1999 DODGE NEON check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 210 of 1200

COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING
First clean system to remove old glycol, see Cooling
System Cleaning.
Fill system using antifreeze described in Coolant
section. Fill 50 percent of capacity with 100 percent
glycol. Then complete filling system with water.
Continue filling system until full, this provides bet-
ter heater performance.Be careful not to spill
coolant on drive belts or the generator.
Fill coolant reserve system to at least the FULL
mark with 50/50 solution. It may be necessary to add
coolant to the reserve tank after three or four warm-
up/cool down cycles to maintain coolant level between
the FULL and ADD marks; if any trapped air was
removed from the system.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WATER PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Remove right inner
splash shield.
(2) Remove accessory drive belts and power steer-
ing pump. Refer to Accessory Drive Belt service in
this section.
(3) Drain cooling system. Refer to Cooling System
Draining in this section.
(4) Support engine from the bottom and remove
right engine mount.
(5) Remove power steering pump bracket bolts and
set pump and bracket assembly aside. Power steering
lines do not need to be disconnected.
(6) Remove right engine mount bracket.
(7) Remove timing belt and timing belt tensioner.
Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(8) Remove camshaft sprockets and inner timing
belt cover. Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.(9) Remove water pump attaching screws to engine
(Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new O-ring gasket in water pump body
O-ring groove (Fig. 15). Use small dabs of Mopart
Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant around the water
pump body to secure O-ring in place during installa-
tion.
CAUTION: Make sure O-ring gasket is properly
seated in water pump groove before tightening
screws. An improperly located O-ring may cause
damage to the O-ring and cause a coolant leak.
(2) Assemble pump body to block and tighten
screws to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.). Pressurize cooling
system to 15 psi with pressure tester and check
water pump shaft seal and O-ring for leaks.
(3) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement.
(4) Install inner timing belt cover.
(5) Install timing belt. Refer to Group 9, Engine
for procedures.
(6) Install right engine mount bracket and engine
mount. Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(7) Fill cooling system. SeeCooling System
Refilling.
(8) Install power steering pump and accessory
drive belts, Refer to Accessory Drive Belts, in this
section.Fig. 13 Draining Cooling System
Fig. 14 Water Pump
Fig. 15 Water Pump Body
PLCOOLING 7 - 17
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 211 of 1200

(9) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
The inlet tube connects the water pump to the
radiator and heater core. This tube is sealed by a
O-ring and held in place by fasteners to the block.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not use any sharp tools to remove
hoses from inlet tube. This may cause the tube to
leak.
(1) Drain cooling system. Refer to procedure out-
lined in this section.
(2) Remove upper radiator hose to access the hose
connections at the inlet tube.
(3) Remove lower radiator hose and heater hose
from the inlet tube (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove the two fasteners that hold the inlet
tube to the block and one fastener that holds the
intake manifold to inlet tube.
(5) Rotate tube while removing the tube from the
engine block (Fig. 17).
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect the O-ring for damage before installing
the tube into the cylinder block (Fig. 17).
(2) Lube O-ring with coolant and install into the
cylinder block opening.
(3) Install two fasteners to the engine block and
the one fastener to the intake manifold. Tighten fas-
teners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Connect lower radiator hose and heater hose to
inlet tube.
(5) Install upper radiator hose.
(6) Fill cooling system. Refer to procedure outlined
in this section.
(7) Pressure system to 104 kPa (15 psi) to check
for leaks.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system to the thermostat level or
below.(2) Remove coolant recovery system (CRS) hose
and thermostat/engine outlet connector bolts (Fig. 18)
or (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove thermostat an O-ring assembly, and
clean sealing surfaces.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the new thermostat assembly into the
thermostat housing/outlet connector. Align vent with
notch in cylinder head.
(2) Install thermostat housing/outlet connector
onto cylinder head and tighten bolts to 12.5 N´m (110
in. lbs.). Connect the coolant recovery system (CRS)
hose.
(3) Refill cooling system (seeRefilling System).
Fig. 16 Water Pump Inlet Tube Hose Connections
Fig. 17 Water Pump Inlet Tube
7 - 18 COOLINGPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 213 of 1200

(5) Connect automatic transmission hoses, if
equipped. Tighten hose clamps to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.).
(6) Slide fan module down into clip(s) on lower
radiator flange (Fig. 21). For dual fan application
install the right fan module first and then the left
fan module. Install retaining screws and tighten to
7.5 N´m (65 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect the cooling fan motor electrical connec-
tor(s).
(8) Install upper radiator hose. Align the hose and
position the clamp so they will not interfere with the
engine or the hood.
