1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 263 of 2053

1F1 -- 100 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAA1F090
Notice:Before removal, the fuel rail assembly may be
cleaned with a spray-type cleaner, following package in-
structions. Do not immerse the fuel rails in liquid clean-
ing solvent. Use care in removing the fuel rail assembly
to prevent damage to the electrical connectors and in-
jector spray tips. Prevent dirt and other contaminants
from entering open lines and passages. Fittings should
be capped and holes plugged during service.
Important:If an injector becomes separated from the
rail and remains in the cylinder head, replace the injector
O-ring seals and the retaining clip.
12. Remove the injectors and the fuel rail carefully.
13. Remove the fuel injector retainer clips.
14. Remove the fuel injectors by pulling them down and
out.
15. Discard the fuel injector O-rings.
16. Lubricate the new fuel injector O-rings with engine
oil. Install the new O-rings on the fuel injectors.
17. Perform a leak check of the fuel rail and fuel injec-
tors.
18. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
YAA1F150
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
Removal and Installation Procedure
1. Relieve the coolant system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature sensor
connector.
Notice:Take care when handling the engine coolant
temperature sensor. Damage to the sensor will affect
the proper operation of the fuel injection system.
4. Remove the engine coolant temperature sensor
from the pump hosing.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque
30 NSm (22 Ib-ft)
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
Page 286 of 2053

1A2 -- 2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
D AEW OO M Y_2000
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationE23 EngineE20 Engine
Engine ModelM161.970M161.940
Displacement (CC)22951998
Cylinder (Bore x Stroke)(mm)90.9 x 88.489.9 x 78.7
Fuel Injection / Ignition SystemMSE 3.53S←
Compression Ratio10.4:19.6:1
Number of Cylinders4←
Camshaft Valve ArrangementDOHC←
Camshaft Drive TypeChain-- Driven←
Max. Output (ps/rpm)149 / 5500135 / 5500
Max. Torque (kgSm/rpm)22.4 / 400019.3 / 4000
Firing Order1--3--4--2←
Ignition TypeDistributorless←
Ignition TimingBTDC 6°±2°←
Va lv e
Tii
IntakeOpen/CloseATDC 19.25°/ ABDC 28.76°ATDC 13.15°/ ABDC 13.57°
Tim in gExhaustOpen/CloseBBDC 20.62°/ BTDC 15.08°BBDC 16.58°/ BTDC 17.05°
Valve Clearance AdjustmentAutomatic Control←
Idle Speed (rpm)750±50←
Fuel Injection Pressure (kg/cm@)3.2 -- 4.2←
Oil Capacity (liter)7.5←
Lubrication TypeForced by Gear Pump←
Oil Filter TypeFull Flow with Paper Filter←
FuelUnleaded Gasoline←
MSE 3.62S/3.53S (Motorsteuer Elektronik : German)
MSE : Engine Control Electronic
3.62S : 6 cylinder version
3.53S : 4 cylinder version
Page 287 of 2053

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2 -- 3
D AEW OO M Y_2000
COMPONENT LOCATOR
FRONT VIEW
1 HFM Sensor
2 Intake Air Duct
3 Cylinder Head Cover
4 Ignition Coil
5 Spark Plug Connector
6 Fuel Distributor
7 Injector
8 Exhaust Camshaft
9 Intake Camshaft
10 Valve Tappet
11 Intake Valve12 Intake Manifold
13 Cylinder Head
14 Exhaust Manifold
15 Dipstick Guide Tube and Gauge
16 Connecting Rod
17 Crankshaft
18 Engine Mounting Bracket
19 Starter
20 Crankcase
21 Oil Pump Sprocket
22 Oil Pan
Page 295 of 2053

1B2 -- 2 M161 ENGINE MECHANICAL
D AEW OO M Y_2000
SPECIFICATIONS
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb-FtLb-In
Fuel Feed and Return Line21 -- 2515 -- 18--
Exhaust Manifold and Pipe3022--
Engine Mounting Nuts7052--
Generator Carrier Bolts2518--
