1999 DODGE NEON weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 733 of 1200

(8) Disconnect throttle body linkage.
(9) Disconnect engine wiring harness.
(10) Disconnect heater hoses.
(11) Discharge Air Conditioning System. Refer to
Group 24, Air Conditioning for procedure.
(12) Hoist vehicle and remove right inner splash
shield (Fig. 15).
(13) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group
7, Cooling System for procedure.
(14) Remove axle shafts. Refer to Group 2, Suspen-
sion and Driveshafts for procedure.
(15) Disconnect exhaust pipe from manifold.
(16) Remove front engine mount.
(17) Manual transmission: Remove power hop
damper.
(18) Lower vehicle. Remove air cleaner assembly.
(19) Remove power steering pump and reservoir,
Set them aside.
(20) Remove A/C compressor.
(21) Remove ground straps to body.
(22) Raise vehicle enough to allow engine dolly
and cradle Special Tools 6135 and 6710 to be
installed under vehicle.
(23) Loosen engine support posts to allow move-
ment for positioning onto engine locating holes and
flange on the engine bedplate. Lower vehicle and
position cradle until the engine is resting on support
posts (Fig. 16). Tighten mounts to cradle frame. This
will keep support posts from moving when removing
or installing engine and transmission.
(24) Install safety straps around the engine to cra-
dle tighten; straps and lock them into position.(25) Raise vehicle enough to see if straps are tight
enough to hold cradle assembly to engine.
(26) Lower vehicle so weight of the engine and
transmission ONLY is on the cradle assembly.
(27) Remove engine and transmission mount thru-
bolts.
(28) Raise vehicle slowly. It may be necessary to
move the engine/transmission assembly with the cra-
dle to allow for removal around body flanges.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position engine and transmission assembly
under vehicle and slowly lower the vehicle over the
engine and transmission.
(2) Align engine and transmission mounts to
attaching points. Install mounting bolts at the right
engine and left transmission mounts. Refer to proce-
dures outlined in this section.
(3) Remove safety straps from engine and trans-
mission assembly. Slowly raise vehicle enough to
remove the engine dolly and cradle.
(4) Install axle shafts. Refer to Group 2, Suspen-
sion and Driveshafts for procedure.
(5) Install transmission and engine braces and
splash shields.
(6) Connect exhaust system to manifold. Refer to
Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold for
procedure and torque specifications.
(7) Install power steering pump and reservoir.
Refer to Group 7, Cooling System Accessory Drive
Section for belt tension adjustment.
Fig. 15 Right Inner Splash Shield
Fig. 16 Positioning Engine Cradle Support Post
Mounts
9 - 20 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 757 of 1200

PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli-
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl-
inder block.Be sure to keep tops of pistons
covered during this operation. Mark piston with
matching cylinder number (Fig. 90).
(2) Remove oil pan. Scribe the cylinder number on
the side of the rod and cap (Fig. 91) for identification.(3) Pistons will have a stamping in the approxi-
mate location shown in (Fig. 90). These stamps will
be either a directional arrow or a weight identifica-
tion for the assembly. L is for light and H is for
heavy. These assemblies should all be the same
weight class. Service piston assemblies are marked
with a S and can be used with either L or H produc-
tion assemblies. The weight designation stamps
should face toward the timing belt side of the engine.
(4) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap boltsDo not use
old bolts if reinstalling connecting rod.Push
each piston and rod assembly out of cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(6) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
(7) Piston and Rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGÐREMOVAL
(1) ID mark on face of upper and intermediate pis-
ton rings must point toward piston crown.
(2) Using a suitable ring expander, remove upper
and intermediate piston rings (Fig. 92).
(3) Remove the upper oil ring side rail, lower oil
ring side rail and then oil ring expander from piston.
(4) Clean ring grooves of any carbon deposits.
PISTON RINGSÐINSTALLATION
(1) Install rings with manufacturers I.D. mark fac-
ing up, to the top of the piston (Fig. 93).
CAUTION: Install piston rings in the following
order:
a. Oil ring expander.
b. Upper oil ring side rail.
