1993 FORD MONDEO fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 4 of 279

0•4Introduction
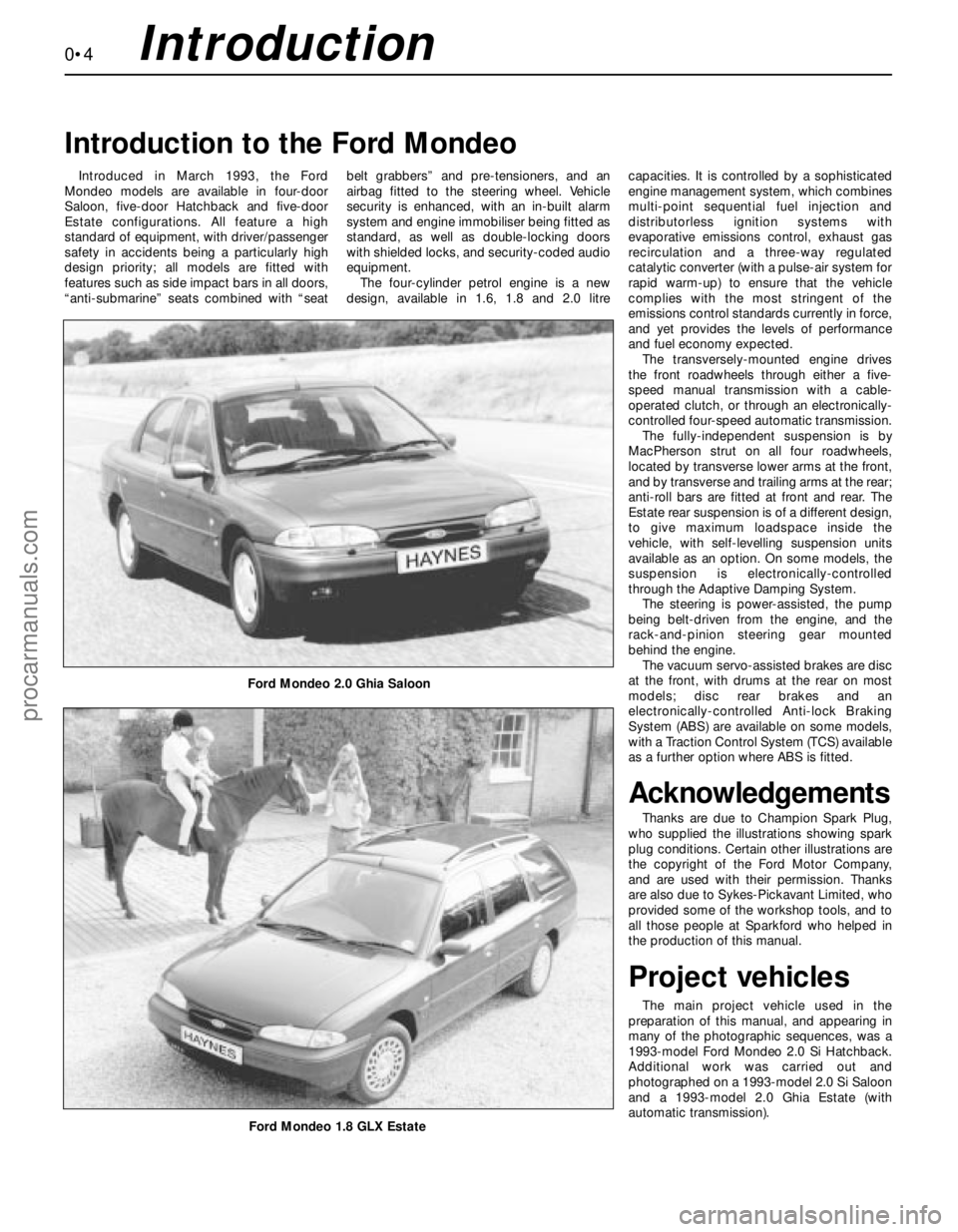
Introduced in March 1993, the Ford
Mondeo models are available in four-door
Saloon, five-door Hatchback and five-door
Estate configurations. All feature a high
standard of equipment, with driver/passenger
safety in accidents being a particularly high
design priority; all models are fitted with
features such as side impact bars in all doors,
“anti-submarine” seats combined with “seatbelt grabbers” and pre-tensioners, and an
airbag fitted to the steering wheel. Vehicle
security is enhanced, with an in-built alarm
system and engine immobiliser being fitted as
standard, as well as double-locking doors
with shielded locks, and security-coded audio
equipment.
The four-cylinder petrol engine is a new
design, available in 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litrecapacities. It is controlled by a sophisticated
engine management system, which combines
multi-point sequential fuel injection and
distributorless ignition systems with
evaporative emissions control, exhaust gas
recirculation and a three-way regulated
catalytic converter (with a pulse-air system for
rapid warm-up) to ensure that the vehicle
complies with the most stringent of the
emissions control standards currently in force,
and yet provides the levels of performance
and fuel economy expected.
