1995 ACURA TL sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 251 of 1771
Emission Control System
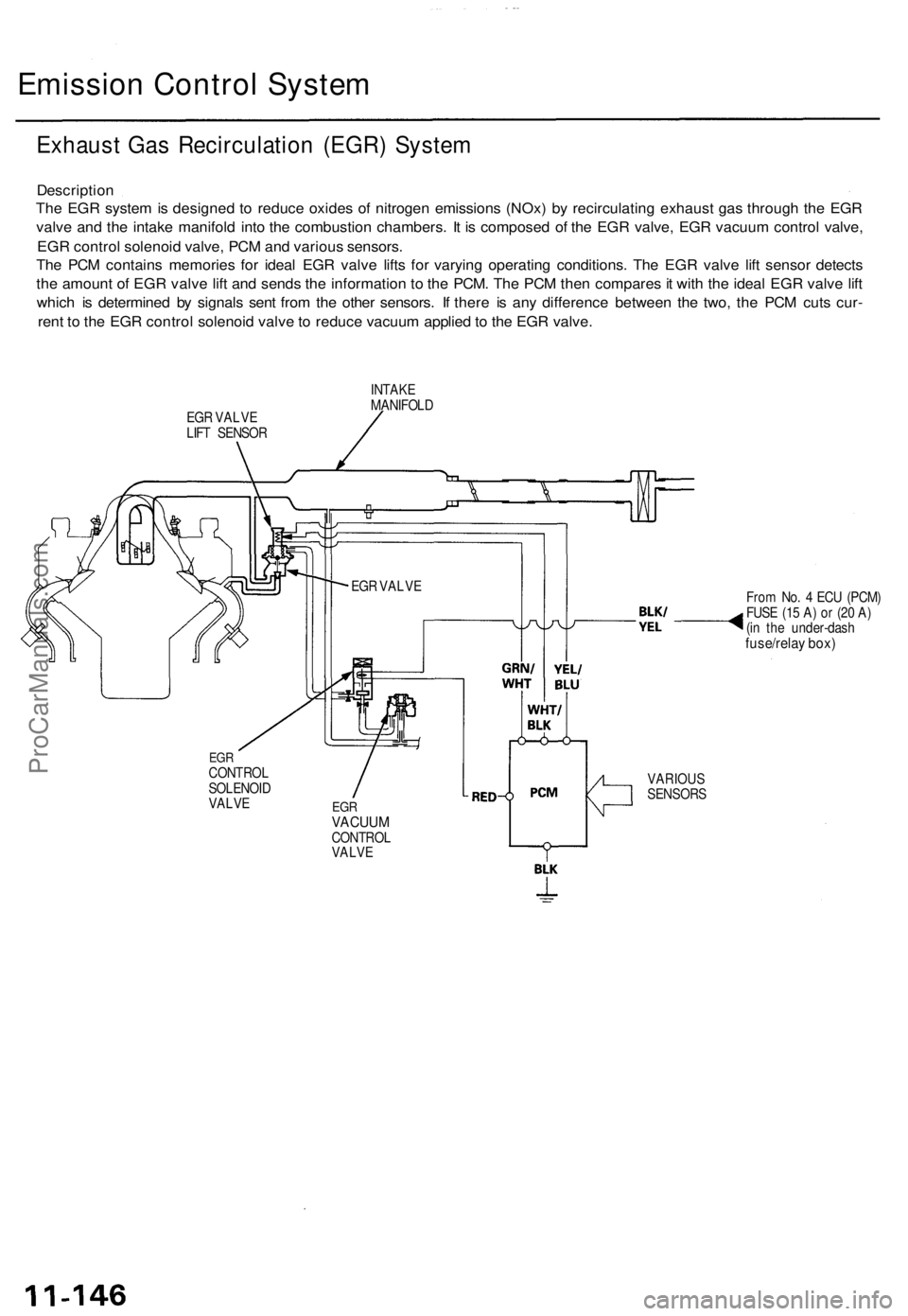
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
Description
The EGR system is designed to reduce oxides of nitrogen emissions (NOx) by recirculating exhaust gas through the EGR
valve and the intake manifold into the combustion chambers. It is composed of the EGR valve, EGR vacuum control valve,
EGR control solenoid valve, PCM and various sensors.
The PCM contains memories for ideal EGR valve lifts for varying operating conditions. The EGR valve lift sensor detects
the amount of EGR valve lift and sends the information to the PCM. The PCM then compares it with the ideal EGR valve lift
which is determined by signals sent from the other sensors. If there is any difference between the two, the PCM cuts cur-
rent to the EGR control solenoid valve to reduce vacuum applied to the EGR valve.
