Page 370 of 4770
ECM (California specification vehicles and except California specification vehicles with A/T)
*�: Only for California specification vehicles.
*�: Except California specification vehicles with A/T.wManifold absolute pressure sensor
wThrottle position sensor
TERMINAL OF ECM (Cont'd)
Manifold absolute pressure sensor VSV for fuel pressure control
Engine coolant temp. sensor No.2 and No.4 injectors
No.1 and No.3 injectors
Intake air temp. sensor VSV for A/C Idle up
Main oxygen sensor Sub oxygen sensor A/T No.1 solenoid
A/T No,2 solenoid Terminal
No.*�
A/T SL solenoid
Power ground
Power ground No.2 injector
No.1 injectorNo.4 injector
No.3 injector
ECM groundVSV for EG RConnection Connection
DistributorDistributor
Distributor Distributor
IAC valve IAC valveSymbol Symbol
Igniter IgniterTerminal
No.*�
± 5S±FE ENGINETERMINALS OF ECMEG1±320
Page 371 of 4770
*�: Only for California specification vehicles.
*�: Except California specification vehicles with A/T.wStoplight switch
w Stoplight
w Park/neutral position switch wDefogger relay
wTaillight relay
Park/neutral position switchPark/neutral position switch
Park/neutral position switch
Malfunction indicator lampData link connector 1 and 2 Data link connector 1 and 2No.1 vehicle speed sensor
Throttle position sensor
Throttle position sensorEGR gas temp. sensor
Circuit opening relay Data link connector 1Data link connector 2
Cruise control ECUO/D main switch Terminal
No.Terminal
No.Connection
A/C amplifier
EFI main relay Sensor ground
Sensor ground
A/C amplifierEFI main relay
Knock sensorStarter relay Connection Symbol
Symbol
Battery
± 5S±FE ENGINETERMINALS OF ECMEG1±321
Page 376 of 4770

REFERENCE VALUE OF ECM DATA
*1: If the engine coolant temp, sensor circuit is open or shorted, the ECM assumes an engine coolant temp, value of 80�C (176�F).
*2: When feedback control is forbidden, 0 V is displayed,
*3: A/T only.Closed throttle position
Wide open throttle
From closed throttle position to wide open throttle
When shifting from ªPº or ªNº position into a position
other than ªPº or ªNºEngine idling at normal operating temp.
increase engine loadEngine cold to hot
Engine idling at normal operating temp.
RPM stable at 2,500 rpm with normal operating temp.
PRM stable at 2,500 rpm with normal operating temp.RPM kept stable (Comparison with tachometer)
During driving (Comparison with speedometer)Below 5�
Above 70�
Gradually increases Approx. 180 ~ 280 mm Hg
Gradually increases
Engine idling at normal operating temp.Engine idling at normal operating temp.Gradually decreases
Approx. 2 ~ 5 msecs
REFERENCE VALUE
Engine at normal operating temp. 75 ± 95�C (185 ± 203�F) *1
Closed throttle position
RICH LEAN is repeated Increase engine speed
No large differences Inspection condition
Gradually increases
No great changes
2.50+ 1.25 V *2
During cranking
PNP SIGNAL *3A/C switch ON ENGINE SPEEDReference value
TARGET A/F LVEHICLE SPD
A/F FB LEFT
A/C SIGNALSTA SIGNAL
CTP SIGNAL30~60% INJECTOR
THROTTLEIAC DUTYIGNITION
G EAR MAPItem
OxLECT
HINT: ECM data can be monitored by TOYOTA hand±held
tester.
1. Hook up the TOYOTA hand±held tester to the DLC2.
2. Monitor ECM data by following the prompts on the tester
screen.
Please refer to the TOYOTA hand±held tester operator's
manual for further details.
± 5S±FE ENGINEREFERENCE VALUE OF ECM DATAEG1±326
Page 377 of 4770

MATRIX CHART OF PROBLEM SYMPTOMS
When the malfunction code is not confirmed in the diagnostic trouble code check and the problem still can
not be confirmed in the basic inspection, then proceed to this step and perform troubleshooting according
to the numbered order given in the table below.
*: Except California specification vehicles.
