1993 FORD MONDEO steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 219 of 279

the specified mileage (or time) since the last
service has been reached.
4To reset the service interval system and
turn off the light, a switch inside the glovebox
must be depressed for a minimum of 4
seconds with the ignition switched on. This
should be carried out by a Ford dealer if the
vehicle is still in the warranty period.
Component renewal
5The following paragraphs describe brief
removal procedures for the auxiliary warning
system components. Disconnect the battery
negative (earth) lead before commencing
work (refer to Chapter 5, Section 1). Refitting
procedures are a reversal of removal.
Display warning bulb
6Remove the control assembly.
7Prise off the cover, and pull out the relevant
bulb and bulbholder.
Low air temperature warning sender
unit
8Remove the front bumper.
9Unclip the sender unit and disconnect the
multi-plug (see illustration).
Engine oil level sensor
10Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
11Place a container beneath the oil level
sensor, to catch any spilt oil.12Unscrew the screws and remove the
cover from the sensor.
13Disconnect the multi-plug.
14Unscrew and remove the sensor, and
remove the seal (see illustration).
Door ajar sensor
15Remove the door lock as described in
Chapter 11, Section 14.
16Unclip the sensor and disconnect the
multi-plug.
Low coolant warning switch
17Refer to Chapter 3, Section 6.
Low washer fluid switch
18Disconnect the multi-plug from the
washer fluid reservoir.
19Drain or syphon out the fluid from the
reservoir.
20Using a screwdriver, lever out the switch
from the reservoir (see illustration).
Service indicator reset switch
21Remove the glove compartment lid as
described in Chapter 11, Section 32.
22Carefully lever out the switch using a
small screwdriver.
23Remove the rear cover and disconnect
the wiring (see illustration).
Control assembly
24Remove the instrument panel surround,
referring to Section 10.25Unscrew the mounting screws,
disconnect the multi-plugs and remove the
assembly.
Bulb failure module
26Remove the lower facia panel from under
the steering wheel.
27Unclip the bulb failure module and
disconnect the multi-plug.
Note: From November 1993, for added
security, a complex Bosch immobiliser system
was fitted to some models. For further details,
refer to your Ford dealer.
1All UK models are fitted with an anti-theft
alarm system, incorporating movement
sensors and an ignition immobiliser. The