EGR VALVE
LIFT SENSOR
INTAKE
MANIFOLD
From No. 4 ECU (PCM)
FUSE (15 A) or (20 A)
(in the under-dash
fuse/relay box)
EGR
CONTROL
SOLENOID
VALVE
EGR
VACUUM
CONTROL
VALVE
VARIOUS
SENSORS
EGR VALVEProCarManuals.com
Page 253 of 1771
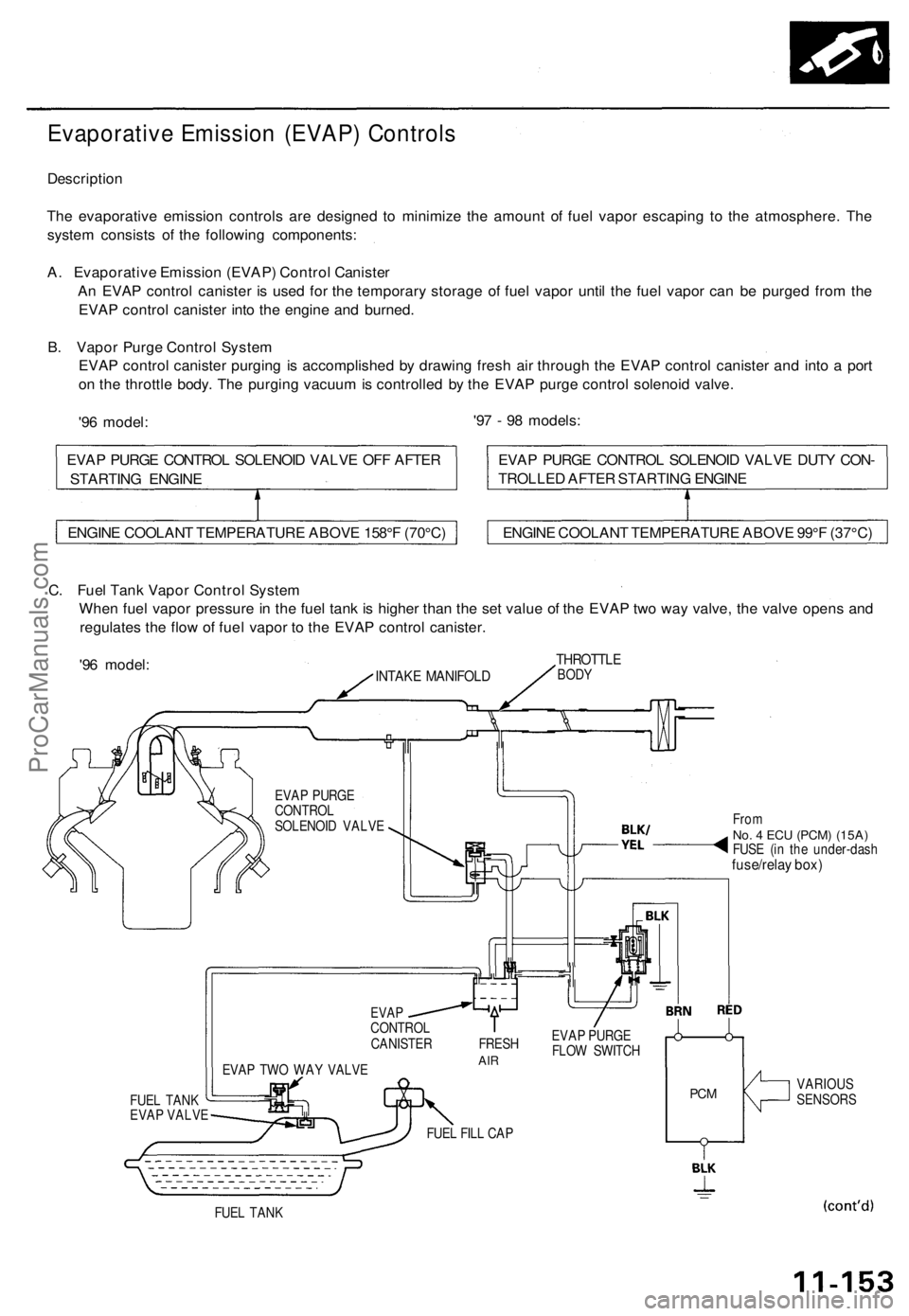
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls
Description
The evaporative emission controls are designed to minimize the amount of fuel vapor escaping to the atmosphere. The
system consists of the following components:
A. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control Canister
An EVAP control canister is used for the temporary storage of fuel vapor until the fuel vapor can be purged from the
EVAP control canister into the engine and burned.
B. Vapor Purge Control System
EVAP control canister purging is accomplished by drawing fresh air through the EVAP control canister and into a port
on the throttle body. The purging vacuum is controlled by the EVAP purge control solenoid valve.
'96 model:
'97 - 98 models:
C. Fuel Tank Vapor Control System
When fuel vapor pressure in the fuel tank is higher than the set value of the EVAP two way valve, the valve opens and
regulates the flow of fuel vapor to the EVAP control canister.