Park/Neutral position switch circuitManifold absolute pressure sensor circuit
VSV circuit for fuel pressure control
Ignition signal circuit (Spark test)
After acceleration pedal depressed
After acceleration pedal released
Switch condition signal circuit
Muffler explosion (after fire)No initial combustion
Back up power source circuit
Hesitation/Poor accelerationNo complete combustion
ECM power source circuit
Starter and Starter relay
Engine control module
High engine idle speed
Low engine idle speedUnder normal condition
During A/C operationEngine does not crank
A/C cut control circuit Starter signal circuit
Soon after starting
Fuel system circuit
When N to D shiftIncorrect first idle
Poor
Driveability
IAC valve circuit Difficult to
start
Injector circuit
Rough idling
Does not
start
Compression
Suspect area
Cold engine
Ignition coil Engine Stall
EG R system
Hot engine
Poor Idling
Spark plug
A/T faultylG±10,30*
IG±11,30 Distributor
Symptom
ST±19,21
See page
IG±8,28* IG±6,26*
Hunting
Surging
EG1±400
EG1±410 EG1±390
EG1±403
EG1±408
EG1±415
EG1±419EG1±383EG1±372
EG1±428EG1±396
EG1 ±424
AX1±68 EG1±23
IN±36
± 5S±FE ENGINEMATRIX CHART OF PROBLEM SYMPTOMSEG1±327
Page 402 of 4770

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
To obtain a high purification rate for the C0, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, a three±
way catalytic converter is used, but for most efficient use of the three±way catalytic converter, the
air±fuel ratio must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air±fuel ra-
tio. The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the
vicinity of the stoichiometric air±fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to detect the oxygen con-
centration in the exhaust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air±fuel ratio.
When the air±fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust increases and the
oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force; 0 V).
When the air±fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air±fuel ratio the oxygen concentration in
the exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (large
electromotive force: 1 V). The ECM judges by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor
whether the air±fuel ratio is RICH or LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if
malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECM is un-
able to perform accurate air±fuel ratio control.
Main oxygen sensor signal voltage is reduced to
between 0.35 V and 0.70 V for 60 sec. under
conditions (a) ± (d).
(2 trip detection logic) *
(a) Engine coolant temp. : 80�C (176�F) or more.
(b) Engine speed : 1,500 rpm or more.