system is activated when the vehicle is
locked.
2The system includes a start inhibitor circuit,
which makes it impossible to start the engine
with the system armed.
3The movement sensors consist of two
ultrasonic units, located in the “B” pillars,
incorporating transmitters and receivers (see
illustrations). The receivers check that the
echo frequency matches the original
frequency. If there is any significant
difference, the system triggers the alarm.
20 Anti-theft alarm system- general
information
12•18 Body electrical system
19.9 Low air temperature sender unit
removal
1 Clip 2 Sender unit 3 Multi-plug19.14 Engine oil level sensor removal
1 Cover 2 Multi-plug 3 Sensor 4 Seal19.20 Removing the low washer fluid
switch
19.23 Service indicator switch removal
1 Lever out the switch 2 Cover 3 Wiring20.3A Disconnecting a movement sensor
multi-plug20.3B Removing a movement sensor
procarmanuals.com
Page 220 of 279
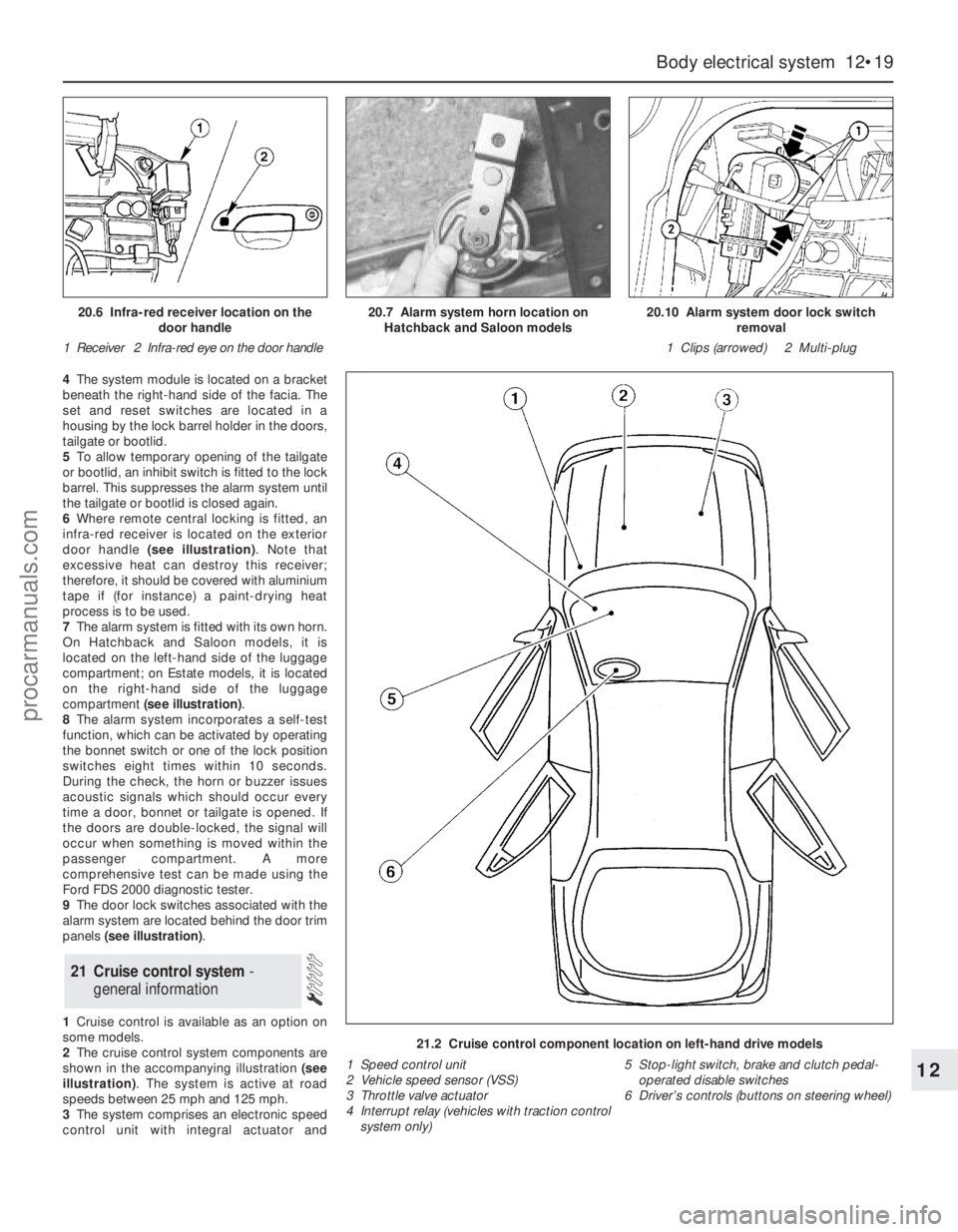
4The system module is located on a bracket
beneath the right-hand side of the facia. The
set and reset switches are located in a
housing by the lock barrel holder in the doors,
tailgate or bootlid.
5To allow temporary opening of the tailgate
or bootlid, an inhibit switch is fitted to the lock
barrel. This suppresses the alarm system until
the tailgate or bootlid is closed again.
6Where remote central locking is fitted, an
infra-red receiver is located on the exterior
door handle (see illustration). Note that
excessive heat can destroy this receiver;
therefore, it should be covered with aluminium
tape if (for instance) a paint-drying heat
process is to be used.
7The alarm system is fitted with its own horn.
On Hatchback and Saloon models, it is
located on the left-hand side of the luggage
compartment; on Estate models, it is located
on the right-hand side of the luggage
compartment (see illustration).
8The alarm system incorporates a self-test
function, which can be activated by operating
the bonnet switch or one of the lock position
switches eight times within 10 seconds.
During the check, the horn or buzzer issues
acoustic signals which should occur every
time a door, bonnet or tailgate is opened. If
the doors are double-locked, the signal will
occur when something is moved within the
passenger compartment. A more
comprehensive test can be made using the
Ford FDS 2000 diagnostic tester.
9The door lock switches associated with the
alarm system are located behind the door trim
panels (see illustration).