(9) For vehicles equipped with dual fans: Install
the battery tray and battery.
(10) Connect negative cable to battery.
(11) Fill cooling system with coolant. Refer to
Cooling System Refillingin this section.
(12) Operate engine until it reaches normal oper-
ating temperature. Check cooling system and auto-
matic transmission for correct fluid levels.
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
REMOVAL
(1) Turn the drain cock stem counterclockwise to
unscrew the stem. When the stem is unscrewed to
the end of the threads, pull the stem (Fig. 23) from
the radiator tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Push the draincock assembly body into the
tank opening.
(2) Tighten the draincock stem by turning clock-
wise to 2.0-2.7 N´m (18-25 in. lbs.).
RADIATOR FANS AND MOTOR
All models use a single speed electric motor driven
cooling system fans. The fan modules includes a
motor, fan blade, and support shroud. The module is
fastened to the radiator by screws.
REMOVAL FAN MODULE
(1) Disconnect fan motor leads from module.
(2) Remove fan module fasteners from radiator
(Fig. 24).
FAN BLADE
There are no repairs to be made to the fan. If the
fan is warped, cracked, or otherwise damaged, it
Fig. 21 Fan Module Mounting
Fig. 22 A/C Condenser to Radiator Mounting Screws
Fig. 23 Draincock
Fig. 24 Servicing Fan Module
7 - 20 COOLINGPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 220 of 1200

NOTE: BLACK OR DARK=0to75%state-of-charge
The battery is INADEQUATELY charged and must
be charged until green dot is visible, (12.4 volts or
greater) before the battery is tested or returned to
use. Refer to Causes of Battery Discharging in this
Group for more information.
NOTE: CLEAR COLOR = Replace Battery
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE, ASSIST BOOST,
LOAD TEST, OR ADD WATER TO THE BATTERY
WHEN CLEAR COLOR DOT IS VISIBLE. PERSONAL
INJURY MAY OCCUR.
A clear color dot shows electrolyte level in battery
is below the test indicator (Fig. 1). Water cannot be
added to a maintenance free battery. The battery
must be replaced. A low electrolyte level may be
caused by an over charging condition. Refer to Gen-
erator Test Procedures on Vehicle.
CAUSES OF BATTERY DISCHARGING
It is normal to have a small 5 to 25 milliamperes
continuous electrical draw from the battery. This
draw will take place with the ignition in the OFF
position, and the courtesy, dome, storage compart-
ments, and engine compartment lights OFF. The con-
tinuous draw is due to various electronic features or
accessories that require electrical current with the
ignition OFF to function properly. When a vehicle is
not used over an extended period of approximately 20
days the IOD fuse should be pulled. The fuse is
located in the power distribution center. removal of
this fuse will reduce the level of battery discharge.
Refer to the Battery Diagnosis and Testing Table for
proper diagnosis.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
²Corroded battery posts, cables or terminals.
²Loose or worn generator drive belt.
²Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system due to equipment or accessories
installed after delivery.
²Slow driving speeds in heavy traffic conditions
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical
systems in use.
²Defective electrical circuit or component causing
excess Ignition Off Draw (IOD). Refer to Battery
Ignition Off Draw (IOD).
²Defective charging system.
²Defective battery.
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD)
High current draw on the battery with the ignition
OFF will discharge a battery. After a dead battery is
recharged, the vehicle ignition off draw (IOD) shouldbe checked. To determine if a high current draw con-
dition exists first check the vehicle with a test lamp.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF.
²Remove key from ignition switch
²Turn off all lights
²Trunk lid is closed
²Engine compartment hood lamp is disconnected
or lamp removed
²Glove box door is closed
²Sun visor vanity lights are OFF
²All doors are closed
²Allow the ignition key lamp system to time out
in approximately 30 seconds, if equipped.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable (Fig. 4).
(3) Connect a 12 Volt test lamp, with a cold resis-
tance of 5-7 ohms, between the battery negative cable
clamp and the negative post (Fig. 5). If test lamp
goes out system is OK. If test lamp lights and stays
ON, go to Test Lamp Stays ON procedure.
TEST LAMP STAYS ON
There is either a short circuit or a fault in an elec-
tronic module. Two fuses in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) feed the modules with ignition off
draw.
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp) (IOD) PDC.
²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp) in PDC
(1) Remove interior lamp and fuel pump fuses. By
removing these fuses all ignition off draw from the
vehicle electronics will be disconnected. The test
lamp should go out. If test lamp goes out go to Step
2. If test lamp does not go out there is a current
draw or short circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams.
