1995 ACURA TL wheel torque
[x] Cancel search: wheel torquePage 257 of 1771

Description
The automatic transmission is a combination of a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with the engine.
Torque Converter, Gears and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine, and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the drive plate is a ring gear which
meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started.
The entire torque converter assembly serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in line with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 4th and 2nd clutches and gears for 4th, 1st, 2nd and reverse (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft). The countershaft includes the 3rd, 1st-hold and reverse clutches, and gears for 3rd, 4th, 1st, 2nd,
reverse and parking. The secondary drive gear is integrated with the countershaft. The gears on the mainshaft are in con-
stant mesh with those on the countershaft. When certain combinations of gears in the transmission are engaged by clutch-
positions.
and
es, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft to provide
Electronic Control
The electronic control system consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four solenoid
valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the throttle valve body, the lin-
ear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valves and the ATF passage body. They are bolted on the lower part of the trans-
mission housing. The regulator valve body, the ATF pump body, and the accumulator body are bolted to the torque con-
verter housing.
The main valve body on '96 model contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift valve, the
4-3 kick-down valve and the Clutch Pressure Control (CPC) valve. The main valve body on '97 model contains the manual
valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift valve, the 4-3 kick-down valve and the main orifice control valve.
The secondary valve body on '96 model contains the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4-3 shift timing valve, the modulator valve
and the accumulator pistons.The secondary valve body on '97 model contains the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4-3 shift tim-
ing valve, the line pressure control valve, the modulator valve and the accumulator pistons. The throttle valve body
includes the throttle valve which is bolted onto the secondary valve body. The linear solenoid is joined to the throttle valve
body. The regulator valve body contains the regulator valve, the lock-up shift valve and the cooler relief valve. Fluid from
the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The ATF pump body contains the lock-up tim-
ing valve, the lock-up control valve and the relief valve. The torque converter check valve is located in the torque converter
housing under the ATF pump body. The accumulator body contains the accumulator pistons. The reverse accumulator and
the 1st-hold accumulator pistons are assembled in the rear cover.
The 1st, 1st-hold, 2nd and reverse clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the 3rd and 4th clutches
receive fluid from the internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a
line to one of the clutches, engaging the clutch and its corresponding gear.
er through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the tim-
ing of the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B, and throttle valve. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
Lock-up Mechanism
In
position, in 2nd, 3rd, and 4th, and
position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque convert-ProCarManuals.com
Page 265 of 1771
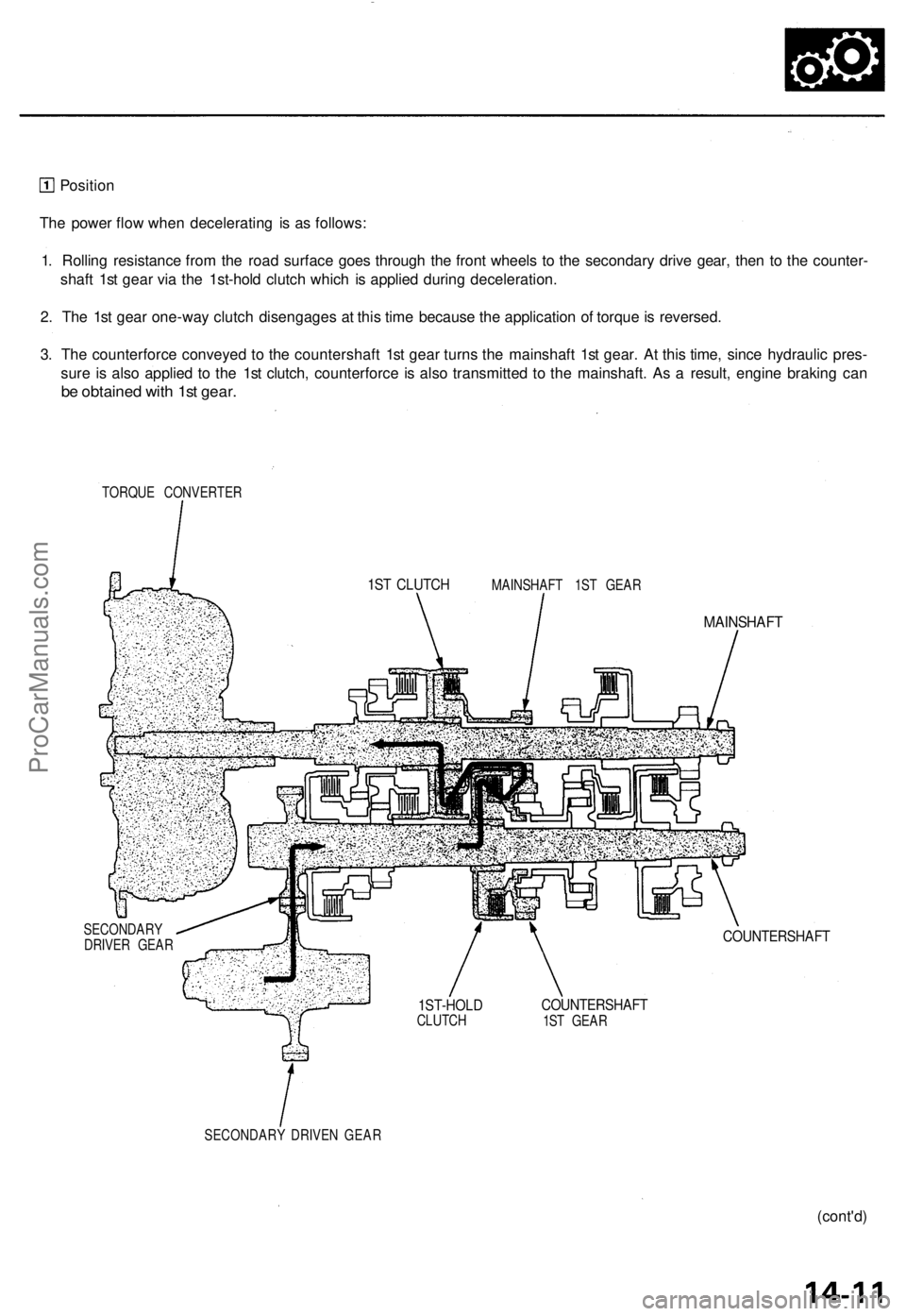
Position
The power flow when decelerating is as follows:
1. Rolling resistance from the road surface goes through the front wheels to the secondary drive gear, then to the counter-