1Cruise control is available as an option on
some models.
2The cruise control system components are
shown in the accompanying illustration (see
illustration). The system is active at road
speeds between 25 mph and 125 mph.
3The system comprises an electronic speed
control unit with integral actuator and
21 Cruise control system -
general information
Body electrical system 12•19
12
21.2 Cruise control component location on left-hand drive models
1 Speed control unit
2 Vehicle speed sensor (VSS)
3 Throttle valve actuator
4 Interrupt relay (vehicles with traction control
system only)5 Stop-light switch, brake and clutch pedal-
operated disable switches
6 Driver’s controls (buttons on steering wheel)
20.6 Infra-red receiver location on the
door handle
1 Receiver 2 Infra-red eye on the door handle20.7 Alarm system horn location on
Hatchback and Saloon models20.10 Alarm system door lock switch
removal
1 Clips (arrowed) 2 Multi-plug
procarmanuals.com
Page 221 of 279

switches mounted in the engine compartment
with a control cable connected to the throttle
valve actuator, driver-operated switches,
brake and clutch pedal switches, an indicator
light, and a road speed sensor.
4The driver-operated switches are mounted
on the steering wheel, and allow the driver to
control the various functions.
5The vehicle speed sensor uses the
speedometer cable drive pinion to generate
pulses which are fed to the speed control unit.
6The stop-light switch, brake pedal switch
and (when applicable) clutch pedal switch are
used to disable the cruise control system. The
stop-light switch is activated when the brake
pedal is applied gently, and the brake pedal
switch is activated when the brake pedal is
applied forcibly.
7An indicator light on the instrument panel is
illuminated when the system is in operation.
8The following paragraphs describe brief
removal procedures for the cruise control
system components. The battery negative
(earth) lead should be disconnected before
commencing work (refer to Chapter 5, Sec-
tion 1). Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Speed control switch
9Remove the steering column upper and
lower shrouds, with reference to Chapter 10.
10Remove the air bag module as described
in Section 29.11Disconnect the multi-plugs, then unscrew
the screws and remove the switch.
Disable switches
12Remove the lower facia panel from under
the steering column.
13Disconnect the multi-plugs from the
clutch switch, brake pedal switch and stop-
light switch.
14To remove the clutch and brake pedal
switches, twist them anti-clockwise. To
remove the stop-light switch, twist it
clockwise (see illustration).
15Refitting is the reverse of removal. To
ensure correct operation of the brake pedal
switches, reset the switch by fully extending
its plunger (see illustration).Depress the
pedal until the distance between it and the
mounting bracket is as shown in Chapter 9,
illustration 25.6. Hold the pedal in this
position, clip the switch securely into position
and gently raise the pedal to the at-rest
position. This will automatically set the
position of the switch.
Speed control actuator
16Remove the air cleaner as described in
Chapter 4.
17Disconnect the actuator cable from the
throttle linkage on the throttle housing, by
releasing the inner cable end fitting from the
segment and unclipping the outer cable from
the bracket.
18Unscrew the actuator mounting bolt, thenslide the actuator out of the mounting pin
holes.
19Disconnect the multi-plug and remove the
assembly.
20Depress the actuating cable cap locking
arm, and remove the cap by turning it anti-
clockwise (see illustration).
21Gently raise the cable retaining lug by a
maximum of 0.5 mm, and push the cable end
out of the slot in the pulley.
22When refitting, make sure that the cable
end locks into the slot in the pulley.
23To locate the cable cap onto the actuator
pulley, keep the cable taut and in the pulley
groove, and pull the throttle linkage end of the
cable to draw the cable cap onto the pulley.
24To refit the cable cap, keep the cable taut
and the pulley still, then refit the cable cap
tabs into the actuator slots; turn the cap
clockwise until the locking arm locates on the
locking stop. Note:Incorrect assembly of the
cable onto the pulley may result in a high idle
speed. Check that the throttle lever is in its
idle position after refitting the actuator.
Removal
Washer reservoir and pump
1Unscrew the bolts, and release the clips to
remove the radiator lower cover.
2Unscrew the mounting bolts, and pull the
reservoir forwards slightly (see illustration).
For better access, it may be necessary to
remove the front bumper.
