1993 FORD MONDEO heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 89 of 279

Chapter 3
Cooling, heating, and air conditioning systems
Air conditioning system - general information
and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Air conditioning system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . 12
Antifreeze - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system checks (coolant leaks,
hose condition) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system electrical switches and sensors -
testing, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Cooling system hoses - disconnection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . 3Cooling system servicing (draining, flushing
and refilling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Heater/air conditioning controls - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . 10
Heater/ventilation components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Pollen filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Radiator and expansion tank - removal, inspection
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Radiator electric cooling fan(s) - testing, removal and refitting . . . . . 5
Thermostat - removal, testing and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Water pump - check, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Coolant
Mixture type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
System pressure
Pressure test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 bars - should hold this pressure for at least 10 seconds
Expansion tank filler cap
Pressure rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 bars approximately - see cap for actual value
Thermostat
Starts to open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88°C
Radiator electric cooling fan
Switches on at:
Single-speed fans, two-speed fans - first stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C
Two-speed fans - second stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103°C
Switches off at:
Single-speed fans, two-speed fans - first stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93°C
Two-speed fans - second stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C
Coolant temperature sensor
Resistance:
At -40°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 860.0 to 900.0 kilohms
At 20°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35.0 to 40.0 kilohms
At 100°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 to 2.5 kilohms
At 120°C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.3 kilohms
Air conditioning system
Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . R134a
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
3
procarmanuals.com
Page 90 of 279

Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Radiator mounting bracket-to-subframe bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Fluid cooler pipe unions - automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Thermostat housing-to-cylinder head bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 15
Water outlet-to-thermostat housing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 11 6 to 8
Coolant temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Coolant temperature gauge sender . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Water pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 13
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2A
Air conditioning compressor mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
3•2 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Engine cooling system
All vehicles covered by this manual employ
a pressurised engine cooling system with
thermostatically-controlled coolant circu-
lation. A water pump mounted on the drivebelt
end of the cylinder block/crankcase pumps
coolant through the engine. The coolant flows
around each cylinder and toward the
transmission end of the engine. Cast-in
coolant passages direct coolant around the
inlet and exhaust ports, near the spark
plug areas and close to the exhaust valve
guides.
A wax pellet type thermostat is located in a
housing at the transmission end of the engine.
During warm-up, the closed thermostat
prevents coolant from circulating through the
radiator. Instead, it returns through the
coolant metal pipe running across the front of
the engine to the radiator bottom hose and
the water pump. The supply to the heater is
made from the rear of the thermostat housing.
As the engine nears normal operating
temperature, the thermostat opens and allows
hot coolant to travel through the radiator,
where it is cooled before returning to the
engine.
The cooling system is sealed by a pressure-
type filler cap in the expansion tank. The
pressure in the system raises the boiling point
of the coolant, and increases the cooling
efficiency of the radiator. When the engine is
at normal operating temperature, the coolant
expands, and the surplus is displaced into the
expansion tank. When the system cools, the
surplus coolant is automatically drawn back
from the tank into the radiator.
Warning: DO NOT attempt to
remove the expansion tank filler
cap, or to disturb any part of the
cooling system, while it or the
engine is hot, as there is a very great risk
of scalding. If the expansion tank filler cap
must be removed before the engine and
radiator have fully cooled down (even
though this is not recommended) the
pressure in the cooling system must first
be released. Cover the cap with a thick
layer of cloth, to avoid scalding, and slowly
unscrew the filler cap until a hissing sound
can be heard. When the hissing hasstopped, showing that pressure is
released, slowly unscrew the filler cap
further until it can be removed; if more
hissing sounds are heard, wait until they
have stopped before unscrewing the cap
completely. At all times, keep well away
from the filler opening.
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your
skin, or with the painted surfaces
of the vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. Never
leave antifreeze lying around in an open
container, or in a puddle in the driveway or
on the garage floor. Children and pets are
attracted by its sweet smell, but antifreeze
is fatal if ingested.
Warning: If the engine is hot, the
electric cooling fan may start
rotating even if the engine is not
running, so be careful to keep
hands, hair and loose clothing well clear
when working in the engine compartment.