shaft 1st gear via the 1st-hold clutch which is applied during deceleration.
2. The 1st gear one-way clutch disengages at this time because the application of torque is reversed.
3. The counterforce conveyed to the countershaft 1st gear turns the mainshaft 1st gear. At this time, since hydraulic pres-
sure is also applied to the 1st clutch, counterforce is also transmitted to the mainshaft. As a result, engine braking can
be obtained with 1st gear.
TORQUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT 1ST GEAR
MAINSHAFT
SECONDARY
DRIVER GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
1ST GEAR
SECONDARY DRIVEN GEAR
(cont'd)
1ST CLUTCH
1ST-HOLD
CLUTCHProCarManuals.com
Page 267 of 1771
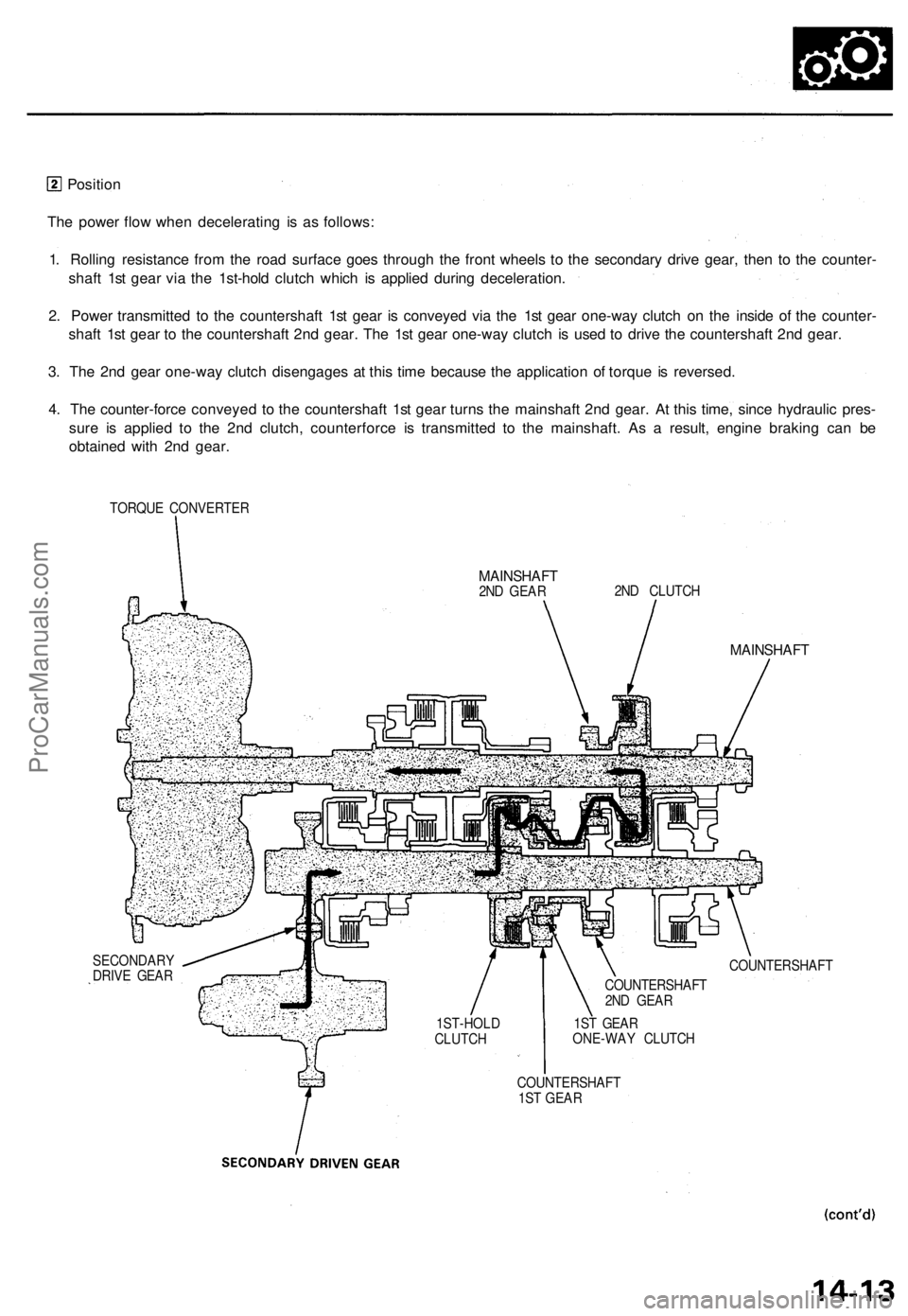
Position
The power flow when decelerating is as follows:
1. Rolling resistance from the road surface goes through the front wheels to the secondary drive gear, then to the counter-
shaft 1st gear via the 1st-hold clutch which is applied during deceleration.
2. Power transmitted to the countershaft 1st gear is conveyed via the 1st gear one-way clutch on the inside of the counter-
shaft 1st gear to the countershaft 2nd gear. The 1st gear one-way clutch is used to drive the countershaft 2nd gear.
3. The 2nd gear one-way clutch disengages at this time because the application of torque is reversed.
4. The counter-force conveyed to the countershaft 1st gear turns the mainshaft 2nd gear. At this time, since hydraulic pres-
sure is applied to the 2nd clutch, counterforce is transmitted to the mainshaft. As a result, engine braking can be
obtained with 2nd gear.
TORQUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT
2ND GEAR
2ND CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
SECONDARY
DRIVE GEAR
1ST-HOLD
CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
1ST GEAR
1ST GEAR
ONE-WAY CLUTCH
COUNTERSHAFT
2ND GEARProCarManuals.com
Page 329 of 1771
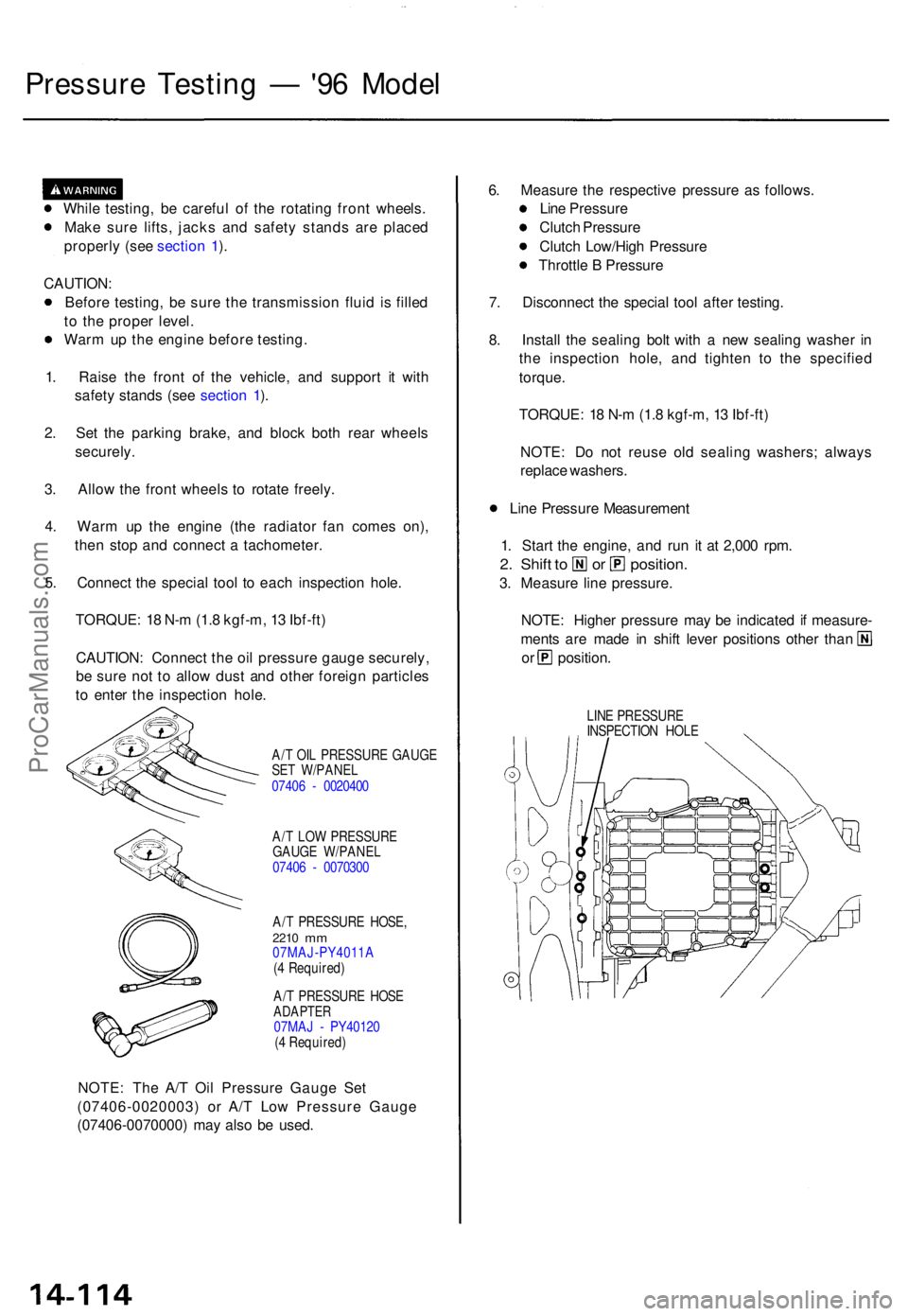
Pressure Testin g — '96 Mode l
