1994 JEEP CHEROKEE 4WD
[x] Cancel search: 4WDPage 30 of 1784
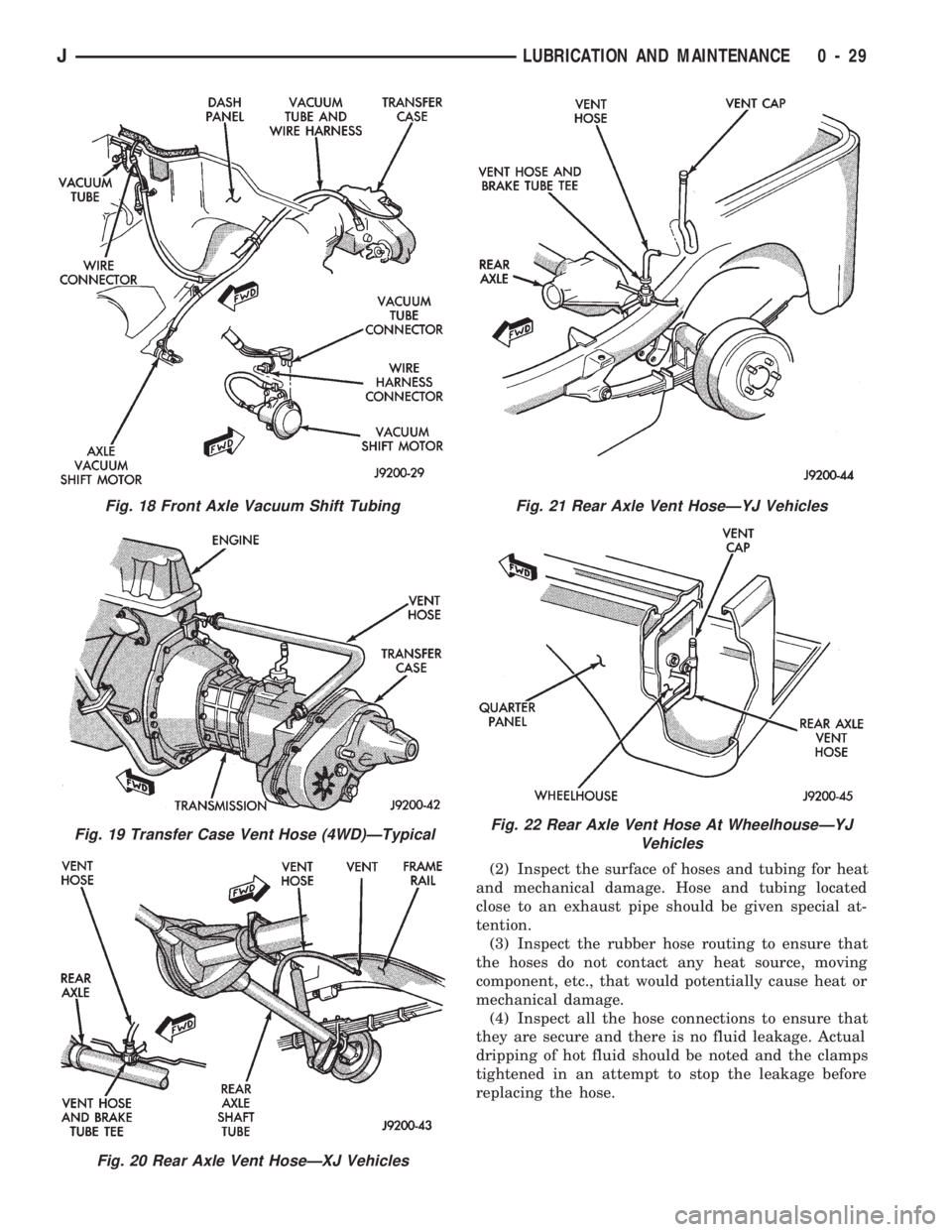
(2) Inspect the surface of hoses and tubing for heat
and mechanical damage. Hose and tubing located
close to an exhaust pipe should be given special at-
tention.
(3) Inspect the rubber hose routing to ensure that
the hoses do not contact any heat source, moving
component, etc., that would potentially cause heat or
mechanical damage.
(4) Inspect all the hose connections to ensure that
they are secure and there is no fluid leakage. Actual
dripping of hot fluid should be noted and the clamps
tightened in an attempt to stop the leakage before
replacing the hose.