Heating system
The heating system consists of a blower fan
and heater matrix (radiator) located in the
heater unit, with hoses connecting the heater
matrix to the engine cooling system. Hot
engine coolant is circulated through the
heater matrix. When the heater temperature
control on the facia is operated, a flap door
opens to expose the heater box to the
passenger compartment. When the blower
control is operated, the blower fan forces air
through the unit according to the setting
selected.
Air conditioning system
See Section 11.
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze to come in
contact with your skin, or with the painted
surfaces of the vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. Antifreeze is
highly toxic if ingested. Never leave antifreeze
lying around in an open container, or in
puddles on the floor; children and pets are
attracted by its sweet smell, and may drink it.
Check with local authorities about disposing
of used antifreeze - many have collection
centres which will see that antifreeze is
disposed of safely.The cooling system should be filled with a
water/ethylene glycol-based antifreeze
solution, of a strength which will prevent
freezing down to at least -25°C, or lower if the
local climate requires it. Antifreeze also
provides protection against corrosion, and
increases the coolant boiling point.
The cooling system should be maintained
according to the schedule described in
Chapter 1. If antifreeze is used that is not to
Ford’s specification, old or contaminated
coolant mixtures are likely to cause damage,
and encourage the formation of corrosion and
scale in the system. Use distilled water with
the antifreeze, if available - if not, be sure to
use only soft water. Clean rainwater is
suitable.
Before adding antifreeze, check all hoses
and hose connections, because antifreeze
tends to leak through very small openings.
Engines don’t normally consume coolant, so if
the level goes down, find the cause and
correct it.
The exact mixture of antifreeze-to-water
which you should use depends on the
relative weather conditions. The mixture
should contain at least 40% antifreeze, but
not more than 70%. Consult the mixture
ratio chart on the antifreeze container
before adding coolant. Hydrometers are
available at most automotive accessory
shops to test the coolant. Use antifreeze
which meets the vehicle manufacturer’s
specifications.
Note:Refer to the warnings given in Section 1
of this Chapter before starting work.
1If the checks described in Chapter 1 reveal
a faulty hose, it must be renewed as follows
(see illustration).
2First drain the cooling system (see Chap-
ter 1); if the antifreeze is not due for renewal,
the drained coolant may be re-used, if it is
collected in a clean container.
3To disconnect any hose, use a pair of pliers
to release the spring clamps (or a screwdriver
to slacken screw-type clamps), then move
them along the hose clear of the union.
Carefully work the hose off its stubs. The
hoses can be removed with relative ease
when new - on an older car, they may have
stuck.
3 Cooling system hoses -
disconnection and renewal
2 Antifreeze - general information
1 General information
procarmanuals.com
Page 91 of 279
4If a hose proves stubborn, try to release it
by rotating it on its unions before attempting
to work it off. Gently prise the end of the hose
with a blunt instrument (such as a flat-bladed
screwdriver), but do not apply too much force,
and take care not to damage the pipe stubs or
hoses. Note in particular that the radiator hose
unions are fragile; do not use excessive force
when attempting to remove the hoses. If all
else fails, cut the hose with a sharp knife, then
slit it so that it can be peeled off in two pieces.
While expensive, this is preferable to buying a
new radiator. Check first, however, that a new
hose is readily available.
5When refitting a hose, first slide the clampsonto the hose, then work the hose onto its
unions. If the hose is stiff, use soap (or
washing-up liquid) as a lubricant, or soften it
by soaking it in boiling water, but take care to
prevent scalding.
6Work each hose end fully onto its union,
then check that the hose is settled correctly
and is properly routed. Slide each clip along
the hose until it is behind the union flared end,
before tightening it securely.
7Refill the system with coolant (see Chap-
ter 1).
8Check carefully for leaks as soon as
possible after disturbing any part of the
cooling system.Note:Refer to the warnings given in Section 1
of this Chapter before starting work.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Unbolt the resonator support bracket from
the engine compartment front crossmember.
Slacken the two clamp screws securing the
resonator to the air mass meter and plenum
chamber hoses, then swing the resonator up
clear of the thermostat housing (see Chap-
ter 4).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new or in good
condition, drain it into a clean container and
re-use it.
4Disconnect the expansion tank coolant
hose and the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing’s water outlet.
5Unbolt the water outlet and withdraw the
thermostat (see illustration). Note the
position of the air bleed valve, and how the
thermostat is installed (which end is facing
outwards).