The transversely-mounted engine drives
the front roadwheels through either a five-
speed manual transmission with a cable-
operated clutch, or through an electronically-
controlled four-speed automatic transmission.
The fully-independent suspension is by
MacPherson strut on all four roadwheels,
located by transverse lower arms at the front,
and by transverse and trailing arms at the rear;
anti-roll bars are fitted at front and rear. The
Estate rear suspension is of a different design,
to give maximum loadspace inside the
vehicle, with self-levelling suspension units
available as an option. On some models, the
suspension is electronically-controlled
through the Adaptive Damping System.
The steering is power-assisted, the pump
being belt-driven from the engine, and the
rack-and-pinion steering gear mounted
behind the engine.
The vacuum servo-assisted brakes are disc
at the front, with drums at the rear on most
models; disc rear brakes and an
electronically-controlled Anti-lock Braking
System (ABS) are available on some models,
with a Traction Control System (TCS) available
as a further option where ABS is fitted.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Champion Spark Plug,
who supplied the illustrations showing spark
plug conditions. Certain other illustrations are
the copyright of the Ford Motor Company,
and are used with their permission. Thanks
are also due to Sykes-Pickavant Limited, who
provided some of the workshop tools, and to
all those people at Sparkford who helped in
the production of this manual.
Project vehicles
The main project vehicle used in the
preparation of this manual, and appearing in
many of the photographic sequences, was a
1993-model Ford Mondeo 2.0 Si Hatchback.
Additional work was carried out and
photographed on a 1993-model 2.0 Si Saloon
and a 1993-model 2.0 Ghia Estate (with
automatic transmission).
Introduction to the Ford Mondeo
Ford Mondeo 2.0 Ghia Saloon
Ford Mondeo 1.8 GLX Estate
procarmanuals.com
Page 5 of 279

Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle, always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on ramps.
Never venture
under a car
which is only
supported by
a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with
heart problems
or a pacemaker.
Don’t work on or
near the ignition
system with the
engine running or the
ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the
hands, face or any other part of
the body to injector spray; the
fuel can penetrate the skin with
potentially fatal results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
0•5Safety First!
procarmanuals.com
Page 40 of 279

1•26Every 60 000 miles
Every 60 000 miles
Refer to Chapter 2, Part A.
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so extra precautions
must be taken when working on
any part of the fuel system. Do not smoke,
or allow open flames or bare light bulbs,
near the work area. Also, do not work in a
garage if a gas appliance with a pilot light is
present. While performing any work on the
fuel system, wear safety glasses, and have
a suitable (Class B) fire extinguisher on
hand. If you spill any fuel on your skin, rinse
it off immediately with soap and water.
1The fuel filter is located at the front right-
hand corner of the fuel tank, just forward of
the vehicle’s right-hand rear jacking point. The
filter performs a vital role in keeping dirt and
other foreign matter out of the fuel system,
and so must be renewed at regular intervals,or whenever you have reason to suspect that
it may be clogged. It is always unpleasant
working under a vehicle - pressure-washing or
hosing clean the underbody in the filter’s
vicinity will make working conditions more
tolerable, and will reduce the risk of getting
dirt into the fuel system.
2Relieve any residual pressure in the system
by removing the fuel pump fuse (No 14) and
starting the engine; allow the engine to idle until
it dies. Turn the engine over once or twice on
the starter, to ensure that all pressure is
released, then switch off the ignition.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the pressure
necessary for the engine to run -
remember that fuel will still be present in
the system components, and take
precautions before disconnecting them.
3Noting the comments made in Section 1 of
Chapter 5, disconnect the battery earth terminal.
4Jack up the rear right-hand side of the
vehicle, and support it securely on an axle stand.
5Using rag to soak up any spilt fuel, release
the fuel feed and outlet pipe unions from the
filter, by squeezing together the protruding
locking lugs on each union, and carefully
pulling the union off the filter stub (seeillustration). Where the unions are colour-
coded, the feed and outlet pipes cannot be
confused; where both unions are the same
colour, note carefully which pipe is connected
to which filter stub, and ensure that they are
correctly reconnected on refitting.
6Noting the arrows and/or other markings on
the filter showing the direction of fuel flow
(towards the engine), slacken the filter clamp
screw and withdraw the filter. Note that the
filter will still contain fuel; care should be
taken, to avoid spillage and to minimise the
risk of fire.
7On installation, slide the filter into its clamp
so that the arrow marked on it faces the
correct way, then slide each pipe union on to
its (correct) respective filter stub, and press it
down until the locking lugs click into their
groove (see illustrations). Tighten the clamp
screw carefully, until the filter is just prevented
from moving; do not overtighten the clamp
screw, or the filter casing may be crushed.
8Refit the fuel pump fuse and reconnect the
battery earth terminal, then switch the ignition
on and off five times, to pressurise the
system. Check for any sign of fuel leakage
around the filter unions before lowering the
vehicle to the ground and starting the engine.
