1997 SSANGYONG KORANDO fuses
[x] Cancel search: fusesPage 987 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have
a basic knowledge of the following items. Without this
knowledge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic
procedures contained in this section.
•Basic Electrical Circuits - You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the meaning
of voltage, current (amps), and resistance (ohms).
You should understand what happens in a circuit
with an open or shorted wire. You should be able to
read and understand a wiring diagram.
Use of Circuit Testing Tools - You should know
how to use a test light and how to bypass
components to test circuits using fused jumper
wires. You should be familiar with a digital
multimeter. You should be able to measure voltage,
resistance, and current, and be familiar with the
controls and how to use them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists
of a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock
components. The conventional brake system includes
a vacuum booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes,
rear disc brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake pipes
and hoses, brake fluid level switch and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator
and the TCS indicator. See “ABS Component Locator”
in this section for the general layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located
between the surge tank and the bulkhead on the left
side of the vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hy-
draulic check valves, two solenoid valves for each
wheel, a hydraulic pump, and two accumulators. The
hydraulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front
calipers and rear calipers by modulating hydraulic
pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Units equipped with TCS add two more valves for each
drive wheel for the purpose of applying the brake to a
wheel that is slipping. This is done with pressure from
the hydraulic pump in the unit. There is also a TCS
indicator lamp on the instrument panel to alert the driver
to the fact that the TCS system is active. The
components identified in the drawing are those added
to the basic ABS 5.3 system to provide traction control.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit withattached EBCM must be replaced. For more
information, refer to “Base Braking Mode” and
“Antilock Braking Mode” in this section.
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(TCS) DESCRIPTION
General Information
The traction control system (TCS) is a traction system
by means of brake intervention only, available in a low
speed range (< 60kph).
It workes on µ - split roads with sidewise different friction
coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive
torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high-µ
side. During TCS active, the TCS information lamp is
blinking.
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a mathe-