Testing
General check
6Before assuming the thermostat is to blame
for a cooling system problem, check the
coolant level, auxiliary drivebelt tension and
condition (see Chapter 1) and temperature
gauge operation.
7If the engine seems to be taking a long time
to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the
thermostat.
8If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the radiator top
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,
preventing the coolant inside the engine from
escaping to the radiator - renew the
thermostat.
4 Thermostat -
removal, testing and refitting
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•3
3
4.5 Unbolt water outlet to withdraw
thermostat
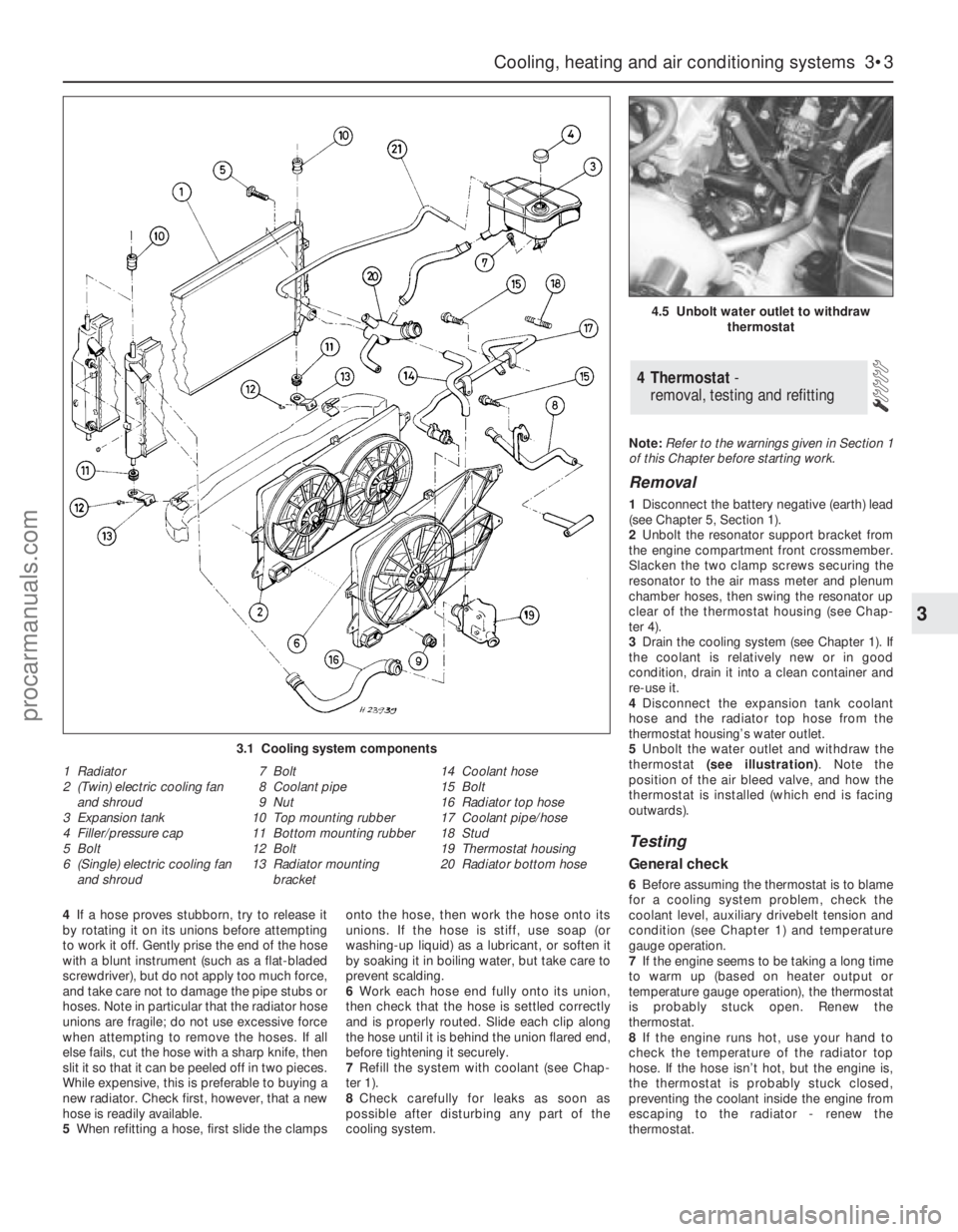
3.1 Cooling system components
1 Radiator
2 (Twin) electric cooling fan
and shroud
3 Expansion tank
4 Filler/pressure cap
5 Bolt
6 (Single) electric cooling fan
and shroud7 Bolt
8 Coolant pipe
9 Nut
10 Top mounting rubber
11 Bottom mounting rubber
12 Bolt
13 Radiator mounting
bracket14 Coolant hose
15 Bolt
16 Radiator top hose
17 Coolant pipe/hose
18 Stud
19 Thermostat housing
20 Radiator bottom hose
procarmanuals.com
Page 95 of 279

Heater blower motor
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Release the four clips (by pulling them out)
securing the passenger side footwell upper
trim panel, then withdraw the panel.