(2) Install the fuel pump fuse. If test lamp lights,
there is a current draw or short circuit in the A14
wiring circuit feed.
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If test lamp goes out, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If test lamp does not go out, there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit feed.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3) Install the interior lamp fuse. If test lamp
lights, there is a current draw or short circuit in the
M01 circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If
test lamp stays out, go to Step 4
(4) Use a multi-meter that has at least a range of
200 milliamperes. Install meter between the battery
negative cable and battery negative post (Fig. 6).
Carefully remove the test lamp without disconnecting
the meter. After all modules time-out the total vehi-
cle IOD should be less than 10 milliamperes. If igni-
tion off draw is more than 10 milliamperes go to Step
5.
(5) Remove both fuses from the Power Distribution
Center:
PLBATTERY 8A - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 230 of 1200

(1) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals (Fig. 7). Refer to the operating instructions
provided with the tester being used.
(2) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location. The 2.5L Diesel Engine, to disable the
engine from starting, disconnect wire connector from
the Fuel Solenoid.
(3) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARKposition or with the clutch pedal depressed and SET
parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(4) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
6).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps or the Diesel engine
above 450 amps, check for engine seizing or faulty
starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps or Diesel engine above 500 amps,
the problem is the starter. Replace the starter refer
to starter removal.
(5) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
Fig. 6 Volt Ampere Tester
Fig. 7 Volt-Ampere Tester Connections
Fig. 4 Test Starter Motor Ground
Fig. 5 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance
PLSTARTING 8B - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 232 of 1200
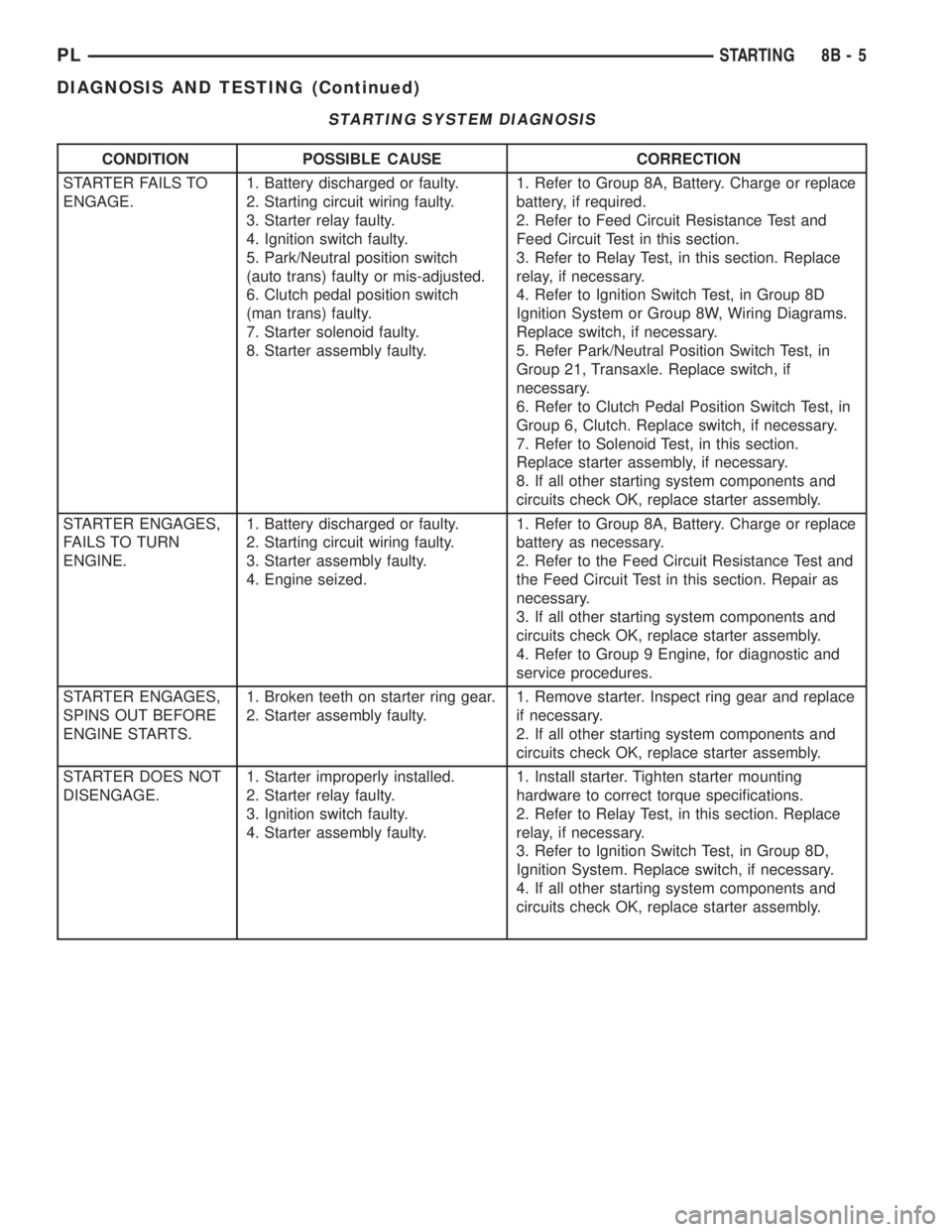
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
ENGAGE.1. Battery discharged or faulty.