Tensioning Pulley Bolt40.5 -- 49.529.9 -- 36.5--
Steering Pump Bolts22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
A/C Bracket Bolts22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
Intake Air Duct Mounting Nuts9--11--80 -- 97
Spark Plug Cover Bolts9--11--80 -- 97
Cylinder Head Cover Bolts9--11--80 -- 97
Magnetic Assembly Bolt9--11--80 -- 97
Cylinder Head Front Cover BoltsM822.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--y
M69--11--80 -- 97
Cylinder Head Bolts55
+90°
+90°41
+90°
+90°
--
Timing Gear Case Cover Bolts22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
Crankshaft Sealing Rear Cover Mounting Bolts9--11--80 -- 97
Vibration Damper Center Bolt200 + 20
+90°+10°148 + 15
+90°+10°--
Connecting Rod Bearing Cap Bolts40
+90°30
+90°--
Flywheel Mounting Bolt45 + 5
+90°+10°33 + 3.7
+90°+10°--
Amarture Bolt in Flywheel3526--
Camshaft Adjuster Flange Bolts18 -- 22
60°±5°13 -- 16
60°±5°--
Intake Flange Shaft Bolts18 -- 22
60°±5°13 -- 16
60°±5°--
Exhaust Camshaft Sprocket Bolts18 -- 22
60°±5°13 -- 16
60°±5°--
Camshaft Bearing Cap Bolts22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
Chain Tensioner Screw Plug4030--
Chain Tensioner Assembly72 -- 8853 -- 65--
Oil Pump Sprocket Bolt29 -- 3521 -- 26--
Tensioning Device Bolts26 -- 3219 -- 24--
Water Pump Pulley22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
Upper Intake Manifold Bolt22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
Lower Intake Mainfold Bolt22.5 -- 27.516.6 -- 20.3--
Flange Bolt to Exhaust Mainfold3022--
Page 423 of 2053

D AEW OO M Y_2000
SECTION 1F2
ENGINE CONTROLS
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless other -
wise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Engine and ECM Problem Check Report 1F2 -- 2....
Specifications 1F2 -- 3............................
Engine Data Display Table 1F2 -- 3.................
Fastener Tightening Specifications 1F2 -- 4..........
Fuel System Specification 1F2 -- 5.................
Temperature vs Resistance 1F2 -- 5................
Special Tools and Equipment 1F2 -- 6..............
Special Tools Table 1F2 -- 6.......................
Schematic and Routing Diagrams 1F2 -- 7..........
ECM Wiring Diagram
(2.3L DOHC -- MSE 3.53S) 1F2 -- 7..............
Diagnosis 1F2 -- 14................................
Failure Code Diagnosis 1F2 -- 14.....................
Clearing Failure Codes 1F2 -- 14...................
Failure Codes Table 1F2 -- 14.....................
Ignition System 1F2 -- 18...........................
Ignition Coil 1F2 -- 20.............................
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 1F2 -- 22.........
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 1F2 -- 26..........
Camshaft Actuator 1F2 -- 30......................
Knock Sensor (KS) 1F2 -- 32......................
Spark Plug 1F2 -- 34.............................
System Voltage 1F2 -- 38.........................
Ignition Switch 1F2 -- 39..........................
Fuel System 1F2 -- 40..............................
Fuel Pump 1F2 -- 42.............................
Fuel Injector 1F2 -- 46............................
Purge Control Valve 1F2 -- 50.....................
Fuel Rail 1F2 -- 52...............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F2 -- 54.................
Induction System 1F2 -- 56..........................
Throttle Valve Actuator 1F2 -- 56...................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F2 -- 60..........
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 1F2 -- 64.
Accelerator Pedal Module 1F2 -- 68................Cooling Fan 1F2 -- 72............................