3Unplug the motor’s electrical connector.
4Lift the motor’s retaining lug slightly, twist
the motor anti-clockwise (seen from beneath)
through approximately 30°, then withdraw the
assembly.
5The motor’s control resistor can be
removed by sliding a slim screwdriver into the
slot provided in one end. Press the
screwdriver in approximately 5 mm against
spring pressure, and prise the resistor out
(see illustration).
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Refit the motor, and twist it
clockwise until the retaining lug engages
securely (see illustration).
Heater matrix
Removal
7Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).8Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
9Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
heater matrix unions protruding through the
engine compartment bulkhead (see
illustrations).
10Working inside the passenger
compartment, remove the trim panels from
each footwell, just in front of the centre
console. Each panel is secured by two
screws. If additional clearance is required, the
centre console can be removed as well (see
Chapter 11), but this is not essential.
11Remove the single screw to release the air
duct in the base of the heater unit (see
illustration).
12Remove the three Torx-type screws (size
T20) securing the air distributor to the heater
unit bottom cover, then release the clips.There is a single plastic clip on each side, and
additional metal clips may be found. Push the
duct up to retract it, and withdraw the air
distributor (see illustration).
13Release the clips - there are two plastic
clips on each side, and additional metal clips
may be found - then withdraw the heater
unit’s bottom cover, complete with the matrix
(see illustration).
14Undo the screw and withdraw the clamp
to separate the matrix from the bottom cover
(see illustration).
Refitting
15Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Additional metal clips may be
required to secure the heater unit’s bottom
cover and the air distributor. Ensure that the
9 Heater/ventilation components
- removal and refitting
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•7
3
9.12 . . . release clips (A) to free air
distributor from base of heater unit - note
clips (B) securing . . .9.13 . . . heater unit’s bottom cover,
complete with matrix9.14 Remove clamp (one screw) to separate
matrix from heater unit’s bottom cover
9.5 Heater blower motor control resistor
can be prised out of heater unit9.6 Ensure blower motor retaining lug
(arrowed) engages securely in heater unit
on reassembly9.9A Coolant pipes to heater matrix must
be disconnected . . .
9.9B . . . but can be reached best from
beneath vehicle (arrowed)9.11 Remove screw to allow air duct to be
retracted into air distributor at base of
heater unit . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 96 of 279
duct is lowered from the air distributor and
secured with its screw.
16Refill the cooling system with the proper
mixture of antifreeze and water (see Chapter
1). Start the engine and allow it to reach
normal operating temperature, indicated by
the radiator top hose becoming hot. Recheck
the coolant level and add more if required,
then check for leaks. Check the operation of
the heater.
Pollen filter
17Refer to Chapter 1.
Blower/air conditioning control
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Remove the ashtray. Referring to the
relevant Sections of Chapter 11, undo the two
upper screws from the centre console and
pull out the cassette storage compartment,
then remove the radio/cassette player.
3Pull the heater control/radio bezel out of the
three clips securing its top edge, pull it
forwards and unplug the switch electrical
connector (where fitted).
4Pull off the heater control knobs, and
remove the screw securing each end of the
heater control unit (see illustration). Pull the
control unit out of the facia.
5Unplug the two electrical connectors from
the blower/air conditioning control. Remove
the retaining screw and withdraw the control,
twisting it to release it from the panel.
Refitting
6Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Check the operation of the control
on completion.
Temperature control
Removal
7Remove the heater control unit as
described in paragraphs 1 to 4 above.
8On vehicles without air conditioning,unhook the operating cable from the
temperature control (see illustration); where
air conditioning is fitted, unplug the control’s
electrical connector. Undo the retaining
screw, and withdraw the control.