Fig. 89 Crankshaft SprocketÐInstallation
Fig. 90 Piston Markings
Fig. 91 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
Fig. 92 Piston RingsÐRemoving and Installing
9 - 44 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 758 of 1200
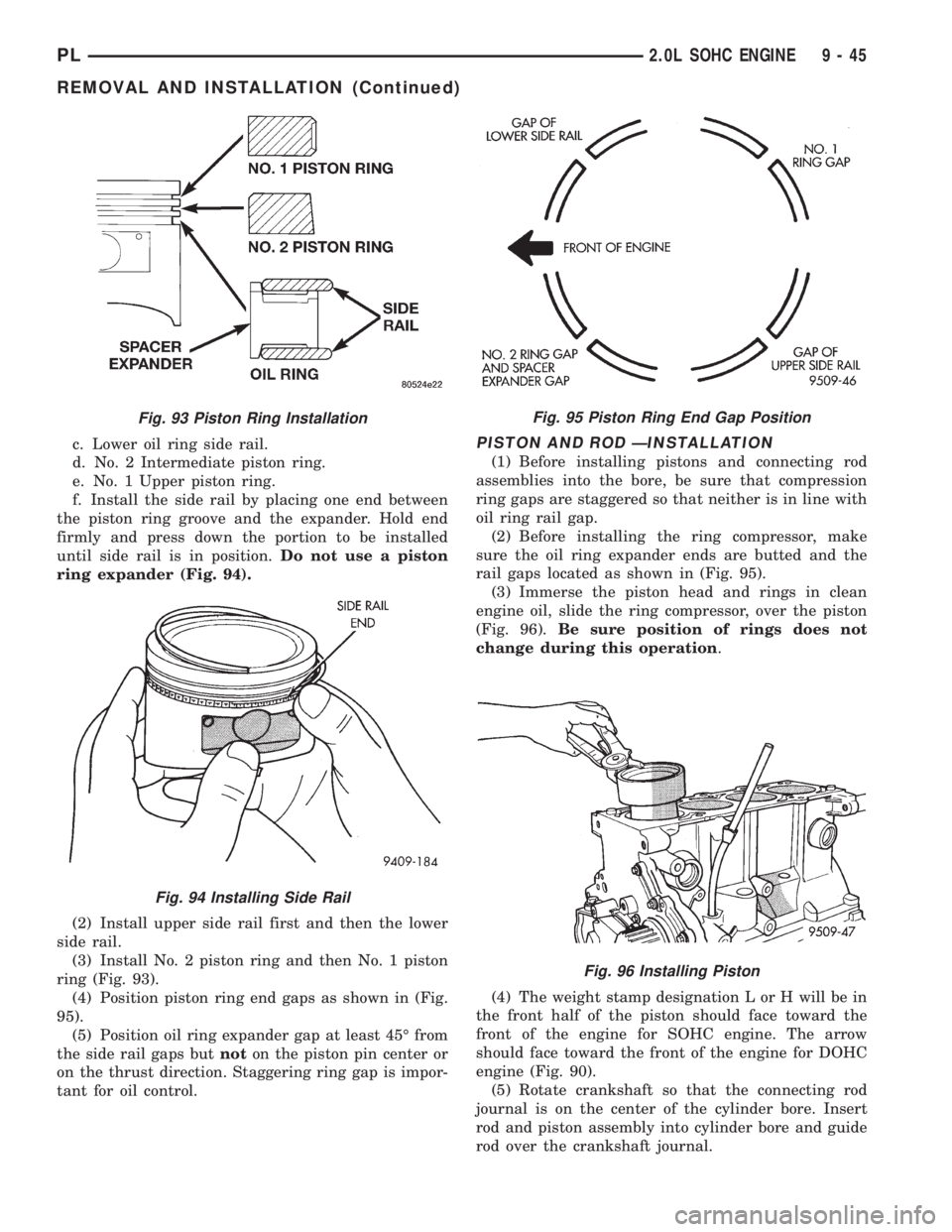
c. Lower oil ring side rail.
d. No. 2 Intermediate piston ring.
e. No. 1 Upper piston ring.
f. Install the side rail by placing one end between
the piston ring groove and the expander. Hold end
firmly and press down the portion to be installed
until side rail is in position.Do not use a piston
ring expander (Fig. 94).
(2) Install upper side rail first and then the lower
side rail.
(3) Install No. 2 piston ring and then No. 1 piston
ring (Fig. 93).
(4) Position piston ring end gaps as shown in (Fig.
95).
(5) Position oil ring expander gap at least 45É from
the side rail gaps butnoton the piston pin center or
on the thrust direction. Staggering ring gap is impor-
tant for oil control.PISTON AND ROD ÐINSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap.
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located as shown in (Fig. 95).
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston
(Fig. 96).Be sure position of rings does not
change during this operation.
