1994 JEEP CHEROKEE Engine mount location
[x] Cancel search: Engine mount locationPage 100 of 1784

INSTALLATIONÐYJ MODELS
(1) Place tank into skid plate. Wrap straps around
tank with strap bolts inserted through holes in skid
plate. Tighten strap nuts to 7.3 Nzm (65 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Raise skid plate/fuel tank until gauge sender wire
connector can be connected to harness connector.
(3) Finish raising skid plate/fuel tank assembly
into position. Tighten mounting nuts to 16 Nzm (12
ft. lbs.) torque. Remove transmission jack.
(4) Connect fuel fill hose and fill vent hose to filler
neck. Tighten hose clamps.
(5) Connect vent hose to vent tube.
(6) Connect fuel supply hose to the supply tube and
fuel return hose to return tube. Tighten hose clamps.
(7) Install fuel filler neck shroud with push clips.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Fill fuel tank. Install filler cap.
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(11) Start vehicle and inspect for leaks.
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
The fuel gauge sending unit is attached to the fuel
pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump Module in the
Fuel Delivery System section of this group.
FUEL TANK PRESSURE RELIEF/ROLLOVER VALVE
The fuel tank is equipped with a pressure relief/
rollover valve (Fig. 8). The dual function valve will
relieve fuel tank pressure and prevent fuel flow
through the fuel tank vent tubes in the event of ac-
cidental vehicle rollover.
The valve consists of a plunger, spring and orifice/
guide plate (Fig. 9). The valve is normally open allowing
fuel vapor to vent to the EVAP canister. Here it is
stored until it can be consumed by the engine (undercontrolled conditions). The plunger seats in the guide
plate at the orifice preventing liquid fuel from reaching
the EVAP canister. This is done if bottom of plunger is
contacted by fuel sloshing in tank when vehicle is cor-
nering.
In the event of accidental vehicle rollover, the valve
is inverted. In this position the plunger is forced
against the guide plate and raw fuel is prevented
from flowing through the valve orifice into the fuel
tank vent tube.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE PRESSURE RELIEF/
ROLLOVER VALVE, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the fuel filler cap and drain fuel tank.
Refer to Fuel Tank Removal.
(3) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal.
(4) The rollover valve is seated in a grommet. Re-
move by prying one side upward and then roll the
grommet out of tank (Fig. 8).
INSTALLATION
(1) Start one side of grommet into opening in fuel
tank. Using finger pressure only, press valve/grom-
met into place.
(2) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Installation.
(3) Fill fuel tank. Install fuel tank filler cap.
(4) Connect negative battery cable.
(5) Start vehicle and check for leaks.
Fig. 8 Valve LocationÐTypical
Fig. 9 Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve Operation
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 15
Page 106 of 1784

Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System for more crank-
shaft position sensor information.
The engine will not operate if the PCM does not re-
ceive a crankshaft position sensor input.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The coolant temperature sensor is installed in the
thermostat housing (Fig. 10) and protrudes into the
water jacket. The sensor provides an input voltage to
the powertrain control module (PCM) relating cool-
ant temperature. The PCM uses this input along
with inputs from other sensors to determine injector
pulse width and ignition timing. As coolant temper-
ature varies, the coolant temperature sensor's resis-
tance changes. The change in resistance results in a
different input voltage to the PCM.
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
Open Loop cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-
fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds. This is done
until normal operating temperatures are reached.
Refer to Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes of Opera-
tion in this section of the group for more information.
EXTENDED IDLE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
OPTIONAL POLICE PACKAGE ONLY
The extended idle switch is used to raise the en-
gine idle speed to approximately 1000 rpm. This is
when the shifter is in either the Park or Neutral po-
sition. A rocker-type 2-wire switch (extended idle
switch) is mounted to the instrument panel. This
switch will supply a ground circuit to the powertrain
control module (PCM).The switch is available
only with 4.0L engine when supplied with the
optional police package.
For testing and diagnosis of this switch and its cir-
cuit, refer to the MFI SystemÐGeneral Diagnosis
section of this group.
IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSEÐPCM INPUT
The ignition circuit sense input tells the powertrain
control module (PCM) the ignition switch has ener-
gized the ignition circuit. Refer to the wiring dia-
grams for circuit information.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The MAP sensor reacts to absolute pressure in the
intake manifold. It provides an input voltage to the
powertrain control module (PCM). As engine load
changes, manifold pressure varies. The change in
manifold pressure causes MAP sensor voltage to
change. The change in MAP sensor voltage results in
a different input voltage to the PCM. The input volt-
age level supplies the PCM with information about
ambient barometric pressure during engine start-up
(cranking) and engine load while the engine is run-
ning. The PCM uses this input along with inputs
from other sensors to adjust air-fuel mixture.
The MAP sensor is mounted on the dash panel.
The sensor is connected to the throttle body with a
vacuum hose and to the PCM electrically.
Fig. 8 Sensor LocationÐ4.0L Engine
Fig. 9 Sensor LocationÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 10 Coolant Temperature SensorÐTypical
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 21
Page 107 of 1784

OVERDRIVE/OVERRIDE SWITCH
On vehicles equipped with overdrive, the power-
train control module (PCM) regulates the 3-4 over-
drive up-shift and down-shift through the overdrive
solenoid.
Refer to Group 21 for more information.
OXYGEN (O2S) SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The O2S sensor is located in the exhaust down pipe
(Fig. 11). It provides an input voltage to the power-
train control module (PCM) relating the oxygen con-
tent of the exhaust gas. The PCM uses this
information to fine tune the air-fuel ratio by adjust-
ing injector pulse width.
The O2S sensor produces voltages from 0 to 1 volt.
This voltage will depend upon the oxygen content of
the exhaust gas in the exhaust manifold. When a
large amount of oxygen is present (caused by a lean
air-fuel mixture), the sensor produces a low voltage.
When there is a lesser amount present (rich air-fuel
mixture) it produces a higher voltage. By monitoring
the oxygen content and converting it to electrical
voltage, the sensor acts as a rich-lean switch.
The oxygen sensor is equipped with a heating ele-
ment that keeps the sensor at proper operating tem-
perature during all operating modes. Maintaining
correct sensor temperature at all times allows the
system to enter into closed loop operation sooner.
In Closed Loop operation, the powertrain control
module (PCM) monitors the O2S sensor input (along
with other inputs). It then adjusts the injector pulse
width accordingly. During Open Loop operation, the
PCM ignores the O2S sensor input and adjusts injec-
tor pulse width to a preprogrammed value (based on
other sensor inputs).
PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
The park/neutral switch is located on the transmis-
sion housing and provides an input to the powertrain
control module (PCM). This will indicate that the au-
tomatic transmission is in Park, Neutral or a drivegear selection. This input is used to determine idle
speed (varying with gear selection), fuel injector
pulse width and ignition timing advance. Refer to
Group 21, Transmissions, for testing, replacement
and adjustment information.
POWER GROUND
The power ground is used to control ground circuits
for the following powertrain control module (PCM)
loads:
²Generator Field Winding
²8 volt (PCM) power supply
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coil
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCHÐPCM
INPUT
A pressure sensing switch is included in the power
steering system (mounted on the high-pressure line).
This switch will be on vehicles equipped with a 2.5L
engine and power steering. The switch (Fig. 12 YJ
Models or Fig. 13 XJ Models) provides an input to
the PCM. This input is provided during periods of
high pump load and low engine rpm; such as during
parking maneuvers. The PCM will then increase the
idle speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor.
This is done to prevent the engine from stalling un-
der the increased load.
When steering pump pressure exceeds 1896 kPa6
172 kPa (275625 psi) the PCM will increase the en-
gine idle speed. This will prevent the engine from
stalling.
SCI RECEIVEÐPCM INPUT
SCI Receive is the serial data communication re-
ceive circuit for the DRB scan tool. The powertrain
control module (PCM) receives data from the DRB
through the SCI Receive circuit.
Fig. 11 Heated Oxygen Sensor LocationÐTypical
Fig. 12 Power Steering Pump Pressure SwitchÐYJ
Models
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 112 of 1784

SPEED CONTROLÐPCM OUTPUT
Speed control operation is regulated by the power-
train control module (PCM). The PCM controls the
vacuum to the throttle actuator through the speed
control vacuum and vent solenoids. Refer to Group
8H for speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies en-
gine rpm values to the instrument cluster tachome-
ter (if equipped). Refer to Group 8E for tachometer
information.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
ALL 2.5L 4 CYL. WITH 3-SPEED AUTO. TRANS
4.0L 6 CYL. YJ MODELS WITH 3-SPEED AUTO.
