2000 DODGE NEON fuses
[x] Cancel search: fusesPage 435 of 1285
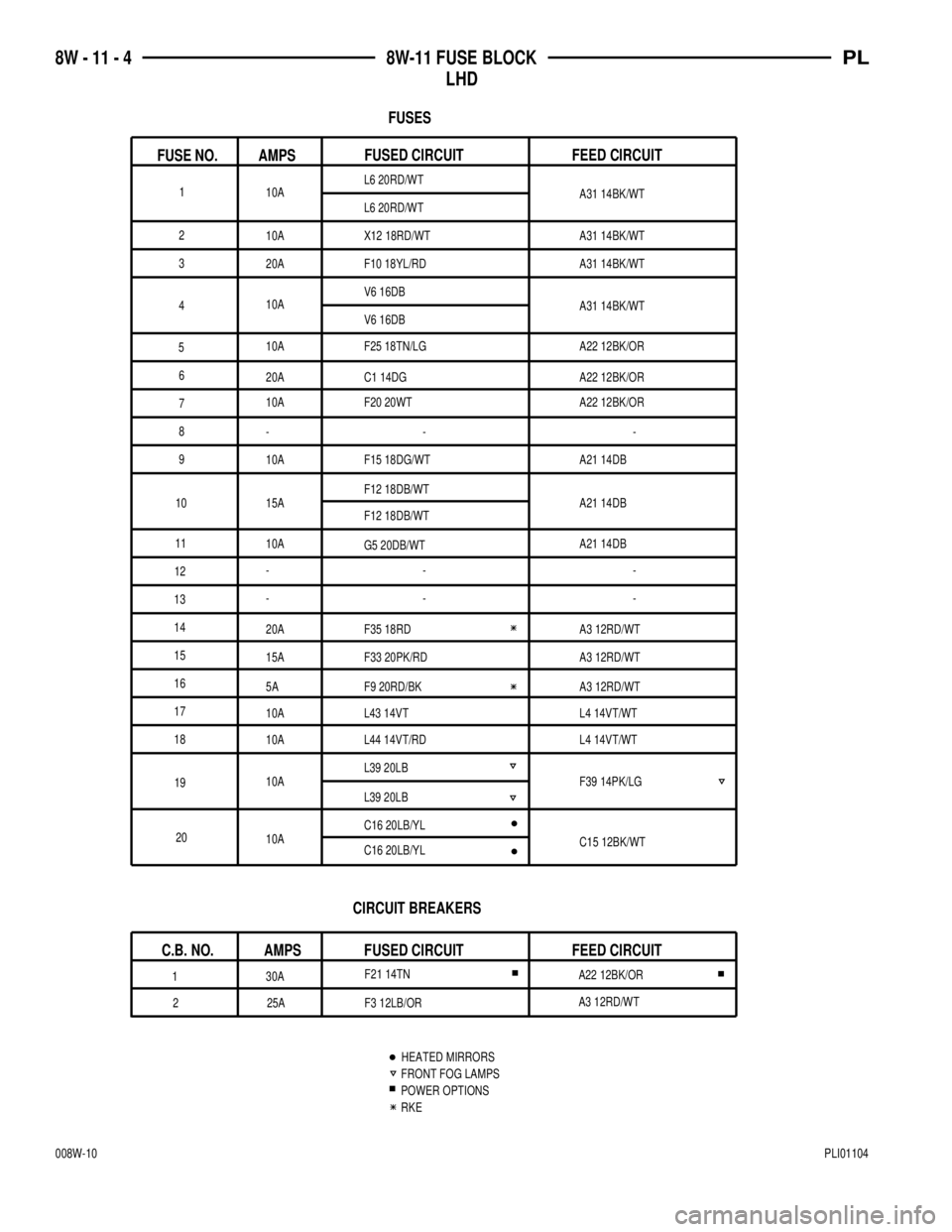
10A 15A 10A
L39 20LB F33 20PK/RD 15A 20A F35 18RD 10AF12 18DB/WT F20 20WT 10A 20A C1 14DG 20A F10 18YL/RDX12 18RD/WT L6 20RD/WT
10A
A31 14BK/WT
A31 14BK/WT
A31 14BK/WT
A22 12BK/OR
A22 12BK/OR
A21 14DB
A21 14DB
A3 12RD/WT
A3 12RD/WT
F39 14PK/LG G5 20DB/WT 10A A22 12BK/ORF25 18TN/LG
10A A21 14DBF15 18DG/WT
5A A3 12RD/WTF9 20RD/BK
10A L4 14VT/WTL44 14VT/RD 10A L4 14VT/WTL43 14VT
10A
C15 12BK/WT C16 20LB/YL
C16 20LB/YL L39 20LB F12 18DB/WT
A22 12BK/OR
A3 12RD/WT
25A F3 12LB/ORF21 14TN
30A
CIRCUIT BREAKERS
C.B. NO. AMPS FUSED CIRCUIT FEED CIRCUIT
RKE
FRONT FOG LAMPS
POWER OPTIONS
AMPS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
FUSE NO.