33 Fuel filter renewal
32 Timing belt renewal
33.5 Squeeze together fuel filter pipe union
locking lugs, then pull pipes off filter stubs -
ensure pipes are correctly reconnected33.7A When installing the new filter,
ensure the arrow showing direction of fuel
flow points towards the engine . . .
Every 3 years
The procedure is similar to that for the
bleeding of the hydraulic system as described
in Chapter 9, except that the brake fluid
reservoir should be emptied by syphoning,and allowance should be made for the old
fluid to be removed from the circuit when
bleeding a section of the circuit.
34 Brake fluid renewal
31.22 Measure the resistance of the spark
plug leads - if any exceeds the specified
maximum value, renew all the leads
the lead to remove built-up dirt and grease.
Once the lead is clean, check for burns, cracks
and other damage. Do not bend the lead
sharply, because the conductor might break.
22Disconnect the lead from the ignition coil
by pressing together the plastic retaining
catches and pulling the end fitting off the coil
terminal. Check for corrosion and for a tight
fit. If a meter with the correct measuring range
is available, measure the resistance of the
disconnected lead from its coil connector to
its spark plug connector (see illustration). If
the resistance recorded for any of the leads
exceeds the value specified, all the leadsshould be renewed as a set. Refit the lead to
the coil, noting that each coil terminal is
marked with its respective cylinder number,
so that there is no risk of mixing up the leads
and upsetting the firing order.
23Inspect the remaining plug leads, ensuring
that each is securely fastened both ends when
the check is complete. If any sign of arcing,
severe connector corrosion, burns, cracks or
other damage is noticed, obtain new spark
plug (HT) leads, renewing them as a set. If new
spark plug leads are to be fitted, remove and
refit them one at a time, to avoid mix-ups in
the firing order.
33.7B . . . secure pipe unions as described -
do not overtighten clamp screw (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 43 of 279
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nm lbf ft
Engine/automatic transmission rear mounting:
Mounting bracket-to-transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 to 49 35 to 36
Mounting-to-subframe bolts - stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Mounting-to-subframe bolts - stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting centre bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120 89
Engine/transmission left-hand mounting:
Bracket-to-transmission nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 61
Mounting centre bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not available
Mounting-to-body bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not available
Engine/transmission right-hand mounting:
Bracket-to-engine and mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 to 90 61 to 66
Mounting-to-body bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84 62
Note:Refer to Part B of this Chapter for remaining torque wrench settings.
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•3
2A
How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to repair
procedures possible while the engine is still
installed in the vehicle, and includes only the
Specifications relevant to those procedures.