TRANS
The transmission mounted torque converter clutch
(TCC) solenoid is used to control the torque con-
verter. The solenoid is controlled through the power-
train control module (PCM) and by the TCC relay.
This relay is used only on vehicles equipped with a
3-speed automatic transmission.
An electrical output signal is sent from the PCM to
the TCC relay after the PCM receives information
from the vehicle speed, MAP, throttle position and
engine coolant temperature sensors. After the TCC
relay receives this necessary information, it will send
a signal to the torque converter clutch solenoid to
control the torque converter.
On YJ models the TCC relay is located in the en-
gine compartment, on the cowl panel and near the
battery (Fig. 24). On XJ models the TCC relay is lo-
cated in the power distribution center (PDC) (Fig.
23).
OPEN LOOP/CLOSED LOOP MODES OF
OPERATION
As input signals to the powertrain control module
(PCM) change, the PCM adjusts its response to the
output devices. For example, the PCM must calculate
different injector pulse width and ignition timing for
idle than it does for wide open throttle (WOT). There
are several different modes of operation that deter-
mine how the PCM responds to the various input sig-
nals.
MODES
²Open Loop
²Closed Loop
During Open Loop modes, the powertrain control
module (PCM) receives input signals and responds
only according to preset PCM programming. Input
from the oxygen (O2S) sensor is not monitored dur-
ing Open Loop modes.
During Closed Loop modes, the PCM will monitor
the oxygen (O2S) sensor input. This input indicates
to the PCM whether or not the calculated injector
pulse width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio. This
ratio is 14.7 parts air-to-1 part fuel. By monitoring
the exhaust oxygen content through the O2S sensor,
the PCM can fine tune the injector pulse width. This
is done to achieve optimum fuel economy combined
with low emission engine performance.
The fuel injection system has the following modes
of operation:
²Ignition switch ON
²Engine start-up (crank)
²Engine warm-up
²Idle
²Cruise
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide open throttle (WOT)
²Ignition switch OFF
The ignition switch On, engine start-up (crank),
engine warm-up, acceleration, deceleration and wide
open throttle modes are Open Loop modes. The idle
and cruise modes, (with the engine at operating tem-
perature) are Closed Loop modes.
IGNITION SWITCH (KEY-ON) MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. When the fuel system
is activated by the ignition switch, the following ac-
tions occur:
²The powertrain control module (PCM) pre-posi-
tions the idle air control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel
strategy.
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant temperature
sensor input. The PCM modifies fuel strategy based
on this input.
Fig. 24 TCC Relay LocationÐYJ Models
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 27
Page 141 of 1784

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the fuel injector(s) into the fuel rail as-
sembly and install retaining clip(s).
(2) Install fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Rail Installation
in this section.
(3) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The Fuel Pump relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Figs. 1 or 2). For location of
this relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC
cover.
FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF) OF APPROXIMATELY 131-269 KPA (19-39
PSI). THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BE-
FORE SERVICING THE FUEL RAIL.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable from bat-
tery.
(3) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release Pro-
cedure as described in the Fuel Delivery System sec-
tion of this Group.
(4) Remove and numerically attach a tag (if fuel
injector is not already tagged), the injector harness
connectors. Do this at each injector (Fig. 7).
(5) Disconnect vacuum line from fuel pressure reg-
ulator (Fig. 7).
(6) Disconnect fuel supply line from fuel rail and
the fuel return line from fuel pressure regulator (Fig.7). Refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps, or
Quick-Connect Fittings. These can both be found in
the Fuel Delivery section of this group.
(7) Remove fuel rail mounting bolts.
On models with automatic transmissions, it may be
necessary to remove automatic transmission throttle
line pressure cable (and bracket). This will aid in fuel
rail assembly removal.
(8) Remove fuel rail by gently rocking until all the
fuel injectors are out of the intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position tips of all fuel injectors into the corre-
sponding injector bore in the intake manifold. Seat
injectors into manifold.
(2) Tighten fuel rail mounting bolts to 27 Nzm (20
ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect injector harness connectors to appro-
priate (tagged) injector.
(4) Connect both fuel lines to fuel rail.
(5) Connect vacuum supply line to fuel pressure
regulator.
(6) Install protective cap to pressure test port fit-
ting.
(7) Install fuel tank cap.