3Disconnect the multi-plugs for the
windscreen washer pump and fluid level
sensor (see illustration).
4Disconnect the hoses from the windscreen
washer pump and (where applicable) from the
headlamp washer pump. Anticipate some loss
of fluid by placing a container beneath the
reservoir.
5Withdraw the reservoir from the vehicle.
6Pull the level sensor, the windscreen
washer pump, and (where applicable) the
22 Windscreen/tailgate washer
system components -
removal and refitting
12•20 Body electrical system
21.14 Removal of the speed control
disable switches
1 Clutch switch 3 Stop-light switch
2 Brake pedal switch21.15 Resetting the brake pedal and stop-
light switches21.20 Removing the actuator cable
locking arm
22.2 Washer reservoir mounting bolts
(arrowed)22.3 Disconnecting the washer pump and
level sensor multi-plugs
procarmanuals.com
Page 223 of 279

1A compact disc (CD) player is available as
an optional extra on most models. On some
models, an autochanger version is available,
which can hold a number of discs at a time.
Removal
2The battery negative (earth) lead should be
disconnected before commencing work.
CD player, or autochanger control
unit
3The procedure is identical to that for the
radio/cassette player described in Section 23.
CD player autochanger
4The CD player autochanger unit is mounted
on the right-hand side of the luggage
compartment. The wiring loom passes up the
“C” pillar, across to the left-hand side “A”
pillar, then to the centre console area.
5Remove the trim cover from the
autochanger unit.
6Unscrew the mounting screws, and remove
the autochanger unit from its mounting
bracket.
7Disconnect the multi-plug and remove the
unit from inside the vehicle.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Remove the door trim panel as described in
Chapter 11.
2Unscrew the cross-head screws, and
withdraw the speaker from the door inner
panel.
3Disconnect the wiring and remove the
speaker.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Prise out the trim cover from the headlining
immediately below the base of the aerial.
2Unscrew the cross-head screw from the
base of the aerial, and remove the aerial mast.
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Warning: Handle the air bag unit
with extreme care, as a
precaution against personal
injury, and always hold it with the
cover facing away from the body. If in
doubt concerning any proposed work
involving the air bag unit or its control
circuitry, consult a Ford dealer or other
qualified specialist.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
Warning: Before proceeding, wait
a minimum of 15 minutes, as a
precaution against accidental
firing of the air bag unit. This
period ensures that any stored energy in
the back-up capacitor is dissipated.
2Rotate the steering wheel so that one of the
mounting bolt holes is visible above the
steering column upper shroud.
3Unscrew and remove the first mounting
bolt, then turn the steering wheel as
necessary and remove the remaining
mounting bolts (see illustration).
4Carefully withdraw the air bag unit from the
steering wheel far enough to disconnect the
wiring multi-plug, then remove it from inside
the vehicle (see illustration). Warning: Stand the unit with the
cover uppermost, and do not
expose it to heat sources in
excess of 100ºC.
Warning: Do not attempt to open
or repair the air bag unit, or apply
any electrical current to it. Do not
use any air bag unit which is visibly
damaged or which has been tampered
with.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
Warning: Before proceeding, wait
a minimum of 15 minutes, as a
precaution against accidental
firing of the air bag unit. This
period ensures that any stored energy in
the back-up capacitor is dissipated.
2Remove the facia panel as described in
Chapter 11.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the module,
by pressing the locking tab upwards and
swivelling the retaining strap.
4Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the module from the vehicle.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Remove the air bag unit as described in
Section 28.
2Disconnect the horn switch multi-plug.
3If fitted, disconnect the multi-plugs for the
cruise control.
4Remove the steering wheel and shrouds.
5Using a small screwdriver, release the
retaining tabs, then remove the clock spring
from the steering column.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but make sure that the steering
wheel is centralised. The clock spring must be
fitted in its central position, with the special
alignment marks aligned and the TOP mark
uppermost. To check for this position, turn the
clock spring housing anti-clockwise until it is
tight, then turn in the opposite direction by
two-and-three-quarter turns.