Fig. 18 Front Axle Vacuum Shift Tubing
Fig. 19 Transfer Case Vent Hose (4WD)ÐTypical
Fig. 20 Rear Axle Vent HoseÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 21 Rear Axle Vent HoseÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 22 Rear Axle Vent Hose At WheelhouseÐYJ
Vehicles
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 29
Page 31 of 1784

CHASSIS AND BODY COMPONENTS
INDEX
page page
Body Components........................ 34
Chassis Component and Wheel Bearing
Lubricants............................ 30
Front Wheel Bearings..................... 31
Headlamps............................. 35Manual Steering GearÐYJ Vehicles.......... 32
Power Brake System...................... 32
Power Steering System.................... 31
Steering Linkage and Ball Studs............. 30
Tires.................................. 34
CHASSIS COMPONENT AND WHEEL BEARING
LUBRICANTS
The chassis component and wheel bearing lubri-
cants that are recommended for Jeeptvehicles are
identified by the NLGI Certification Symbol (Fig. 1).
The symbol contains a coded designation that identi-
fies the usage and quality of the lubricant.
The letterGdesignates wheel bearing lubricant.
LetterLdesignates chassis lubricant. When the let-
ters are combined the lubricant can be used for dual
applications. The suffix lettersCandBdesignate the
level of the lubricant for the application. The letterC
represents level available for wheel bearing lubricant
(G) and the letterBrepresents level available for
chassis lubricant (L).
STEERING LINKAGE AND BALL STUDS
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The general condition of the steering linkage (Fig.
2) should be inspected and the ball studs should be
lubricated:
²2WD vehicles Ð after each 24 000-km (15,000-
miles) or six-months interval of vehicle operation has
elapsed; or
²4WD vehicles Ð after each 12 000-km (7,500-
miles) or six-months interval of vehicle operation has
elapsed.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATION
Steering linkage should be lubricated with a dual-
purpose, lithium-base lubricant that is identified as
NLGI GC-LB lubricant.
INSPECTION/LUBRICATION
(1) Inspect the steering linkage. Examine the tie
rods and the drag link for bending, and the ball
studs for looseness and excessive wear.
(2) Replace, as necessary, all torn/ruptured ball-
stud seals and damaged/defective steering linkage
components.
CAUTION: Use care to prevent lubricant from con-
tacting the brake rotors.
(3) Lubricate the ball studs:
²clean the tips of the Zerk type lubrication fittings
on the tie-rod and drag-link ball-stud ends to avoid
lubricant contamination;
²lubricate the ball studs with high quality, dual-
purpose, lithium base chassis/wheel bearing lubri-
cant (NLGI GC-LB lubricant);
²cease the lubricant pressure when lubricant begins
to freely exit the base of the seal, or if the seal be-
gins to expand; and
²wipe the excess lubricant from the exterior sur-
faces of the ball joints and the adjacent surfaces.
Fig. 1 NLGI Lubricant Container Certification/
Identification Symbol
Fig. 2 Steering Components (XJ)ÐTypical
0 - 30 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 38 of 1784

FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE
CONTENTS
page page
AXLE NOISE/VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS....... 16
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT............... 5
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
MODEL 30 AXLE AND TUBE AXLE (2WD) . . 20TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS................ 47
XJ FRONT SUSPENSION................. 10
YJ FRONT SUSPENSION................. 13
GENERAL INFORMATION
FRONT SUSPENSION
XJ VEHICLES
The Cherokee front suspension is a link/coil design
comprised of (Fig. 1);
²Drive axle (4WD), tube axle (2WD)
²Track bar
²Stabilizer bar
²Upper and lower suspension arms
²Coil springs
²Dual-action shock absorbers²Jounce bumpers (used to limit the travel of the
suspension)
The link/coil suspension allows each wheel to adapt
to different road surfaces without greatly affecting
the opposite wheel. Wheels are attached to a hub/
bearings which bolts to the knuckles. The hub/bear-
ing is not serviceable and is replaced as a unit.
Steering knuckles pivot on replaceable ball studs at-
tached to the axle tube yokes.
The upper and lower suspension arms are different
lengths, with bushings at both ends. They bolt the
Fig. 1 XJ Front Suspension
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 1
Page 58 of 1784

Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information regarding temperature range,
viscosity and fluid level.
