1993 FORD MONDEO heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 12 of 279
0•12
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
A)Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition is
switched off.
B)Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.C)Make sure that the booster battery is
the same voltage as the discharged
one in the vehicle.
D)If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehcles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
E)Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting will get you out
of trouble, but you must correct
whatever made the battery go
flat in the first place. There are
three possibilities:
1The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack
or broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3The battery itself is at fault
(electrolyte low, or battery worn out).
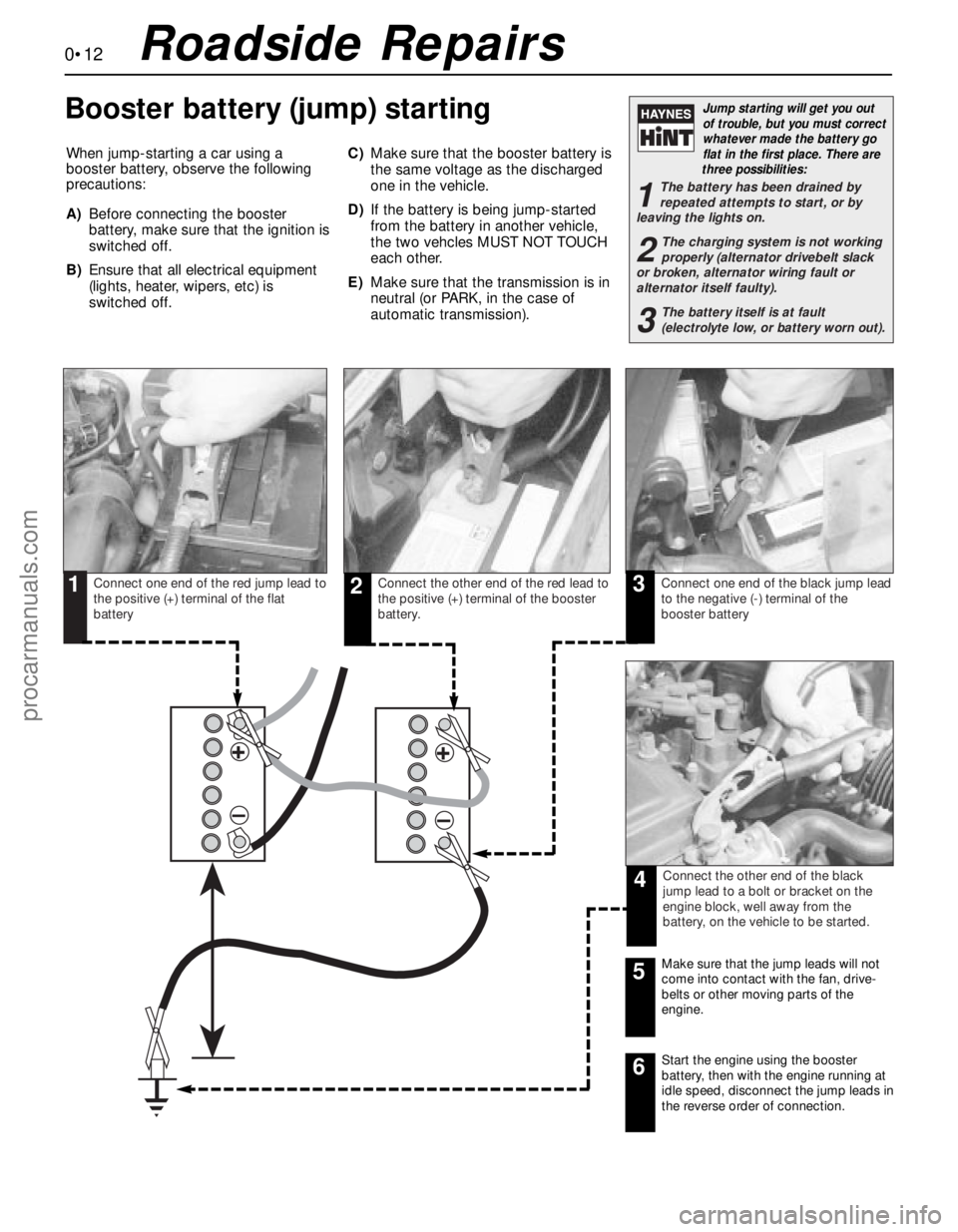
Connect one end of the red jump lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the booster
battery.Connect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started.
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan, drive-
belts or other moving parts of the
engine.5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads in
the reverse order of connection.6
Roadside Repairs
Booster battery (jump) starting
procarmanuals.com
Page 28 of 279
being felt when its pulley is rotated clockwise,
and a smooth return to the limit of its travel
when released.
