1994 JEEP CHEROKEE display
[x] Cancel search: displayPage 310 of 1784

circles, in not less than 48 seconds. The CAL light
will go off and the compass is now calibrated.
(5) Reset variation number. This step must be
done every time step 2 is performed.
If CAL light does not go off, either there is ex-
cessive magnetism near the compass or the unit
is defective. Repeat the degaussing and calibra-
tion procedures at least one more time.
If the wrong direction is still indicated, the
area selected may be too close to a magnetic
source. Repeat the calibration procedure in an-
other location.
DEGAUSSING PROCEDURE
The tool used to degauss or demagnetize the forward
console attaching screw and roof panel is the Miller
Tool 6029. Equivalent units must be rated as continu-
ous duty for 110/115 volts, 60Hz with a field strength of
over 350 gauss at 1/4 inch beyond the tip of the probe.
In this degaussing procedure the degaussing tool is
used to demagnetize both the roof panel and console
forward mounting screw.
(1) Be sure the ignition switch is in the OFF posi-
tion before you begin the degaussing procedures.
CAUTION: Keep the degaussing tool at least 2 inches
away from the compass area when plugging it in.
(2) Plug the degaussing tool into a standard
110/115 volt AC outlet.
CONSOLE FORWARD MOUNTING SCREW
(3) Slowly approach the head of the forward
mounting screw with the plastic coated tip of the de-
gaussing tool. Contact the head of the screw for
about two seconds.
(4) With the degaussing tool still energized, slowly
back it away from the screw until the tool is at least
2 inches from the screw head then unplug the tool.
ROOF PANEL
(5) Place an 8 1/2 X 11 piece of paper on the center
of the roof at the windshield, oriented lengthwise
from front to rear. The purpose of the paper is pro-
tect the roof panel from scratches and define the area
to be degaussed (Fig. 2). Figure 2 shows the recom-
mended sweep pattern of 1/2 inch between passes in
a sweeping zig-zag pattern.
(6) Plug in the degaussing tool. Keep the tool at
least 2 inches away from the compass unit.
(7) Slowly approach the center of the roof panel at
the windshield with the degaussing tool plugged in.
(8) Contact the roof panel with the tip of the tool
(be sure template is in place to avoid scratching the
roof panel). Using slow sweeping motions of 1/2 inch
between sweeps, move the tool approximately 49ei-
ther side of the centerline and at least 11 inches
back from the windshield.(9) With the degaussing tool still energized, slowly
back it away from the roof panel until the tip is at
least 2 inches from the roof then unplug the tool.
(10) Calibrate the compass and set the variance as
described.
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
The self-diagnostic test is used to verify the com-
pass is working properly electrically. This can be
used to confirm that the display and all of its seg-
ments are operating properly. Initiate the self-diag-
nostic test as follows:
(1) With the ignition switch in the OFF position si-
multaneously press and hold the COMP/TEMP but-
ton and the US/METRIC button.
(2) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(3) Continue to hold both buttons until the display
performs a walking segment test. In this test all of
the compass points are displayed along with various
number combinations. These combinations verify
that all segments work. To repeat the test, press the
COMP/TEMP button.
(4) Press the US/METRIC button, and all segments
will light simultaneously for about 2 seconds. To re-
peat the test, press the COMP/TEMP button.
(5) Press the US/METRIC button to return to nor-
mal operation.
Fig. 2 Roof Degaussing Pattern
JOVERHEAD CONSOLE 8C - 5
Page 311 of 1784
(6) Should any segment in any of the digit positions
fail to light, the unit is defective and should be re-
placed.
THERMOMETER AND SENSOR SYSTEM REPAIR
PROCEDURES
This portion of the display consists of a sensor, the
circuit and display devoted to the temperature mea-
suring and display. The sensor is mounted at the
center of the vehicle below the grille, behind the
front bumper (Fig. 3).
If an electrical component breaks it will diagnose as
an open or short circuit. The system reports SC when
the sensor is exposed to temperatures in excess of 140ÉF
or if the circuit is shorted. If the temperature is below
-40ÉF or an open exists, the system will display OC.