A/C Compressor Relay 1F2 -- 73...................
Cruise Control Switch 1F2 -- 74....................
Traction Control System (TCS) 1F2 -- 75............
Stop Lamp Switch 1F2 -- 76.......................
Engine RPM 1F2 -- 77............................
Exhaust System 1F2 -- 78...........................
Catalytic Converter 1F2 -- 78......................
Oxygen Sensor 1F2 -- 80.........................
Engine Control Module 1F2 -- 86.....................
Serial Data Communication 1F2--88...............
Internal Failure 1F2 -- 90..........................
Electronic Throttle Controller Safety
Malfunction 1F2 -- 92...........................
Immobilizer 1F2 -- 94.............................
Maintenance and Repair 1F2 -- 95..................
On -- Vehicle Service 1F2 -- 95........................
Discharging the Pressure in Fuel System 1F2 -- 95...
Fuel Pump 1F2 -- 95.............................
Fuel Filter 1F2 -- 96..............................
Fuel Tank 1F2 -- 97..............................
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1F2 -- 98.................
Fuel Rail and Injector 1F2 -- 99....................
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 1F2 -- 100......
Throttle Body (Integrated with the
Actuator) 1F2 -- 101............................
Hot Film Air Mass (HFM) Sensor 1F2 -- 102.........
Knock Sensor 1F2 -- 102..........................
Pedal Position Sensor 1F2 -- 103...................
Oxygen Sensor 1F2 -- 103........................
Purge Control Valve 1F2 -- 104....................
Canister 1F2 -- 104...............................
Camshaft Position Sensor 1F2 -- 104...............
Crankshaft Position Sensor 1F2 -- 105..............
Engine Control Module 1F2 -- 105..................
Page 427 of 2053

M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 5
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
Use Only Unleaded Fuel Rated at 89
Octane or Higher
Fuel quality and additives contained in fuel have a s ig n if i-
cant effect on power output, drivability, and life of the en-
gine.
Fuel with too low an octane number can cause engine
knock.
Caution: Use of fuel with an octane number lower
than 89 may damage engine and exhaust system.
Notice:To prevent accidental use of leaded fuel, the
nozzles for leaded fuel are larger, andwill not fit the fuel
filler neck of your vehicle.
Do Not Use Methanol
Fuels containing methanol (wood alcohol) should not be
used in vehicle.This type of fuel can reduce vehicle performance and
damage components of the fuel system.
Caution: Use of methanol may damage the fuel sys -
tem.
Vehicle Fueling from Drums or Storage
Containers
For safety reasons (particularly when using noncom-
mercial fueling systems) fuel containers, pumps and
hoses must be properly earthed.
Static electricity build up can occur under certain atmo-
spheric and fuel flow conditions if unearthed hoses, par-
ticularly plastic, are fitted to the fuel-- dispensing pump.
It is therefore recommended that earthed pumps with in-
tegrally earthed hoses be used, and that storage con-
tainers be properly earthed during all noncommercial
fueling operations.