11If the original drivebelt is being refitted,
use the marks or notes made on removal, to
ensure that it is installed to run in the same
direction as it was previously. To fit the
drivebelt, arrange it on the grooved pulleys so
that it is centred in their grooves, and not
overlapping their raised sides (note that the
flat surface of the drivebelt is engaged on the
idler, tensioner and water pump pulleys) and
routed correctly (see illustrations). Start at
the top, and work down to finish at the
crankshaft pulley; rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise, slip the drivebelt onto the
crankshaft pulley, then release the tensioner
again.
12Using a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, rotate the crankshaft through at
least two full turns clockwise to settle the
drivebelt on the pulleys, then check that the
drivebelt is properly installed.
13Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover and
roadwheel, then lower the vehicle to the
ground.
Caution: Renewal of air
conditioning hoses must be left
to a dealer service department or
air conditioning specialist who has the
equipment to depressurise the systemsafely. Never remove air conditioning
components or hoses until the system has
been depressurised.
General
1High temperatures in the engine
compartment can cause the deterioration of
the rubber and plastic hoses used for engine,
accessory and emission systems operation.
Periodic inspection should be made for
cracks, loose clamps, material hardening and
leaks.
2Carefully check the large top and bottom
radiator hoses, along with the other smaller-
diameter cooling system hoses and metal
pipes; do not forget the heater hoses/pipes
which run from the engine to the bulkhead,
and those to the engine oil cooler (where
fitted). Inspect each hose along its entire
length, replacing any that is cracked, swollen
or shows signs of deterioration. Cracks may
become more apparent if the hose is
squeezed (see illustration). If you are using
non-Ford specification antifreeze, and so
have to renew the coolant every two years or
so, it’s a good idea to renew the hoses at that
time, regardless of their apparent condition.
3Make sure that all hose connections are
tight. A leak in the cooling system will usually
show up as white- or rust-coloured deposits
on the areas adjoining the leak; if the spring
clamps that are used to secure the hoses in
this system appear to be slackening, they
should be renewed to prevent the possibility
of leaks.
4Some other hoses are secured to theirfittings with clamps. Where clamps are used,
check to be sure they haven’t lost their
tension, allowing the hose to leak. If clamps
aren’t used, make sure the hose has not
expanded and/or hardened where it slips over
the fitting, allowing it to leak.
12 Underbonnet check for fluid
leaks and hose condition
1•14
11.11A When installing the auxiliary
drivebelt, make sure that it is centred - it
must not overlap either edge of the
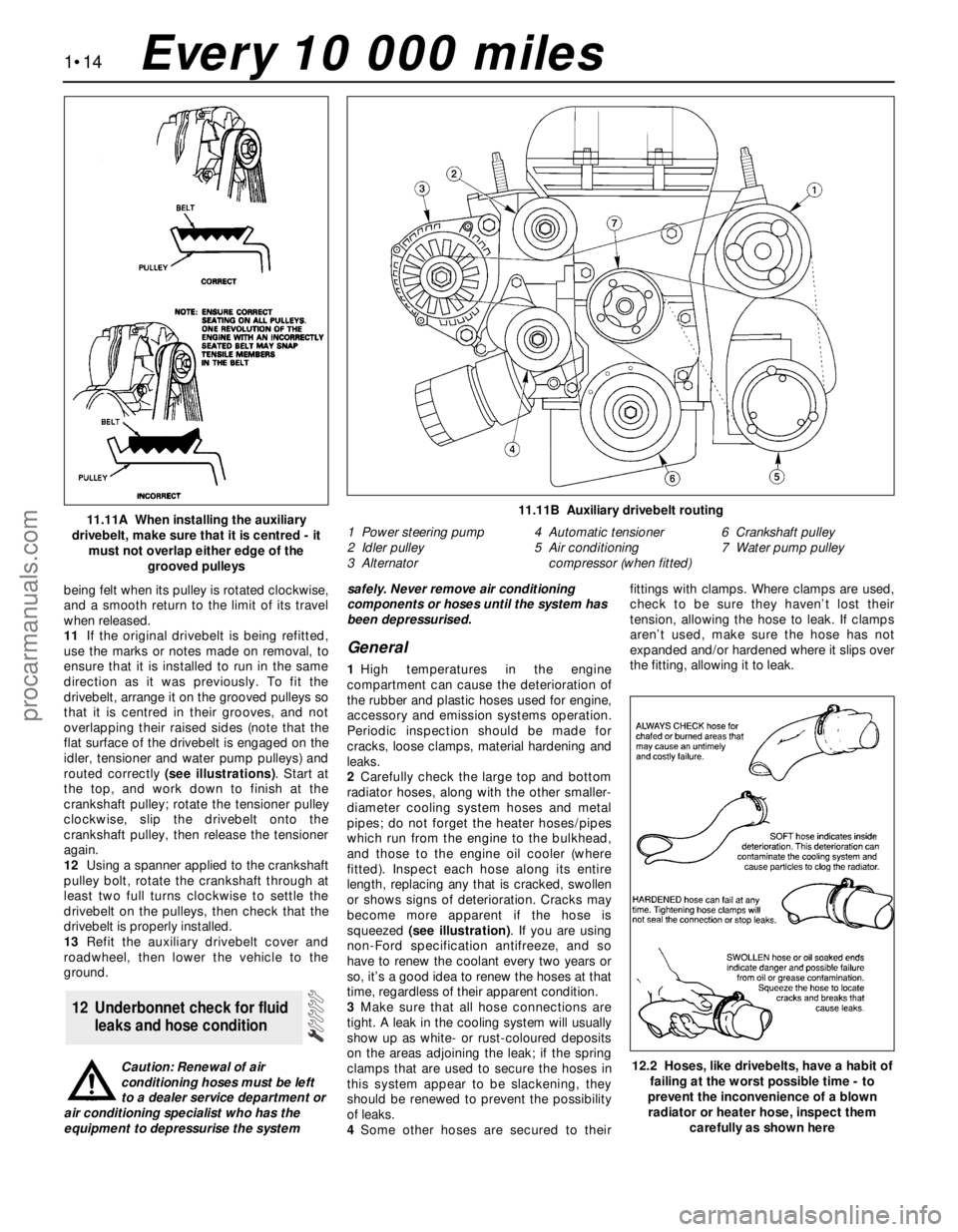
grooved pulleys11.11B Auxiliary drivebelt routing
1 Power steering pump
2 Idler pulley
3 Alternator4 Automatic tensioner
5 Air conditioning
compressor (when fitted)6 Crankshaft pulley
7 Water pump pulley
12.2 Hoses, like drivebelts, have a habit of
failing at the worst possible time - to
prevent the inconvenience of a blown