To diagnose the temperature sensor perform the
following procedures. If the sensor and wiring are
OK then the electronic module is defective and
should be replaced.
SENSOR TEST
(1) Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
(2) Measure resistance of sensor. At -40ÉF the re-
sistance is 336K ohms. At 140ÉF the resistance is
2.488K ohms. If resistance is NOT between these two
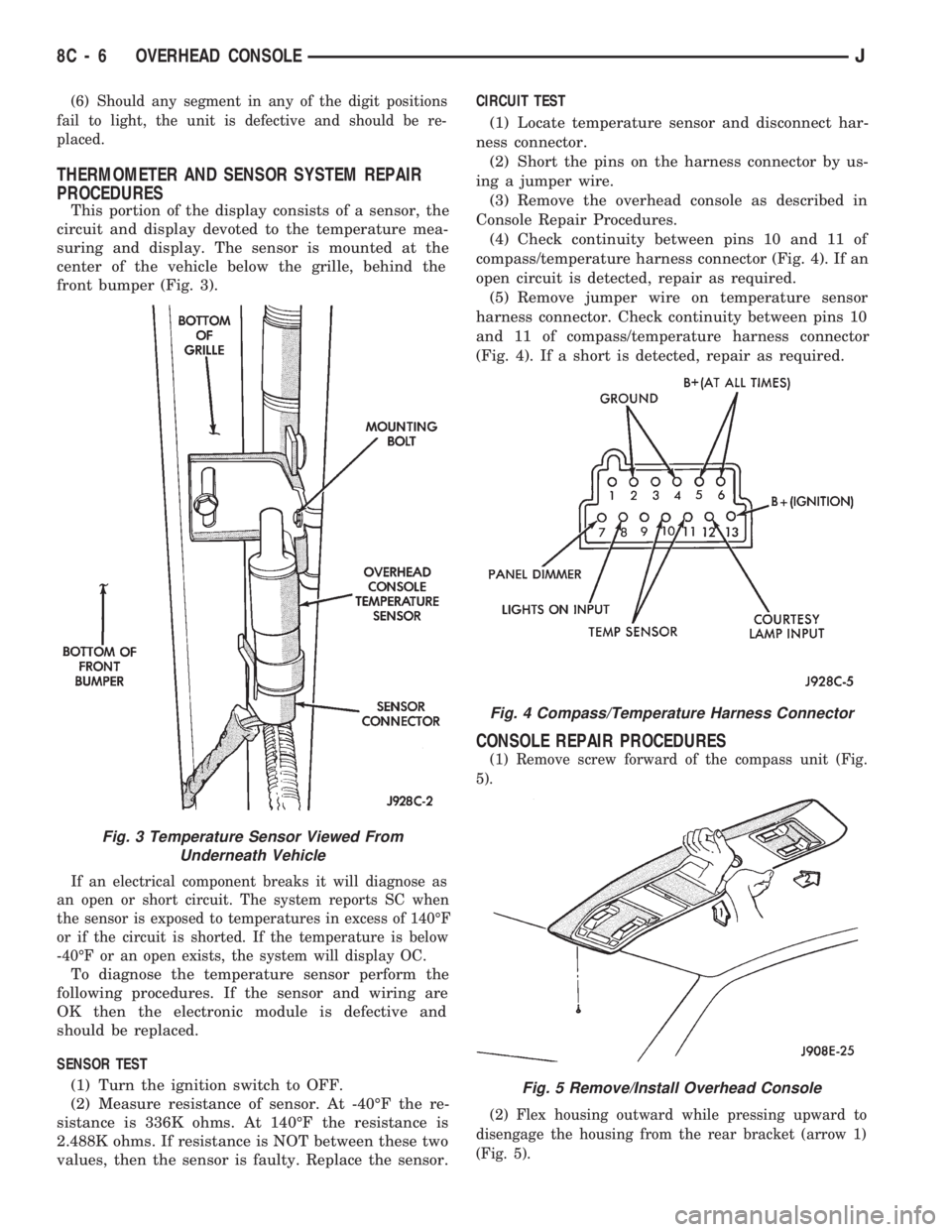
values, then the sensor is faulty. Replace the sensor.CIRCUIT TEST
(1) Locate temperature sensor and disconnect har-
ness connector.