(4) The weight stamp designation L or H will be in
the front half of the piston should face toward the
front of the engine for SOHC engine. The arrow
should face toward the front of the engine for DOHC
engine (Fig. 90).
(5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Insert
rod and piston assembly into cylinder bore and guide
rod over the crankshaft journal.
Fig. 93 Piston Ring Installation
Fig. 94 Installing Side Rail
Fig. 95 Piston Ring End Gap Position
Fig. 96 Installing Piston
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 45
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 765 of 1200

CYLINDER BORE INSPECTION
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 117). The cyl-
inder bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
with the fitting of pistons and rings in order that
specified clearances may be maintained.Refer to
Honing Cylinder Bores outlined in the Stan-
dard Service Procedures for specification and
procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 117). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston Specification
Chart for specifications.
SPECIFICATIONS
2.0L SOHC
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter. . . .87.4924 - 87.5076 mm
(3.4446 - 3.4452.in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)........0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Taper (Max.)..............0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
Pistons (Federal Emission)
Clearance 17.5 mm (11/16 in.) from bottom
of skirt. . . .0.012 - 0.044 mm (0.0004 - 0.0017 in.)
Weight........325 - 335 grams (11.47 - 11.82 oz.)
Land Clearance (Diametrical) . . .0.734 - 0.797 mm
(0.029 - 0.031 in.)
Piston Length...............64mm(2.520 in.)
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 1 .3.989 - 4.188 mm
(0.157 - 0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 2 .4.462 - 4.661 mm
(0.176 - 0.184 in.)
Piston Ring Groove DepthNo. 3 . .3.847 - 4.131 mm
(0.151 - 0.163 in.)
Pistons (Low Emission VehicleÐLEV)
Clearance 10.42 mm (0.42 in.) from bottom of
skirt......0.018 ± 0.50 mm (0.0008 ± 0.0020 in.)
Weight.......320 ± 329 grams (11.29 ± 11.60 oz.)
Land Clearance (Diametrical) . . .0.758 ± 0.790 mm
(0.0299 ± 0.0312 in.)
Piston Length..............55.8 mm (2.197 in.)
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 1 .3.989 - 4.188 mm
(0.157 - 0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 2 .4.462 - 4.661 mm
(0.176 - 0.184 in.)
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 3 .3.847 - 4.131 mm
(0.151 - 0.163 in.)
Fig. 117 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATION CHART
Standard Bore Max. Out-of-
RoundMax. Taper
87.5 mm (3.445
in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Standard Piston Size
Federal
Emission:87.463 - 87.481 mm (3.4434 -
3.4441 in.)
Low Emmision
Vehicle (LEV):87.456 - 87.474 mm (3.4432 -
3.4439 in.)
Piston to Bore Clearance
Federal
Emission:0.012 - 0.044 mm (0.0005 - 0.0017
in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):0.018 - 0.050 mm (0.0008 - 0.0020
in.)
Measurements taken at Piston Size Location.
9 - 52 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 766 of 1200

Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston. . . .0.008 - 0.020 mm (0.0003 -
0.0008 in.)
In Rod (Interference) . . .0.018 - 0.043 mm (0.0007 -
0.0017 in.)
Diameter .20.998 - 21.003 mm (0.8267 - 0.8269 in.)
End Play.............................None
Length.......74.75 - 75.25 mm (2.943 - 2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring Gap Top Compression Ring . . .0.23 - 0.52 mm
(0.009 - 0.020 in.)
Ring Gap 2nd Compression Ring . . .0.49 - 0.78 mm
(0.019 - 0.031 in.)
Ring Gap Oil Control (Steel Rails). .0.23 - 0.66 mm
(0.009 - 0.026 in.)
Ring Side Clearance Both Compression
Rings......0.025 - 0.065 mm (0.0010 - 0.0026 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack) .0.004 - 0.178 mm (0.0002 - 0.0070
in.)
Ring Width Compression Rings. . . .1.17 - 1.19 mm
(0.046 - 0.047 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack) . .2.854 - 3.008 mm (0.1124 - 0.1184
in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance......0.026 - 0.059 mm (0.001 -
0.0023 in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter......20.96 - 20.98 mm
(0.8252 - 0.8260 in.)
Large End Bore Diameter. . . .50.991 - 51.005 mm
(2.0075 - 2.0081 in.)
Side Clearance . .0.13 - 0.38 mm (0.005 - 0.015 in.)