(c) Load driving (EX. A/T in overdrive (5th for
M/T), A/C ON, Flat road, 50 mph (80km/h)).
(d) Main oxygen sensor signal voltage :
Alternating above and below 0.45 V.Diagnostic Trouble Code Detecting Condition
wMain oxygen sensor circuit.
wMain oxygen sensor.
*See page EG1±307Trouble Area
DTC 21 Main Oxygen Sensor Circuit
DTC No.
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±352
Page 403 of 4770
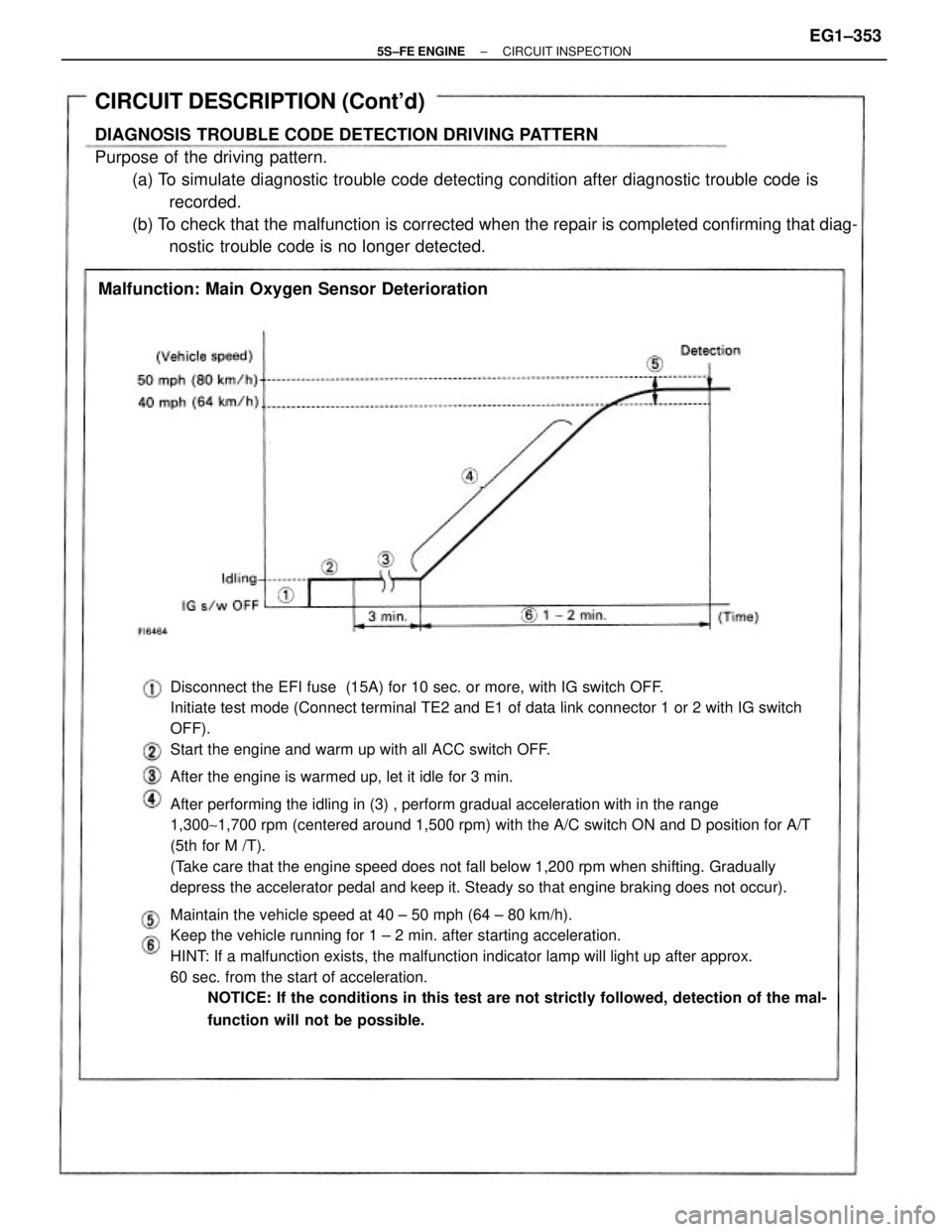
Disconnect the EFI fuse (15A) for 10 sec. or more, with IG switch OFF.
Initiate test mode (Connect terminal TE2 and E1 of data link connector 1 or 2 with IG switch
OFF).
Start the engine and warm up with all ACC switch OFF.
After the engine is warmed up, let it idle for 3 min.
After performing the idling in (3) , perform gradual acceleration with in the range
1,300~1,700 rpm (centered around 1,500 rpm) with the A/C switch ON and D position for A/T
(5th for M /T).
(Take care that the engine speed does not fall below 1,200 rpm when shifting. Gradually
depress the accelerator pedal and keep it. Steady so that engine braking does not occur).
Maintain the vehicle speed at 40 ± 50 mph (64 ± 80 km/h).
Keep the vehicle running for 1 ± 2 min. after starting acceleration.
HINT: If a malfunction exists, the malfunction indicator lamp will light up after approx.
60 sec. from the start of acceleration.
NOTICE: If the conditions in this test are not strictly followed, detection of the mal-
function will not be possible.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION (Cont'd)
DIAGNOSIS TROUBLE CODE DETECTION DRIVING PATTERN
Purpose of the driving pattern.
(a) To simulate diagnostic trouble code detecting condition after diagnostic trouble code is
recorded.
(b) To check that the malfunction is corrected when the repair is completed confirming that diag-
nostic trouble code is no longer detected.
Malfunction: Main Oxygen Sensor Deterioration
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±353
Page 404 of 4770
Are there any other codes (besides code 21)
being output ?Go to relevant diagnostic trouble code
chart.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
WIRING DIAGRAM
Replace main oxygen sensor.YES
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±354
Page 405 of 4770
wWith the engine racing (4,000 rpm) measure wave±
form between terminals OX1 and E1 of engine con±
trol module.
HINT: The correct waveform appears as shown in the
illustration on the left, oscillating between approx. 0.1 V
and 0.9 V.
If the oxygen sensor is deteriorated, the amplitude of
the voltage is reduced as shown on the left.
INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE Reference
± 5S±FE ENGINECIRCUIT INSPECTIONEG1±355