matical model and TCS is switched passive if the calcu-
lated temperature is greater than a threshold value (500
°C).
TCS is permitted again, when the calculated tempera-
ture is less than 350 °C.
Control Algorithm
The input signals for the control algorithm are the
filtered wheel speed signals from the ABS speed
processing.
With the speed difference of the driven wheels, the
control deviation is calculated.
If the control deviation exceeds a certain threshold
value, the wheel with the greater slip is braked actively.
The threshold value depends on the vehicle speed:
It is reduced with increasing vehicle speed down to a
constant value.
KAA4F010
Page 1013 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-30 ABS AND TCS
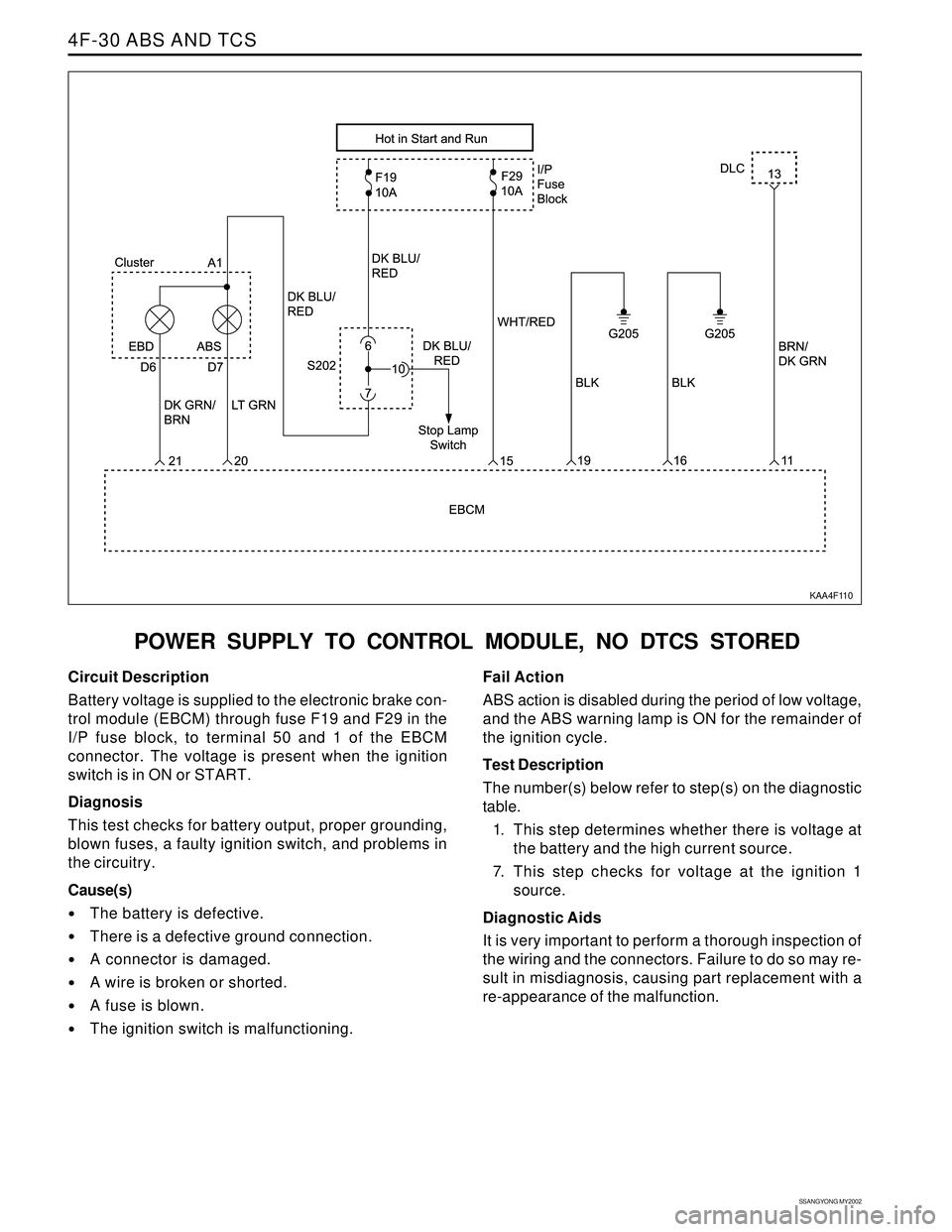
POWER SUPPLY TO CONTROL MODULE, NO DTCS STORED
KAA4F110
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied to the electronic brake con-
trol module (EBCM) through fuse F19 and F29 in the
I/P fuse block, to terminal 50 and 1 of the EBCM
connector. The voltage is present when the ignition
switch is in ON or START.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, a faulty ignition switch, and problems in
the circuitry.
Cause(s)
The battery is defective.
There is a defective ground connection.
A connector is damaged.
A wire is broken or shorted.
A fuse is blown.
The ignition switch is malfunctioning.Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,
and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of
the ignition cycle.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may re-
sult in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a
re-appearance of the malfunction.
Page 1067 of 2053
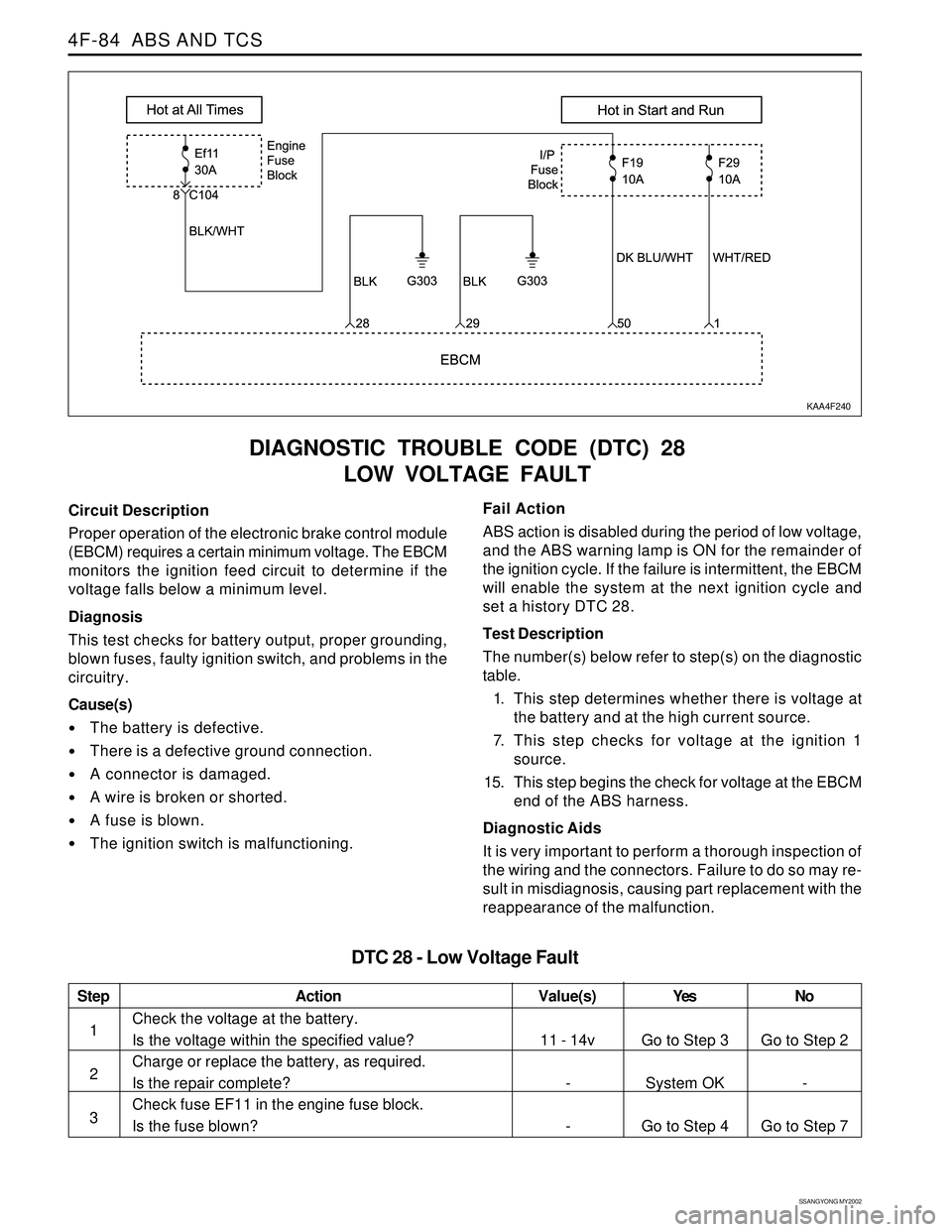
SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-84 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 28
LOW VOLTAGE FAULT
KAA4F240
Circuit Description
Proper operation of the electronic brake control module
(EBCM) requires a certain minimum voltage. The EBCM
monitors the ignition feed circuit to determine if the
voltage falls below a minimum level.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, faulty ignition switch, and problems in the
circuitry.
Cause(s)
The battery is defective.
There is a defective ground connection.
A connector is damaged.
A wire is broken or shorted.
A fuse is blown.
The ignition switch is malfunctioning.Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,
and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of
the ignition cycle. If the failure is intermittent, the EBCM
will enable the system at the next ignition cycle and
set a history DTC 28.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and at the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
15. This step begins the check for voltage at the EBCM
end of the ABS harness.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may re-
sult in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the
reappearance of the malfunction.
Step
1
2
3
Action