30 Air bag clock spring-
removal and refitting
29 Air bag control module -
removal and refitting
28 Air bag unit (driver’s side) -
removal and refitting
27 Radio aerial -
removal and refitting
26 Speakers -
removal and refitting
25 Compact disc player -
removal and refitting
12•22 Body electrical system
28.3 Unscrewing an air bag mounting bolt28.4 Disconnecting the air bag wiring
multi-plug (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 265 of 279

REF•6Fault Finding
Engine 1
m mEngine backfires
m mEngine difficult to start when cold
m mEngine difficult to start when hot
m mEngine fails to rotate when attempting to start
m mEngine hesitates on acceleration
m mEngine idles erratically
m mEngine lacks power
m mEngine misfires at idle speed
m mEngine misfires throughout the driving speed range
m mEngine noises
m mEngine rotates but will not start
m mEngine runs-on after switching off
m mEngine stalls
m mEngine starts but stops immediately
m mOil pressure warning light illuminated with engine running
m mStarter motor noisy or excessively-rough in engagement
Cooling system 2
m
mCorrosion
m mExternal coolant leakage
m mInternal coolant leakage
m mOvercooling
m mOverheating
Fuel and exhaust systems 3
m
mExcessive fuel consumption
m mExcessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
m mFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
Clutch 4
m
mClutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears)
m mClutch slips (engine speed increases with no increase
in vehicle speed)
m mJudder as clutch is engaged
m mNoise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
m mPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
Manual transmission 5
m
mJumps out of gear
m mLubricant leaks
m mNoisy in neutral with engine running
m mNoisy in one particular gear
m mVibration
Automatic transmission 6
m
mEngine will not start in any gear, or starts in gears
other than Park or Neutral
m mFluid leakage
m mGeneral gear selection problems
m mTransmission fluid brown, or has burned smell
m mTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or
has no drive in forward or reverse gears
m mTransmission will not downshift (kickdown) with
accelerator fully depressed
Driveshafts 7
m mClicking or knocking noise on turns (at slow speed on full-lock)
m mVibration when accelerating or decelerating
Braking system 8
m
mBrake pedal feels spongy when depressed
m mBrakes binding
m mExcessive brake pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m mExcessive brake pedal travel
m mJudder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel when braking
m mNoise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when brakes applied
m mRear wheels locking under normal braking
m mVehicle pulls to one side under braking
Suspension and steering systems 9
m
mExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners, or during
braking
m mExcessive play in steering
m mExcessively-stiff steering
m mLack of power assistance
m mTyre wear excessive
m mVehicle pulls to one side
m mWandering or general instability
m mWheel wobble and vibration
Electrical system 10
m
mBattery will not hold a charge for more than a few days
m mCentral locking system inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mElectric windows inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mHorn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mIgnition warning light fails to come on
m mIgnition warning light remains illuminated with engine running
m mInstrument readings inaccurate or erratic
m mLights inoperative
m mWindscreen/tailgate washers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
m mWindscreen/tailgate wipers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
procarmanuals.com
Page 269 of 279

6 Automatic transmission
REF•10Fault Finding
Note:Due to the complexity of the automatic transmission and its
electronic control system, it is difficult for the home mechanic to
properly diagnose and service this unit. For problems other than the
following, the vehicle should be taken to a dealer service department
or automatic transmission specialist.
Fluid leakage
m mAutomatic transmission fluid is usually deep red in colour. Fluid
leaks should not be confused with engine oil, which can easily be
blown onto the transmission by airflow.
m mTo determine the source of a leak, first remove all built-up dirt and
grime from the transmission housing and surrounding areas, using
a degreasing agent, or by steam-cleaning. Drive the vehicle at low
speed, so airflow will not blow the leak far from its source. Raise
and support the vehicle, and determine where the leak is coming
from. The following are common areas of leakage:
(a) Housing joints (Chapters 1 and 7, Part B).
(b) Dipstick tube (Chapters 1 and 7, Part B).
(c) Transmission-to-fluid cooler pipes/unions (Chapters 3 and 7,
Part B).
(d) Speedometer drive pinion O-ring (Chapter 7, Part B).
(e) Differential side gear oil seals (Chapter 7, Part B).
Transmission fluid brown, or has burned smell
m mTransmission fluid level low, or fluid in need of renewal (Chapter 1).