(2) Short the pins on the harness connector by us-
ing a jumper wire.
(3) Remove the overhead console as described in
Console Repair Procedures.
(4) Check continuity between pins 10 and 11 of
compass/temperature harness connector (Fig. 4). If an
open circuit is detected, repair as required.
(5) Remove jumper wire on temperature sensor
harness connector. Check continuity between pins 10
and 11 of compass/temperature harness connector
(Fig. 4). If a short is detected, repair as required.
CONSOLE REPAIR PROCEDURES
(1) Remove screw forward of the compass unit (Fig.
5).
(2) Flex housing outward while pressing upward to
disengage the housing from the rear bracket (arrow 1)
(Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Compass/Temperature Harness Connector
Fig. 5 Remove/Install Overhead Console
Fig. 3 Temperature Sensor Viewed From
Underneath Vehicle
8C - 6 OVERHEAD CONSOLEJ
Page 323 of 1784
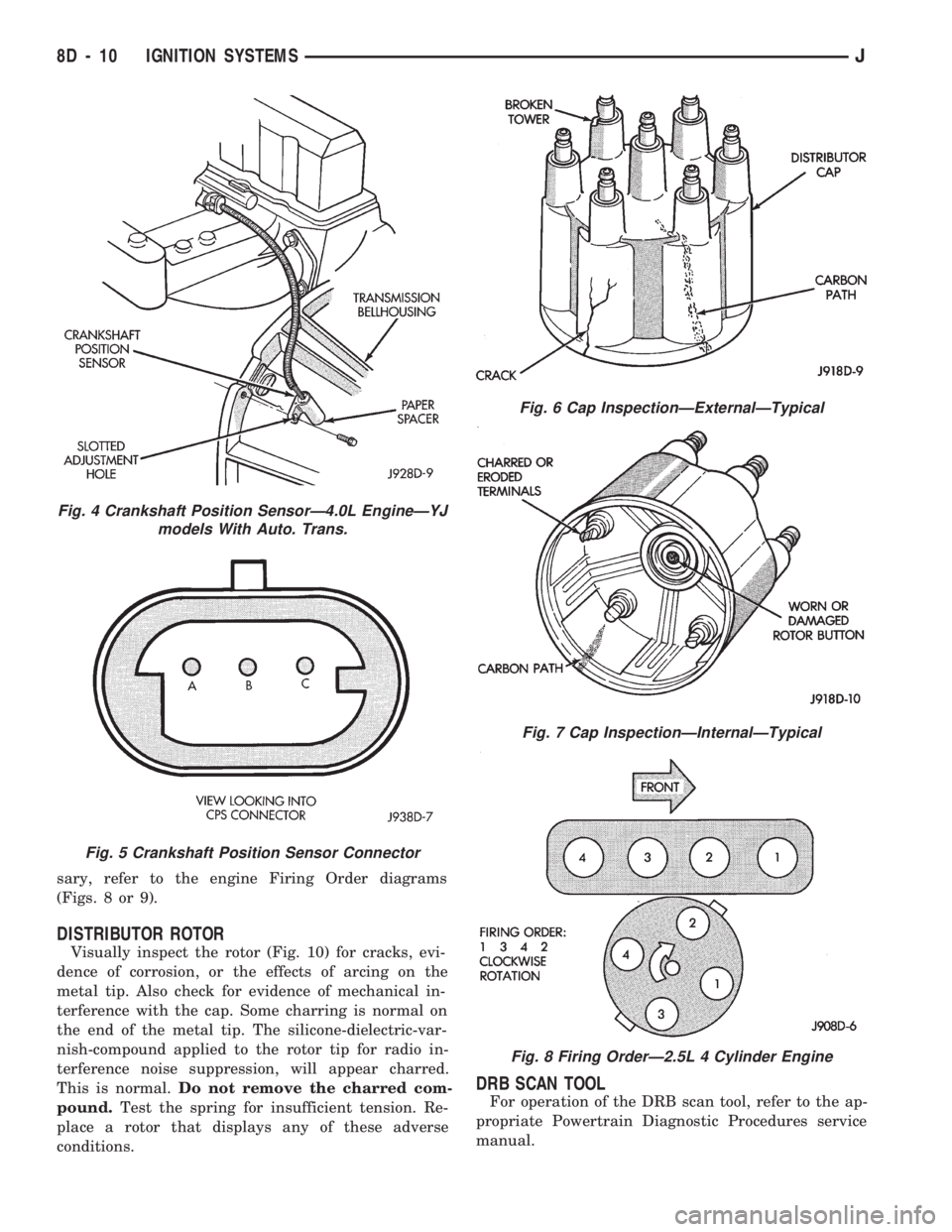
sary, refer to the engine Firing Order diagrams
(Figs. 8 or 9).
