER PUMP
Turn the pulley and check that the water pump bear±
ing moves smoothly and quietly.
(c) Install the water inlet with the 2 nuts.
Torque: 8.8 N±m (90 kgf±cm. 78 in.±lbf)
WATER PUMP INSTALLATION
± 5S±FE ENGINECOOLING SYSTEMEG1±244