Transmission will not downshift (kickdown) with
accelerator pedal fully depressed
m mLow transmission fluid level (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect selector cable adjustment (Chapter 7, Part B).
m mEngine management system fault (Chapters 1, 4, 5 and 6).
General gear selection problems
m
mChapter 7, Part B, deals with checking and adjusting the selector
cable on automatic transmissions. The following are common
problems which may be caused by a poorly-adjusted cable:
(a) Engine starting in gears other than Park or Neutral.
(b) Indicator on gear selector lever pointing to a gear other than the
one actually being used.
(c) Vehicle moves when in Park or Neutral.
(d) Poor gear shift quality or erratic gear changes.
Refer to Chapter 7, Part B for the selector cable adjustment
procedure.
Engine will not start in any gear, or starts in gears
other than Park or Neutral
m mIncorrect selector lever position sensor adjustment (Chapter 7,
Part B).
m mIncorrect selector cable adjustment (Chapter 7, Part B).
Transmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no
drive in forward or reverse gears
m mThere are many probable causes for the above problems, but the
home mechanic should be concerned with only one possibility -
fluid level. Before taking the vehicle to a dealer or transmission
specialist, check the fluid level and condition of the fluid as
described in Chapter 1. Correct the fluid level as necessary, or
change the fluid if needed. If the problem persists, professional
help will be necessary.
7 Driveshafts
Clicking or knocking noise on turns (at slow speed
on full-lock)
m mLack of constant velocity joint lubricant (Chapter 8).
m mWorn outer constant velocity joint (Chapter 8).
Vibration when accelerating or decelerating
m
mWorn inner constant velocity joint (Chapter 8).
m mBent or distorted driveshaft (Chapter 8).
8 Braking system
Note:Before assuming that a brake problem exists, make sure that the tyres are in good condition and correctly inflated, that the front wheel
alignment is correct, and that the vehicle is not loaded with weight in an unequal manner. Apart from checking the condition of all pipe and hose
connections, any faults occurring on the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) should be referred to a Ford dealer for diagnosis - the same applies to the
components of the Traction Control System (TCS).
Vehicle pulls to one side under braking
m mWorn, defective, damaged or contaminated front or rear brake
pads/shoes on one side (Chapter 1).
m mSeized or partially-seized front or rear brake caliper/wheel cylinder
piston (Chapter 9).
m mA mixture of brake pad/shoe lining materials fitted between sides
(Chapter 1).
m mBrake caliper mounting bolts loose (Chapter 9).
m mRear brake backplate mounting bolts loose (Chapter 9).
m mWorn or damaged steering or suspension components (Chap-
ter 10).
Noise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when brakes
applied
m mBrake pad or shoe friction lining material worn down to metal
backing (Chapter 1).
m mExcessive corrosion of brake disc or drum (may be apparent after
the vehicle has been standing for some time) (Chapter 1).
m mForeign object (stone chipping, etc) trapped between brake disc
and splash shield (Chapter 1).
Excessive brake pedal travel
m mInoperative rear brake self-adjust mechanism (Chapter 9).
m mFaulty master cylinder (Chapter 9).
m mAir in hydraulic system (Chapter 9).
procarmanuals.com
Page 270 of 279

REF•11Fault Finding
9 Suspension and steering systems
Note:Before diagnosing suspension or steering faults, be sure that the trouble is not due to incorrect tyre pressures, mixtures of tyre types, or
binding brakes. Apart from checking the condition of all electrical connections, any faults occurring on the Adaptive Damping System should be
referred to a Ford dealer for diagnosis.
Vehicle pulls to one side
m mDefective tyre (Chapter 1).
m mExcessive wear in suspension or steering components (Chap-
ter 10).
m mIncorrect front wheel alignment (Chapter 10).
m mAccident damage to steering or suspension components (Chap-
ter 10).
Wheel wobble and vibration
m mFront roadwheels out of balance (vibration felt mainly through the
steering wheel) (Chapter 1).
m mRear roadwheels out of balance (vibration felt throughout the
vehicle) (Chapter 1).
m mRoadwheels damaged or distorted (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty or damaged tyre (Chapter 1).
m mWorn steering or suspension joints, bushes or components
(Chapter 10).
m mRoadwheel nuts loose (Chapter 1).