radiator or heater hose, inspect them
carefully as shown here
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 35 of 279

pleated-paper type filter, it cannot be washed
or re-oiled. If it cannot be cleaned
satisfactorily with compressed air, discard
and renew it.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
8Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; ensure that the element and
housing are securely seated, so that unfiltered
air cannot enter the passenger compartment.
Note:If the antifreeze used is Ford’s own, or of
similar quality, the coolant need not be
renewed for the life of the vehicle. If the
vehicle’s history is unknown, if antifreeze of
lesser quality is known to be in the system, or
simply if you prefer to follow conventional
servicing intervals, the coolant should be
changed periodically (typically, every 2 years)
as described here. Refer also to the
information in Section 2 of this Chapter.
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Flush contaminated areas
immediately with plenty of water. Don’t
store new coolant, or leave old coolant
lying around, where it’s accessible to
children or pets - they’re attracted by its
sweet smell. Ingestion of even a small
amount of coolant can be fatal! Wipe up
garage-floor and drip-pan spills
immediately. Keep antifreeze containers
covered, and repair cooling system leaks
as soon as they’re noticed.
Warning: Never remove the
expansion tank filler cap when
the engine is running, or has just
been switched off, as the cooling system
will be hot, and the consequent escaping
steam and scalding coolant could cause
serious injury.
Coolant draining
Warning: Wait until the engine is
cold before starting this
procedure.1To drain the system, first remove the
expansion tank filler cap (see Section 3).
2If the additional working clearance is
required, raise the front of the vehicle and
support it securely on axle stands.
3Remove the radiator undershield (eight or
nine screws), then place a large drain tray
underneath, and unscrew the radiator drain
plug; direct as much of the escaping coolant
as possible into the tray (see illustrations).
System flushing
4With time, the cooling system may
gradually lose its efficiency, as the radiator
core becomes choked with rust, scale
deposits from the water, and other sediment
(refer also to the information at the start of
Section 2). To minimise this, as well as using
only good-quality antifreeze and clean soft
water, the system should be flushed as
follows whenever any part of it is disturbed,
and/or when the coolant is renewed.
5With the coolant drained, refit the drain plug
and refill the system with fresh water. Refit the
expansion tank filler cap, start the engine and
warm it up to normal operating temperature,
then stop it and (after allowing it to cool down
completely) drain the system again. Repeat as
necessary until only clean water can be seen
to emerge, then refill finally with the specified
coolant mixture.
6If only clean, soft water and good-quality
antifreeze (even if not to Ford’s specification)
has been used, and the coolant has been
renewed at the suggested intervals, the above
procedure will be sufficient to keep clean the
system for a considerable length of time. If,however, the system has been neglected, a
more thorough operation will be required, as
follows.