DISTRIBUTOR ROTOR
Visually inspect the rotor (Fig. 10) for cracks, evi-
dence of corrosion, or the effects of arcing on the
metal tip. Also check for evidence of mechanical in-
terference with the cap. Some charring is normal on
the end of the metal tip. The silicone-dielectric-var-
nish-compound applied to the rotor tip for radio in-
terference noise suppression, will appear charred.
This is normal.Do not remove the charred com-
pound.Test the spring for insufficient tension. Re-
place a rotor that displays any of these adverse
conditions.
DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual.
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L EngineÐYJ
models With Auto. Trans.
Fig. 5 Crankshaft Position Sensor Connector
Fig. 6 Cap InspectionÐExternalÐTypical
Fig. 7 Cap InspectionÐInternalÐTypical
Fig. 8 Firing OrderÐ2.5L 4 Cylinder Engine
8D - 10 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 329 of 1784

For diagnostics, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual for operation
of the DRB scan tool.
SPARK PLUGS
For spark plug removal, cleaning, gap adjustment
and installation, refer to the Component Removal/In-
stallation section of this group.
Faulty carbon and/or gas fouled plugs generally
cause hard starting, but they will clean up at higher
engine speeds. Faulty plugs can be identified in a
number of ways: poor fuel economy, power loss, de-
crease in engine speed, hard starting and, in general,
poor engine performance.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indi-
cates that a problem exists in the corresponding
cylinder. Replace spark plugs at the intervals recom-
mended in the maintenance chart in Group 0, Lubri-
cation and Maintenance.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
following Spark Plug Condition section of this group.
CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
(Fig. 24). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than ap-
proximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km (1000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed, have the gap set and then be installed.Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with
MMT causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be
coated with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can
be misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the
combustion chamber. Spark plug performance is not
affected by MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are ba-
sically carbon (Fig. 24). A dry, black deposit on one
or two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking
valves or defective spark plug cables. Cold (carbon)
fouling of the entire set of spark plugs may be caused
by a clogged air filter or repeated short operating
times (short trips).
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Electrode gap bridging may be traced to loose de-
posits in the combustion chamber. These deposits ac-
cumulate on the spark plugs during continuous stop-
and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
subjected to a high torque load, deposits partially liq-
uefy and bridge the gap between electrodes (Fig. 25).
This short circuits the electrodes. Spark plugs with
electrode gap bridging can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS
Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 26). They may appear to be harmful, but
this is a normal condition caused by chemical addi-
tives in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Notice that accumula-
tion on the ground electrode and shell area may be
heavy, but the deposits are easily removed. Spark
Fig. 24 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
Fig. 25 Electrode Gap Bridging
8D - 16 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 332 of 1784

With the ignition key in the ON position and en-
gine not running, check the sensor output voltage at
the center terminal wire of the connector. Check this
at idle (throttle plate closed) and at wide open throt-
tle (WOT). At idle, sensor output voltage should be
greater than 200 millivolts. At wide open throttle,
sensor output voltage must be less than 4.8 volts.
The output voltage should increase gradually as the
throttle plate is slowly opened from idle to WOT.
OXYGEN SENSOR TESTS
For diagnosis, removal or installation, refer to
Group 14, Fuel Systems in this manual.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
FOR IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor certain ignition system cir-
cuits:
EXAMPLE:
If a reference signal is not being detected during
engine cranking from the crankshaft position sensor,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) number 11 can be
observed at the Check Engine Lamp.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit of-
ten enough to indicate an actual problem, a DTC is
stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory
for eventual display to the service technician. If the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the DTC after 51 engine starts.