(8) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(9) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF)
OF APPROXIMATELY 100 KPA (14.5 PSI). BEFORE
SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP, FUEL LINES, FUEL
FILTER OR FUEL INJECTOR, THE FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group. See Fuel Pressure Release procedure.
FUEL TANKS
Refer to the Fuel Tank section of this group for re-
moval/installation procedures.
FUEL TANK PRESSURE RELIEF/ROLLOVER VALVE
Refer to the Fuel Tank section of this group for re-
moval/installation procedures.
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures. Also refer
to Quick-Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery sec-
tion of this group.
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTOR
The IAC motor is mounted to the throttle body ad-
jacent to the throttle position sensor (Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Fuel Injector HarnessÐTypical
14 - 56 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 143 of 1784

(3) Lower the vehicle.
PARK NEUTRAL SWITCH
Refer to Group 21, Transmissions for park neutral
switch service.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCHÐ2.5L
ENGINE ONLY
The power steering pressure switch is installed in
the power steering high pressure hose (Figs. 11 or
12).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
power steering pressure switch.
(2) Place a small container or shop towel beneath
the switch to collect any excess fluid.
(3) Remove the switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the power steering switch.
(2) Connect the electrical connector to the switch.(3) Check power steering fluid and add as neces-
sary.
(4) Start the engine and again check power steer-
ing fluid. Add fluid if necessary.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
On XJ models, the PCM is located in the engine
compartment next to the air cleaner (Fig. 13). On YJ
models, the PCM is located in the engine compart-
ment behind the windshield washer fluid reservoir
(Fig. 14).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable at the
battery.
(2) YJ Models Only: Remove the windshield
washer fluid tank.
(3) Loosen the 60-Way connector mounting bolt
(Figs. 13 or 14).
(4) Remove the electrical connector by pulling
straight back.
(5) Remove the three PCM mounting bolts.
(6) Remove PCM.
Fig. 11 Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐYJ Models
Fig. 12 Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐXJ Models
Fig. 13 PCM LocationÐXJ Models
Fig. 14 PCM LocationÐYJ Models
14 - 58 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 144 of 1784

INSTALLATION
(1) After the PCM electrical connector has been
separated from the PCM, inspect the pins for corro-
sion, being spread apart, bent or misaligned. Also in-
spect the pin heights in the connector. If the pin
heights are different, this would indicate a pin has
separated from the connector. Repair as necessary.
(2) Install PCM. Tighten three mounting bolts to 1
Nzm (9 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Engage 60-way connector into PCM. Tighten
connector mounting bolt to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) YJ Models: Install windshield washer fluid
tank.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures.
THROTTLE BODY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect air cleaner hose from throttle body.
(3) Disconnect idle air control motor and throttle
position sensor wire connectors.
(4) Disconnect accelerator cable, throttle cable (au-
tomatic transmission) and speed control cable (if
equipped) from throttle arm (Fig. 15).
(5) Remove throttle body mounting bolts, throttle
body and gasket. Discard old gasket (Fig. 16).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install throttle body and new gasket. Tighten
throttle body mounting bolts to 12 Nzm (9 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Connect idle air control motor and throttle po-
sition sensor wire connectors.
(3) Connect throttle linkage to throttle arm.CAUTION: When the automatic transmission throttle
cable is connected, it MUST be adjusted.
(4) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
connect and adjust the transmission line pressure ca-
ble. Refer to Group 21, Transmissions for adjustment
procedure.
(5) Install air cleaner hose to throttle body.
(6) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
The TPS is mounted to the throttle body (Figs. 17
or 18).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect TPS electrical connector.
(2) Remove TPS mounting bolts.
(3) Remove TPS.