7First drain the coolant, then disconnect the
radiator top and bottom hoses. Insert a
garden hose into the top hose, and allow
water to circulate through the radiator until it
runs clean from the bottom outlet.
8To flush the engine, insert the garden hose
into the thermostat water outlet, and allow
water to circulate until it runs clear from the
bottom hose. If, after a reasonable period, the
water still does not run clear, the radiator
should be flushed with a good proprietary
cleaning agent.
9In severe cases of contamination, reverse-
flushing of the radiator may be necessary. To
do this, remove the radiator (Chapter 3), invert
it, and insert the garden hose into the bottom
outlet. Continue flushing until clear water runs
from the top hose outlet. A similar procedure
can be used to flush the heater matrix.
10The use of chemical cleaners should be
necessary only as a last resort. Normally,
regular renewal of the coolant will prevent
excessive contamination of the system.
Coolant filling
11With the cooling system drained and
flushed, ensure that all disturbed hose unions
28 Coolant renewal
1•21
1
28.3A Remove the screws (arrowed) and
withdraw the radiator undershield . . .
28.3B . . . to unscrew the radiator drain
plug (arrowed) and empty the cooling
system. Try to protect yourself from
coolant splashing into your eyes or onto
your skin, catching as much of it as
possible in the drain tray
27.3 Remove screws (arrowed) to release
cowl grille panel . . .27.5A . . . release clips to lift out pollen
filter housing . . .27.5B . . . then withdraw pollen filter
element
Every 20 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 36 of 279

are correctly secured, and that the radiator
drain plug is securely tightened. Refit the
radiator undershield, noting that it is located
by three clips at its front edge; tighten the
retaining screws securely (see illustration). If
it was raised, lower the vehicle to the ground.
12Prepare a sufficient quantity of the
specified coolant mixture (see below); allow
for a surplus, so as to have a reserve supply
for topping-up.
13Slowly fill the system through the
expansion tank; since the tank is the highest
point in the system, all the air in the system
should be displaced into the tank by the rising
liquid. Slow pouring reduces the possibility of
air being trapped and forming air-locks.
14Continue filling until the coolant level
reaches the expansion tank “MAX” level line,
then cover the filler opening to prevent
coolant splashing out.
15Start the engine and run it at idle speed,
until it has warmed-up to normal operating
temperature and the radiator electric cooling
fan has cut in; watch the temperature gauge
to check for signs of overheating. If the level in
the expansion tank drops significantly, top-up
to the “MAX” level line, to minimise the
amount of air circulating in the system.
16Stop the engine, allow it to cool down
completely(overnight, if possible), then
uncover the expansion tank filler opening and
top-up the tank to the “MAX” level line. Refit
the filler cap, tightening it securely, and washoff any spilt coolant from the engine
compartment and bodywork.
17After refilling, always check carefully all
components of the system (but especially any
unions disturbed during draining and flushing)
for signs of coolant leaks. Fresh antifreeze has
a searching action, which will rapidly expose
any weak points in the system.
18 Note:If, after draining and refilling the
system, symptoms of overheating are found
which did not occur previously, then the fault
is almost certainly due to trapped air at some
point in the system, causing an air-lock and
restricting the flow of coolant; usually, the air
is trapped because the system was refilled too
quickly. In some cases, air-locks can be
released by tapping or squeezing the various
hoses. If the problem persists, stop the engine
and allow it to cool down completely, before
unscrewing the expansion tank filler cap or
disconnecting hoses to bleed out the trapped
air.
Antifreeze mixture
19If the antifreeze used is not to Ford’s
specification, it should always be renewed at
the suggested intervals. This is necessary not
only to maintain the antifreeze properties, but
also to prevent the corrosion which would
otherwise occur as the corrosion inhibitors
become progressively less effective. Always
use an ethylene glycol-based antifreeze which
is suitable for use in mixed-metal cooling
systems.
20If the antifreeze used is to Ford’s
specification, the levels of protection it affords
are indicated in the Specifications Section of
this Chapter. To give the recommended
standardmixture ratio for this antifreeze, 40%
(by volume) of antifreeze must be mixed with
60% of clean, soft water; if you are using any
other type of antifreeze, follow its
manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the
correct ratio. It is best to make up slightly
more than the system’s specified capacity, so
that a supply is available for subsequent
topping-up.
21Before adding antifreeze, the cooling
system should be completely drained,
preferably flushed, and all hoses checked forcondition and security. As noted earlier, fresh
antifreeze will rapidly find any weaknesses in
the system.