Certain criteria must be met for a DTC to be en-
tered into PCM memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine rpm, engine temperature and/or
input voltage to the PCM.
A DTC indicates that the PCM has recognized an
abnormal signal in a circuit or the system. A DTC
may indicate the result of a failure, but never iden-
tify the failed component directly.
It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit
may not be entered into memory even though a mal-
function has occurred. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) in Group 14, Fuel Systems for additional in-
formation.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be dis-
played by cycling the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On
within three seconds and observing the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp. This lamp was formerly referred to
as the Check Engine Lamp. The lamp is located on
the instrument panel.
They can also be displayed through the use of the
Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB) scan tool. The DRB
connects to the data link connector in the enginecompartment (Figs. 32 or 33). For operation of the
DRB, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
EXAMPLES:
²If the lamp flashes 1 time, pauses and flashes 1
more time, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
number 11 is indicated.
²If the lamp flashes 3 times, pauses and flashes 5
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 35 is indicated.
After any stored DTC information has been ob-
served, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored
information.
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, the DRB scan
tool must be used to erase a DTC. Refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
Fig. 32 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 33 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 19
Page 349 of 1784

other side. When coolant temperature is too high the
switch closes providing a path to ground, and the indi-
cator bulb lights.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer displays the engine speed (RPM).
With the engine running, the tachometer receives an
engine speed signal from the Powertrain Control
Module pin 43 (values shown in Specifications chart).
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER SYSTEM
The speedometer/odometer system consists of an elec-
tric speedometer and pushbutton reset odometer
mounted in the cluster. The system also includes the
wire harness from the cluster to the vehicle speed sen-
sor at the transmission, and the adapter and pinion in
the transmission. A signal is sent from a transmission
mounted vehicle speed sensor to the speedometer/odom-
eter circuitry through the wiring harness. Refer to
Group 21 - Transmission for selecting the proper pinion,
and selecting and indexing the proper adapter.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge pointer position is controlled by a
magnetic field created by electrical current flow through
the coils within the gauge. A change in current flow will
change the magnetic field which changes the pointer po-
sition. The fuel level sender is a variable resistor that
changes electrical resistance with a change of the level
of fuel in the tank (values shown in Specifications
chart).
LOW FUEL WARNING LAMP
The low fuel warning lamp will light when the fuel
level falls below approximately 4 gallons. A low fuel
warning module controls when the lamp will light.
When the module senses 66.5 ohms or less from the
fuel level sender for 10 continuous seconds, the lamp
will light. The lamp will remain on until the module
senses 63.5 ohms or more from the fuel level sender
for 20 continuous seconds.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have an
optional upshift indicator lamp. The lamp is controlled
by the Powertrain Control Module. The lamp lights to
indicate when the driver should shift to the next high-
est gear for best fuel economy. The Powertrain Control
Module will turn the lamp off after 3 to 5 seconds if the
upshift is not performed. The lamp will remain off until
the vehicle stops accelerating and is brought back to the
range of lamp operation or shifted into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally illuminated when
the ignition switch is turned ON and is turned off
when the engine is started. The lamp will be lighted
during engine operation according to engine speed
and load.
BRAKE INDICATOR LAMP
The brake indicator lamp warns the driver that the
parking brake is applied or that hydraulic pressure in
the split brake system is unequal.
Voltage is supplied through the brake indicator
bulb to 3 switches. A path to ground for the current
is available if:
²The brake warning switch is closed (with unequal
brake system hydraulic pressures), or
²
The ignition switch is in the START position (to test
the bulb), or
²The park brake switch is closed (with the parking
brake applied).
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) INDICATOR
LAMP
The anti-lock brake system (ABS) lamp lights to in-
dicate a system self-check is in process at vehicle
start-up. If light remains on after start-up or comes
on and stays on while driving, it may indicate that
the ABS system has detected a malfunction or has
become inoperative.