Refitting
9Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; check the operation of the control
on completion.
Air distribution control
Removal
10Remove the heater control unit as
described in paragraphs 1 to 4 above. Unplug
the electrical connectors, and unhook the
operating cable (where fitted) to withdraw the
unit (see illustration).
11Use a pair of slim screwdrivers to release
the clips on each side of the control, then
withdraw the control from the unit.
Refitting
12Refitting is the reverse of the removalprocedure. Check the operation of the
controls on completion.
General information
The air conditioning system consists of a
condenser mounted in front of the radiator, an
evaporator mounted adjacent to the heater
matrix, a compressor mounted on the engine,
an accumulator/dehydrator, and the plumbing
connecting all of the above components - this
contains a choke (or “venturi”) mounted in the
inlet to the evaporator, which creates the drop
in pressure required to produce the cooling
effect (see illustration).
A blower fan forces the warmer air of the
passenger compartment through the
evaporator core (rather like a radiator in
reverse), transferring the heat from the air to
11 Air conditioning system -
general information and
precautions
10 Heater/air conditioning
controls- removal and refitting
3•8 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
10.4 Remove screws (arrowed) securing
each end of heater control unit10.8 Unhooking operating cable from
temperature control - note retaining screw
(arrowed)10.10 Unplugging electrical connectors
from rear of heater control unit
11.1 Air conditioning system components
1 Quick-release Schrader valve-type
coupling - high-pressure side
2 Quick-release Schrader valve-type
coupling - low-pressure side
3 Pressure-cycling switch - low-pressure side4 Accumulator/dehydrator
5 Compressor
6 Condenser
7 Pressure-regulating switch - high-pressure
side
procarmanuals.com
Page 97 of 279

the refrigerant. The liquid refrigerant boils off
into low-pressure vapour, taking the heat with
it when it leaves the evaporator.
Precautions
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until
after the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant should be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Always wear eye protection
when disconnecting air conditioning
system fittings.
When an air conditioning system is fitted, it
is necessary to observe the following special
precautions whenever dealing with any part of
the system, its associated components, and
any items which necessitate disconnection of
the system:
(a) While the refrigerant used - R134a - is
less damaging to the environment than
the previously-used R12, it is still a very
dangerous substance. It must not be
allowed into contact with the skin or eyes,
or there is a risk of frostbite. It must also
not be discharged in an enclosed space -
while it is not toxic, there is a risk of
suffocation. The refrigerant is heavier than
air, and so must never be discharged over
a pit.
(b) The refrigerant must not be allowed to
come in contact with a naked flame,
otherwise a poisonous gas will be created
- under certain circumstances, this can
form an explosive mixture with air. For
similar reasons, smoking in the presence
of refrigerant is highly dangerous,
particularly if the vapour is inhaled
through a lighted cigarette.
(c) Never discharge the system to the
atmosphere - R134a is not an ozone-
depleting ChloroFluoroCarbon (CFC) as is
R12, but is instead a hydrofluorocarbon,
which causes environmental damage by
contributing to the “greenhouse effect” if
released into the atmosphere.
(d) R134a refrigerant must notbe mixed with
R12; the system uses different seals (now
green-coloured, previously black) and has
different fittings requiring different tools,
so that there is no chance of the two
types of refrigerant becoming mixed
accidentally.
(e) If for any reason the system must be
disconnected, entrust this task to your
Ford dealer or a refrigeration engineer.
(f) It is essential that the system be
professionally discharged prior to using
any form of heat - welding, soldering,
brazing, etc - in the vicinity of the system,
before having the vehicle oven-dried at a
temperature exceeding 70°C after
repainting, and before disconnecting any
part of the system.Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until after the
system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant should be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Cap or plug the pipe lines as
soon as they are disconnected, to prevent
the entry of moisture. Always wear eye
protection when disconnecting air
conditioning system fittings.
Note: This Section refers to the components
of the air conditioning system itself - refer to
Sections 9 and 10 for details of components
common to the heating/ventilation system.
Condenser
1Have the refrigerant discharged at a dealer
service department or an automotive air
conditioning repair facility.
2Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
3Remove the radiator undershield (see
Chapter 1).
4Using the Ford service tool 34-001,
disconnect the refrigerant lines from the
condenser. Immediately cap the open fittings,
to prevent the entry of dirt and moisture.