22After filling with antifreeze, a label should
be attached to the expansion tank, stating the
type and concentration of antifreeze used,
and the date installed. Any subsequent
topping-up should be made with the same
type and concentration of antifreeze. If
topping-up using antifreeze to Ford’s
specification, note that a 50/50 mixture is
permissible, purely for convenience.
23Do not use engine antifreeze in the
windscreen/tailgate washer system, as it will
damage the vehicle’s paintwork. A screen
wash additive should be added to the washer
system in its maker’s recommended
quantities.
General cooling system checks
24The engine should be cold for the cooling
system checks, so perform the following
procedure before driving the vehicle, or after it
has been shut off for at least three hours.
25Remove the expansion tank filler cap (see
Section 3), and clean it thoroughly inside and
out with a rag. Also clean the filler neck on the
expansion tank. The presence of rust or
corrosion in the filler neck indicates that the
coolant should be changed. The coolant
inside the expansion tank should be relatively
clean and transparent. If it is rust- coloured,
drain and flush the system, and refill with a
fresh coolant mixture.
26Carefully check the radiator hoses and
heater hoses along their entire length; renew
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated (see Section 12).
27Inspect all other cooling system
components (joint faces, etc.) for leaks. A leak
in the cooling system will usually show up as
white- or rust-coloured deposits on the area
adjoining the leak. Where any problems of this
nature are found on system components,
renew the component or gasket with
reference to Chapter 3.
28Clean the front of the radiator with a soft
brush to remove all insects, leaves, etc,
embedded in the radiator fins. Be careful not
to damage the radiator fins, or cut your fingers
on them.
1•22
28.11 Ensure radiator undershield is
located securely in three clips at front
edge (arrowed) when refitting
Every 30 000 miles
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years
1The air filter element is located in the air
cleaner assembly on the left-hand side of the
engine compartment. Release the clips, and
lift the air cleaner cover (see illustrations). If
the additional working clearance is required,
unclip the cover from the air mass meter, and
withdraw it completely.
2Lift out the element, and wipe out thehousing (see illustration). Check that no
foreign matter is visible, either in the air intake
or in the air mass meter.
3If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition; note that the small foam filter in the
rear right-hand corner of the air cleaner
housing must be cleaned whenever the air
filter element is renewed (see Section 30).
4If you are checking the element for any
other reason, inspect its lower surface; if it is
oily or very dirty, renew the element. If it is
only moderately dusty, it can be re-used byblowing it clean from the upper to the lower
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
pleated-paper type filter, it cannot be washed
or re-oiled. If it cannot be cleaned
satisfactorily with compressed air, discard
and renew it.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
Caution: Never drive the vehicle
with the air cleaner filter element
removed. Excessive engine wear could
result, and backfiring could even cause a
fire under the bonnet.
29 Air filter element renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 47 of 279

throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4.
Where fitted, disconnect also the cruise
control actuator cable (see Chapter 12).
3Remove the timing belt upper cover (see
Section 9).
4Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover union (see
illustration).
5Unplug the HT leads from the spark plugs
and withdraw them, unclipping the leads from
the cover.
6Working progressively, unscrew the
cylinder head cover retaining bolts, noting the
spacer sleeve and rubber seal at each, then
withdraw the cover (see illustration).
7Discard the cover gasket; this mustbe
renewed whenever it is disturbed. Check that
the sealing faces are undamaged, and that
the rubber seal at each retaining bolt is
serviceable; renew any worn or damaged
seals.
8On refitting, clean the cover and cylinder
head gasket faces carefully, then fit a new
gasket to the cover, ensuring that it locates
correctly in the cover grooves (see
illustration).
9Refit the cover to the cylinder head, then
insert the rubber seal and spacer sleeve at
each bolt location (see illustration). Start all
bolts finger-tight, ensuring that the gasket
remains seated in its groove.
10Working in a diagonal sequence from the
centre outwards, and in two stages (see
Specifications), tighten the cover bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting.
11Refit the HT leads, clipping them into
place so that they are correctly routed; each
is numbered, and can also be identified by
the numbering on its respective coil terminal.
12Reconnect the crankcase breather hose,
and refit the timing belt upper cover.
Reconnect and adjust the accelerator cable,
then refit the air cleaner assembly cover with
the air mass meter, the resonator and the
plenum chamber (see Chapter 4).
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system. Don’t smoke,
or allow naked flames or bare light bulbs in
or near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas appliance
(such as a clothes dryer or water heater) is
installed. If you spill petrol on your skin,
rinse it off immediately. Have a fire
extinguisher rated for petrol fires handy,
and know how to use it.
Removal
1Park the vehicle on firm, level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly, and slacken the
nuts securing the right-hand front roadwheel.