'96 model:
INTAKE MANIFOLD
THROTTLE
BODY
EVAP PURGE
CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
FUEL TANK
EVAP VALVE
EVAP TWO WAY VALVE
From
No. 4 ECU
(PCM) (15A)
FUSE (in the under-dash
fuse/relay box)
EVAP
CONTROL
CANISTER FRESH
AIR
EVAP PURGE
FLOW SWITCH
FUEL FILL CAP
PCM
VARIOUS
SENSORS
FUEL TANK
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE ABOVE 158°F (70°C)
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE ABOVE 99°F (37°C)
EVAP PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE DUTY CON-
TROLLED AFTER STARTING ENGINE
EVAP PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE OFF AFTER
STARTING ENGINEProCarManuals.com
Page 254 of 1771
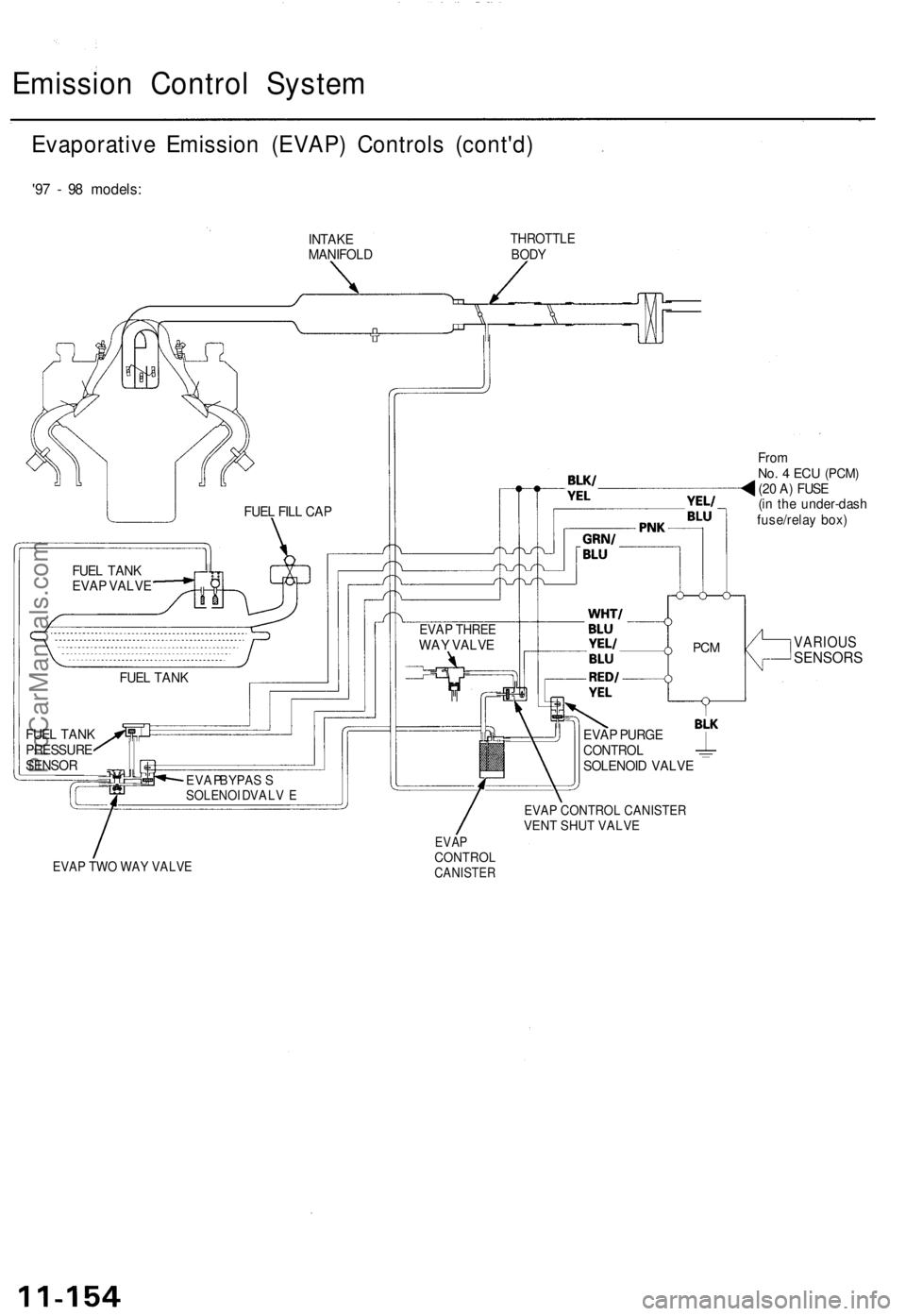
Emission Contro l Syste m
Evaporativ e Emissio n (EVAP ) Control s (cont'd )
'97 - 9 8 models :
INTAKE
MANIFOL DTHROTTL EBODY
FromNo. 4 EC U (PCM )(20 A ) FUS E
(i n th e under-das h
fuse/rela y box )
EVAP CONTROL CANISTERVENT SHUT VALVE
EVAP TWO WAY VALVE
EVAPCONTROLCANISTER
VARIOU SSENSOR S
EVAP BYPAS SSOLENOI D VALV E
FUEL TAN K
FUE L TAN K
PRESSUR E
SENSO RFUE
L TAN K
EVA P VALV E FUE
L FIL L CA P
PCM
EVA P PURG ECONTRO LSOLENOI D VALV E
EVAP THRE EWAY VALV E
ProCarManuals.com
Page 257 of 1771

Description
The automatic transmission is a combination of a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with the engine.