CAUTION: If the axle is submerged in water, the lu-
bricant must be replaced immediately to avoid the
possibility of premature axle failure.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐXJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails slightly in behind the lower
suspension arm frame brackets.
(2) Remove the front wheels.
(3) Remove the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(4) On 4WD vehicles, disconnect the axle vent
hose.
(5) On 4WD vehicles, mark the drive shaft yoke
and axle pinion yoke for alignment reference. Discon-
nect the drive shaft from the axle.
(6) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link at the axle
bracket.
(7) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
bracket.
(8) Disconnect the track bar from the axle bracket.
(9) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckle. Disconnect the steering dampener
from the axle bracket.
(10) Support the axle with a hydraulic jack under
the differential.
(11) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(12) Lower the jack enough to remove the axle.
The coil springs will drop with the axle.
(13) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: All suspension components that use rub-
ber bushings should be tightened with the vehicle
at the ride height. It is important to have the
springs supporting the weight of the vehicle when
the fasteners are torqued. If the springs are not at
their normal ride position, vehicle ride comfort
could be affected along with premature rubber
bushing wear. Rubber bushings must never be lu-
bricated.
(1) Install the springs and retainer clip. Tighten
the retainer bolts to 21 Nzm (16 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Support the axle on a hydraulic jack under the
differential. Position the axle under the vehicle.
(3) Raise the axle with a floor jack and align it
with the spring pads.(4) Position the upper and lower suspension arm at
the axle bracket. Install bolts and nuts finger
tighten.
(5) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt.Do not tighten at this time.
It is important that the springs support the
weight of the vehicle when the track bar is con-
nected. If the springs are not at their usual po-
sition, the vehicle ride comfort could be affected.
(6) Install the shock absorber and tighten the bolt
to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 95 Nzm (70 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Install the drag link and tie rod to the steering
knuckles and tighten the nuts to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.)
torque. Install the steering dampener to the axle
bracket and tighten the nut to 75 Nzm (55 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(9) Install the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(10) On 4WD vehicles, connect the vent hose to the
tube fitting.
(11) On 4WD vehicles, align the reference marks
and connect the drive shaft to the axle yoke. Tighten
the U-joint clamp bolts to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Check differential lubricant and add if neces-
sary.
(13) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(14) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(15) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts to 75
Nzm (55 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the lower suspension
arm nuts to 115 Nzm (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 100 Nzm (74 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Check the front wheel alignment.
DRIVE AXLE ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENTÐYJ
VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle and position support stands
under the frame rails slightly behind the spring
frame brackets.
(2) Remove the front wheels.
(3) Remove the brake components and ABS brake
sensor (if equipped). Refer to Group 5ÐBrakes.
(4) Disconnect the axle vent hose and axle shift
motor vacuum harness.
(5) Mark the drive shaft yoke and axle pinion yoke
for alignment reference. Disconnect the drive shaft
from the axle.
(6) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link at the axle
bracket.
(7) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
bracket.
(8) Disconnect the track bar from the axle bracket.
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 21
Page 145 of 1784
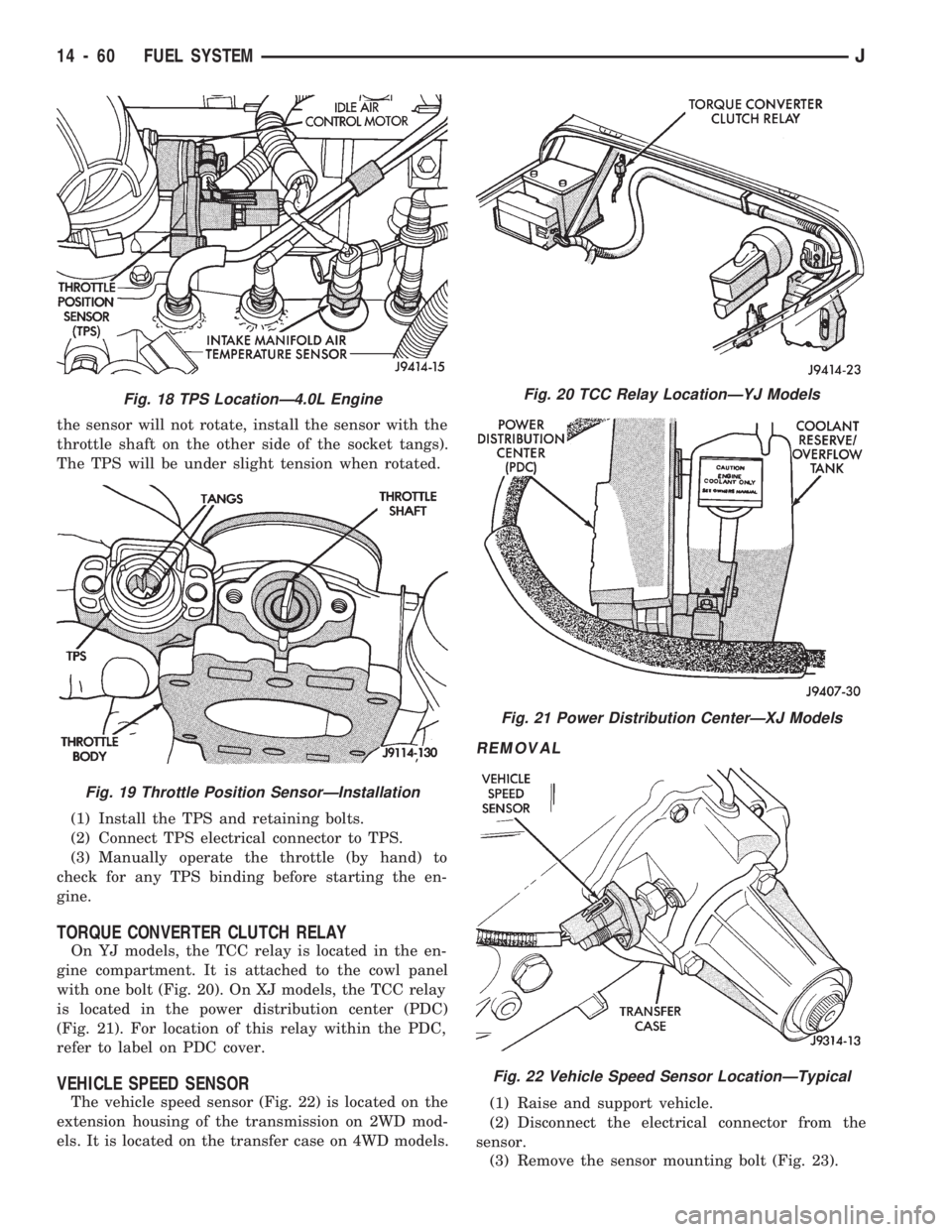
the sensor will not rotate, install the sensor with the
throttle shaft on the other side of the socket tangs).
The TPS will be under slight tension when rotated.
(1) Install the TPS and retaining bolts.
(2) Connect TPS electrical connector to TPS.
(3) Manually operate the throttle (by hand) to
check for any TPS binding before starting the en-
gine.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAY
On YJ models, the TCC relay is located in the en-
gine compartment. It is attached to the cowl panel
with one bolt (Fig. 20). On XJ models, the TCC relay
is located in the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 21). For location of this relay within the PDC,
refer to label on PDC cover.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 22) is located on the
extension housing of the transmission on 2WD mod-
els. It is located on the transfer case on 4WD models.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
sensor.
(3) Remove the sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 23).
Fig. 18 TPS LocationÐ4.0L Engine
Fig. 19 Throttle Position SensorÐInstallation
Fig. 20 TCC Relay LocationÐYJ Models
Fig. 21 Power Distribution CenterÐXJ Models
Fig. 22 Vehicle Speed Sensor LocationÐTypical
14 - 60 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 348 of 1784

INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES
GROUP INDEX
page page
INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJ..... 1INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJ.... 14
INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJE
CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS........ 3
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GENERAL INFORMATION.. 1
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER SERVICE PROCEDURES... 5
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 13
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
4WD Indicator Lamp........................ 2
Anti-Lock Brake Indicator Lamp............... 2
Brake Indicator Lamp....................... 2
Coolant Temperature Gauge................. 1
Coolant Temperature Indicator Lamp........... 1
Fuel Gauge.............................. 2
Low Fuel Warning Lamp..................... 2Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)...... 2
Oil Pressure Gauge....................... 1
Oil Pressure Indicator Lamp.................. 1
Speedometer/Odometer System.............. 2
Tachometer.............................. 2
Upshift Indicator Lamp...................... 2
Voltmeter............................... 1
With the ignition switch in the ON or START posi-
tion, voltage supplied to the instrument cluster is lim-
ited by fuse #17. The voltage is supplied to all the
gauges and indicator lamps through the instrument
cluster printed circuit.