2Relieve the fuel system pressure (see
Chapter 4).3Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
4Unplugging the two electrical connectors
and disconnecting the vacuum hose (where
fitted), remove the air cleaner assembly cover
with the air mass meter, the resonator and the
plenum chamber (see Chapter 4).
5Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4 -
where fitted, disconnect also the cruise
control actuator cable (see Chapter 12).
6Disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover union.
7Unbolt the upper part of the exhaust
manifold heat shield; unclip the coolant hose
to allow it to be withdrawn. Slacken the
sleeve nut securing the EGR pipe to the
manifold, remove the two screws securing
the pipe to the ignition coil bracket, then
unscrew the sleeve nut securing the pipe to
the EGR valve - see Chapter 6 for full details if
required.
8Remove the two screws securing the wiring
“rail” to the top of the manifold - this is simply
so that it can be moved as required to reach
the manifold bolts. Unplug their electrical
connectors to disconnect the camshaft
position sensor and the coolant temperature
sensor, then unclip the wiring from the ignition
coil bracket, and secure it to the manifold.
9Remove the three screws securing the
wiring “rail” to the rear of the manifold.
Releasing its wire clip, unplug the large
electrical connector (next to the fuel pressure
regulator) to disconnect the wiring of themanifold components from the engine wiring
loom.
10Marking or labelling them as they are
unplugged, disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
(a) One from the rear of the throttle housing
(only the one hose - there is no need to
disconnect the second hose running to
the fuel pressure regulator).
(b) One from the union on the manifold’s left-
hand end.
(c) The braking system vacuum servo unit
hose (see Chapter 9 for details).
(d) One from the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve.
11Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then undo the fuel
feed and return lines connecting the engine to
the chassis (see Chapter 4). Plug or cap all
open fittings.
12Unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe and the earth lead from the cylinder
head rear support plate/engine lifting eye,
then unscrew the bolt securing the support
plate/lifting eye to the alternator mounting
bracket.
13Unscrew the six nuts securing the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting
bracket, then withdraw the bracket.
14Remove the alternator (see Chapter 5).
15Unbolt the alternator mounting bracket
from the rear of the cylinder block and
withdraw it, together with the cylinder head
rear support plate/engine lifting eye (see
illustration).
6 Inlet manifold -
removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•7
2A
5.8 Ensure gasket is located correctly in
cover groove5.6 Removing cylinder head cover
5.9 Ensure rubber seal is fitted to each
cover bolt spacer, as shown6.15 Alternator mounting bracket must be
unbolted from rear of cylinder block to
permit access to inlet manifold nut
procarmanuals.com
Page 59 of 279

then an ordinary socket extension bar and an
angle gauge, to tighten the cylinder head
bolts in the stages given in the Specifications
Section of this Chapter (see illustrations).
Note:Once tightened correctly, following this
procedure, the cylinder head bolts do not
require check-tightening, and must notbe re-
torqued.
33Refit the hydraulic tappets (if removed),
the camshafts, their oil seals and pulleys (see
Sections 10, 11, 12 and 13, as appropriate).
Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley, and
rotate the crankshaft clockwise to return the
pulley notches to the position described in
paragraph 8 of Section 10.
34Refit the timing belt and covers, checking
the camshaft alignment (valve timing) and
setting the timing belt tension, as described in
Section 10.
35The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points:
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) When reassembling the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting,
renew the self-locking nuts, and do not
allow the mounting to twist as the middle
two of the bracket’s six nuts are
tightened.
(c) Refill the cooling system, and top-up the
engine oil.
(d) Check all disturbed joints for signs of oil
or coolant leakage, once the engine has
been restarted and warmed-up to normal
operating temperature.
Removal
Note:To carry out this task with the
engine/transmission installed in the vehicle
requires the assistance of at least one person,
plus the equipment necessary to raise and
support the front of the vehicle (high enough
that the sump can be withdrawn from
underneath), and to lift and support the
complete engine/transmission unit 2 to 3 inches from its mountings while the vehicle
is raised. Precise details of the procedure will
depend on the equipment available - the
following is typical.
The full procedure outlined below must be
followed, so that the mating surfaces can be
cleaned and prepared to achieve an oil-tight
joint on reassembly, and so that the sump
can be aligned correctly; depending on your
skill and experience, and the tools and
facilities available, it may be that this task can
be carried out only with the engine removed
from the vehicle.
Note that the sump gasket must be
renewed whenever it is disturbed.
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
2Drain the engine oil, then clean and refit the
engine oil drain plug, tightening it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Although not
strictly necessary as part of the dismantling
procedure, owners are advised to remove
and discard the oil filter, so that it can be
renewed with the oil (see Chapter 1).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
4Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union and from the (heater)
coolant pipe. Unbolt the coolant pipe from
the sump; if they will prevent sump removal,
disconnect or release the coolant hoses from
the oil cooler unions (where fitted).