While testing , b e carefu l o f th e rotatin g fron t wheels .
Mak e sur e lifts , jack s an d safet y stand s ar e place d
properl y (se e sectio n 1 ).
CAUTION :
Befor e testing , b e sur e th e transmissio n flui d i s fille d
t o th e prope r level .
War m u p th e engin e befor e testing .
1 . Rais e th e fron t o f th e vehicle , an d suppor t i t wit h
safet y stand s (se e sectio n 1 ).
2 . Se t th e parkin g brake , an d bloc k bot h rea r wheel s
securely .
3 . Allo w th e fron t wheel s t o rotat e freely .
4 . War m u p th e engin e (th e radiato r fa n come s on) ,
the n sto p an d connec t a tachometer .
5 . Connec t th e specia l too l t o eac h inspectio n hole .
TORQUE : 1 8 N- m (1. 8 kgf-m , 1 3 Ibf-ft )
CAUTION : Connec t th e oi l pressur e gaug e securely ,
b e sur e no t t o allo w dus t an d othe r foreig n particle s
t o ente r th e inspectio n hole .
A/T OI L PRESSUR E GAUG E
SE T W/PANE L
0740 6 - 002040 0
A/ T LO W PRESSUR E
GAUG E W/PANE L
0740 6 - 007030 0
A/ T PRESSUR E HOSE ,
2210 mm07MAJ-PY4011 A
( 4 Required )
A/ T PRESSUR E HOS E
ADAPTE R07MAJ - PY4012 0
( 4 Required )
NOTE: Th e A/ T Oi l Pressur e Gaug e Se t
(07406-0020003 ) o r A/ T Lo w Pressur e Gaug e
(07406-0070000 ) ma y als o b e used . 6
. Measur e th e respectiv e pressur e a s follows .
Lin e Pressur e
Clutc h Pressur e
Clutc h Low/Hig h Pressur e
Throttl e B Pressur e
7 . Disconnec t th e specia l too l afte r testing .
8 . Instal l th e sealin g bol t wit h a ne w sealin g washe r i n
th e inspectio n hole , an d tighte n t o th e specifie d
torque .
TORQUE : 1 8 N- m (1. 8 kgf-m , 1 3 Ibf-ft )
NOTE : D o no t reus e ol d sealin g washers ; alway s
replac e washers .
Lin e Pressur e Measuremen t
1 . Star t th e engine , an d ru n i t a t 2,00 0 rpm .
2. Shif t t o o r position .
3. Measur e lin e pressure .
NOTE : Highe r pressur e ma y b e indicate d if measure -
ments ar e mad e i n shif t leve r position s othe r tha n
or position .