Since these procedures are based on the
assumption that the engine is installed in the
vehicle, if the engine has been removed from
the vehicle and mounted on a stand, some of
the preliminary dismantling steps outlined will
not apply.
Information concerning engine/transmission
removal and refitting, and engine overhaul, can
be found in Part B of this Chapter, which also
includes the Specifications relevant to those
procedures.
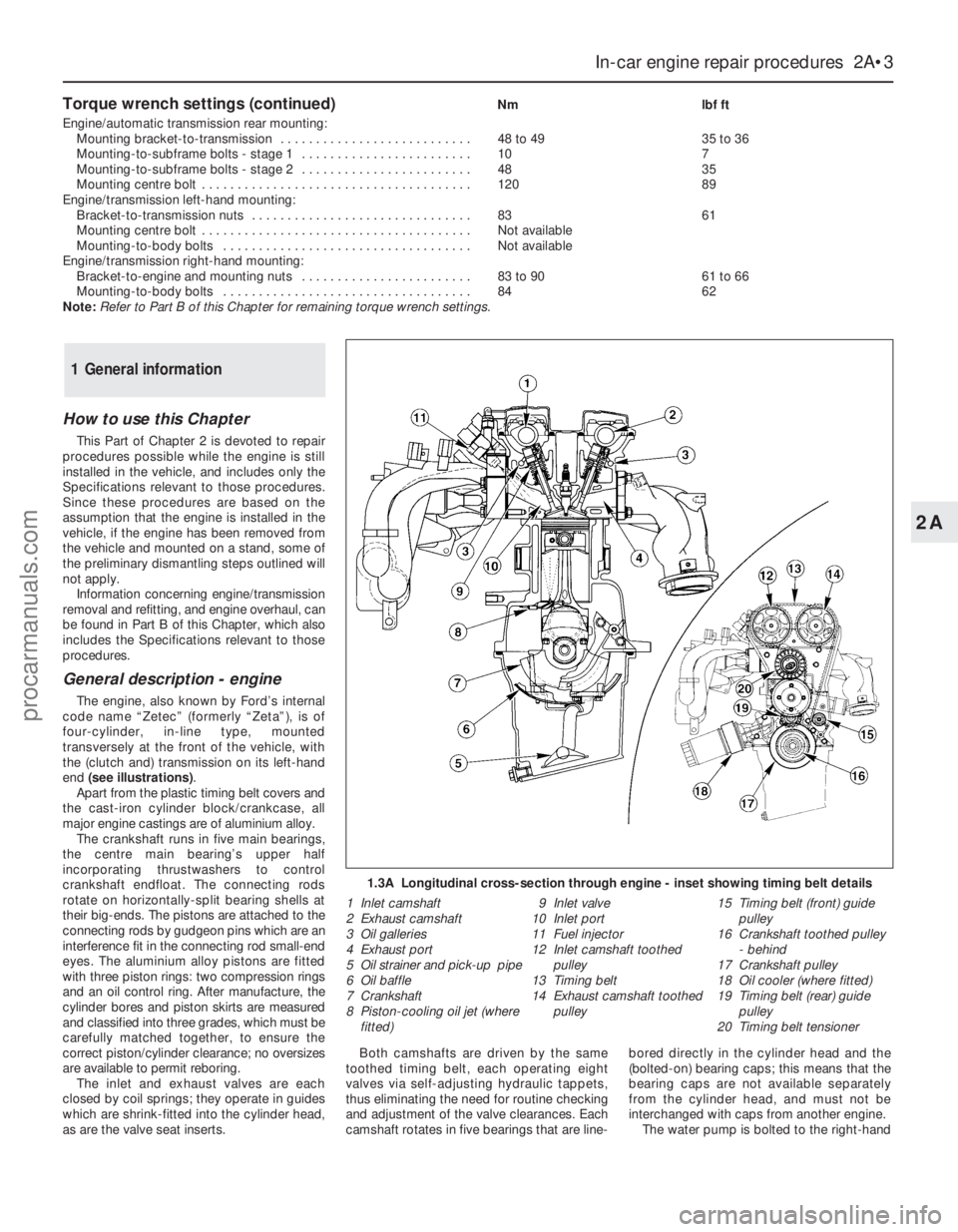
General description - engine
The engine, also known by Ford’s internal
code name “Zetec” (formerly “Zeta”), is of
four-cylinder, in-line type, mounted
transversely at the front of the vehicle, with
the (clutch and) transmission on its left-hand
end (see illustrations).
Apart from the plastic timing belt covers and
the cast-iron cylinder block/crankcase, all
major engine castings are of aluminium alloy.
The crankshaft runs in five main bearings,
the centre main bearing’s upper half
incorporating thrustwashers to control
crankshaft endfloat. The connecting rods
rotate on horizontally-split bearing shells at
their big-ends. The pistons are attached to the
connecting rods by gudgeon pins which are an
interference fit in the connecting rod small-end
eyes. The aluminium alloy pistons are fitted
with three piston rings: two compression rings
and an oil control ring. After manufacture, the
cylinder bores and piston skirts are measured
and classified into three grades, which must be
carefully matched together, to ensure the
correct piston/cylinder clearance; no oversizes
are available to permit reboring.
The inlet and exhaust valves are each
closed by coil springs; they operate in guides
which are shrink-fitted into the cylinder head,
as are the valve seat inserts.Both camshafts are driven by the same
toothed timing belt, each operating eight
valves via self-adjusting hydraulic tappets,
thus eliminating the need for routine checking
and adjustment of the valve clearances. Each
camshaft rotates in five bearings that are line-bored directly in the cylinder head and the
(bolted-on) bearing caps; this means that the
bearing caps are not available separately
from the cylinder head, and must not be
interchanged with caps from another engine.
The water pump is bolted to the right-hand
1 General information
1.3A Longitudinal cross-section through engine - inset showing timing belt details
1 Inlet camshaft
2 Exhaust camshaft
3 Oil galleries
4 Exhaust port
5 Oil strainer and pick-up pipe
6 Oil baffle
7 Crankshaft
8 Piston-cooling oil jet (where
fitted)9 Inlet valve
10 Inlet port
11 Fuel injector
12 Inlet camshaft toothed
pulley
13 Timing belt
14 Exhaust camshaft toothed
pulley15 Timing belt (front) guide
pulley
16 Crankshaft toothed pulley
- behind
17 Crankshaft pulley
18 Oil cooler (where fitted)
19 Timing belt (rear) guide
pulley
20 Timing belt tensioner
procarmanuals.com
Page 44 of 279
end of the cylinder block, inboard of the
timing belt, and is driven with the power
steering pump and alternator by a flat
“polyvee”-type auxiliary drivebelt from the
crankshaft pulley.
When working on this engine, note that
Torx-type (both male and female heads) and
hexagon socket (Allen head) fasteners are
widely used; a good selection of bits, with the
necessary adaptors, will be required, so that
these can be unscrewed without damage
and, on reassembly, tightened to the torque
wrench settings specified.