2. Starting circuit wiring faulty.
3. Starter relay faulty.
4. Ignition switch faulty.
5. Park/Neutral position switch
(auto trans) faulty or mis-adjusted.
6. Clutch pedal position switch
(man trans) faulty.
7. Starter solenoid faulty.
8. Starter assembly faulty.1. Refer to Group 8A, Battery. Charge or replace
battery, if required.
2. Refer to Feed Circuit Resistance Test and
Feed Circuit Test in this section.
3. Refer to Relay Test, in this section. Replace
relay, if necessary.
4. Refer to Ignition Switch Test, in Group 8D
Ignition System or Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
Replace switch, if necessary.
5. Refer Park/Neutral Position Switch Test, in
Group 21, Transaxle. Replace switch, if
necessary.
6. Refer to Clutch Pedal Position Switch Test, in
Group 6, Clutch. Replace switch, if necessary.
7. Refer to Solenoid Test, in this section.
Replace starter assembly, if necessary.
8. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
STARTER ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. Battery discharged or faulty.
2. Starting circuit wiring faulty.
3. Starter assembly faulty.
4. Engine seized.1. Refer to Group 8A, Battery. Charge or replace
battery as necessary.
2. Refer to the Feed Circuit Resistance Test and
the Feed Circuit Test in this section. Repair as
necessary.
3. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
4. Refer to Group 9 Engine, for diagnostic and
service procedures.
STARTER ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT BEFORE
ENGINE STARTS.1. Broken teeth on starter ring gear.
2. Starter assembly faulty.1. Remove starter. Inspect ring gear and replace
if necessary.
2. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
STARTER DOES NOT
DISENGAGE.1. Starter improperly installed.
2. Starter relay faulty.
3. Ignition switch faulty.
4. Starter assembly faulty.1. Install starter. Tighten starter mounting
hardware to correct torque specifications.
2. Refer to Relay Test, in this section. Replace
relay, if necessary.
3. Refer to Ignition Switch Test, in Group 8D,
Ignition System. Replace switch, if necessary.
4. If all other starting system components and
circuits check OK, replace starter assembly.
PLSTARTING 8B - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 238 of 1200

Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²Accessories being left on with the engine not
running
²A faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. See Ignition-Off Draw Test
in Group 8A, Battery for more information.
The following procedures may be used to correct a
problem diagnosed as a charging system fault.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(2) Inspect all fuses in the fuseblock module and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.(3) Inspect the electrolyte level in the battery.