Go to Step 3
System OK
Go to Step 4Go to Step 2
-
Go to Step 7 11 - 14v
-
-
Check the voltage at the battery.
Is the voltage within the specified value?
Charge or replace the battery, as required.
Is the repair complete?
Check fuse EF11 in the engine fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?
DTC 28 - Low Voltage Fault
Value(s) Yes No
Page 1082 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-99
SSANGYONG MY2002
REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
Caution: Brake Fluid may irritate eyes and skin. In
case of contact, take the following actions:
Eye contact - rinse thoroughly with water.
Skin contact - wash with soap and water.
Ingestion - consult a physician immediately.
Caution: To help avoid personal injury due to poor
braking. DO NOT Tap into the vehicle’s brake system
to operate a trailer brake system.
Notice: When fasteners are removed, always reinstall
them at the same location from which they were
removed. If a fastener needs to be replaced, use the
correct part number fastener for is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. Fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread-locking compound will be called out.
The correct torque values must be used when installing
fasteners that require them. If the above procedures
are not followed, parts or system damage could result.
Notice: Use only DOT-3 equivalent hydraulic brake
fluid. The use of DOT-5 (silicone) brake fluid is not
recommended. Reduced brake performance or
durability may result.
Notice: Avoid spilling brake fluid on any the vehicle’s
painted surfaces, wiring, cables or electrical
connectors. Brake fluid will damage paint and electrical
connections. If any fluid is spilled on the vehicle, flush
the area with water to lessen the damage.
Electronic System Service Precautions
Take care to avoid electronic brake control module
(EBCM) circuit overloading. In testing for opens or
shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any circuit
unless instructed to do so by the diagnostic procedure.
Test circuits only with a high-impedance multi-meter.
Never remove or apply power to any control module
with the ignition switch in the ON position. Always turn
the ignition to the OFF position before removing or
connecting battery cables, fuses or connectors.
General Service Precautions
Disconnect the EBCM connector before performing any
vehicle welding work using an electric arc welder.
Do not attempt to disassemble any component
designated as nonserviceable. The hydraulic modulator
and the EBCM can be separated from each other and
replaced separately but cannot be serviced. They have
no replaceable parts, and there is no replaceable parts,
and there is no access to the components they contain.
Bleeding System
Replacement modulators are shipped already filled
and bled. In normal procedures requiring removal of
the modulator, such as to replace the EBCM, air will
not enter the modulator, and normal bleeding will be
all that is needed.