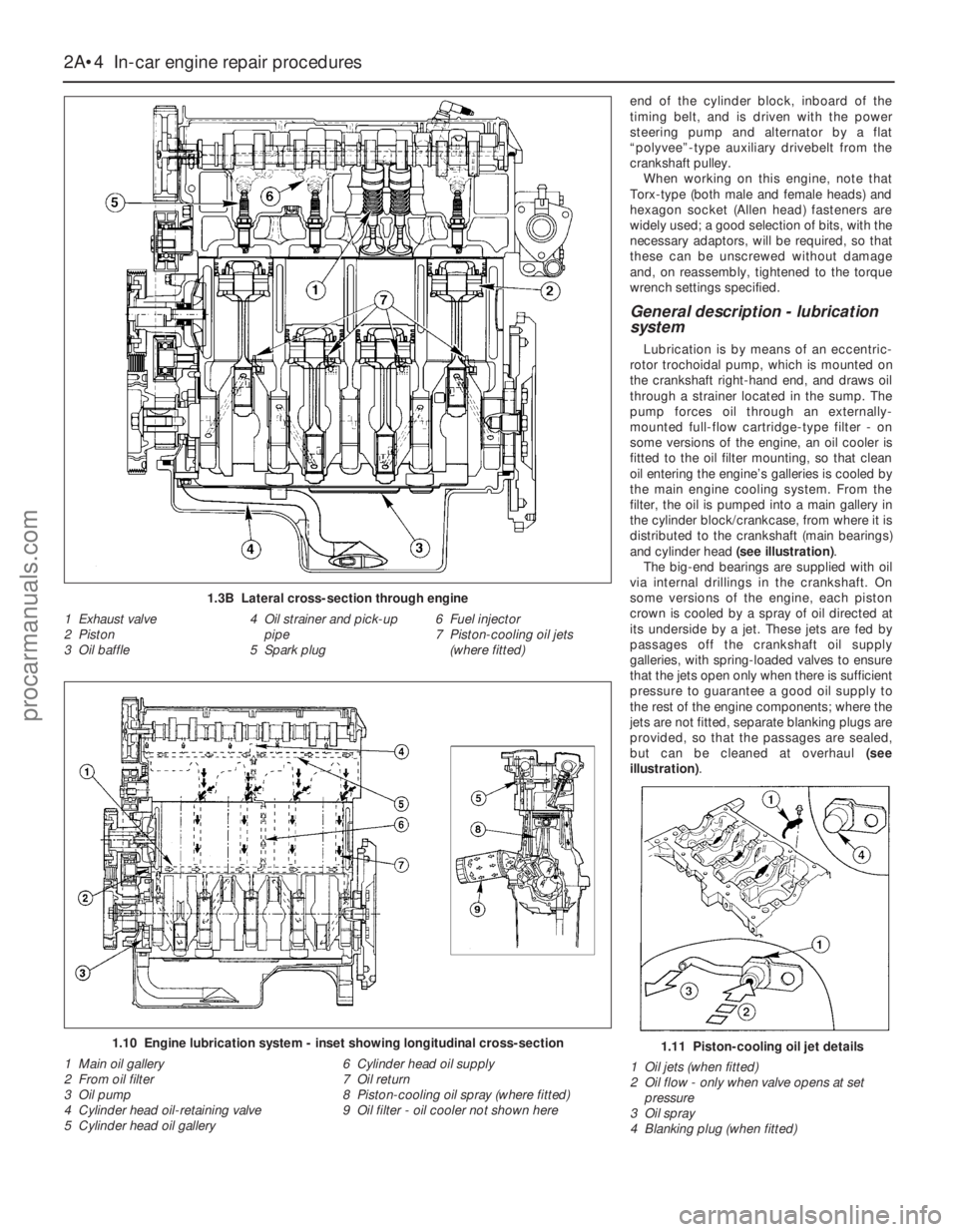
General description - lubrication
system
Lubrication is by means of an eccentric-
rotor trochoidal pump, which is mounted on
the crankshaft right-hand end, and draws oil
through a strainer located in the sump. The
pump forces oil through an externally-
mounted full-flow cartridge-type filter - on
some versions of the engine, an oil cooler is
fitted to the oil filter mounting, so that clean
oil entering the engine’s galleries is cooled by
the main engine cooling system. From the
filter, the oil is pumped into a main gallery in
the cylinder block/crankcase, from where it is
distributed to the crankshaft (main bearings)
and cylinder head (see illustration).
The big-end bearings are supplied with oil
via internal drillings in the crankshaft. On
some versions of the engine, each piston
crown is cooled by a spray of oil directed at
its underside by a jet. These jets are fed by
passages off the crankshaft oil supply
galleries, with spring-loaded valves to ensure
that the jets open only when there is sufficient
pressure to guarantee a good oil supply to
the rest of the engine components; where the
jets are not fitted, separate blanking plugs are
provided, so that the passages are sealed,
but can be cleaned at overhaul (see
illustration).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
1.3B Lateral cross-section through engine
1 Exhaust valve
2 Piston
3 Oil baffle4 Oil strainer and pick-up
pipe
5 Spark plug6 Fuel injector
7 Piston-cooling oil jets
(where fitted)
1.10 Engine lubrication system - inset showing longitudinal cross-section
1 Main oil gallery
2 From oil filter
3 Oil pump
4 Cylinder head oil-retaining valve
5 Cylinder head oil gallery6 Cylinder head oil supply
7 Oil return
8 Piston-cooling oil spray (where fitted)
9 Oil filter - oil cooler not shown here1.11 Piston-cooling oil jet details
1 Oil jets (when fitted)
2 Oil flow - only when valve opens at set
pressure
3 Oil spray
4 Blanking plug (when fitted)
procarmanuals.com
Page 45 of 279

The cylinder head is provided with two oil
galleries, one on the inlet side and one on the
exhaust, to ensure constant oil supply to the
camshaft bearings and hydraulic tappets. A
retaining valve (inserted into the cylinder
head’s top surface, in the middle, on the inlet
side) prevents these galleries from being
drained when the engine is switched off. The
valve incorporates a ventilation hole in its
upper end, to allow air bubbles to escape
from the system when the engine is restarted.