5Unscrew the two bolts securing the powersteering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
6Unplug the electrical connector(s) to
disconnect the oxygen sensor and, where
fitted, the oil level sensor wiring - unclip the
connectors to release the wiring where
necessary.
7Where the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, trace the fluid cooler lines from
the transmission to the radiator, and release
them from any clips etc, so that they have as
much movement as possible.
8Remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1).
9Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then either unhook all the system’s
rubber mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle, or
remove only the downpipe/catalytic converter
(see Chapter 4 for details).
10Unscrew the sump-to-transmission bolts,
also any securing the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate.
11Unplugging the two electrical connectors,
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head cover, remove
the complete air cleaner assembly with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
12Take the weight of the engine/
transmission unit using the lifting eyes
provided on the cylinder head; bolt on
15 Sump - removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•19
2A
14.32B . . . and to third stage using angle
gauge14.32C Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence
Note:View from rear of vehicle15.12 Equipment must be available to raise
and support engine/transmission unit while
vehicle is raised, to allow sump removal
14.30 Refitting cylinder head - note
fabricated guide studs (arrowed)14.32A Tightening cylinder head bolts (to
first and second stages) using torque
wrench . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 70 of 279

safely and with relative ease, and which may
have to be hired or borrowed, includes (in
addition to the engine hoist) a heavy-duty trolley
jack, a strong pair of axle stands, some wooden
blocks, and an engine dolly (a low, wheeled
platform capable of taking the weight of the
engine/transmission, so that it can be moved
easily when on the ground). A complete set of
spanners and sockets (as described in the front
of this manual) will obviously be needed,
together with plenty of rags and cleaning
solvent for mopping-up spilled oil, coolant and
fuel. If the hoist is to be hired, make sure that
you arrange for it in advance, and perform all of
the operations possible without it beforehand.
This will save you money and time.
Plan for the vehicle to be out of use for
quite a while. A machine shop will be required
to perform some of the work which the do-it-
yourselfer can’t accomplish without special
equipment. These establishments often have
a busy schedule, so it would be a good idea
to consult them before removing the engine,
to accurately estimate the amount of time
required to rebuild or repair components that
may need work.
Always be extremely careful when removing
and installing the engine/transmission.
Serious injury can result from careless
actions. By planning ahead and taking your
time, the job (although a major task) can be
accomplished successfully.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when disconnecting
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow naked flames or bare light
bulbs in or near the work area, and don’t
work in a garage where a natural gas
appliance (such as a clothes dryer or water
heater) is installed. If you spill petrol on
your skin, rinse it off immediately. Have a
fire extinguisher rated for petrol fires
handy, and know how to use it.Note: Read through the entire Section, as well
as reading the advice in the preceding Section,
before beginning this procedure. The engine
and transmission are removed as a unit,
lowered to the ground and removed from
underneath, then separated outside the vehicle.
Removal
1Park the vehicle on firm, level ground, apply
the handbrake firmly, and slacken the nuts
securing both front roadwheels.
2Relieve the fuel system pressure (see
Chapter 4).
3Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1. For better access
the battery may be removed completely (see
Chapter 5).
4Place protective covers on the wings and
engine compartment front crossmember, then
remove the bonnet (see Chapter 11).
5Whenever you disconnect any vacuum
lines, coolant and emissions hoses, wiring
loom connectors, earth straps and fuel lines
as part of the following procedure, always
label them clearly, so that they can be
correctly reassembled.
6Unplug the two electrical connectors,disconnect the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnect the crankcase breather hose
from the cylinder head cover, then remove the
complete air cleaner assembly, with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
7Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then undo the fuel
feed and return lines connecting the engine to
the chassis (see Chapter 4). Plug or cap all
open fittings (see illustration).
8Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4 -
where fitted, also disconnect the cruise
control actuator cable (see Chapter 12).
Secure the cable(s) clear of the
engine/transmission.
9Releasing its wire clip, unplug the power
steering pressure switch electrical connector,
then unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe and the earth lead from the cylinder head
rear support plate/engine lifting eye (see
illustrations).
10Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above), disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
4 Engine/transmission -
removal and refitting
2B•4 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.7 Note colour-coding of unions when
disconnecting fuel feed and return lines4.9A Unplug the power steering pressure
switch electrical connector . . .4.9B . . . unbolt the power steering high-
pressure pipe . . .
Whenever any wiring is disconnected, . . . vacuum hoses and pipes should
mark or label it as shown, to ensure be similarly marked
correct reconnection . . .