If air enters the hydraulic modulator, or if an unfilled
modulator is installed, use the brake bleeding program
in the scan tool to bleed the modulator. Manual
bleeding of the hydraulic modulator is not possible.
Page 1679 of 2053
LIGHTING SYSTEM 9B-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURE
HEAD LAMPS
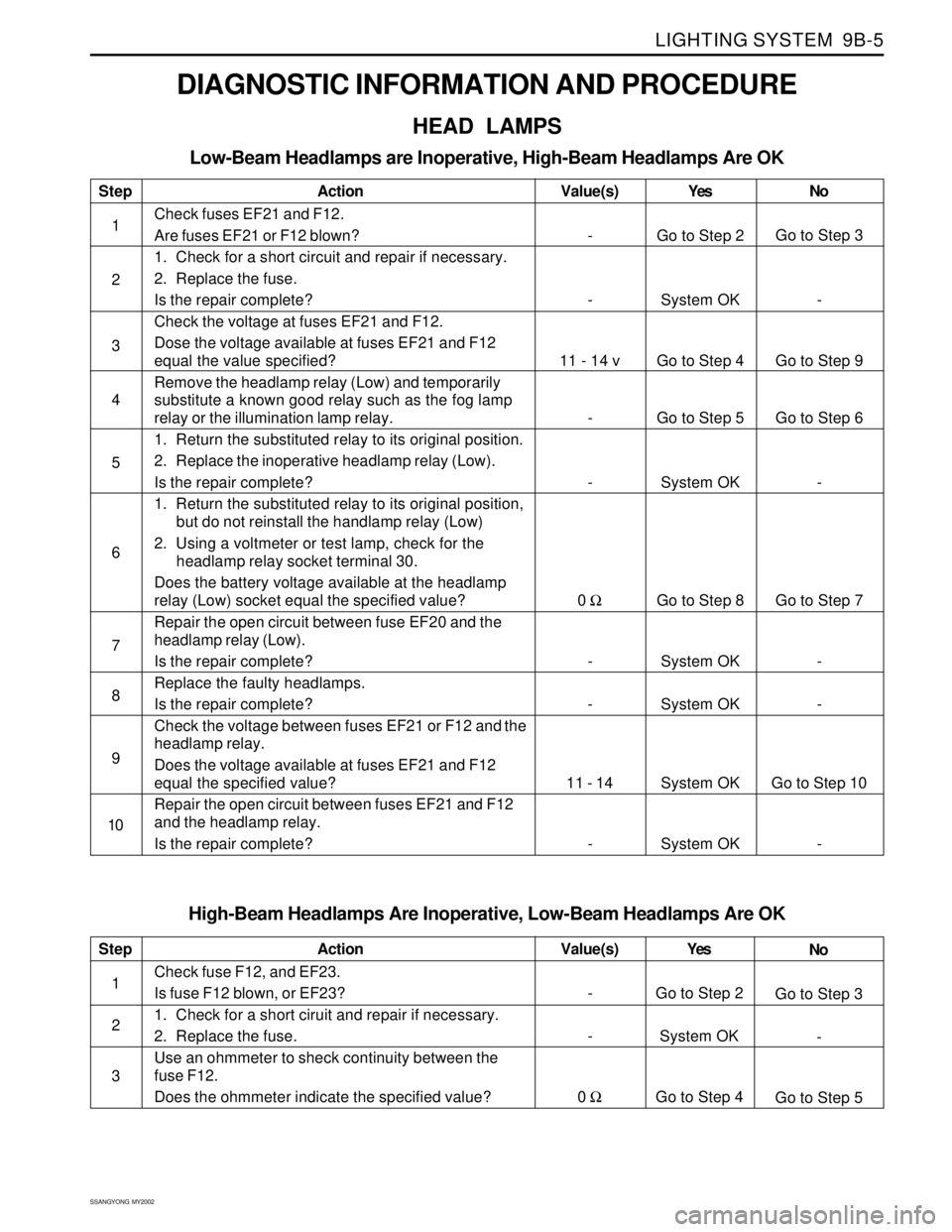
Low-Beam Headlamps are Inoperative, High-Beam Headlamps Are OK
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Action
Check fuses EF21 and F12.
Are fuses EF21 or F12 blown?
1. Check for a short circuit and repair if necessary.
2. Replace the fuse.
Is the repair complete?
Check the voltage at fuses EF21 and F12.
Dose the voltage available at fuses EF21 and F12
equal the value specified?
Remove the headlamp relay (Low) and temporarily
substitute a known good relay such as the fog lamp
relay or the illumination lamp relay.