Total Weight (Less Bearing) . .543 grams (1.20 lbs.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal Diameter......47.9924 -
48.0076 mm (1.8894 - 1.8900 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)......0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)............0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical Clearance
No.1-5 ...0.022 - 0.062 mm (0.0008 - 0.0024 in.)
End Play.....0.09 - 0.24 mm (0.0035 - 0.0094 in.)
Main Bearing Journals
Diameter . .51.9924 - 52.0076 mm (2.0469 - 2.0475
in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)......0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)............0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Rocker Arm Shaft Diameter . . .19.996 ± 19.984mm
(0.786 ± 0.7867 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft Retainers (Width)
Intake (All)................28.46 mm (1.12 in.)
Exhaust....1 & 5 29.20 mm (1.14in.) 2, 3, and 4 -
40.45 mm (1.59 in.)
Rocker Arm/Hydraulic Lash Adjuster *
Rocker Arm Inside Diameter. . . .20.00 ± 20.02 mm
(0.787 ± 0.788 in.)Rocker Arm Shaft Clearance. . . .0.016 ± 0.054 mm
(0.0006 ± 0.0021 in.)
Body Diameter.....22.949 ± 22.962 mm (0.9035 ±
0.9040 in.)
Plunger Travel Minimum (Dry) .2.2 mm (0.087 in.)
Rocker Arm Ratio....................1.4 to 1
Cylinder Head Camshaft Bearing Diameter
No.1 .....41.20 ± 41.221 mm (1.622 ± 1.6228 in.)
No.2 .......41.6 ± 41.621 mm (1.637 ± 1.638 in.)
No.3 .......42.0 ± 42.021 mm (1.653 ± 1.654 in.)
No.4 .......42.4 ± 42.421 mm (1.669 ± 1.670 in.)
No.5 ......42.8 ± 42.821 mm (1.685 ± 1.6858 in.)
Camshaft Journal Diameter
No. 1 . . . .41.128 ± 41.147 mm (1.619 ± 1.6199 in.)
No.2 .....41.528 ± 41.547 mm (1.634 ± 1.635 in.)
No.3 .....41.928 ± 41.947 mm (1.650 ± 1.651 in.)
No.4 .....42.328 ± 42.374 mm (1.666 ± 1.668 in.)
No. 5 . . . .42.728 ± 42.747 mm (1.682 ± 1.6829 in.)
Diametrical Bearing Clearance . .0.053 ± 0.093 mm
(0.0027 ± 0.003 in.)
Max. Allowable............0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
End Play...........0.05 ± 0.39 mm (0.0059 in.)
Lift (Zero Lash )
Intake.....................7.2 mm (0.283 in.)
Exhaust..................7.03 mm (0.277 in.)
Valve Timing Exhaust Valve**
Closes (ATDC)..........................5.4É
Opens (BBDC).........................43.7É
Duration............................229.1É
Valve Timing Intake Valve **
Closes (ABDC)........................41.1É
Opens (ATDC).........................13.9É
Duration............................207.2É
Valve Overlap...........................0É
Cylinder Head
Material....................Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness (Compressed) . . .1.15 mm (0.045
in.)
Valve Seat
Angle.................................45É
Runout (Max.)...............0.050 mm (0.002)
Width (Finish) Intake and Exhaust. . . .0.75 ± 1.25
mm (0.030 ± 0.049 in.)
Valve Guide Finished
Diameter I.D. . .5.975 ± 6.000 mm (.235 ± .236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter (Std.)......11.0±11.02 mm
(0.4330 ± 0.4338 in.)
Valves
Face Angle Intake and Exhaust......45±45-1/2É
Head Diameter Intake . .32.12 ± 33.37 mm (1.303 ±
1.313 in.)
Head Diameter Exhaust . .28.57 ± 28.83 mm (1.124
± 1.135 in.)