With the ignition switch in the OFF position, volt-
age is not supplied to the instrument cluster and the
gauges do not indicate any vehicle condition.
VOLTMETER
The voltmeter measures battery or generator out-
put voltage, whichever is greater.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The oil pressure gauge pointer position is controlled
by a magnetic field created by electrical current flow
through the coils within the gauge. A change in current
flow will change the magnetic field which changes the
pointer position. The oil pressure sender is a variable
resistor that changes electrical resistance with a change
in oil pressure (values shown in Specifications chart).
OIL PRESSURE INDICATOR LAMP
Voltage is supplied to one side of the indicator bulb
and the oil pressure switch is connected to the other
side. When oil pressure is too low the switch closes
providing a path to ground, and the indicator bulb
lights.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE
The coolant temperature gauge pointer position is
controlled by a magnetic field created by electrical
current flow through the coils within the gauge. A
change in current flow will change the magnetic field
which changes the pointer position. The coolant tem-
perature sensor is a thermistor that changes electri-
cal resistance with a change in coolant temperature
(values shown in Specifications chart).
COOLANT TEMPERATURE INDICATOR LAMP
Voltage is supplied to one side of the indicator bulb
and the coolant temperature switch is connected to the
JINSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES 8E - 1
Page 349 of 1784

other side. When coolant temperature is too high the
switch closes providing a path to ground, and the indi-
cator bulb lights.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer displays the engine speed (RPM).
With the engine running, the tachometer receives an
engine speed signal from the Powertrain Control
Module pin 43 (values shown in Specifications chart).
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER SYSTEM
The speedometer/odometer system consists of an elec-
tric speedometer and pushbutton reset odometer
mounted in the cluster. The system also includes the
wire harness from the cluster to the vehicle speed sen-
sor at the transmission, and the adapter and pinion in
the transmission. A signal is sent from a transmission
mounted vehicle speed sensor to the speedometer/odom-
eter circuitry through the wiring harness. Refer to
Group 21 - Transmission for selecting the proper pinion,
and selecting and indexing the proper adapter.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge pointer position is controlled by a
magnetic field created by electrical current flow through
the coils within the gauge. A change in current flow will
change the magnetic field which changes the pointer po-
sition. The fuel level sender is a variable resistor that
changes electrical resistance with a change of the level
of fuel in the tank (values shown in Specifications
chart).
LOW FUEL WARNING LAMP
The low fuel warning lamp will light when the fuel
level falls below approximately 4 gallons. A low fuel
warning module controls when the lamp will light.
When the module senses 66.5 ohms or less from the
fuel level sender for 10 continuous seconds, the lamp
will light. The lamp will remain on until the module
senses 63.5 ohms or more from the fuel level sender
for 20 continuous seconds.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have an
optional upshift indicator lamp. The lamp is controlled
by the Powertrain Control Module. The lamp lights to
indicate when the driver should shift to the next high-
est gear for best fuel economy. The Powertrain Control
Module will turn the lamp off after 3 to 5 seconds if the
upshift is not performed. The lamp will remain off until
the vehicle stops accelerating and is brought back to the
range of lamp operation or shifted into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally illuminated when
the ignition switch is turned ON and is turned off
when the engine is started. The lamp will be lighted
during engine operation according to engine speed
and load.
BRAKE INDICATOR LAMP
The brake indicator lamp warns the driver that the
parking brake is applied or that hydraulic pressure in
the split brake system is unequal.
Voltage is supplied through the brake indicator
bulb to 3 switches. A path to ground for the current
is available if:
²The brake warning switch is closed (with unequal
brake system hydraulic pressures), or
²
The ignition switch is in the START position (to test
the bulb), or
²The park brake switch is closed (with the parking
brake applied).
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) INDICATOR
LAMP
The anti-lock brake system (ABS) lamp lights to in-
dicate a system self-check is in process at vehicle
start-up. If light remains on after start-up or comes
on and stays on while driving, it may indicate that
the ABS system has detected a malfunction or has
become inoperative.
4WD INDICATOR LAMP
COMMAND-TRAC 4WD
The PART TIME lamp lights when the vehicle is en-
gaged in four-wheel drive mode. Voltage is supplied to
one side of the indicator bulb. A switch in the transfer
case area is connected to the other side of the indicator
bulb. When the switch is closed, a path to ground is pro-
vided and the indicator bulb lights.