1. Return the substituted relay to its original position.
2. Replace the inoperative headlamp relay (Low).
Is the repair complete?
1. Return the substituted relay to its original position,
but do not reinstall the handlamp relay (Low)
2. Using a voltmeter or test lamp, check for the
headlamp relay socket terminal 30.
Does the battery voltage available at the headlamp
relay (Low) socket equal the specified value?
Repair the open circuit between fuse EF20 and the
headlamp relay (Low).
Is the repair complete?
Replace the faulty headlamps.
Is the repair complete?
Check the voltage between fuses EF21 or F12 and the
headlamp relay.
Does the voltage available at fuses EF21 and F12
equal the specified value?
Repair the open circuit between fuses EF21 and F12
and the headlamp relay.
Is the repair complete?Yes
Go to Step 2
System OK
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
System OK
Go to Step 8
System OK
System OK
System OK
System OKNo
Go to Step 3
-
Go to Step 9
Go to Step 6
-
Go to Step 7
-
-
Go to Step 10
- Value(s)
-
-
11 - 14 v
-
-
0 Ω
-
-
11 - 14
-
High-Beam Headlamps Are Inoperative, Low-Beam Headlamps Are OK
Step
1
2
3Action
Check fuse F12, and EF23.
Is fuse F12 blown, or EF23?
1. Check for a short ciruit and repair if necessary.
2. Replace the fuse.
Use an ohmmeter to sheck continuity between the
fuse F12.
Does the ohmmeter indicate the specified value?Yes
Go to Step 2
System OK
Go to Step 4No
Go to Step 3
-
Go to Step 5 Value(s)
-
-
0 Ω
Page 1682 of 2053
SSANGYONG MY2002
9B-8 LIGHTING SYSTEM
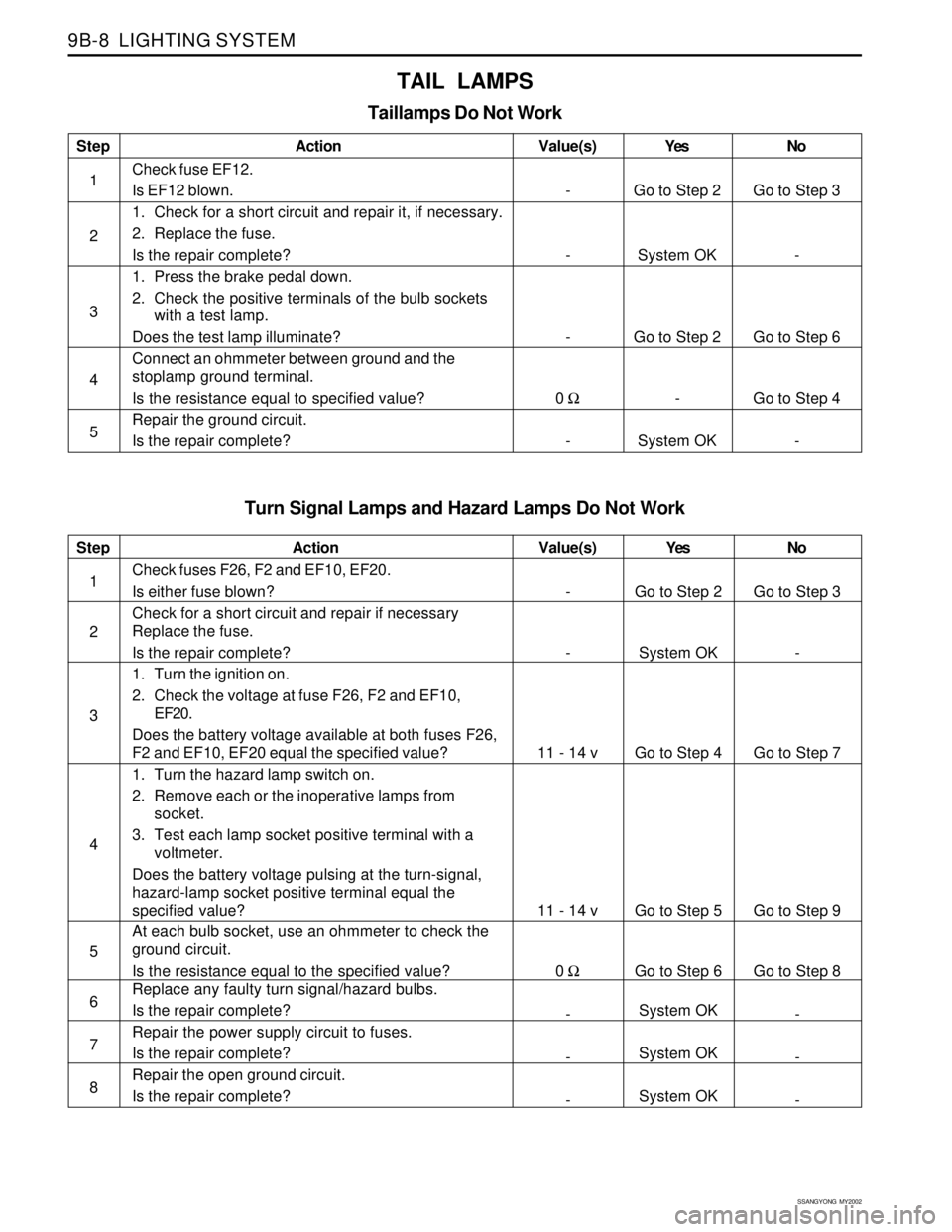
Turn Signal Lamps and Hazard Lamps Do Not Work
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8Action
Check fuses F26, F2 and EF10, EF20.