FUSES
- - -
-- -
FEED CIRCUIT FUSED CIRCUIT
10A
L6 20RD/WT
V6 16DB
V6 16DBA31 14BK/WT
HEATED MIRRORS -- -
1
2
8W - 11 - 4 8W-11 FUSE BLOCK
LHDPL
008W-10PLI01104
Page 436 of 1285
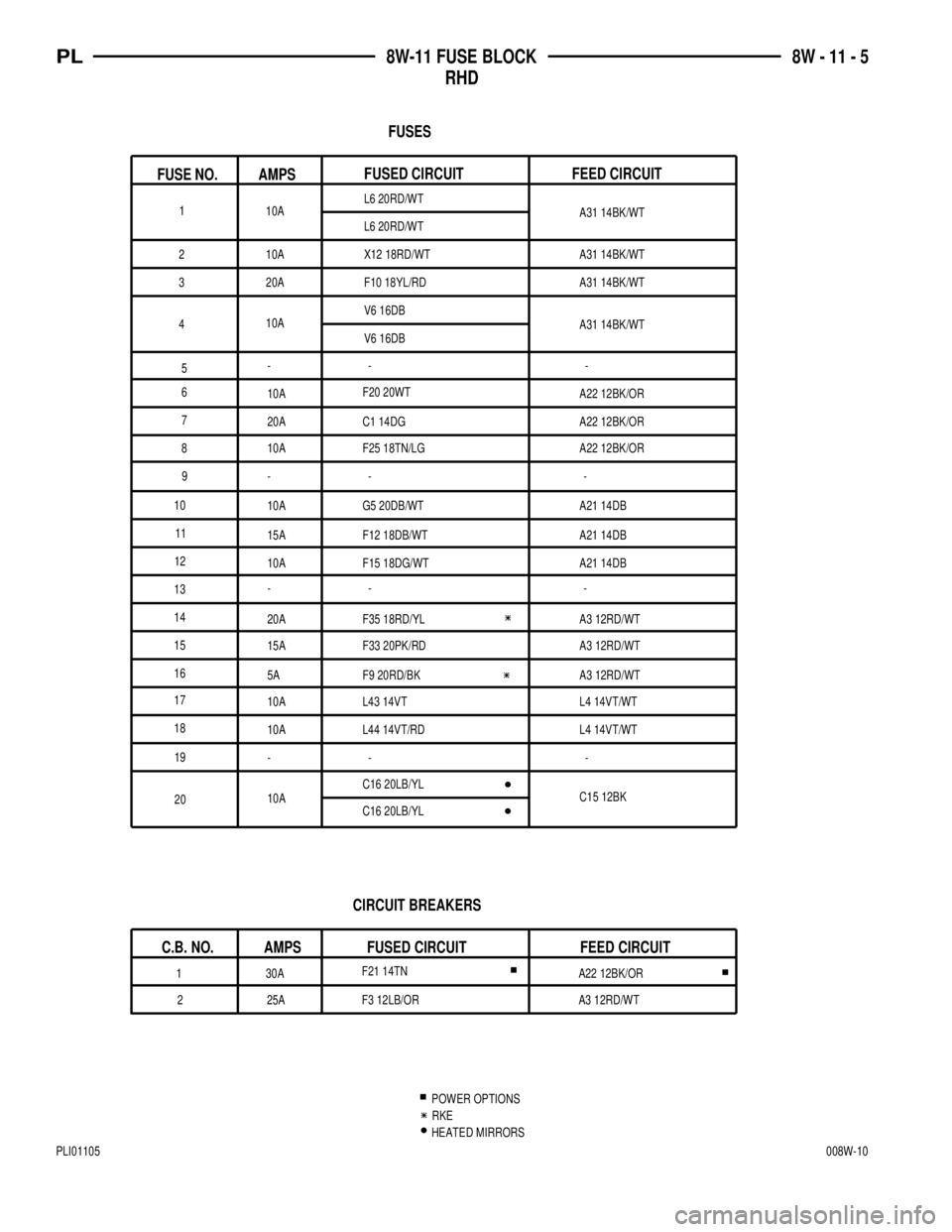
F33 20PK/RD 15A A3 12RD/WT
5A A3 12RD/WTF9 20RD/BK
A22 12BK/OR
A3 12RD/WT
25A F3 12LB/ORF21 14TN
30A
CIRCUIT BREAKERS
C.B. NO. AMPS FUSED CIRCUIT FEED CIRCUIT
HEATED MIRRORS
RKE
POWER OPTIONS
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
FUSES
G5 20DB/WT
20A F35 18RD/YLF15 18DG/WT 10A 10A F25 18TN/LGF20 20WT
10A A22 12BK/OR
A21 14DB
A3 12RD/WT 20A A22 12BK/ORC1 14DG
A22 12BK/OR
A21 14DB F12 18DB/WT 15A 10A A21 14DB
-- --- -- - -
10A L43 14VT L4 14VT/WT
L4 14VT/WT 10A L44 14VT/RD
C16 20LB/YL
10AC15 12BK
C16 20LB/YL
10A
20A F10 18YL/RDX12 18RD/WT L6 20RD/WT
10A
A31 14BK/WT
A31 14BK/WT
A31 14BK/WT
AMPS
1
2
3
4
FUSE NO.FEED CIRCUIT FUSED CIRCUIT
10A
L6 20RD/WT
V6 16DB