LINE PRESSUR E
INSPECTIO N HOL E
ProCarManuals.com
Page 333 of 1771
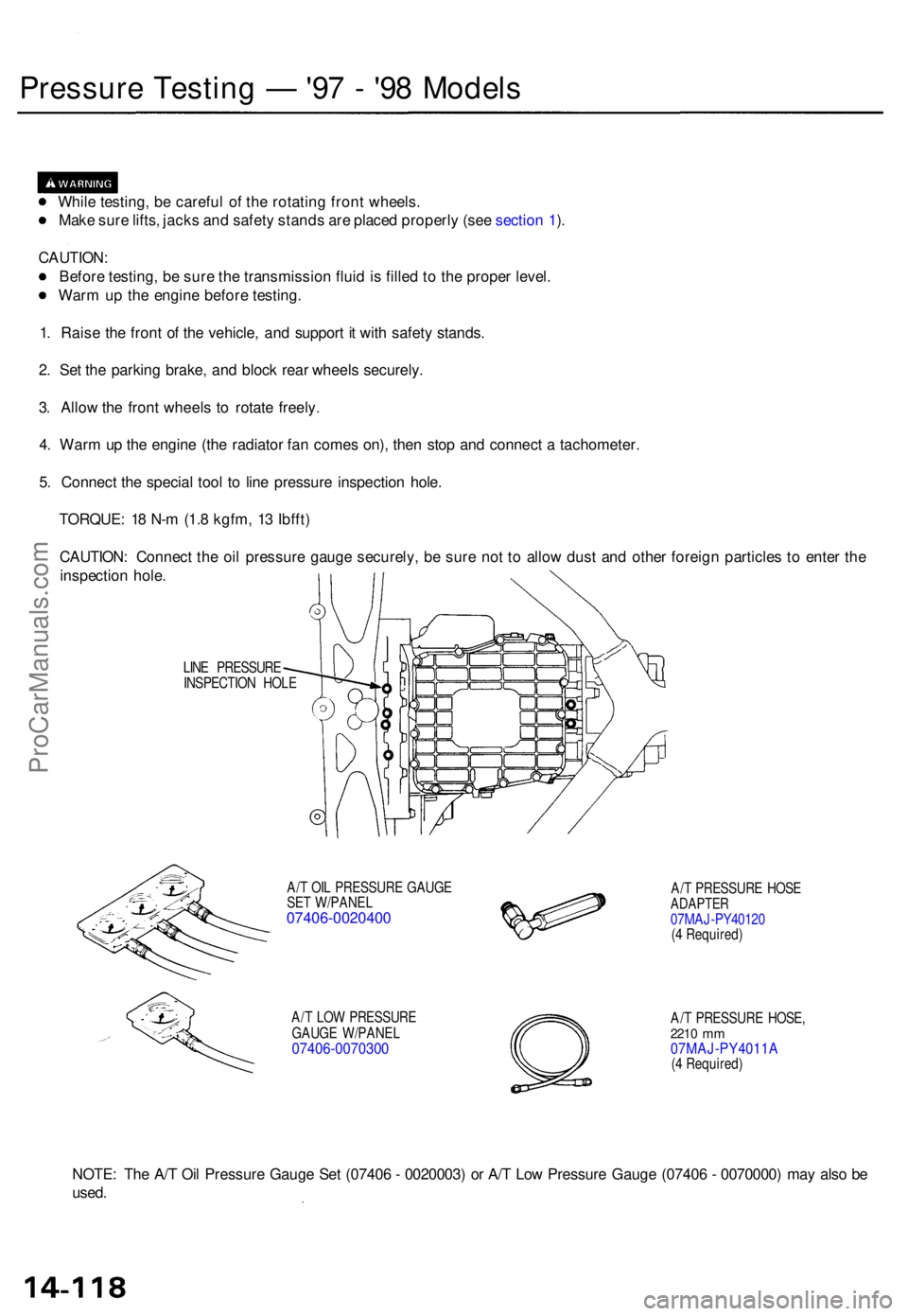
Pressure Testin g — '97 - '9 8 Model s
While testing , b e carefu l o f th e rotatin g fron t wheels .
Mak e sur e lifts , jack s an d safet y stand s ar e place d properl y (se e sectio n 1 ).
CAUTION :
Befor e testing , b e sur e th e transmissio n flui d is fille d to th e prope r level .
War m u p th e engin e befor e testing .
1 . Rais e th e fron t o f th e vehicle , an d suppor t i t wit h safet y stands .
2 . Se t th e parkin g brake , an d bloc k rea r wheel s securely .
3 . Allo w th e fron t wheel s t o rotat e freely .
4 . War m u p th e engin e (th e radiato r fa n come s on) , the n sto p an d connec t a tachometer .
5 . Connec t th e specia l too l t o lin e pressur e inspectio n hole .
TORQUE : 1 8 N- m (1. 8 kgfm , 1 3 Ibfft )
CAUTION : Connec t th e oi l pressur e gaug e securely , b e sur e no t t o allo w dus t an d othe r foreig n particle s t o ente r th e
inspectio n hole .