Excessive pitching and/or rolling around corners, or
during braking
m mDefective shock absorbers (Chapter 10).
m mBroken or weak coil spring and/or suspension component (Chap-
ter 10).
m mWorn or damaged anti-roll bar or mountings (Chapter 10).
Wandering or general instability
m
mIncorrect front wheel alignment (Chapter 10).
m mWorn steering or suspension joints, bushes or components
(Chapter 10).
m mRoadwheels out of balance (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty or damaged tyre (Chapter 1).
m mRoadwheel nuts loose (Chapter 1).
m mDefective shock absorbers (Chapter 10).
Excessively-stiff steering
m
mLack of steering gear lubricant (Chapter 10).
m mSeized track-rod end balljoint or suspension balljoint (Chapter 10).
m mBroken or slipping auxiliary drivebelt (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect front wheel alignment (Chapter 10).
m mSteering rack or column bent or damaged (Chapter 10).
Excessive play in steering
m
mWorn steering column universal joint(s) or flexible coupling
(Chapter 10).
m mWorn steering track-rod end balljoints (Chapter 10).
m mWorn rack-and-pinion steering gear (Chapter 10).
m mWorn steering or suspension joints, bushes or components
(Chapter 10).
Lack of power assistance
m mBroken or slipping auxiliary drivebelt (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect power steering fluid level (Chapter 1).
m mRestriction in power steering fluid hoses (Chapter 10).
m mFaulty power steering pump (Chapter 10).
m mFaulty rack-and-pinion steering gear (Chapter 10).
Tyre wear excessive
Tyres worn on inside or outside edges
m
mTyres under-inflated (wear on both edges) (Chapter 1).
m mIncorrect camber or castor angles (wear on one edge only)
(Chapter 10).
m mWorn steering or suspension joints, bushes or components
(Chapter 10).
m mExcessively-hard cornering.
m mAccident damage.
Tyre treads exhibit feathered edges
m
mIncorrect toe setting (Chapter 10).
Tyres worn in centre of tread
m
mTyres over-inflated (Chapter 1).
Tyres worn on inside and outside edges
m
mTyres under-inflated (Chapter 1).
Tyres worn unevenly
m
mTyres out of balance (Chapter 1).
m mExcessive wheel or tyre run-out (Chapter 1).
m mWorn shock absorbers (Chapter 10).
m mFaulty tyre (Chapter 1).
Brake pedal feels spongy when depressed
m
mAir in hydraulic system (Chapter 9).
m mDeteriorated flexible rubber brake hoses (Chapter 9).
m mMaster cylinder mounting nuts loose (Chapter 9).
m mFaulty master cylinder (Chapter 9).
Excessive brake pedal effort required to stop
vehicle
m mFaulty vacuum servo unit (Chapter 9).
m mDisconnected, damaged or insecure brake servo vacuum hose
(Chapter 9).
m mPrimary or secondary hydraulic circuit failure (Chapter 9).
m mSeized brake caliper or wheel cylinder piston(s) (Chapter 9).
m mBrake pads or brake shoes incorrectly fitted (Chapter 9).
m mIncorrect grade of brake pads or brake shoes fitted (Chapter 1).
m mBrake pads or brake shoe linings contaminated (Chapter 1).
Judder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel
when braking
m mExcessive run-out or distortion of front discs or rear drums
(Chapter 9).
m mBrake pad or brake shoe linings worn (Chapter 1).
m mBrake caliper or rear brake backplate mounting bolts loose
(Chapter 9).
m mWear in suspension or steering components or mountings (Chapter 10).
Brakes binding
m
mSeized brake caliper or wheel cylinder piston(s) (Chapter 9).
m mFaulty handbrake mechanism (Chapter 9).
m mFaulty master cylinder (Chapter 9).
Rear wheels locking under normal braking
m
mRear brake shoe linings contaminated (Chapter 1).
m mFaulty brake pressure regulator (Chapter 9).
procarmanuals.com
Page 272 of 279
REF•13Glossary of Technical Terms
A
ABS (Anti-lock brake system)A system,
usually electronically controlled, that senses
incipient wheel lockup during braking and
relieves hydraulic pressure at wheels that are
about to skid.