SELECT-TRAC 4WD
The four-wheel drive icon or FULL TIME lamp
lights when the vehicle is engaged in full time four-
wheel drive mode. The PART TIME lamp lights when
the vehicle is in part time four-wheel drive mode.
Voltage is supplied to one side of the indicators.
Switches in the transfer case area are connected to
the other side of the indicator bulbs. When a switch
is closed, a path to ground is provided and the indi-
cator bulb lights.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)
lights each time the ignition switch is turned ON and
stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.
If the PCM receives an incorrect signal or no signal
from certain sensors or emission related systems the
lamp is turned on (pin 32 of PCM). This is a warning
that the PCM has recorded a system or sensor mal-
function. In some cases when a diagnostic trouble
code is declared the PCM will go into a limp-in mode
in an attempt to keep the system operating. It sig-
nals an immediate need for service.
The lamp also can be used to display diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC). Cycle the ignition switch ON,
OFF, ON, OFF, ON within 5 seconds. This will allow
any trouble codes stored in the PCM memory to be
displayed in a series of flashes representing digits.
8E - 2 XJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESJ
Page 350 of 1784

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
4WD Indicator Inoperative................... 4
Anti-Lock Indicator......................... 4
Brake Indicator Inoperative.................. 4
Coolant Temperature Gauge Inoperative........ 3
Coolant Temperature Indicator Inoperative....... 3
Fuel Gauge Inoperative..................... 3
Gauges and Indicators Inoperative............ 3
Instrument Panel Lamps.................... 4
Low Fuel Warning Inoperative................ 4
Low Washer Indicator Inoperative............. 4Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)...... 4
Oil Pressure Gauge Inoperative............... 3
Oil Pressure Indicator Inoperative............. 3
Radio/Clock Illumination.................... 4
Seat Belt Indicator........................ 4
Speedomete/Odometer Inoperative............. 3
Tachometer Inoperative..................... 3
Upshift Indicator Inoperative................. 4
Voltmeter Inoperative....................... 3
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER INOPERATIVE
(1) Check for continuity in the wire between the
vehicle speed sensor and cluster connector pin A5.
(2) With the ignition switch in the ON position,
check for battery voltage across pin A8 (B+) and pin
B2 (ground).
(3) Perform vehicle speed sensor test. Refer to the
appropriate vehicle Diagnostic Test Procedures man-
ual.
(4) If all the previous tests prove good, replace
speedometer/odometer.
GAUGES AND INDICATORS INOPERATIVE
(1) Remove and inspect fuse #17. Replace as re-
quired.
(2) Measure resistance at instrument cluster con-
nector terminal A3. Meter should read zero ohms. If
not, repair open to ground.
VOLTMETER INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON. Voltmeter should
read battery voltage. If not, go to step 2.
(2) Measure voltage at instrument cluster connec-
tor terminal A8. Meter should read battery voltage.
If OK, replace meter. If not, repair open to fuse #17.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Disconnect oil pressure sender connector (Fig.
1). Needle goes to H. If not, go to step 3.
(3) Touch oil pressure sender connector to ground.
Needle goes to L. If OK, replace sender. If not, repair
open to gauge (instrument cluster connector terminal
B7).
OIL PRESSURE INDICATOR INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Touch oil pressure switch connector to ground.
Lamp should light. If OK, replace switch. If bulb is
OK, repair open to instrument cluster connector ter-
minal B7.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Disconnect coolant temperature sender connec-
tor. Needle goes to C. If not, go to step 3.
(3) Touch coolant temperature sender connector to
ground. Needle goes to H. If OK, replace sender. If
not, repair open to gauge (instrument cluster connec-
tor terminal A1).
COOLANT TEMPERATURE INDICATOR
INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Touch coolant temperature indicator connector
to ground. Lamp should light. If OK, replace switch.
If bulb is OK, repair open to instrument cluster con-
nector terminal A1.
TACHOMETER INOPERATIVE
Tachometer input is from the Powertrain Control
Module pin 43. Use the DRB scan tool to test.
FUEL GAUGE INOPERATIVE
(1) Turn ignition switch to ON.
(2) Disconnect fuel gauge sender connector. Needle
should go to E.
Fig. 1 Oil Pressure Sending UnitÐ4.0L
JXJ INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES 8E - 3