4WD INDICATOR LAMP
COMMAND-TRAC 4WD
The PART TIME lamp lights when the vehicle is en-
gaged in four-wheel drive mode. Voltage is supplied to
one side of the indicator bulb. A switch in the transfer
case area is connected to the other side of the indicator
bulb. When the switch is closed, a path to ground is pro-
vided and the indicator bulb lights.
SELECT-TRAC 4WD
The four-wheel drive icon or FULL TIME lamp
lights when the vehicle is engaged in full time four-
wheel drive mode. The PART TIME lamp lights when
the vehicle is in part time four-wheel drive mode.
Voltage is supplied to one side of the indicators.
Switches in the transfer case area are connected to
the other side of the indicator bulbs. When a switch
is closed, a path to ground is provided and the indi-
cator bulb lights.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)
lights each time the ignition switch is turned ON and
stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.
If the PCM receives an incorrect signal or no signal
from certain sensors or emission related systems the
lamp is turned on (pin 32 of PCM). This is a warning
that the PCM has recorded a system or sensor mal-
function. In some cases when a diagnostic trouble
code is declared the PCM will go into a limp-in mode
in an attempt to keep the system operating. It sig-
nals an immediate need for service.
The lamp also can be used to display diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC). Cycle the ignition switch ON,
OFF, ON, OFF, ON within 5 seconds. This will allow
any trouble codes stored in the PCM memory to be
displayed in a series of flashes representing digits.
8E - 2 XJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 351 of 1784

(3) Connect a jumper between terminal A and B on
the body half of the fuel gauge sender connector. The
gauge should move to F. If gauge is OK, replace
sender. If not, go to step 4.
(4) Measure resistance of sender. Meter should
read 105 to 5 ohms. If OK, go to step 5. If not, re-
place sender.
(5) Check for an open between sender connector
and gauge. If OK, replace gauge. If not, repair open
to gauge.
LOW FUEL WARNING INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Disconnect terminal B1 of the instrument clus-
ter connector. Wait at least 10 seconds. Lamp (LED)
should light. If OK, replace sender. If not, replace
low fuel warning module.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Ground pin 7 of connector B. Lamp should
light. If not, replace bulb. If OK, continue with
step 3.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Check for conti-
nuity between connector B pin 2 and pin 54 of the
Powertrain Control Module. If OK, replace PCM. If
not, repair open.
BRAKE INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Apply parking
brake, brake warning switch connector unplugged.
(2) Jumper brake warning switch connector termi-
nal B to ground. Lamp should light. If bulb is OK,
repair open to indicator.
(3) Turn ignition switch to OFF. Measure resis-
tance between brake warning switch connector ter-
minal A and ground. Meter should read zero ohms. If
OK, check switch and/or brake system. If not, repair
open to park brake switch ground.
4WD INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Apply parking brake, start engine, vehicle in
4WD Lock or 4WD.
(2) Unplug switch and touch harness side of wire
to ground. Lamp should light. If OK, check switch
operation, replace if bad. If bulb is OK, repair open
to indicator.
LOW WASHER INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Jumper 12 volts to fluid level switch connector
terminal B. Lamp should light. If not, go to step 3.
(3) Measure resistance between terminal B and
ground. Meter should read zero ohms. If not, repair
open to bulb. If OK, go to step 4.
(4) Measure voltage at fluid level switch connector
terminal A. Meter should read battery voltage. If
OK, replace switch. If not, repair open to fuse.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE)
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Jumper Powertrain Control Module terminal 2
to ground. Lamp should light. If bulb is OK, check
for open to instrument cluster connector terminal 2.
ANTI-LOCK INDICATOR
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Jumper instrument cluster connector terminal
6 to ground. Lamp should light. If bulb is OK, check
wiring for an open to module. Refer to Group 5 -
Brakes.
SEAT BELT INDICATOR
Jumper instrument cluster connector terminal 15
to 12 volts. Lamp should light. If not, replace bulb. If
OK, check wiring for an open to buzzer module. Re-
fer to Group 8U - Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems.
RADIO/CLOCK ILLUMINATION
With the ignition switch in ACCESSORY or ON,
power comes from the radio fuse. It then goes
through the normally closed contacts of the radio il-
lumination relay to the radio at connector terminal
11.