Torque Converter, Gears and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine, and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the drive plate is a ring gear which
meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started.
The entire torque converter assembly serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in line with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 4th and 2nd clutches and gears for 4th, 1st, 2nd and reverse (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft). The countershaft includes the 3rd, 1st-hold and reverse clutches, and gears for 3rd, 4th, 1st, 2nd,
reverse and parking. The secondary drive gear is integrated with the countershaft. The gears on the mainshaft are in con-
stant mesh with those on the countershaft. When certain combinations of gears in the transmission are engaged by clutch-
positions.
and
es, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft to provide
Electronic Control
The electronic control system consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four solenoid
valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the throttle valve body, the lin-
ear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valves and the ATF passage body. They are bolted on the lower part of the trans-
mission housing. The regulator valve body, the ATF pump body, and the accumulator body are bolted to the torque con-
verter housing.
The main valve body on '96 model contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift valve, the
4-3 kick-down valve and the Clutch Pressure Control (CPC) valve. The main valve body on '97 model contains the manual
valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift valve, the 4-3 kick-down valve and the main orifice control valve.
The secondary valve body on '96 model contains the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4-3 shift timing valve, the modulator valve
and the accumulator pistons.The secondary valve body on '97 model contains the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4-3 shift tim-
ing valve, the line pressure control valve, the modulator valve and the accumulator pistons. The throttle valve body
includes the throttle valve which is bolted onto the secondary valve body. The linear solenoid is joined to the throttle valve
body. The regulator valve body contains the regulator valve, the lock-up shift valve and the cooler relief valve. Fluid from
the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The ATF pump body contains the lock-up tim-
ing valve, the lock-up control valve and the relief valve. The torque converter check valve is located in the torque converter
housing under the ATF pump body. The accumulator body contains the accumulator pistons. The reverse accumulator and
the 1st-hold accumulator pistons are assembled in the rear cover.
The 1st, 1st-hold, 2nd and reverse clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the 3rd and 4th clutches
receive fluid from the internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a
line to one of the clutches, engaging the clutch and its corresponding gear.
er through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the tim-