5Unbolt the condenser (see illustration 7.5)
and lift it out of the vehicle. Store it upright, to
prevent oil loss.
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7If a new condenser was installed, add 20 cc
of refrigerant oil to the system.
8Have the system evacuated, charged and
leak-tested by the specialist who discharged
it.
Evaporator
9The evaporator is mounted with the heater
matrix. Apart from the need to have the
refrigerant discharged, and to use Ford
service tools 34-001 and 34-003 to
disconnect the lines, the procedure is as
described in Section 9 of this Chapter.
10On reassembly, if a new evaporator was
installed, add 20 cc of refrigerant oil to the
system.
11Have the system evacuated, charged and
leak-tested by the specialist who discharged
it.
Compressor
12Have the refrigerant discharged at a
dealer service department or an automotive
air conditioning repair facility.
13Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead (see Chapter 5, Section 1).
14Remove the radiator undershield (see
Chapter 1).15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Unbolt the compressor from the cylinder
block/crankcase, press it to one side, and
unscrew the clamping bolt to disconnect the
refrigerant lines. Plug the line connections,
swing the compressor upright, unplug its
electrical connector, then withdraw the
compressor from the vehicle. Note:Keep the
compressor level during handling and storage.
If the compressor has seized, or if you find
metal particles in the refrigerant lines, the
system must be flushed out by an air
conditioning technician, and the
accumulator/dehydrator must be renewed.
17Prior to installation, turn the compressor
clutch centre six times, to disperse any oil that
has collected in the head.
18Refit the compressor in the reverse order
of removal; renew all seals disturbed.
19If you are installing a new compressor,
refer to the compressor manufacturer’s
instructions for adding refrigerant oil to the
system.
20Have the system evacuated, charged and
leak-tested by the specialist that discharged
it.
Accumulator/dehydrator
21Have the refrigerant discharged at a
dealer service department or an automotive
air conditioning repair facility.
22Disconnect the battery negative (earth)
lead (see Chapter 5, Section 1).
23The accumulator/dehydrator, which acts
as a reservoir and filter for the refrigerant, is
located in the left-hand front corner of the
engine compartment. Using the Ford service
tool 34-003, disconnect the refrigerant line
next to the accumulator/dehydrator from the
compressor. Immediately cap the open
fittings, to prevent the entry of dirt and
moisture, then unplug the pressure-cycling
switch electrical connector (see illustration).
24Remove the radiator undershield (see
Chapter 1).
25Unbolt the accumulator/dehydrator from
the front suspension subframe.
26Using the Ford service tool 34-003,
disconnect the lower refrigerant line from the
accumulator/dehydrator. It may be necessary
12 Air conditioning system
components -
removal and refitting
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•9
3
12.23 Unplug pressure-cycling switch
electrical connector (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 100 of 279

This Chapter is concerned with those
features of the engine management system
that supply clean fuel and air to the engine,
meter it in the required proportions, and
dispose of the results. Since the emission
control sub-systems modify the functions of
both the fuel and exhaust sub-systems, all of
which are integral parts of the whole engine
management system, there are many cross-
references to Chapters 5 and 6. Information
on the electronic control system, its fault
diagnosis, sensors and actuators, is given in
Chapter 6.
The air intake system consists of several
plastics components designed to eliminate
induction roar as much as possible. The air
intake tube (opening behind the direction
indicator/headlight assembly) is connected,
via small and large resonators located under
the front left-hand wing, to the air cleaner
assembly in the engine compartment. Once it
has passed through the filter element and the
air mass meter, the air enters the plenum
chamber mounted above the throttle housing
and inlet manifold; the resonator mounted in
the engine compartment further reduces noise
levels.
The fuel system consists of a plastic tank
(mounted under the body, beneath the rear
seats), combined metal and plastic fuel hoses,
an electric fuel pump mounted in the fuel tank,
and an electronic fuel injection system.
The exhaust system consists of an exhaust
manifold, the front downpipe and catalytic
converter and, on production-fit systems, a
rear section incorporating two or three
silencers and the tailpipe assembly. The
service replacement exhaust system consists
of three or four sections: the front
downpipe/catalytic converter, the
intermediate pipe and front silencer, and the
tailpipe and rear silencer. On some versions,
the tailpipe is in two pieces, with two rear
silencers. The system is suspended
throughout its entire length by rubber
mountings.