LINE PRESSUR E
INSPECTIO N HOL E
A/ T OI L PRESSUR E GAUG E
SE T W/PANE L
07406-0020400
A/T LO W PRESSUR E
GAUG E W/PANE L
07406-007030 0
A/T PRESSUR E HOS EADAPTE R07MAJ-PY4012 0
( 4 Required )
A/ T PRESSUR E HOSE ,
2210 mm07MAJ-PY4011 A(4 Required )
NOTE: Th e A/ T Oi l Pressur e Gaug e Se t (0740 6 - 0020003 ) o r A/ T Lo w Pressur e Gaug e (0740 6 - 0070000 ) ma y als o b e
used .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 488 of 1771
Steering Gearbo x
Installatio n (cont'd )
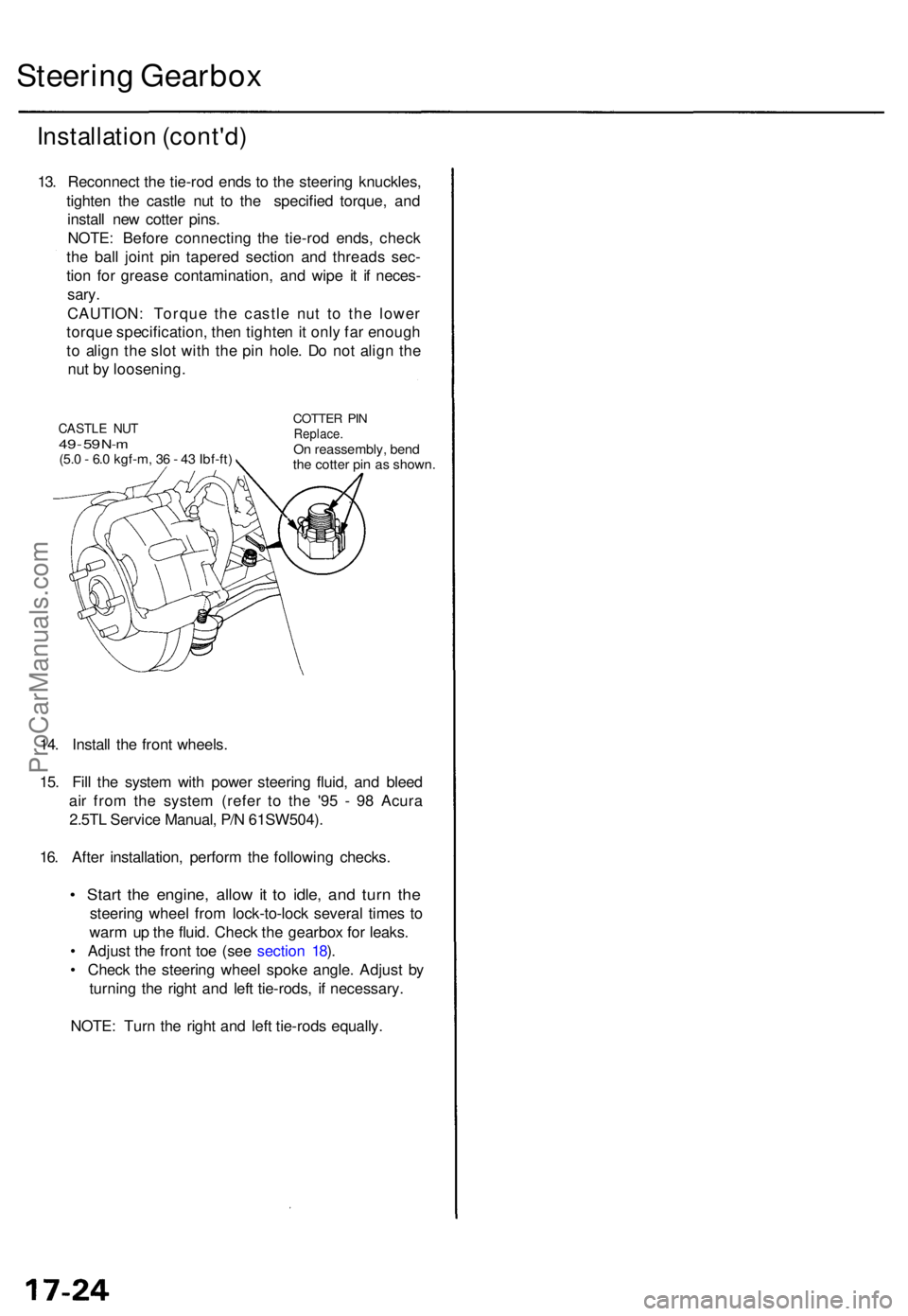
13. Reconnec t th e tie-ro d end s t o th e steerin g knuckles ,
tighte n th e castl e nu t t o th e specifie d torque , an d
instal l ne w cotte r pins .
NOTE : Befor e connectin g th e tie-ro d ends , chec k
th e bal l join t pi n tapere d sectio n an d thread s sec -
tio n fo r greas e contamination , an d wip e i t i f neces -
sary.
CAUTION : Torqu e th e castl e nu t t o th e lowe r
torqu e specification , the n tighte n it onl y fa r enoug h
t o alig n th e slo t wit h th e pi n hole . D o no t alig n th e
nu t b y loosening .
14 . Instal l th e fron t wheels .