Is either fuse blown?
Check for a short circuit and repair if necessary
Replace the fuse.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition on.
2. Check the voltage at fuse F26, F2 and EF10,
EF20.
Does the battery voltage available at both fuses F26,
F2 and EF10, EF20 equal the specified value?
1. Turn the hazard lamp switch on.
2. Remove each or the inoperative lamps from
socket.
3. Test each lamp socket positive terminal with a
voltmeter.
Does the battery voltage pulsing at the turn-signal,
hazard-lamp socket positive terminal equal the
specified value?
At each bulb socket, use an ohmmeter to check the
ground circuit.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Replace any faulty turn signal/hazard bulbs.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the power supply circuit to fuses.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open ground circuit.
Is the repair complete?Yes
Go to Step 2
System OK
Go to Step 4
Go to Step 5
Go to Step 6
System OK
System OK
System OKNo
Go to Step 3
-
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 9
Go to Step 8
-
-
- Value(s)
-
-
11 - 14 v
11 - 14 v
0 Ω
-
-
-
TAIL LAMPS
Taillamps Do Not Work
Step
1
2
3
4
5Action
Check fuse EF12.
Is EF12 blown.
1. Check for a short circuit and repair it, if necessary.
2. Replace the fuse.
Is the repair complete?
1. Press the brake pedal down.
2. Check the positive terminals of the bulb sockets
with a test lamp.
Does the test lamp illuminate?
Connect an ohmmeter between ground and the
stoplamp ground terminal.
Is the resistance equal to specified value?
Repair the ground circuit.
Is the repair complete?Yes
Go to Step 2
System OK
Go to Step 2
-
System OKNo
Go to Step 3
-
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 4
- Value(s)
-
-
-
0 Ω
-
Page 1683 of 2053
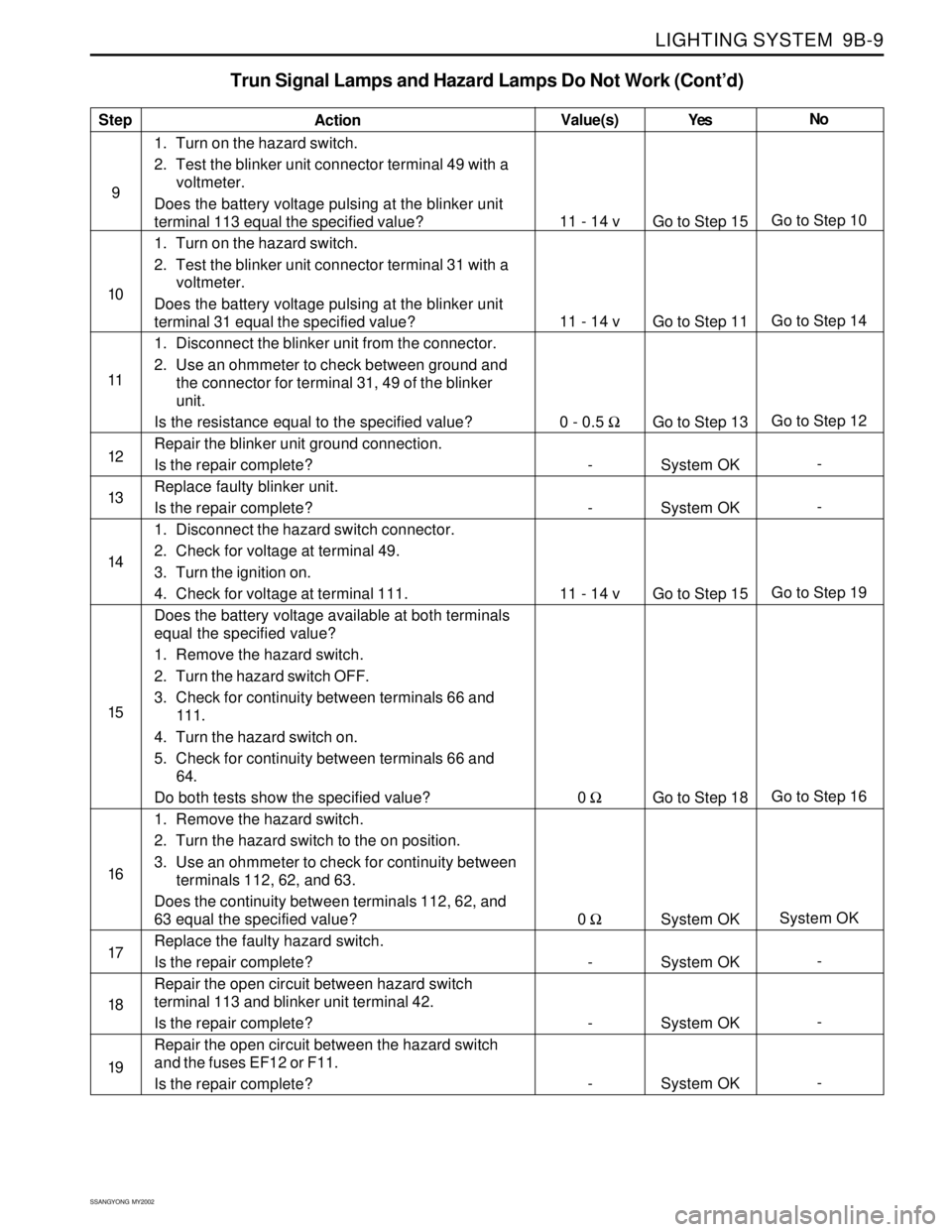