ing of the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B, and throttle valve. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
Lock-up Mechanism
In
position, in 2nd, 3rd, and 4th, and
position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque convert-ProCarManuals.com
Page 273 of 1771
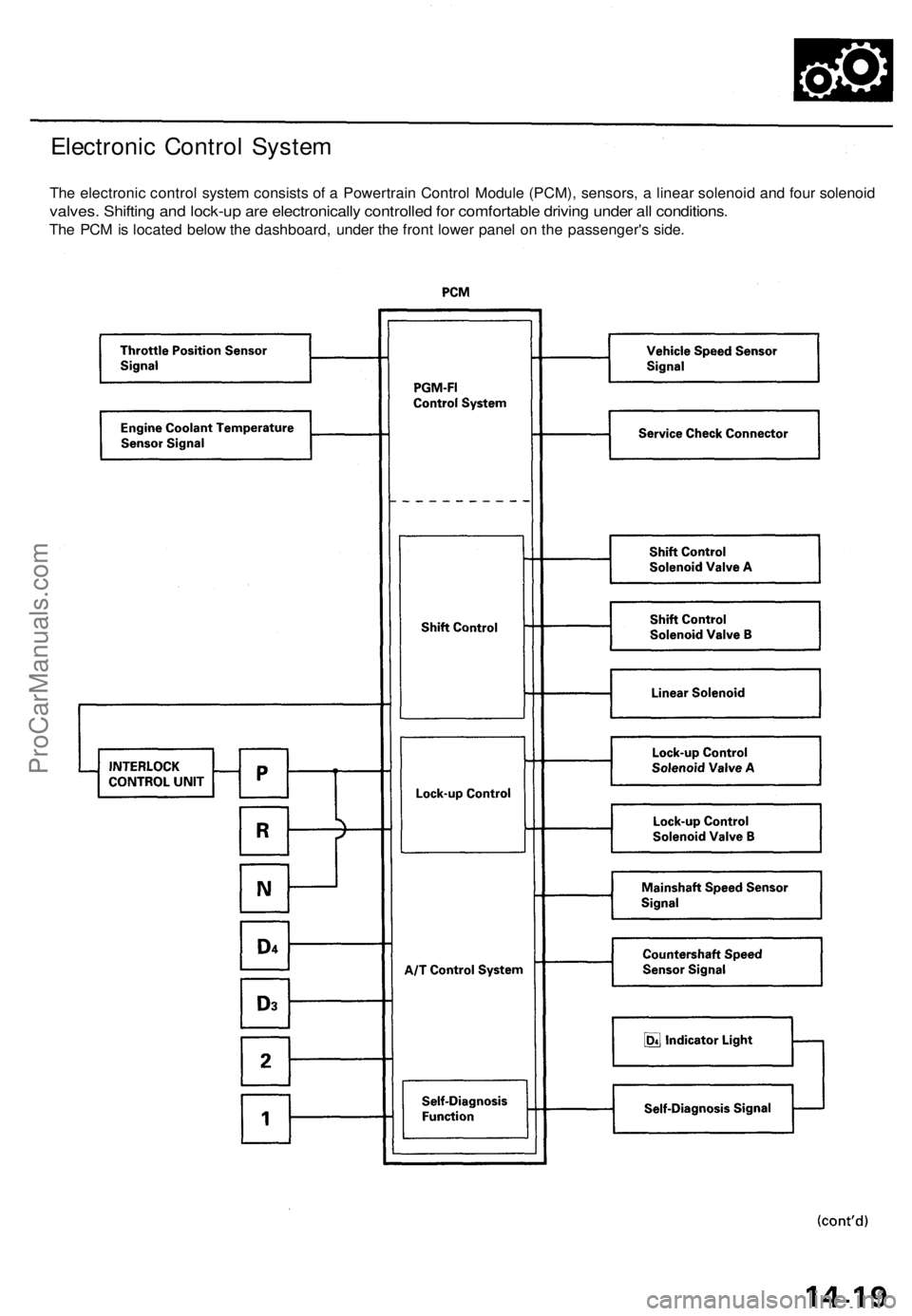
Electronic Control System
The electronic control system consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four solenoid
valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side.ProCarManuals.com
Page 274 of 1771
Description
Electronic Contro l Syste m (cont'd )
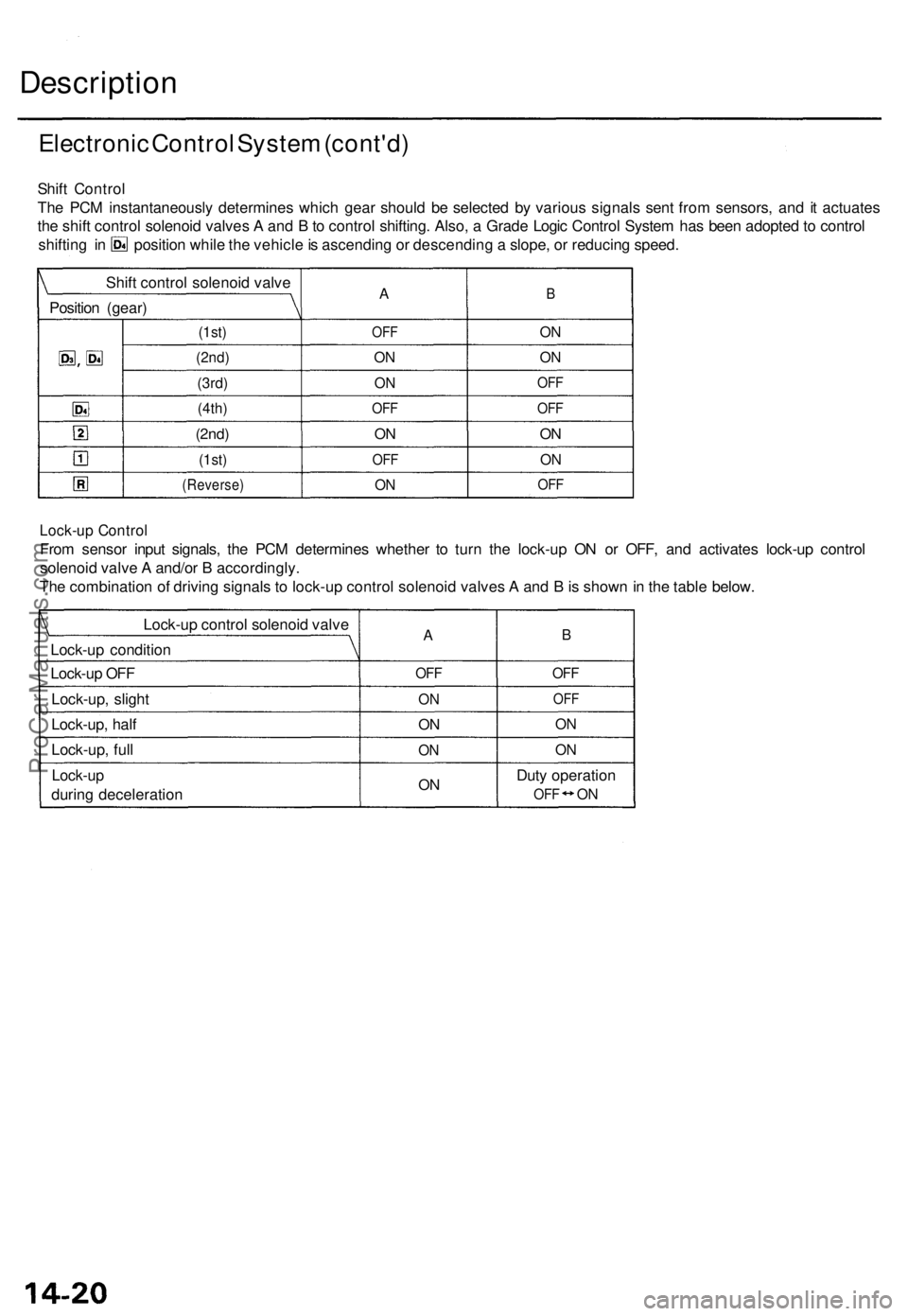
Lock-up Contro l
From senso r inpu t signals , th e PC M determine s whethe r t o tur n th e lock-u p O N o r OFF , an d activate s lock-u p contro l
solenoi d valv e A and/o r B accordingly .
Th e combinatio n o f drivin g signal s t o lock-u p contro l solenoi d valve s A an d B is show n in th e tabl e below .
Shif
t Contro l
Th e PC M
instantaneously determine s whic h gea r shoul d b e selecte d b y variou s signal s sen t fro m sensors , an d i t actuate s
th e shif t contro l solenoi d valve s A an d B to contro l shifting . Also , a Grad e Logi c Contro l Syste m ha s bee n adopte d to contro l
shifting in positio n whil e th e vehicl e is ascendin g o r descendin g a slope , o r reducin g speed .
Shif t contro l solenoi d valv e
Positio n (gear )
(1st)
A
OFF
(2nd )
(3rd)
(4th)
(2nd )
(1st)
(Reverse )
ON
O N
OF F
ON
OF F
ON
B
O N
O N
OF F
OF F
ON
O N
OF F
Dut y operatio n
ONOF FON
O N
AB
OF F
OF F
ON
O N
OF F
ON
ON
Lock-u p contro l solenoi d valv e
Lock-u p conditio n
Lock-u p OF F
Lock-up , sligh t