Masking tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations of components and brackets.
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 279

inner wing panel, release the engine
wiring loom and refit the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(g) Secure the engine wiring loom neatly to
the engine/transmission so that it cannot
be damaged as the unit is removed from
the vehicle.
14Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield; unclip the coolant hose to allow
the upper part to be withdrawn.
15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Unbolt the power steering pump (see
Chapter 10); secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
17Raise the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands, then remove the front
roadwheels. Drain the cooling system and (if
the engine is to be dismantled) drain the
engine oil and remove the oil filter (see
Chapter 1). Also drain the transmission as
described in the relevant Part of Chapter 7.
18Withdraw the lower part of the exhaust
manifold heat shield.
19Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then unhook all the system’s rubber
mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle (see
Chapter 4 for details).
20Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, mark their positions, then
disconnect the gearchange linkage and
transmission support rods from the rear of the
transmission. Unscrew the retaining nuts, and
withdraw the gear linkage heat shield from the
underbody. Unbolt the rear end of the linkage
from the underbody, swivel the linkage around
to the rear, and tie it to the underbody (see
Chapter 7, Part A, for details).
21Disconnect both anti-roll bar links from
their respective suspension strut - note the
flexible brake hose bracket attached to each
link stud - and both track rod ends from their
steering knuckles. Unfasten the clamp bolt
securing each front suspension lower arm
balljoint to its steering knuckle (see Chap-
ter 10 for details). Check that both balljoints
can be released from the knuckle assemblies
when required, but leave them in place for thetime being, secured by the clamp bolts if
necessary.
22Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unbolt the accumulator/
dehydrator from the subframe; secure it as far
as possible (without disconnecting the
system’s hoses) clear of the engine/
transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
23Unbolt the steering gear from the
subframe; if the bolts are not accessible from
above, a Ford service tool will be required to
reach them from underneath the vehicle (see
Chapter 10 for details).
24Unscrew the two bolts securing the power
steering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
25Hold the radiator in its raised position, by
inserting split pins through the holes in the
rear of the engine compartment front
crossmember and into the radiator’s upper
mounting extensions. Unbolt the radiator
mounting brackets from the subframe; note
that they are handed, and are marked to
ensure correct refitting (see illustrations).
Collect and store the bottom mounting
rubbers for safekeeping, noting which way up
they are fitted.
26Unbolt the engine/transmission rear
mounting from the subframe - where the
vehicle is fitted with automatic transmission, a
separate damper may be fitted beneath the
subframe, which must be unbolted to reach
the mounting’s fasteners. Where the vehicle is
fitted with manual transmission, also unscrew
the mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting bracket from the transmission.
27Unscrew the engine/transmission front
mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting from the subframe, noting the
location of the wiring connector bracket.
28Use white paint or similar (do not use a
sharp-pointed scriber, which might break the
underbody protective coating and cause
rusting) to mark the exact relationship of the
subframe to the underbody. Unscrew the four
mounting bolts from the subframe (note their
different-sized washers - see also illus-tration 4.47A) and allow the subframe to hang
down on the suspension lower arm balljoints.
Disconnect the balljoints one at a time from
the steering knuckle assemblies (see Chap-
ter 10) and lower the subframe to the ground;
withdraw the subframe from under the
vehicle.
29Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above) and catching as much as possible of
the escaping coolant in the drain tray,
disconnect the cooling system hoses and
pipes as follows - refer to Chapter 3 for further
details, if required:
(a) Remove the radiator top hose.
(b) Remove the (heater) hose running from
the thermostat to the engine
compartment bulkhead union.
(c) Disconnect from the thermostat the hose
running to the expansion tank - secure the
hose clear of the working area.
(d) Disconnect from the thermostat the
coolant hose/pipe which runs to the
radiator bottom hose.
(e) Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union, from the (sump) heater
coolant pipe and from the water pump
union - secure the hose clear of the
working area.
(f) Unbolt the (heater) coolant pipe from the
sump, trace the pipe/hose round to the
engine compartment bulkhead union,
disconnecting (where fitted) the oil cooler
hoses from the cooler unions, then
remove it.
(g) Unless the vehicle has air conditioning
fitted, secure the radiator as far forwards
as possible while it is in its raised position;
if air conditioning is fitted, remove the
radiator completely (see Chapter 3).
30Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unplug the compressor’s
electrical connector, and unbolt the
compressor from the engine (see
illustration). Secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
2B•6 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.25A Use split pins as shown to secure
radiator in its raised position . . .
4.25B . . . while you unbolt the bottom
mountings (arrowed) - note that the
mountings are handed, and do not lose the
mounting rubbers
4.30 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to release
air conditioning compressor from engine
procarmanuals.com