While the crankshaft and camshaft
bearings and the hydraulic tappets receive a
pressurised supply, the camshaft lobes and
valves are lubricated by splash, as are all
other engine components.
Valve clearances - general
It is necessary for a clearance to exist
between the tip of each valve stem and the
valve operating mechanism, to allow for the
expansion of the various components as the
engine reaches normal operating
temperature.
On most older engine designs, this meant
that the valve clearances (also known as
“tappet” clearances) had to be checked and
adjusted regularly. If the clearances were
allowed to be too slack, the engine would be
very noisy, its power output would suffer, and
its fuel consumption would increase. If the
clearances were allowed to be too tight, the
engine’s power output would be reduced,
and the valves and their seats could be
severely damaged.
The engines covered in this manual,
however, employ hydraulic tappets which use
the lubricating system’s oil pressure
automatically to take up the clearance
between each camshaft lobe and its
respective valve stem. Therefore, there is no
need for regular checking and adjustment of
the valve clearances, but it is essential that
onlygood-quality oil of the recommended
viscosity and specification is used in the
engine, and that this oil is always changed at
the recommended intervals. If this advice is
not followed, the oilways and tappets may
become clogged with particles of dirt, or
deposits of burnt (inferior) engine oil, so that
the system cannot work properly; ultimately,
one or more of the tappets may fail, and
expensive repairs may be required.
On starting the engine from cold, there will
be a slight delay while full oil pressure builds
up in all parts of the engine, especially in the
tappets; the valve components, therefore,
may well “rattle” for about 10 seconds or so,
and then quieten. This is a normal state of
affairs, and is nothing to worry about,
provided that all tappets quieten quickly and
stay quiet.
After the vehicle has been standing for
several days, the valve components may
“rattle” for longer than usual, as nearly all the
oil will have drained away from the engine’s
top end components and bearing surfaces.
While this is only to be expected, care mustbe taken not to damage the engine under
these circumstances - avoid high speed
running until all the tappets are refilled with oil
and operating normally. With the vehicle
stationary, hold the engine at no more than a
fast idle speed (maximum 2000 to 2500 rpm)
for 10 to 15 seconds, or until the noise
ceases. Do not run the engine at more than
3000 rpm until the tappets are fully recharged
with oil and the noise has ceased.
If the valve components are thought to be
noisy, or if a light rattle persists from the top
end after the engine has warmed up to
normal operating temperature, take the
vehicle to a Ford dealer for expert advice.
Depending on the mileage covered and the
usage to which each vehicle has been put,
some vehicles may be noisier than others;
only a good mechanic experienced in these
engines can tell if the noise level is typical for
the vehicle’s mileage, or if a genuine fault
exists. If any tappet’s operation is faulty, it
must be renewed (Section 13).
The following major repair operations can
be accomplished without removing the
engine from the vehicle. However, owners
should note that any operation involving the
removal of the sump requires careful
forethought, depending on the level of skill
and the tools and facilities available; refer to
the relevant text for details.
(a) Compression pressure - testing.
(b) Cylinder head cover - removal and
refitting.
(c) Timing belt covers - removal and refitting.
(d) Timing belt - renewal.
(e) Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys
- removal and refitting.
(f) Camshaft oil seals - renewal.
(g) Camshafts and hydraulic tappets -
removal and refitting.
(h) Cylinder head - removal, overhaul and
refitting.
(i) Cylinder head and pistons -
decarbonising.
(j) Sump - removal and refitting.
(k) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
(l) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
(m) Piston/connecting rod assemblies -
removal and refitting (but see note below).
(n) Flywheel/driveplate - removal and
refitting.
(o) Engine/transmission mountings - removal
and refitting.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and will help to keep dirt
out of the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet, to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint; special covers are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for component/
gasket or seal replacement, the repairs can
generally be made with the engine in the
vehicle. The intake and exhaust manifold
gaskets, sump gasket, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place.
Exterior components such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
without lifting out the engine, camshaft and
valve component servicing can also be
accomplished with the engine in the vehicle,
as can renewal of the timing belt and toothed
pulleys.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine
in the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved, and because of the
amount of preliminary dismantling work
required - these operations are therefore
covered in Part B of this Chapter.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel systems, a compression
test can provide diagnostic clues as to the
engine’s condition. If the test is performed
regularly, it can give warning of trouble before
any other symptoms become apparent.