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 53
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 772 of 1200
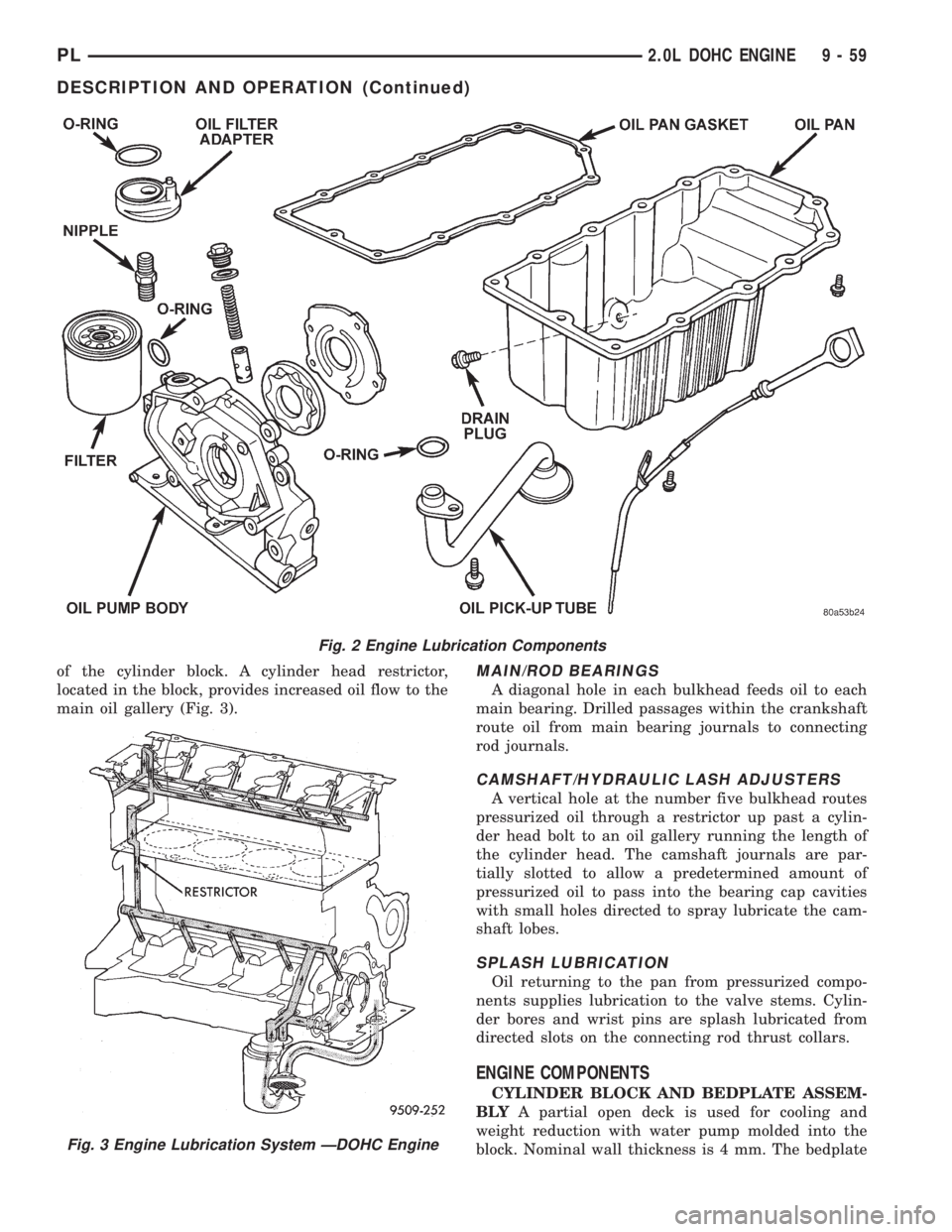
of the cylinder block. A cylinder head restrictor,
located in the block, provides increased oil flow to the
main oil gallery (Fig. 3).MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up past a cylin-
der head bolt to an oil gallery running the length of
the cylinder head. The camshaft journals are par-
tially slotted to allow a predetermined amount of
pressurized oil to pass into the bearing cap cavities
with small holes directed to spray lubricate the cam-
shaft lobes.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
BLYA partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication Components
Fig. 3 Engine Lubrication System ÐDOHC Engine
PL2.0L DOHC ENGINE 9 - 59
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 773 of 1200

incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFTA nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket pro-
vides motive power; via timing belt to the camshaft
sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONSThe DOHC EngineDO NOThave pro-
vision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hex
head cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly.
PISTON RINGSThe piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package contains of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADFeatures a Dual Over Head
Camshaft (DOHC), 4 valves per cylinder cross flow
design. The valves are arranged in two in-line banks,
with the ports of the bank of two intake valves per
cylinder facing toward the radiator side of engine
and ports of the bank of two exhaust valves per cyl-
inder facing toward the dash panel. Incorporates
powder metal valve guides and seats. Integral oil gal-
leys within the cylinder head supplies oil to the
hydraulic lash adjusters, camshaft and valve mecha-
nisms.