Lock-up , hal f
Lock-up , ful l
Lock-u p
during deceleratio n
ProCarManuals.com
Page 275 of 1771
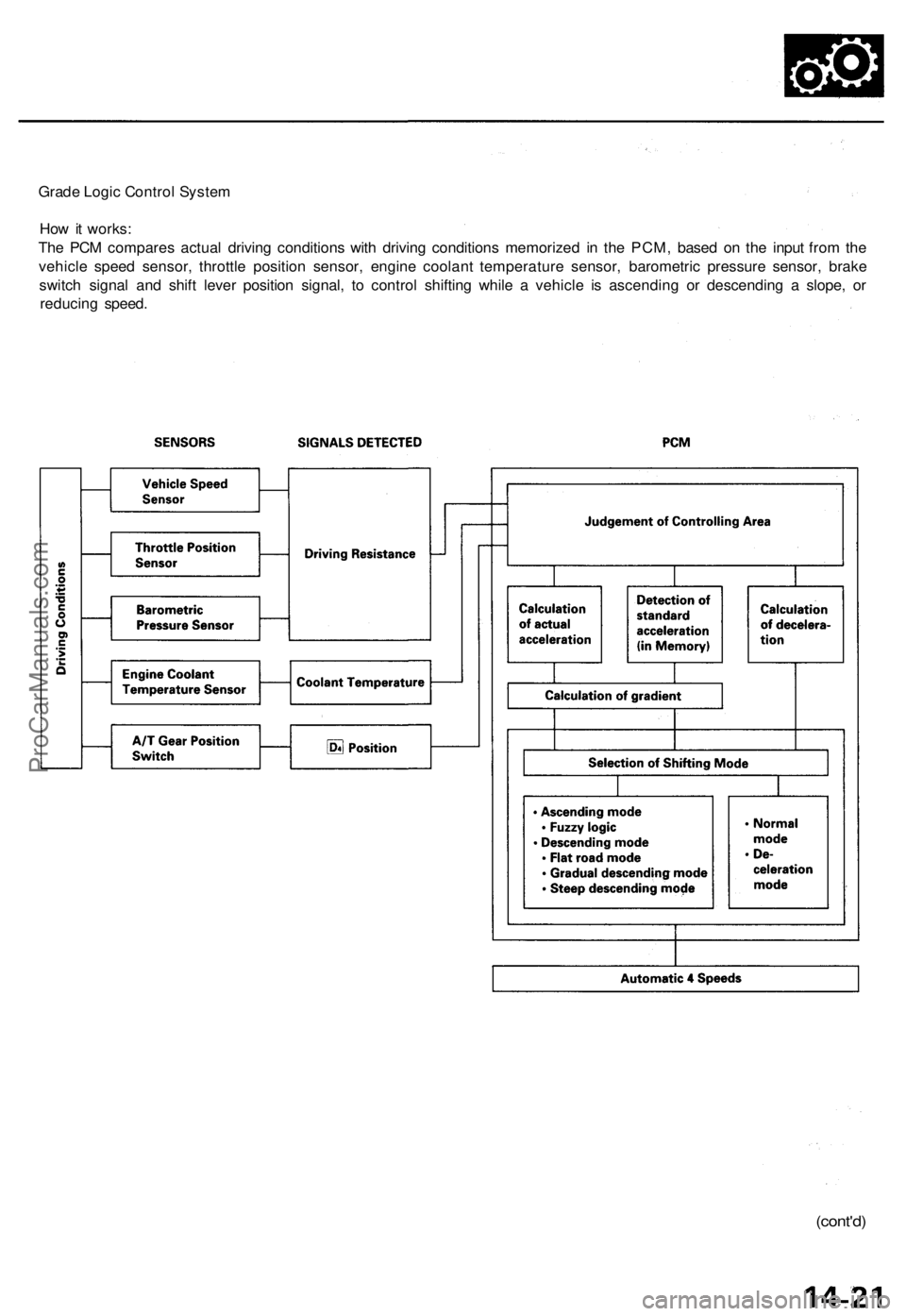
Grade Logic Control System
How it works:
The PCM compares actual driving conditions with driving conditions memorized in the PCM, based on the input from the
vehicle speed sensor, throttle position sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor, barometric pressure sensor, brake
switch signal and shift lever position signal, to control shifting while a vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or
reducing speed.
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.com
Page 302 of 1771
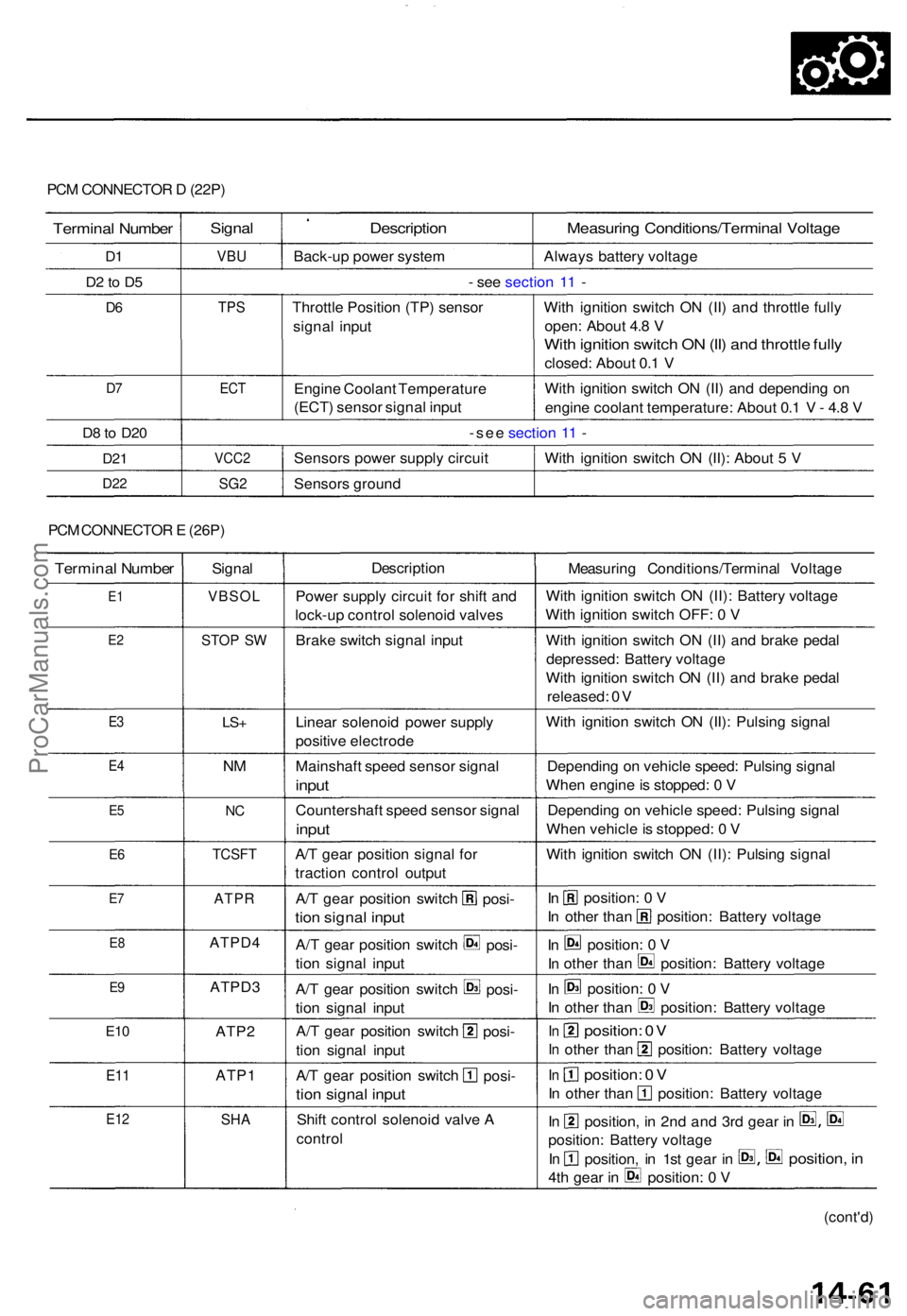
PCM CONNECTO R D (22P )
Termina l Numbe r
D1
D 2 to D 5
D6
D7
D 8 to D2 0
D21
D2 2
Signa l
VBU
Descriptio n
Back-up powe r syste m
Measurin g Conditions/Termina l Voltag e
Always batter y voltag e
- se e sectio n 1 1 -
TP S
EC T
Throttl e Positio n (TP ) senso r
signa l inpu t
Engin e Coolan t Temperatur e
(ECT ) senso r signa l inpu t Wit
h ignitio n switc h O N (II ) an d throttl e full y
open : Abou t 4. 8 V
Wit h ignitio n switc h O N (II ) an d throttl e full y
closed : Abou t 0. 1 V
Wit h ignitio n switc h O N (II ) an d dependin g o n
engin e coolan t temperature : Abou t 0. 1 V - 4. 8 V
-se e sectio n 1 1 -
VCC 2
SG2
Sensor s powe r suppl y circui t
Sensor s groun d Wit
h ignitio n switc h O N (II) : Abou t 5 V
PC M CONNECTO R E (26P )
(cont'd )
Termina l Numbe r
E1
E2
Signa l Descriptio
n
Measuring Conditions/Termina l Voltag e
Powe r suppl y circui t fo r shif t an d
lock-u p contro l solenoi d valve s
VBSO L