TEMPERATURE VS RESISTANCE
°C°FECT sensorIAT sensor°C°FOHMS (Ω)
Temperature vs Resistance Values (Approximate)
13026688102
120248111. 6127
110230143159
100212202202
90194261261
80176340340
70158452452
60140609609
50122835835
40113116 61166
308616621662
206824202420
105036043604
03254995499
-- 1 01486098609
-- 2 0-- 41385013850
-- 3 0-- 2 22296022960
-- 4 0-- 4 03926039260
Page 436 of 2053
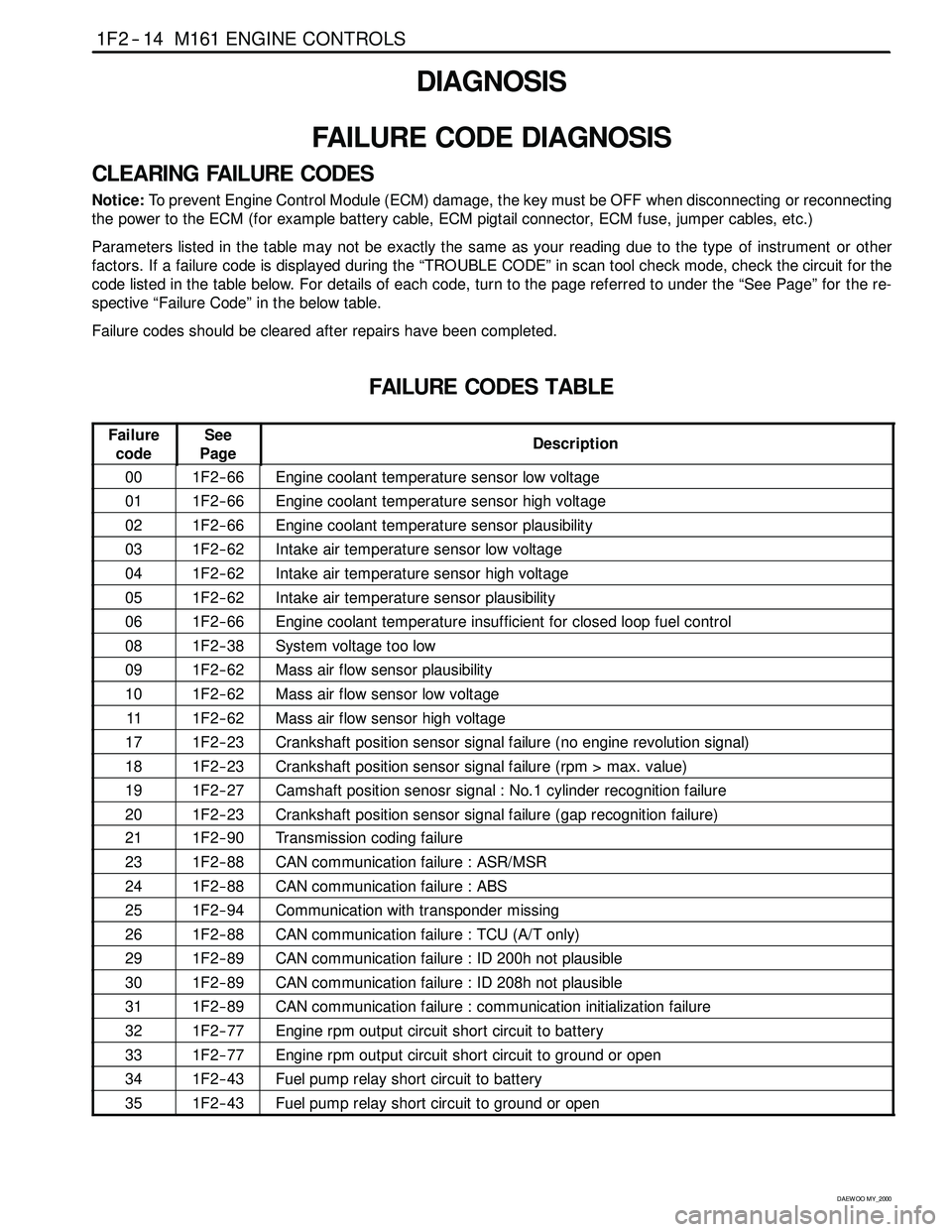
1F2 -- 14 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
DIAGNOSIS
FAILURE CODE DIAGNOSIS
CLEARING FAILURE CODES
Notice:To prevent Engine Control Module (ECM) damage, the key must be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting
the power to the ECM (for example battery cable, ECM pigtail connector, ECM fuse, jumper cables, etc.)
Parameters listed in the table may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other
factors. If a failure code is displayed during the “TROUBLE CODE” in scan tool check mode, check the circuit for the
code listed in the table below. For details of each code, turn to the page referred to under the “See Page” for the re-
spective “Failure Code” in the below table.