CAMSHAFTSThe nodular iron camshafts have
six bearing journals and 2 cam lobes per cylinder.
Flanges at the rear journals control camshaft end
play. Provision for cam position sensor is located on
the intake camshaft at the rear of cylinder head. A
hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control at the
front of the camshaft.
VA LV E SFour valves per cylinder are actuated by
roller cam followers which pivot on stationary
hydraulic lash adjusters. All valves have 6 mm diam-
eter chrome plated valve stems. The valve sizes are
34.8 mm (1.370 inch.) diameter intake valves and
30.5 mm (1.20 inch.) diameter exhaust valves. Viton
rubber valve stem seals are integral with the springseats. Valve springs, spring retainers, and locks are
conventional.
INTAKE MANIFOLDThe intake manifold is a
two piece aluminum casting, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch fan design
enhances low and mid-speed torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDThe exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
If any of the following parts have been changed or
replaced:
²Camshaft
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Camshaft Position Sensor Target Magnet
²Cylinder Block
²Cylinder Head
²Water Pump
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Timing Belt and Timing Belt Tensioner
The camshaft and crankshaft timing relearn proce-
dure must be performed. Refer to the component
Removal and Installation procedure outlined in this
Group.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 4). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
9 - 60 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 779 of 1200

(18) Lower vehicle. Remove air cleaner assembly.
(19) Remove power steering pump and reservoir,
Set them aside.
(20) Remove A/C compressor.
(21) Remove ground straps to body.
(22) Raise vehicle enough to allow engine dolly
and cradle Special Tools 6135 and 6710 to be
installed under vehicle.
(23) Loosen engine support posts to allow move-
ment for positioning onto engine locating holes and
flange on the engine bedplate. Lower vehicle and
position cradle until the engine is resting on support
posts (Fig. 17). Tighten mounts to cradle frame. This
will keep support posts from moving when removing
or installing engine and transmission.
(24) Install safety straps around the engine to cra-
dle tighten; straps and lock them into position.
(25) Raise vehicle enough to see if straps are tight
enough to hold cradle assembly to engine.
(26) Lower vehicle so weight of the engine and
transmission ONLY is on the cradle assembly.
(27) Remove engine and transmission mount thru-
bolts.
(28) Raise vehicle slowly. It may be necessary to
move the engine/transmission assembly with the cra-
dle to allow for removal around body flanges.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position engine and transmission assembly
under vehicle and slowly lower the vehicle over the
engine and transmission.(2) Align engine and transmission mounts to
attaching points. Install mounting bolts at the right
engine and left transmission mounts. Refer to proce-
dures outlined in this section.
(3) Remove safety straps from engine and trans-
mission assembly. Slowly raise vehicle enough to
remove the engine dolly and cradle.
(4) Install axle shafts. Refer to Group 2, Suspen-
sion and Driveshafts for procedure.
(5) Install transmission and engine braces and
splash shields.
(6) Connect exhaust system to manifold. Refer to
Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold for
procedure and torque specifications.
(7) Install power steering pump and reservoir.
Refer to Group 7, Cooling System Accessory Drive
Section for belt tension adjustment.
(8) Install A/C compressor and hoses. Refer to
Group 24, Heater and Air Conditioning for procedure.
(9) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System Accessory Drive Section for belt ten-
sion adjustment.
(10) Install front engine mount. Refer to this sec-
tion for procedure.
(11) Manual transmission: Install power hop
damper.
(12) Install inner splash shield. Install wheels and
tires.
(13)Manual Transmission:Connect clutch cable
and linkages. Refer to Group 6, Manual Transaxle
Clutch.
(14)Automatic Transmission:Connect shifter
and kickdown linkage. Refer to Group 21, Transaxle
for procedures.
(15) Connect fuel line and heater hoses.
(16) Install ground straps. Connect engine and
throttle body connections and harnesses. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical for procedure.
(17) Connect throttle body linkage. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System for procedure.
(18) Install radiator and shroud assembly. Install
radiator hoses. Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for filling procedure.
(19) Install battery tray and battery. Set Power-
train Control Module (PCM) into place.
(20) Install air cleaner and hoses.
(21) Install oil filter. Fill engine crankcase with
proper oil to correct level.
(22) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
Fig. 17 Positioning Engine Cradle Support Post
Mounts
9 - 66 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)