2The engine must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature, the oil level
must be correct, the battery must be fully
charged, and the spark plugs must be
removed. The aid of an assistant will be
required also.
3Disable the ignition system by unplugging
the ignition coil’s electrical connector, and
remove fuse 14 to disconnect the fuel pump.
4Fit a compression tester to the No 1
cylinder spark plug hole - the type of tester
which screws into the plug thread is to be
preferred.
5Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter
motor; after one or two revolutions, the
compression pressure should build up to a
maximum figure, and then stabilise. Record
the highest reading obtained.
6Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
7At the time of writing, no compression
3 Compression test -
description and interpretation
2 Repair operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•5
2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 46 of 279

specifications were available from Ford, but a
typical reading would be in excess of 12 bars.
All cylinders should produce very similar
pressures; any difference greater than 10%
indicates the existence of a fault. Note that the
compression should build up quickly in a
healthy engine; low compression on the first
stroke, followed by gradually-increasing
pressure on successive strokes, indicates worn
piston rings. A low compression reading on the
first stroke, which does not build up during
successive strokes, indicates leaking valves or a
blown head gasket (a cracked head could also
be the cause). Deposits on the undersides of the
valve heads can also cause low compression.
8If the pressure in any cylinder is
considerably lower than the others, introduce
a teaspoonful of clean oil into that cylinder
through its spark plug hole, and repeat the
test.
9If the addition of oil temporarily improves
the compression pressure, this indicates that
bore or piston wear is responsible for the
pressure loss. No improvement suggests that
leaking or burnt valves, or a blown head
gasket, may be to blame.
10A low reading from two adjacent cylinders
is almost certainly due to the head gasket
having blown between them; the presence of
coolant in the engine oil will confirm this.
11If one cylinder is about 20 percent lower
than the others and the engine has a slightly
rough idle, a worn camshaft lobe or faulty
hydraulic tappet could be the cause.
12If the compression is unusually high, the
combustion chambers are probably coated
with carbon deposits. If this is the case, the
cylinder head should be removed and
decarbonised.
13On completion of the test, refit the spark
plugs, then reconnect the ignition system and
fuel pump.
General
1Top Dead Centre (TDC) is the highest point
in its travel up-and-down its cylinder bore
that each piston reaches as the crankshaftrotates. While each piston reaches TDC both
at the top of the compression stroke and
again at the top of the exhaust stroke, for the
purpose of timing the engine, TDC refers to
the piston position (usually No 1 piston) at the
top of its compression stroke.
2It is useful for several servicing procedures
to be able to position the engine at TDC.
3No 1 piston and cylinder are at the right-
hand (timing belt) end of the engine (right-
and left-hand are always quoted as seen from
the driver’s seat). Note that the crankshaft
rotates clockwise when viewed from the
right-hand side of the vehicle.
Locating TDC
4Remove all the spark plugs (Chapter 1).
5Disconnect both battery leads - see
Chapter 5, Section 1 - unless the starter
motor is to be used to turn the engine.
6Apply the handbrake and ensure that the
transmission is in neutral, then jack up the
front right-hand side of the vehicle and
support on an axle stand. Remove the
roadwheel.
7Remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1) to expose the crankshaft pulley
and timing marks.
8It is best to rotate the crankshaft using a
spanner applied to the crankshaft pulley bolt;
however, it is possible also to use the starter
motor (switched on either by an assistant
using the ignition key, or by using a remote
starter switch) to bring the engine close to
TDC, then finish with a spanner. If the starter
is used, be sure to disconnect the battery
leads immediately it is no longer required.
9Note the two pairs of notches in the inner
and outer rims of the crankshaft pulley. In the
normal direction of crankshaft rotation
(clockwise, seen from the right-hand side of the
vehicle) the first pair of notches are irrelevant to
the vehicles covered in this manual, while the
second pair indicate TDC when aligned with
the rear edge of the raised mark on the sump.
Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until the
second pair of notches align with the edge of
the sump mark; use a straight edge extended
out from the sump if greater accuracy is
required (see illustrations).10Nos 1 and 4 cylinders are now at TDC,
one of them on the compression stroke.
Remove the oil filler cap; if No 4 cylinder
exhaust cam lobe is pointing to the rear of the
vehicle and slightly downwards, it is No 1
cylinder that is correctly positioned. If the
lobe is pointing horizontally forwards, rotate
the crankshaft one full turn (360°) clockwise
until the pulley notches align again, and the
lobe is pointing to the rear and slightly down.
No 1 cylinder will then be at TDC on the
compression stroke.
11Once No 1 cylinder has been positioned
at TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for
any of the other cylinders can then be located
by rotating the crankshaft clockwise 180° at a
time and following the firing order (see
Specifications).
12An alternative method of locating TDC is
to remove the cylinder head cover (see
Section 5) and to rotate the crankshaft
(clockwise, as described in paragraph 8
above) until the inlet valves for the cylinder
concerned have opened and just closed
again. Insert a length of wooden dowel
(approximately 150 mm/6 in long) or similar
into the spark plug hole until it rests on the
piston crown, and slowly further rotate the
crankshaft (taking care not to allow the dowel
to be trapped in the cylinder) until the dowel
stops rising - the piston is now at the top of
its compression stroke, and the dowel can be
removed.