LIGHTING SYSTEM 9B-9
SSANGYONG MY2002
Trun Signal Lamps and Hazard Lamps Do Not Work (Cont’d)
Step
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19Action
1. Turn on the hazard switch.
2. Test the blinker unit connector terminal 49 with a
voltmeter.
Does the battery voltage pulsing at the blinker unit
terminal 113 equal the specified value?
1. Turn on the hazard switch.
2. Test the blinker unit connector terminal 31 with a
voltmeter.
Does the battery voltage pulsing at the blinker unit
terminal 31 equal the specified value?
1. Disconnect the blinker unit from the connector.
2. Use an ohmmeter to check between ground and
the connector for terminal 31, 49 of the blinker
unit.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the blinker unit ground connection.
Is the repair complete?
Replace faulty blinker unit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the hazard switch connector.
2. Check for voltage at terminal 49.
3. Turn the ignition on.
4. Check for voltage at terminal 111.
Does the battery voltage available at both terminals
equal the specified value?
1. Remove the hazard switch.
2. Turn the hazard switch OFF.
3. Check for continuity between terminals 66 and
111.
4. Turn the hazard switch on.
5. Check for continuity between terminals 66 and
64.
Do both tests show the specified value?
1. Remove the hazard switch.
2. Turn the hazard switch to the on position.
3. Use an ohmmeter to check for continuity between
terminals 112, 62, and 63.
Does the continuity between terminals 112, 62, and
63 equal the specified value?
Replace the faulty hazard switch.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open circuit between hazard switch
terminal 113 and blinker unit terminal 42.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open circuit between the hazard switch
and the fuses EF12 or F11.