V6 16DBA31 14BK/WT
-- -
1
2
PL8W-11 FUSE BLOCK
RHD8W - 11 - 5
PLI01105008W-10
Page 496 of 1285
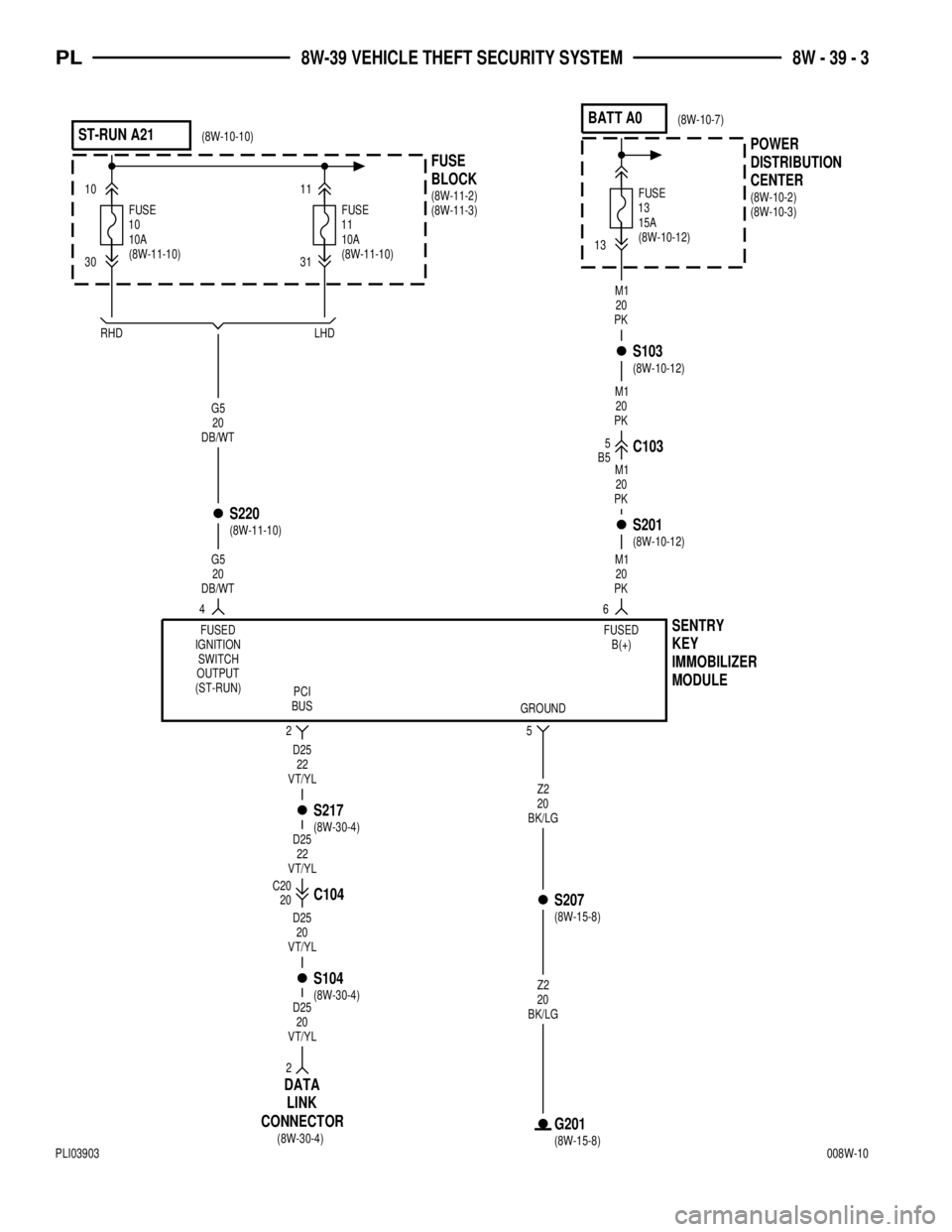
POWER
DISTRIBUTION
CENTER BLOCK FUSEST-RUN A21BATT A0
10A
FUSE
11
10A
FUSE
1013FUSE15A
30 10 11
3113
4
26
5
MODULE IMMOBILIZER
KEY
SENTRY
B5C1035
D25
20
VT/YL
D25
20
VT/YL
D25
22
VT/YL
D25
22
VT/YL
S217
C104
S104C20
20
2
CONNECTORLINK DATA
S207
G201
Z2
20
BK/LG
Z2
20
BK/LG
M1
20
PK
M1
20
PK
M1
20
PK
S220
S201 S103
G5
20
DB/WT
G5
20
DB/WT
LHD RHD
FUSED
IGNITION
SWITCH
OUTPUT
(ST-RUN)
PCI
BUS
GROUNDFUSED
B(+)
M1
20
PK
(8W-10-2)
(8W-10-3) (8W-11-2)
(8W-11-3) (8W-10-10)(8W-10-7)
(8W-11-10) (8W-11-10)(8W-10-12)
(8W-30-4)
(8W-30-4)
(8W-30-4)(8W-15-8)
(8W-15-8) (8W-11-10)
(8W-10-12) (8W-10-12)
PL8W-39 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM 8W - 39 - 3
PLI03903008W-10
Page 845 of 1285

²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C pressure transducer
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in response to MAP
sensor feedback.
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
If decel fuel shutoff is detected, downstream oxy-
gen sensor diagnostics is performed.WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to the Emission sec-
tion for On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
OPERATION
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information see On-Board Diagnostics.
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
The Power Distribution Center (PDC) is located
next to the battery (Fig. 1). The PDC contains the
starter relay, radiator fan relay, A/C compressor
clutch relay, auto shutdown relay, fuel pump relay
and several fuses.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various
engine and vehicle operations through devices that
are referred to as PCM Outputs.