STOP S WBrak e switc h signa l inpu t
E3
E 4
E5
E 6
E7
E 8
E9
E1 0
E1 1
E1 2SH A
ATP 1
ATP2
ATPD
3
ATPD 4
ATPR
TCSF T
NC
NM
LS +Linea r solenoi d powe r suppl y
positiv e electrod e
Mainshaf t spee d senso r signa l
input
Countershaf t spee d senso r signa l
input
A/T gea r positio n signa l fo r
tractio n contro l outpu t
Shif t contro l solenoi d valv e A
contro l Wit
h ignitio n switc h O N (II) : Batter y voltag e
Wit h ignitio n switc h OFF : 0 V
Wit h ignitio n switc h O N (II ) an d brak e peda l
depressed : Batter y voltag e
Wit h ignitio n switc h O N (II ) an d brak e peda l
released : 0 V
Wit h ignitio n switc h O N (II) : Pulsin g signa l
Dependin g o n vehicl e speed : Pulsin g signa l
Whe n engin e is stopped : 0 V
Dependin g o n vehicl e speed : Pulsin g signa l
Whe n vehicl e is stopped : 0 V
Wit h ignitio n switc h O N (II) : Pulsin g signa l
posi -
posi -
posi -
posi -
posi -A/T gea r positio n switc h
tion signa l inpu t
A/T gea r positio n switc h
tion signa l inpu t
A/T gea r positio n switc h
tio n signa l inpu t
A/ T gea r positio n switc h
tio n signa l inpu t
A/ T gea r positio n switc h
tio n signa l inpu t
position , i n
position : 0 V
4t h gea r i n
position
, i n 2n d an d 3r d gea r i n
position : Batter y voltag e
In
Inposition , i n 1s t gea r i n
position
: Batter y voltag e
I n othe r tha n
Inposition : 0 V
In
In othe r tha n
position
: 0 V
position : Batter y voltag e
In
I n
othe r tha n
position : 0 V
position : Batter y voltag e
position
: Batter y voltag e
I n othe r tha n
position
: 0 V
In
In
I n
position : 0 V
othe r tha n position : Batter y voltag e
ProCarManuals.com