INSTALLATION
The throttle shaft end of the throttle body slides
into a socket in the TPS (Fig. 19). The TPS must be
installed so that it can be rotated a few degrees. (If
Fig. 16 Throttle
BodyÐRemoval/InstallationÐTypical
Fig. 17 TPS LocationÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 15 Cables at Throttle Body
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 59
Page 145 of 1784
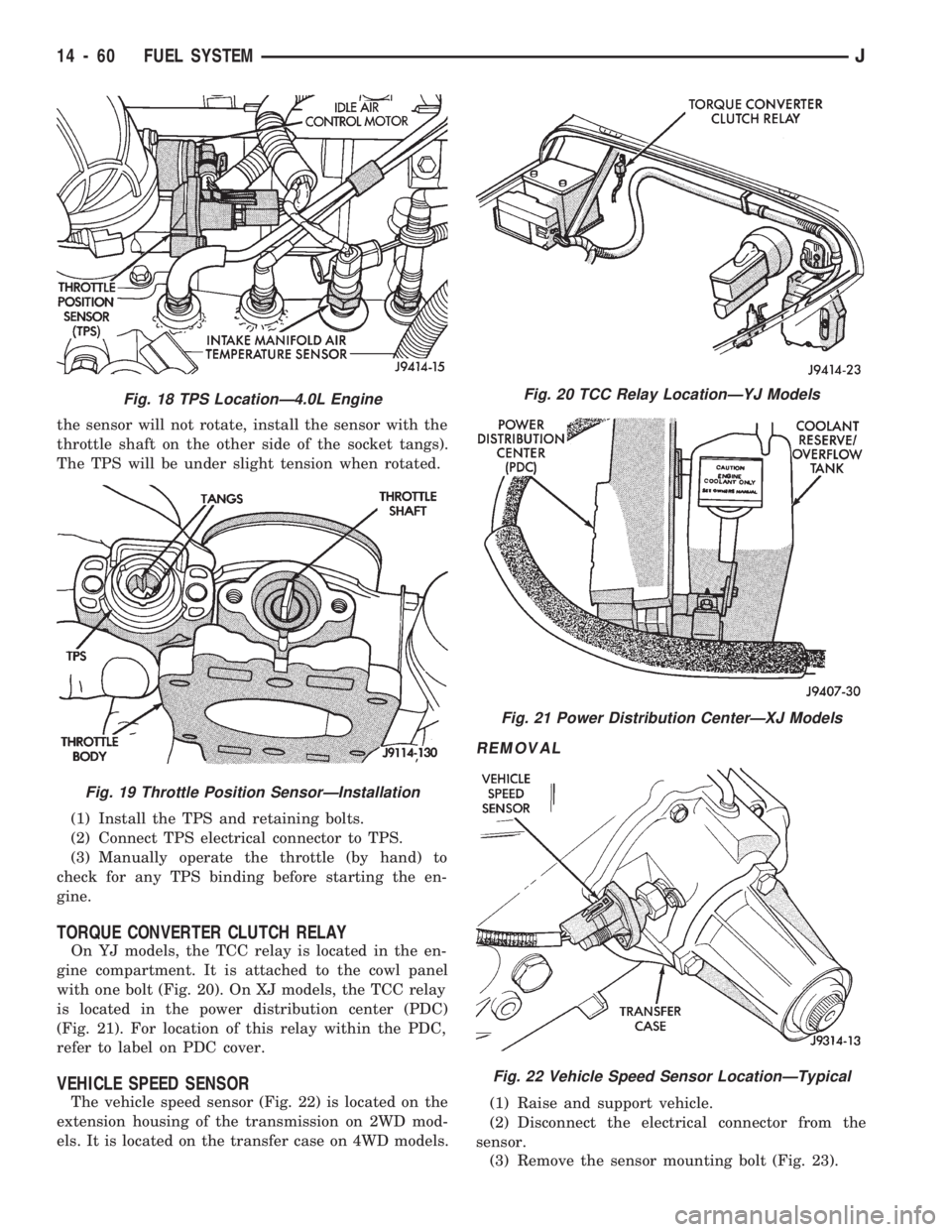
the sensor will not rotate, install the sensor with the
throttle shaft on the other side of the socket tangs).
The TPS will be under slight tension when rotated.
(1) Install the TPS and retaining bolts.
(2) Connect TPS electrical connector to TPS.
(3) Manually operate the throttle (by hand) to
check for any TPS binding before starting the en-
gine.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAY
On YJ models, the TCC relay is located in the en-
gine compartment. It is attached to the cowl panel
with one bolt (Fig. 20). On XJ models, the TCC relay
is located in the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 21). For location of this relay within the PDC,
refer to label on PDC cover.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 22) is located on the
extension housing of the transmission on 2WD mod-
els. It is located on the transfer case on 4WD models.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
sensor.
(3) Remove the sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 23).
Fig. 18 TPS LocationÐ4.0L Engine
Fig. 19 Throttle Position SensorÐInstallation
Fig. 20 TCC Relay LocationÐYJ Models
Fig. 21 Power Distribution CenterÐXJ Models
Fig. 22 Vehicle Speed Sensor LocationÐTypical
14 - 60 FUEL SYSTEMJ