13There is a “dead” area around TDC (as
the piston stops rising, pauses and then
begins to descend) which makes difficult the
exact location of TDC by this method; if
accuracy is required, either establish carefully
the exact mid-point of the dead area, or refer
to the timing marks (paragraph 9 above).
1Unplug the two electrical connectors and
disconnect the vacuum hose (where fitted),
then remove the air cleaner assembly cover
with the air mass meter, the resonator and the
plenum chamber (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
5 Cylinder head cover-
removal and refitting
4 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
No 1 piston - locating
2A•6 In-car engine repair procedures
4.9A Do not use crankshaft pulley’s first
pair of notches “A” - align second pair of
notches “B” with raised rib on sump “C” . . .4.9B . . . using a straight edge extended
out from the sump (arrowed) if greater
accuracy is required5.4 Disconnecting crankcase breather
hose from cylinder head cover union
procarmanuals.com
Page 57 of 279

23If using Ford’s recommended procedure,
fit new oil seals to the camshafts as
described in paragraph 5 of Section 12.
24Using the marks and notes made on
dismantling to ensure that each is refitted to
its original camshaft, refit the toothed pulleys
to the camshafts, tightening the retaining
bolts loosely (see illustration). Slip the timing
belt back onto the pulleys (refer to para-
graph 21 of Section 10) and tighten the bolts
securely - use the forked holding tool
described in paragraph 18 of Section 10.
25The remainder of the reassembly
procedure, including checking the camshaft
alignment (valve timing) and setting the timing
belt tension, is as described in paragraphs 17
to 27 of Section 10.
Removal
Note:The following text assumes that the
cylinder head will be removed with both inlet
and exhaust manifolds attached; this
simplifies the procedure, but makes it a bulky
and heavy assembly to handle - an engine
hoist will be required, to prevent the risk of
injury, and to prevent damage to any delicate
components as the assembly is removed and
refitted. If it is wished first to remove the
manifolds, proceed as described in Sections
6 and 7 of this Chapter; amend the following
procedure accordingly.1Relieve the fuel system pressure (see
Chapter 4).
2With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
3Whenever you disconnect any vacuum
lines, coolant and emissions hoses, wiring
loom connectors, earth straps and fuel lines
as part of the following procedure, always
label them clearly, so that they can be
correctly reassembled.
4Unplugging the two electrical connectors,
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head cover, remove
the complete air cleaner assembly with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
5Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then undo the fuel
feed and return lines connecting the engine to
the chassis (see Chapter 4). Plug or cap all
open fittings.
6Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4 -where fitted, disconnect also the cruise control
actuator cable (see Chapter 12). Secure the
cable(s) clear of the engine/transmission.
7Unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe from the cylinder head rear support
plate/engine lifting eye, and from the front
support plate/pump bracket. Releasing its
wire clip, unplug the power steering pressure
switch electrical connector, then unbolt the
earth lead from the cylinder head rear support
plate/engine lifting eye.
8Remove the three screws securing the
wiring “rail” to the rear of the manifold.
Releasing its wire clip, unplug the large
electrical connector (next to the fuel pressure
regulator) to disconnect the engine wiring from
the main loom (see illustration). Unplug the
electrical connectors on each side of the
ignition coil, and the single connector from
beneath the front of the thermostat housing, to
disconnect the coil and coolant temperature
gauge sender wiring (see illustration).
9Marking or labelling them as they are
unplugged, disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
(a) One from the rear of the throttle housing
(only the one hose - there is no need to
disconnect the second hose running to
the fuel pressure regulator).
(b) One from the union on the inlet manifold’s
left-hand end (see illustration).
(c) The braking system vacuum servo unit
hose (see Chapter 9 for details).
(d) Disconnect all vacuum hoses from the
Exhaust Gas Recirculation system
components - one from the EGR valve
and two from the EGR pipe. (Note that
these last two are of different sizes, as are
their pipe stubs, so that they can only be
connected the correct way round.)
10Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield; unclip the coolant hose to allow the
upper part to be withdrawn. Either remove the
dipstick and tube, or swing them out of the way.
11Unscrew the single bolt securing the
pulse-air filter housing to the engine/
transmission front mounting bracket, then
disconnect its vacuum hose.
12Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
13Disconnect all coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing (see illustration).
14 Cylinder head -
removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•17
2A
14.9 Disconnect vacuum hoses (arrowed)
as described in text14.13 Disconnect all coolant hoses
(arrowed) from thermostat housing
13.24 . . . while camshaft toothed pulleys
are refitted14.8A Release wire clip to unplug engine
wiring loom connector from inlet manifold14.8B Unplug connectors (arrowed) to
disconnect ignition coil wiring
Masking tape and/or a touch-
up paint applicator work
well for marking items.
Take instant photos, or
sketch the locations of components
and brackets.
procarmanuals.com