PCM Inputs:
14 - 24 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1242 of 1285

BLOWER MOTOR VIBRATION AND/OR NOISE
DIAGNOSIS
The resistor block supplies the blower motor with
varied voltage (low and middle speeds) or battery
voltage (high speed).
CAUTION: Stay clear of the blower motor and resis-
tor block (Hot). Do not operate the blower motor
with the resistor block removed from the heater-A/C
housing.
Refer to the Blower Motor Vibration/Noise chart
for diagnosis.
COMPRESSOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS
Excessive noise while the A/C is being used, can be
caused by loose mounts, loose clutch, or high operat-
ing pressure. Verify compressor drive belt condition,
proper refrigerant charge and head pressure before
compressor repair is performed.
If the A/C drive belt slips at initial start-up, it does
not necessarily mean the compressor has failed.
With the close tolerances of a compressor it is pos-
sible to experience a temporary lockup. The longer
the A/C system is inactive, the more likely the condi-
tion to occur.
This condition is the result of normal refrigerant
movement within the A/C system caused by temper-
ature changes. The refrigerant movement may wash
the oil out of the compressor.
EVAPORATOR PROBE TEST
The work area and vehicle must be between 16É C
(60É F) and 32É C (90É F) when testing the switch.
(1) Disconnect the three wire connector from the
evaporator probe lead located behind the glove box
(Fig. 12).
(2) Start engine and set A/C to low blower motor
speed, panel, full cool, and RECIRC.
(3) Using a voltmeter, check for battery voltage
between Pin 1 and 2. If no voltage is detected, there
is no power to the switch. Check wiring and fuses.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit diag-
nosis.
(4) Using a voltmeter, check for battery voltage
between Pin 1 and Pin 3. If no voltage is detected,
there is no voltage from the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If voltage
is OK, connect a jumper wire between Pin 1 and Pin
3. The compressor clutch should engage. If the clutch
engages, remove the jumper wire immediately and go
to Step 5. If the compressor clutch does not engage,
check the operation of the clutch and repair as nec-
essary.(5) If compressor clutch engages, connect the evap-
orator probe 3-way connector. The compressor clutch
should engage or cycle depending on evaporator tem-
perature. If OK, go to Step 6. If not OK, replace the
clutch cycling switch.
(6) The engine running and the A/C set to:
²Blower motor on low speed
²Panel position
²Full cool
²RECIRC.
Close all doors and windows. Place a thermometer in
the center discharge vent.
(7) If the clutch does not begin to cycle off between
2É C to 7É C (35É F to 45É F), verify that the evapo-
rator probe is fully installed and not loose in evapo-
rator. If it is not properly installed, install probe and
retest outlet temperature. If the evaporator probe is
properly installed, replace the clutch cycling switch.
EXPANSION VALVE
NOTE: Expansion valve tests should be performed
after compressor tests.
Liquid CO2 is required to test the expansion
valve. It is available from most welding supply facil-
ities. CO2 is also available from companies which
service and sell fire extinguishers.
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in the
General Information section of this Group. The work
area and vehicle must be 21É to 27ÉC (70É to 85ÉF)
when testing expansion valve. To test the expansion
valve:
(1) Connect a charging station or manifold gauge
set to the refrigerant system service ports.
(2) Disconnect wire connector at low pressure cut-
off switch (Fig. 13). Using a jumper wire, jump ter-
minals inside wire connector boot.
(3) Close all doors, windows and vents to the pas-
senger compartment.
(4) Set Heater-A/C control to A/C, full heat, floor,
RECIRC. and high blower.
(5) Start the engine and hold the idle speed (1000
rpm). After the engine has reached running temper-
ature, allow the passenger compartment to heat up.
This will create the need for maximum refrigerant
flow into the evaporator.
(6) If the refrigerant charge is sufficient, discharge
(high pressure) gauge should read 965 to 2620 kPa
(140 to 380 psi). Suction (low pressure) gauge should
read 103 to 2417 kPa (15 to 35 psi). If system cannot
achieve proper pressure readings, replace the expan-
sion valve. If pressure is correct, proceed with test.
PLHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)