Extreme caution should be exercised when
dealing with either the fuel or exhaust
systems. Fuel is a primary element for
combustion. Be very careful! The exhaust
system is an area for exercising caution, as it
operates at very high temperatures. Serious
burns can result from even momentary
contact with any part of the exhaust system,
and the fire risk is ever-present. The catalytic
converter in particular runs at very high
temperatures - refer to the information in
Chapter 6.
Warning: Many of the procedures
in this Chapter require the
removal of fuel lines and
connections, which may result in
some fuel spillage. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautionswhen you work on any part of the fuel
system. Don’t smoke, or allow open flames
or bare light bulbs, near the work area.
Don’t work in a garage where a natural
gas-type appliance (such as a water
heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot light is
present. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand. Before carrying out any operation
on the fuel system, refer also to the
precautions given in “Safety first!” at the
beginning of this manual, and follow them
implicitly. Petrol is a highly-dangerous and
volatile liquid, and the precautions
necessary when handling it cannot be
overstressed.
Warning: The fuel system will
remain pressurised for long
periods of time after the engine is
switched off - this pressure must
be released before any part of the system
is disturbed. Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra precautions
when you work on any part of the fuel
system. Don’t smoke, or allow open flames
or bare light bulbs, near the work area.
Don’t work in a garage where a natural
gas-type appliance (such as a water
heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot light is
present. If you spill any fuel on your skin,
rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
1The fuel system referred to in this Chapter
is defined as the fuel tank and tank-mounted
fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit, the fuel
filter, the fuel injectors and the pressure
regulator in the injector rail, and the metal
pipes and flexible hoses of the fuel lines
between these components. All these contain
fuel, which will be under pressure while the
engine is running and/or while the ignition is
switched on.
2The pressure will remain for some time after
the ignition has been switched off, and must
be relieved before any of these components is
disturbed for servicing work.
3The simplest method is simply to
disconnect the fuel pump’s electrical supply
while the engine is running - either by
removing the fuel pump fuse (number 14), or
by lifting the red button on the fuel cut-off
switch (see Section 13) - and to allow the
engine to idle until it dies through lack of fuel
pressure. Turn the engine over once or twice
on the starter to ensure that all pressure is
released, then switch off the ignition; do not
forget to refit the fuse (or depress the redbutton, as appropriate) when work is
complete.
4The Ford method of depressurisation is to
use service tool 29-033 fitted to the fuel rail
pressure test/release fitting - a Schrader-type
valve with a blue plastic cap, located on the
union of the fuel feed line and the fuel rail - to
release the pressure, using a suitable
container and wads of rag to catch the spilt
fuel. Do notsimply depress the valve core to
release fuel pressure - droplets of fuel will
spray out, with a consequent risk of fire, and
of personal injury through fuel getting into
your eyes.
Warning: Either procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run. Remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
5Note that, once the fuel system has been
depressurised and drained (even partially), it
will take significantly longer to restart the
engine - perhaps several seconds of cranking
- before the system is refilled and pressure
restored.
Warning: The fuel system
pressure must be released before
any part of the system is
disturbed - see Section 2. Petrol
is extremely flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on any part of
the fuel system. Don’t smoke, or allow
open flames or bare light bulbs, near the
work area. Don’t work in a garage where a
natural gas-type appliance (such as a
water heater or clothes dryer) with a pilot
light is present. If you spill any fuel on your
skin, rinse it off immediately with soap and
water. When you perform any kind of work
on the fuel system, wear safety glasses,
and have a Class B type fire extinguisher
on hand.
Disconnecting and connecting
quick-release couplings
1Quick-release couplings are employed at all
unions in the fuel feed and return lines.
2Before disconnecting any fuel system
component, relieve the residual pressure in
the system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
3 Fuel lines and fittings-
general information
2 Fuel system - depressurisation
1 General information and
precautions
4•2 Fuel and exhaust systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 103 of 279

which pulley, disconnect the first cable end
nipple from the throttle actuator’s upper
pulley, then slide the cable outer upwards out
of the actuator housing. Disconnect the
second cable in the same way from the
actuator’s lower pulley.
6Working in the passenger compartment,
reach up to the top of the accelerator pedal.