Replace battery if electrolyte level is low.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in Group 7, Cooling Sys-
tem.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to Group 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect connections at generator field, battery
output, and ground terminals. Also check ground con-
nection at engine. They should all be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
PLCHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 242 of 1200
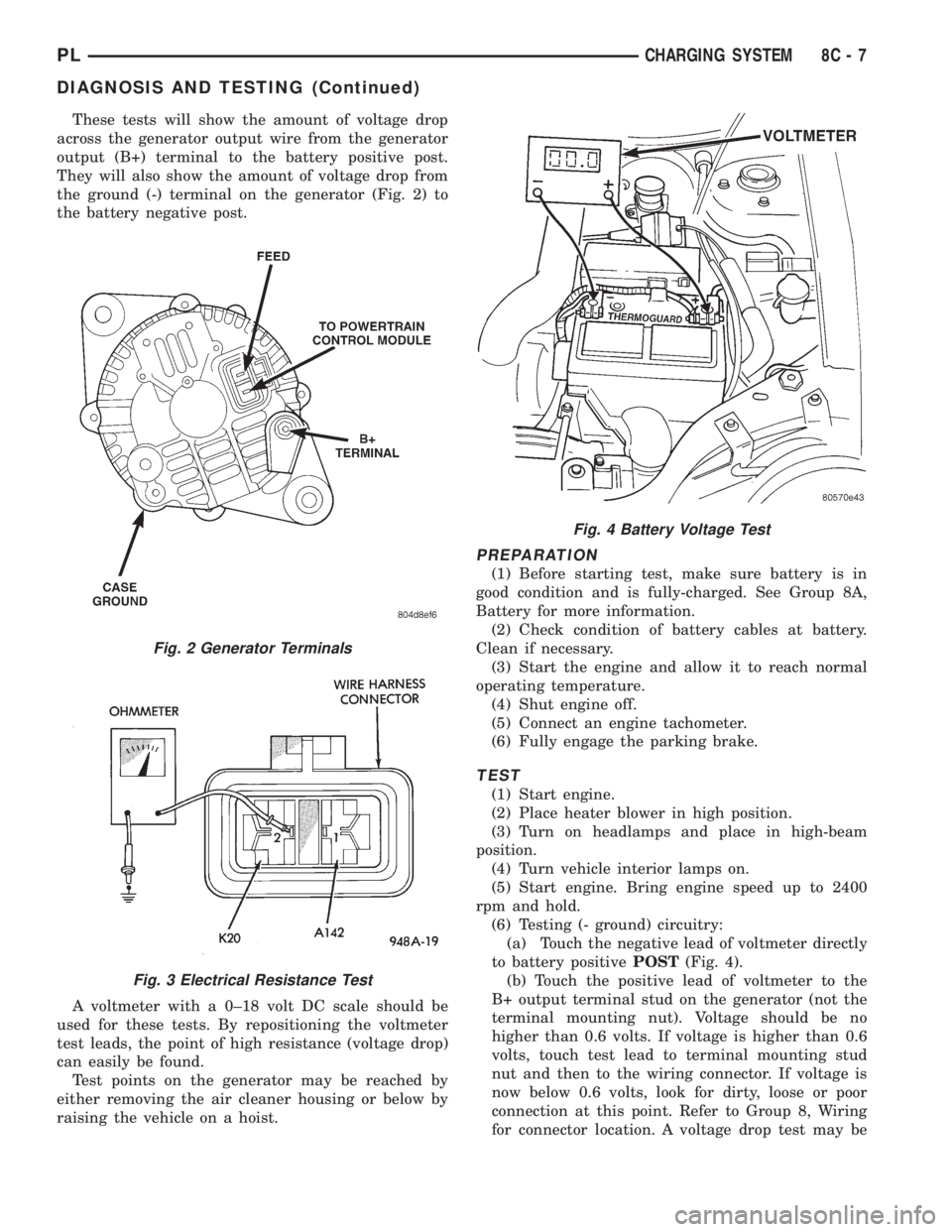
These tests will show the amount of voltage drop
across the generator output wire from the generator
output (B+) terminal to the battery positive post.
They will also show the amount of voltage drop from
the ground (-) terminal on the generator (Fig. 2) to
the battery negative post.
A voltmeter with a 0±18 volt DC scale should be
used for these tests. By repositioning the voltmeter
test leads, the point of high resistance (voltage drop)
can easily be found.
Test points on the generator may be reached by
either removing the air cleaner housing or below by
raising the vehicle on a hoist.
PREPARATION
(1) Before starting test, make sure battery is in
good condition and is fully-charged. See Group 8A,
Battery for more information.
(2) Check condition of battery cables at battery.
Clean if necessary.
(3) Start the engine and allow it to reach normal
operating temperature.
(4) Shut engine off.
(5) Connect an engine tachometer.
(6) Fully engage the parking brake.
TEST
(1) Start engine.
(2) Place heater blower in high position.
(3) Turn on headlamps and place in high-beam
position.
(4) Turn vehicle interior lamps on.
(5) Start engine. Bring engine speed up to 2400
rpm and hold.
(6) Testing (- ground) circuitry:
(a) Touch the negative lead of voltmeter directly
to battery positivePOST(Fig. 4).
(b) Touch the positive lead of voltmeter to the
B+ output terminal stud on the generator (not the
terminal mounting nut). Voltage should be no
higher than 0.6 volts. If voltage is higher than 0.6
volts, touch test lead to terminal mounting stud
nut and then to the wiring connector. If voltage is
now below 0.6 volts, look for dirty, loose or poor
connection at this point. Refer to Group 8, Wiring
for connector location. A voltage drop test may be
Fig. 2 Generator Terminals
Fig. 3 Electrical Resistance Test
Fig. 4 Battery Voltage Test
PLCHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)