15 . Fil l th e syste m wit h powe r steerin g fluid , an d blee d
ai r fro m th e syste m (refe r t o th e '9 5 - 9 8 Acur a
2.5T L Servic e Manual , P/ N 61SW504) .
16 . Afte r installation , perfor m th e followin g checks .
• Star t th e engine , allo w it t o idle , an d tur n th e
steerin g whee l fro m lock-to-loc k severa l time s t o
war m u p th e fluid . Chec k th e gearbo x fo r leaks .
• Adjus t th e fron t to e (se e sectio n 18 ).
• Chec k th e steerin g whee l spok e angle . Adjus t b y
turning the righ t an d lef t tie-rods , i f necessary .
NOTE : Tur n th e righ t an d lef t tie-rod s equally .
CASTLE NU T49 - 5 9 N- m(5. 0 - 6. 0 kgf-m , 3 6 - 4 3 Ibf-ft )
COTTE R PI NReplace .On reassembly , ben d
th e cotte r pi n a s shown .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 493 of 1771
Torque Specification s
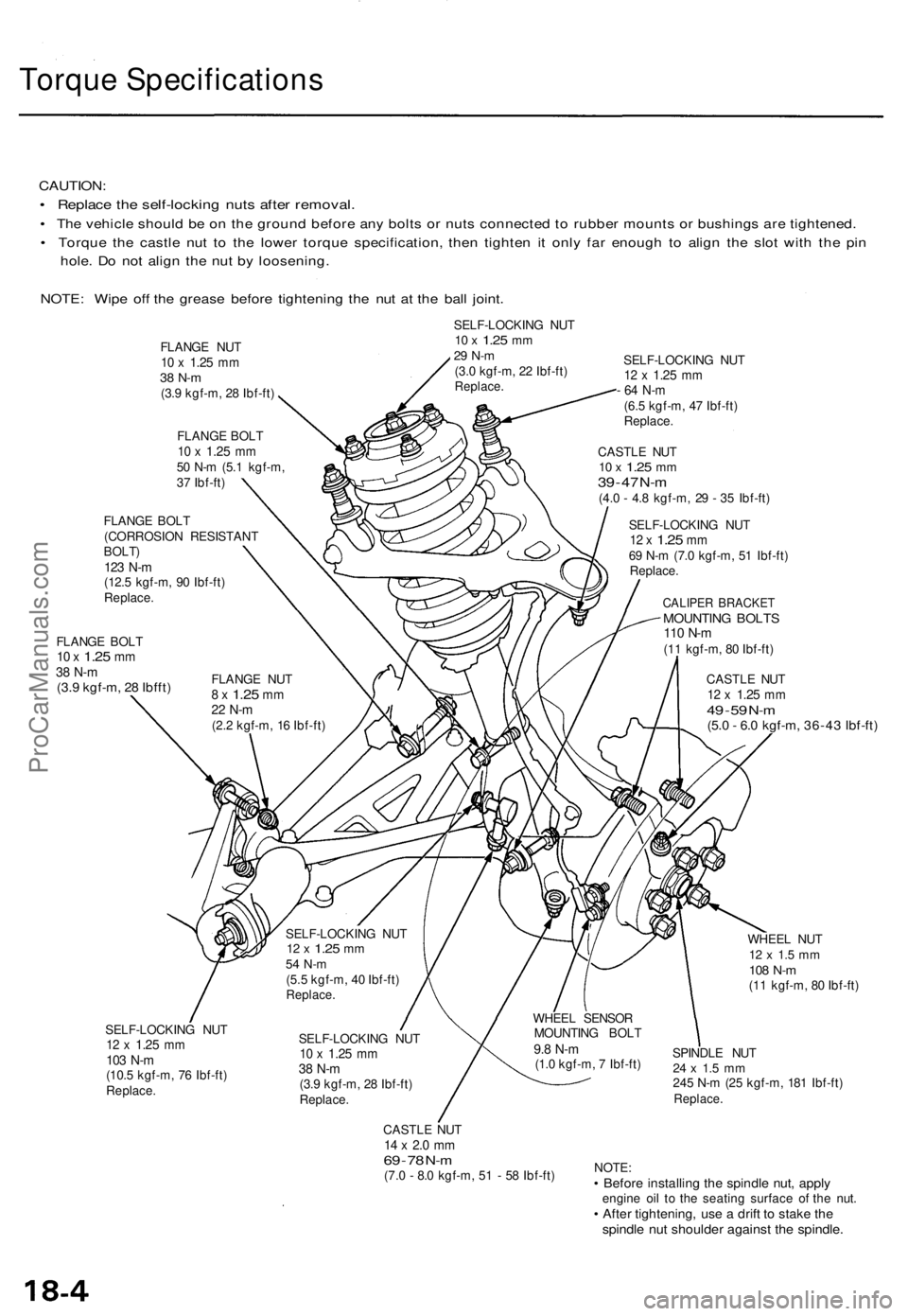
CAUTION:
• Replac e th e self-lockin g nut s afte r removal .