Pulling the headlamp switch to ON energizes the
radio illumination relay. This closes the normally
open contacts of the relay, and the brightness for the
radio display is controlled by the headlamp switch
rheostat. The back-lighting for the radio is also con-
trolled by the headlamp rheostat through radio con-
nector terminal 10.
Refer to Group 8F - Audio Systems, for radio illu-
mination relay diagnosis.
INSTRUMENT PANEL LAMPS
Voltage is supplied at all times from the 40 amp
Maxi fuse (located in the Power Distribution Center)
through the park lamps fuse to the headlamp switch.
The circuit continues through the instrument lamps
fuse to the individual instrument panel lamps to
ground. Lamp brightness is controlled by turning the
headlamp switch knob.
DIAGNOSIS
(1) Turn parking lamps ON.
(2) Check park lamps fuse. Replace as required.
(3) Check instrument lamps fuse. Replace as re-
quired.
(4) Measure voltage at battery side of instrument
lamps fuse with rheostat turned counterclockwise to
clockwise (LO to HI). Meter should read zero volts to
battery voltage. If not, replace headlamp switch.
(5) Measure resistance at ground side of instru-
ment lamps fuse with parking lamps OFF. Meter
should read almost zero ohms (except bulb filament).
If not, repair open to ground. If zero ohms, 12 volt
supply wire from fuse is shorted to ground, repair short.
8E - 4 XJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 361 of 1784

INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJE
CONTENTS
page page
GAUGE PACKAGE DIAGNOSIS............ 22
GAUGE PACKAGE GENERAL INFORMATION . 22
GAUGE PACKAGE SERVICE PROCEDURES . . 24
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS....... 14INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GENERAL INFORMATION.14
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SERVICE PROCEDURES.. 17
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 27
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GENERAL INFORMATION
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER SYSTEM
The speedometer/odometer system consists of an
electric speedometer and pushbutton reset odometer
mounted in the cluster. The system also includes the
wire harness from the cluster to the vehicle speed
sensor at the transmission, and the adapter and pin-
ion in the transmission. A signal is sent from a
transmission mounted vehicle speed sensor to the
speedometer/odometer circuitry through the wiring
harness. Refer to Group 21 - Transmission for select-
ing the proper pinion, and selecting and indexing the
proper adapter.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer displays the engine speed (RPM).
With the engine running, the tachometer receives anengine speed signal from the Powertrain Control
Module pin 43 (values shown in Specifications chart).
INDICATOR LAMPS
The Brake, Upshift (2.5L with 5 speed transmis-
sion except California), and Malfunction Indicator
(Check Engine) lamps are located in the indicator
lamp panel above the steering column. The lamps
share a common battery feed connection through the
ignition switch and fuse #9.
The turn signals, high beam indicator, seat belt re-
minder, hazard lamp, master lighting and illumina-
tion bulbs are supplied battery voltage through
various switches and share a common ground.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Brake Indicator Lamp...................... 16
DiagnosingÐAll Lamps Out................. 16
Instrument Panel Illumination Lamps.......... 16
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)..... 16Seat Belt Reminder Lamp................... 16
Speedometer............................ 14
Tachometer............................. 14
Upshift Indicator Lamp..................... 16
SPEEDOMETER
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the vehicle speed sensor connector.
(3) Connect a voltmeter between the black wire
pin of the connector and ground.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(5) Check for approximately 5 volts. If OK, per-
form vehicle speed sensor test. Refer to the appropri-
ate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual. If not
OK, continue with step 6.
(6) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.(7) Check continuity between vehicle speed sensor
connector and terminal 13 of instrument cluster con-
nector. If OK, replace speedometer. If not OK, repair
open circuit.
TACHOMETER
(1) Tachometer input is from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) pin 43. Use the DRB scan tool to
perform actuator test. If OK, continue with step 2. If
not, replace PCM.
(2) Check for continuity between cluster connector
pin 12 and PCM pin 43. If OK, replace tachometer. If
not, repair open circuit.
8E - 14 YJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