Failure codes should be cleared after repairs have been completed.
FAILURE CODES TABLE
Failure
codeSee
PageDescription
001F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor low voltage
011F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor high voltage
021F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature sensor plausibility
031F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor low voltage
041F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor high voltage
051F2 -- 62Intake air temperature sensor plausibility
061F2 -- 66Engine coolant temperature insufficient for closed loop fuel control
081F2 -- 38System voltage too low
091F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor plausibility
101F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor low voltage
111F2 -- 62Mass air flow sensor high voltage
171F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (no engine revolution signal)
181F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (rpm > max. value)
191F2 -- 27Camshaft position senosr signal : No.1 cylinder recognition failure
201F2 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor signal failure (gap recognition failure)
211F2 -- 90Transmission coding failure
231F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : ASR/MSR
241F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : ABS
251F2 -- 94Communication with transponder missing
261F2 -- 88CAN communication failure : TCU (A/T only)
291F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 200h not plausible
301F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : ID 208h not plausible
311F2 -- 89CAN communication failure : communication initialization failure
321F2 -- 77Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to battery
331F2 -- 77Engine rpm output circuit short circuit to ground or open
341F2 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to battery
351F2 -- 43Fuel pump relay short circuit to ground or open
Page 458 of 2053

1F2 -- 40 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FUEL SYSTEM
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating condi-
tions. The fuel is delivered to the engine by the individual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold near each
cylinder.
The main fuel control sensors are the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and the oxygen (O2) sensors.
The MAF sensor monitors the mass flow of the air being drawn into the engine. An electrically heated element is
mounted in the intake air stream, where it is cooled by the flow of incoming air. Engine Control Module (ECM) modu-
lates the flow of heating current to maintain the temperature differential between the heated film and the intake air at a
constant level. The amount of heating current required to maintain the temperature thus provides an index for the
mass air flow. This concept automatically compensates for variations in air density, as this is one of the factors that
determines the amount of warmth that the surrounding air absorbs from the heated element. MAF sensor is located
between the air filter and the throttle valve.
Under high fuel demands, the MAF sensor reads a high mass flow condition, such as wide open throttle. The ECM
uses this information to enrich the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on-- time, to provide the correct amount of
fuel. When decelerating, the mass flow decreases. This mass flow change is sensed by the MAF sensor and read by
the ECM, which then decreases the fuel injector on-- time due to the low fuel demand conditions.
The O2 sensors are located in the exhaust pipe before catalytic converter. The O2 sensors indicate to the ECM the
amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas, and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling the fuel
injectors. The best air/fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which allows the catalytic converter to
operate most efficiently. Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system
is called a “closed loop” system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to determine how much fuel to provide to the engine. The fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions, called ‘‘modes”.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel pump relay on for 1 second. The fuel pump then builds fuel
pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor and the Throttle Position (TP) sensor
and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting the engine. This ranges from 1.5 to 1 at -- 36°C(--33°F) coolant
temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 94°C (201°F) coolant temperature. The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by changing how long the fuel injector is turned on and off. This is done by ‘‘pulsing” the fuel injectors for
very short times.
Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ‘‘open loop” and ‘‘closed loop”.
Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 690 rpm, thesystem goes into “open loop” operation. In “open loop”, the
ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the ECT sensor and the
MAF sensor. The ECM stays in “open loop” until the following conditions are met:
DThe O2 has a varying voltage output, showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
DThe ECT sensor is above a specified temperature (22.5°C).
DA specific amount of time has elapsed after starting the engine.
Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with different engines and are stored in the Electronically Erasable
Programmable Read -- Only Memory (EEPROM). When these conditions are met, thesystem goes into “closed loop”
operation. In “closed loop”, the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on-- time) based on the signals from the
O2 sensors. This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position and airflow and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and airflow and reduces the amount of fuel. When deceleration is
very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short periods of time.