Air bag An inflatable bag hidden in the
steering wheel (driver’s side) or the dash or
glovebox (passenger side). In a head-on
collision, the bags inflate, preventing the
driver and front passenger from being thrown
forward into the steering wheel or windscreen.
Air cleanerA metal or plastic housing,
containing a filter element, which removes
dust and dirt from the air being drawn into the
engine.
Air filter elementThe actual filter in an air
cleaner system, usually manufactured from
pleated paper and requiring renewal at regular
intervals.
Allen keyA hexagonal wrench which fits into
a recessed hexagonal hole.
Alligator clipA long-nosed spring-loaded
metal clip with meshing teeth. Used to make
temporary electrical connections.
AlternatorA component in the electrical
system which converts mechanical energy
from a drivebelt into electrical energy to
charge the battery and to operate the starting
system, ignition system and electrical
accessories.
Ampere (amp)A unit of measurement for the
flow of electric current. One amp is the
amount of current produced by one volt
acting through a resistance of one ohm.
Anaerobic sealerA substance used to
prevent bolts and screws from loosening.
Anaerobic means that it does not require
oxygen for activation. The Loctite brand is
widely used.
AntifreezeA substance (usually ethylene
glycol) mixed with water, and added to a
vehicle’s cooling system, to prevent freezing
of the coolant in winter. Antifreeze also
contains chemicals to inhibit corrosion and
the formation of rust and other deposits that
would tend to clog the radiator and coolant
passages and reduce cooling efficiency.
Anti-seize compoundA coating that
reduces the risk of seizing on fasteners that
are subjected to high temperatures, such as
exhaust manifold bolts and nuts.
AsbestosA natural fibrous mineral with great
heat resistance, commonly used in the
composition of brake friction materials.Asbestos is a health hazard and the dust
created by brake systems should never be
inhaled or ingested.
AxleA shaft on which a wheel revolves, or
which revolves with a wheel. Also, a solid
beam that connects the two wheels at one
end of the vehicle. An axle which also
transmits power to the wheels is known as a
live axle.
AxleshaftA single rotating shaft, on either
side of the differential, which delivers power
from the final drive assembly to the drive
wheels. Also called a driveshaft or a halfshaft.
BBall bearingAn anti-friction bearing
consisting of a hardened inner and outer race
with hardened steel balls between two races.
BearingThe curved surface on a shaft or in a
bore, or the part assembled into either, that
permits relative motion between them with
minimum wear and friction.
Big-end bearingThe bearing in the end of
the connecting rod that’s attached to the
crankshaft.
Bleed nippleA valve on a brake wheel
cylinder, caliper or other hydraulic component
that is opened to purge the hydraulic system
of air. Also called a bleed screw.
Brake bleedingProcedure for removing air
from lines of a hydraulic brake system.
Brake discThe component of a disc brake
that rotates with the wheels.Brake drumThe component of a drum brake
that rotates with the wheels.
Brake liningsThe friction material which
contacts the brake disc or drum to retard the
vehicle’s speed. The linings are bonded or
riveted to the brake pads or shoes.
Brake padsThe replaceable friction pads
that pinch the brake disc when the brakes are
applied. Brake pads consist of a friction
material bonded or riveted to a rigid backing
plate.
Brake shoeThe crescent-shaped carrier to
which the brake linings are mounted and
which forces the lining against the rotating
drum during braking.
Braking systemsFor more information on
braking systems, consult the Haynes
Automotive Brake Manual.
Breaker barA long socket wrench handle
providing greater leverage.
BulkheadThe insulated partition between
the engine and the passenger compartment.
CCaliperThe non-rotating part of a disc-brake
assembly that straddles the disc and carries
the brake pads. The caliper also contains the
hydraulic components that cause the pads to
pinch the disc when the brakes are applied. A
caliper is also a measuring tool that can be set
to measure inside or outside dimensions of an
object.
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
sprockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
CanisterA container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
charcoal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
CarburettorA device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desired power output from a spark ignition
internal combustion engine.
CastellatedResembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
CastorIn wheel alignment, the backward or
forward tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
rearward at the top.
Canister
Brake bleeding
Bearing
Air filter
procarmanuals.com