Pull the end fitting and collar out of the pedal,
then release the cable inner wire through the
slot in the pedal. Tie a length of string to the
end of the cable.
7Returning to the engine compartment, pull
the cable through the bulkhead until the string
can be untied and the pedal-to-actuator cable
removed.
Refitting
8Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Use the string to draw the pedal-
to-actuator cable through the bulkhead.
Ensure that each cable end is connected to
the correct actuator pulley.
9Adjust both cables as described below.
Adjustment
Note:Both sections of the cable must be
adjusted together, even if only one has been
disturbed.
10Remove the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
11Remove the metal clip from the adjuster
of each cable section (see illustration), and
lubricate the adjusters’ grommets with soapy
water.
12Remove any slack by pulling both cable
outers as far as possible out of their
respective adjusters.
13Unplug the TCS throttle actuator’s
electrical connector, and prise off its cover.
Lock both pulleys together by pushing a
locking pin (a pin punch or a similar tool of
suitable size) into their alignment holes.
Disconnect the actuator-to-throttle housing
cable’s end nipple from the throttle linkage.
14Have an assistant depress the accelerator
pedal fully. The pedal-to-actuator cable outer
will move back into the adjuster; hold it there,
and refit the clip.
15Connect the actuator-to-throttle housing
cable end nipple to the throttle linkage, andcheck that the cable outer’s grommet is
correctly secured in the housing bracket.
16Again have the assistant depress the
accelerator pedal fully. The actuator-to-
throttle housing cable outer will move back
into the adjuster; hold it there, and refit the
clip.
17Remove the locking pin from the pulleys.
Check that the throttle valve moves smoothly
and easily from the fully-closed to the fully-
open position and back again, as the
assistant depresses and releases the
accelerator pedal. Re-adjust the cable(s) if
required.
18When the setting is correct, refit the TCS
throttle actuator’s cover and electrical
connector, then refit the plenum chamber (see
Section 4).
1Disconnect the cable inner wire from the
pedal - see Section 5 or 6, as appropriate.
2Undo the retaining nuts and bolt, then
withdraw the pedal assembly (see
illustration).
3Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Adjust the cable(s) as described in
the relevant Section of this Chapter.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a Class B type
fire extinguisher on hand.
Fuel pump operation check
1Switch on the ignition and listen for the fuel
pump (the sound of an electric motor running,
audible from beneath the rear seats). Assuming
there is sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump
should start and run for approximately one or
two seconds, then stop, each time the ignition
is switched on. Note:If the pump runs
continuously all the time the ignition is switched
on, the electronic control system is running in
the backup (or “limp-home”) mode referred to
by Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
ECU itself, and the vehicle should therefore be
taken to a Ford dealer for a full test of the
complete system, using the correct diagnostic
equipment; do not waste time trying to test the
system without such facilities.
2Listen for fuel return noises from the fuel
pressure regulator. It should be possible to
feel the fuel pulsing in the regulator and in the
feed hose from the fuel filter.
3If the pump does not run at all, check the
fuse, relay and wiring (see Chapter 6).
Fuel pressure check
3A fuel pressure gauge, equipped with an
adaptor to suit the Schrader-type valve on the
fuel rail pressure test/release fitting
(identifiable by its blue plastic cap, and
located on the union of the fuel feed line and
the fuel rail) is required for the following
procedure. If the Ford special tool 29-033 is
available (see Section 2), the tool can be
attached to the valve, and a conventional-type
pressure gauge attached to the tool.
4If using the service tool, ensure that its tap
is turned fully anti-clockwise, then attach it to
the valve. Connect the pressure gauge to the
service tool. If using a fuel pressure gauge
with its own adaptor, connect it in accordance
with its maker’s instructions (see illustration).
5Start the engine and allow it to idle. Note
the gauge reading as soon as the pressure
stabilises, and compare it with the pressure
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
(a) If the pressure is high, check for a
restricted fuel return line. If the line is
clear, renew the pressure regulator.
8 Fuel pump/fuel pressure -
check
7 Accelerator pedal -
removal and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4
6.11 Location of TCS throttle actuator-to-
throttle housing cable adjuster (arrowed)7.2 Removing the accelerator pedal
assembly8.4 A fuel pressure gauge, equipped with
an adaptor to suit the Schrader-type valve
on the fuel rail pressure test/release fitting,
is needed to check fuel pressure
procarmanuals.com