• Th e vehicl e shoul d b e o n th e groun d befor e an y bolt s o r nut s connecte d t o rubbe r mount s o r bushing s ar e tightened .
• Torqu e th e castl e nu t t o th e lowe r torqu e specification , the n tighte n i t onl y fa r enoug h t o alig n th e slo t wit h th e pi n
hole . D o no t alig n th e nu t b y loosening .
NOTE : Wip e of f th e greas e befor e tightenin g th e nu t a t th e bal l joint .
SELF-LOCKIN G NU T10 x 1.2 5 mm29 N- m(3.0 kgf-m , 2 2 Ibf-ft )Replace .
FLANGE BOL T10 x 1.2 5 mm38 N- m(3.9 kgf-m , 2 8 Ibfft )
SELF-LOCKIN G NU T12 x 1.2 5 mm
- 6 4 N- m
(6.5 kgf-m , 4 7 Ibf-ft )Replace .
CASTLE NU T10 x 1.2 5 mm39 - 4 7 N- m(4. 0 - 4. 8 kgf-m , 2 9 - 3 5 Ibf-ft )
SELF-LOCKIN G NU T
12 x 1.2 5 mm69 N- m (7. 0 kgf-m , 5 1 Ibf-ft )
Replace .
CALIPER BRACKE TMOUNTING BOLT S110 N- m(11 kgf-m , 8 0 Ibf-ft )
CASTL E NU T
12 x 1.2 5 mm49 - 5 9 N- m(5. 0 - 6. 0 kgf-m , 36-4 3 Ibf-ft )
SELF-LOCKIN G NU T12 x 1.2 5 mm103 N- m(10. 5 kgf-m , 7 6 Ibf-ft )Replace .
SELF-LOCKIN G NU T10 x 1.2 5 mm38 N- m(3.9 kgf-m , 2 8 Ibf-ft )Replace .
CASTLE NU T14 x 2. 0 m m69 - 7 8 N- m(7. 0 - 8. 0 kgf-m , 5 1 - 5 8 Ibf-ft ) WHEE
L NU T
12 x 1. 5 m m108 N- m(11 kgf-m , 8 0 Ibf-ft )
SPINDL E NU T
24 x 1. 5 m m245 N- m (2 5 kgf-m , 18 1 Ibf-ft )Replace .
NOTE:• Befor e installin g th e spindl e nut , appl yengin e oi l t o th e seatin g surfac e o f th e nut .• Afte r tightening , us e a drif t t o stak e th espindl e nu t shoulde r agains t th e spindle .
FLANGE NU T10 x 1.2 5 mm38 N- m(3.9 kgf-m , 2 8 Ibf-ft )
FLANG E BOL T
10 x 1.2 5 mm50 N- m (5. 1 kgf-m ,
3 7 Ibf-ft )
FLANG E NU T
8 x 1.2 5 mm22 N- m(2.2 kgf-m , 1 6 Ibf-ft )
FLANG
E BOL T
(CORROSIO N RESISTAN T
BOLT)123 N- m(12. 5 kgf-m , 9 0 Ibf-ft )Replace .
WHEEL SENSO R
MOUNTIN G BOL T
9.8 N- m(1.0 kgf-m , 7 Ibf-ft )
SELF-LOCKIN
G NU T
12 x 1.2 5 mm54 N- m(5.5 kgf-m , 4 0 Ibf-ft )Replace .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 585 of 1771

Check for Wear and Damage
The starter should crank the engine smoothly and steadily.
If the starter engages, but cranks the engine erratically,
remove it, and inspect the starter drive gear and torque
converter ring gear for damage.
• Check the drive gear overrunning clutch for binding
or slipping when the armature is rotated with the
drive gear held. If the clutch is damaged, replace the
clutch assembly.
Check Cranking Voltage and Current Draw
Cranking voltage should be no less than 8.0 volts.
Current draw should be no more than 450 amperes.
If cranking voltage is too low, or current draw too high,
check for:
Dead or low battery
Open circuit in starter armature commutator segments
Starter armature dragging
Shorted armature winding
Excessive drag in engine
Check Cranking rpm
Engine speed during cranking should be above 100 rpm.
If speed is too low, check for:
Loose battery or starter terminals
Excessively worn starter brushes
Open circuit in commutator segments
Dirty or damaged helical spline or drive gear
Defective drive gear overrunning clutch
Check Starter Disengagement
With the shift lever in or , turn the ignition switch to
"START (III)", and release to "ON (II)". The starter drive
gear should disengage from the flywheel ring gear when
you release the key.
If the drive gear hangs upon the flywheel ring gear, check
for:
• Solenoid plunger and switch malfunction
• Dirty drive gear assembly or damaged overrunning
clutchProCarManuals.com