Is the repair complete?Yes
Go to Step 15
Go to Step 11
Go to Step 13
System OK
System OK
Go to Step 15
Go to Step 18
System OK
System OK
System OK
System OKNo
Go to Step 10
Go to Step 14
Go to Step 12
-
-
Go to Step 19
Go to Step 16
System OK
-
-
- Value(s)
11 - 14 v
11 - 14 v
0 - 0.5 Ω
-
-
11 - 14 v
0 Ω
0 Ω
-
-
-
Page 1684 of 2053
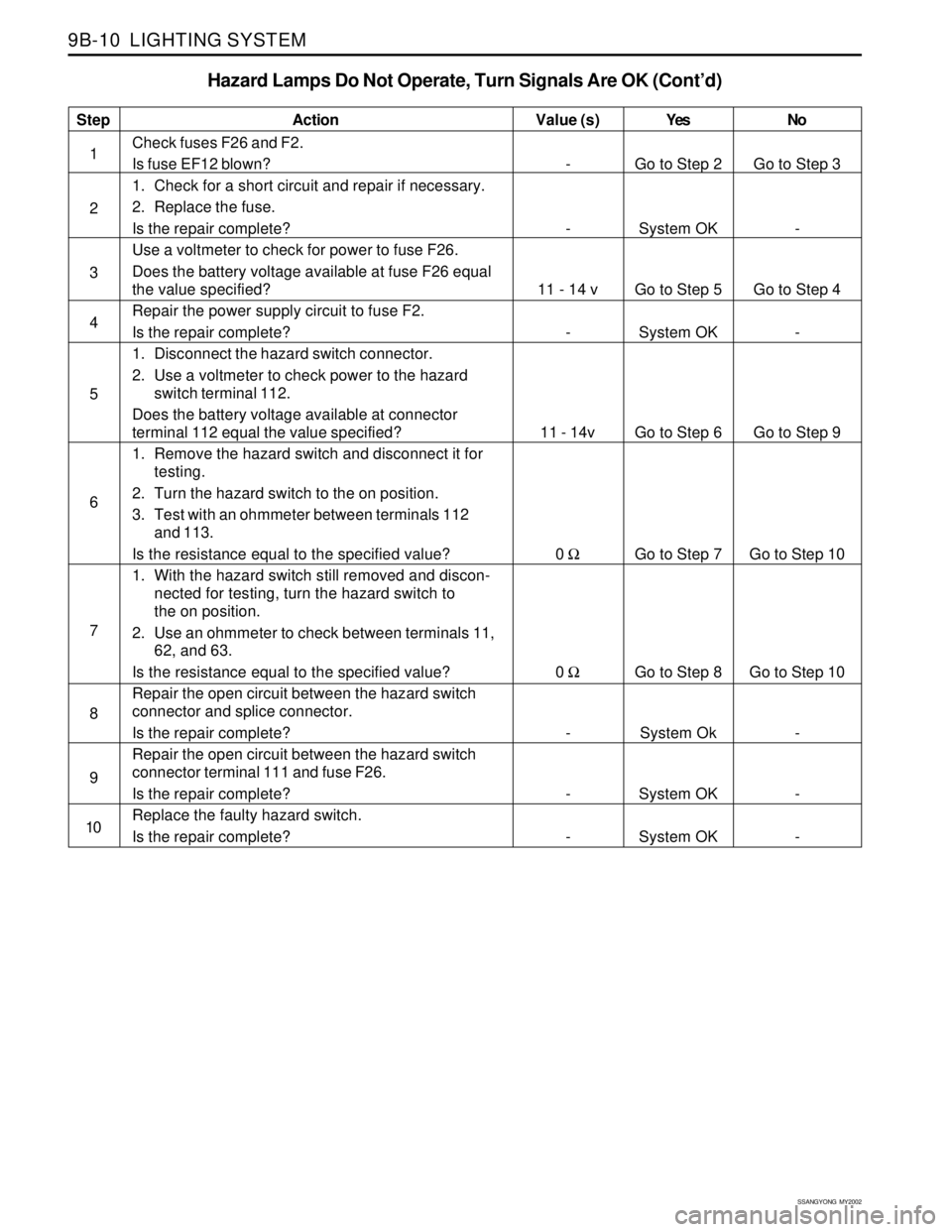
SSANGYONG MY2002
9B-10 LIGHTING SYSTEM
Hazard Lamps Do Not Operate, Turn Signals Are OK (Cont’d)
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Action
Check fuses F26 and F2.
Is fuse EF12 blown?
1. Check for a short circuit and repair if necessary.
2. Replace the fuse.
Is the repair complete?
Use a voltmeter to check for power to fuse F26.
Does the battery voltage available at fuse F26 equal
the value specified?
Repair the power supply circuit to fuse F2.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the hazard switch connector.
2. Use a voltmeter to check power to the hazard
switch terminal 112.
Does the battery voltage available at connector
terminal 112 equal the value specified?
1. Remove the hazard switch and disconnect it for
testing.
2. Turn the hazard switch to the on position.
3. Test with an ohmmeter between terminals 112
and 113.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
1. With the hazard switch still removed and discon-
nected for testing, turn the hazard switch to
the on position.
2. Use an ohmmeter to check between terminals 11,
62, and 63.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?
Repair the open circuit between the hazard switch
connector and splice connector.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open circuit between the hazard switch
connector terminal 111 and fuse F26.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the faulty hazard switch.
Is the repair complete?Yes
Go to Step 2
System OK
Go to Step 5
System OK
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 8
System Ok
System OK
System OKNo
Go to Step 3
-
Go to Step 4
-
Go to Step 9
Go to Step 10
Go to Step 10
-
-
- Value (s)
-
-
11 - 14 v
-
11 - 14v
0 Ω
0 Ω
-
-
-