1993 FORD MONDEO brake pads replacement
[x] Cancel search: brake pads replacementPage 33 of 279
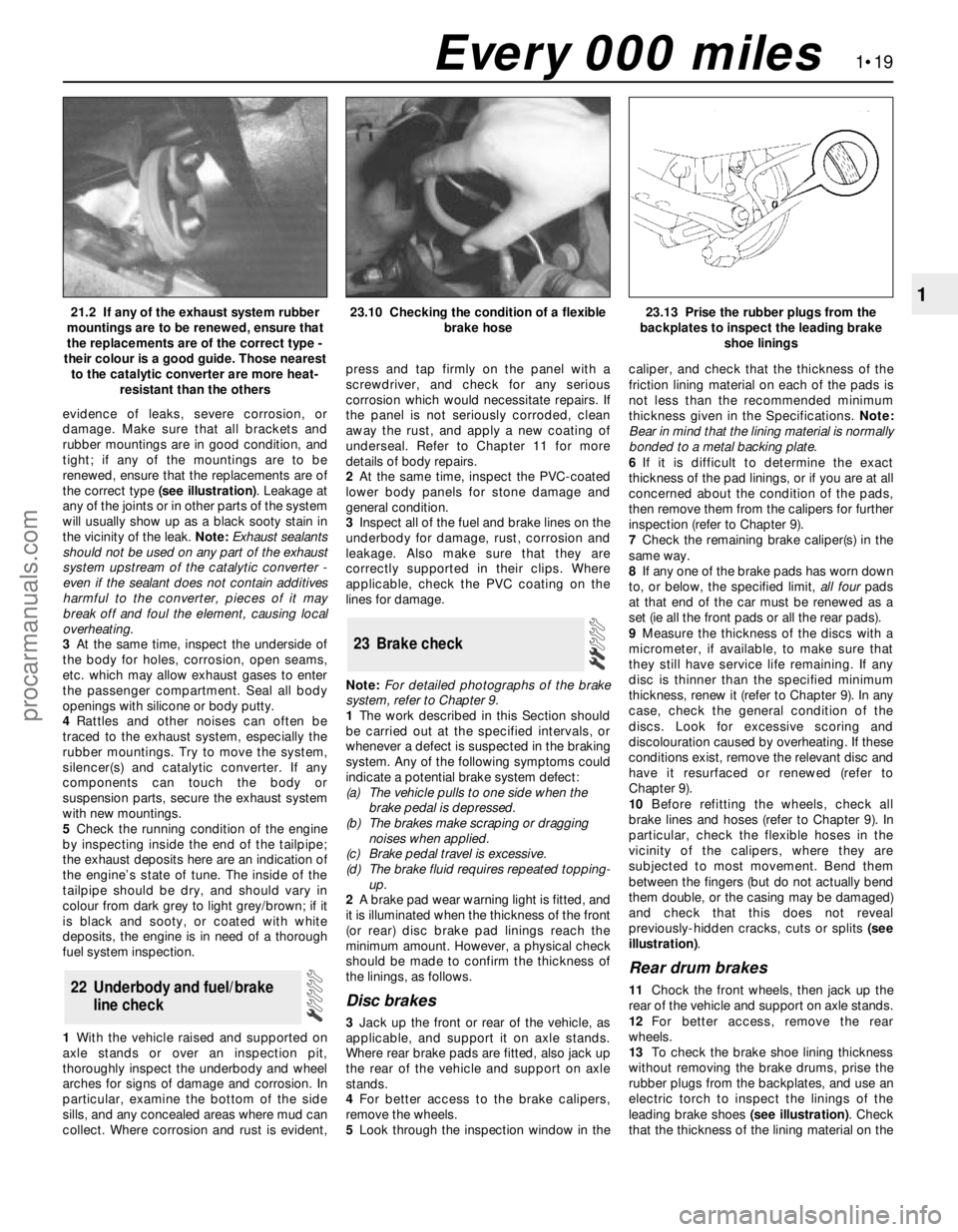
evidence of leaks, severe corrosion, or
damage. Make sure that all brackets and
rubber mountings are in good condition, and
tight; if any of the mountings are to be
renewed, ensure that the replacements are of
the correct type (see illustration). Leakage at
any of the joints or in other parts of the system
will usually show up as a black sooty stain in
the vicinity of the leak. Note:Exhaust sealants
should not be used on any part of the exhaust
system upstream of the catalytic converter -
even if the sealant does not contain additives
harmful to the converter, pieces of it may
break off and foul the element, causing local
overheating.
3At the same time, inspect the underside of
the body for holes, corrosion, open seams,
etc. which may allow exhaust gases to enter
the passenger compartment. Seal all body
openings with silicone or body putty.
4Rattles and other noises can often be
traced to the exhaust system, especially the
rubber mountings. Try to move the system,
silencer(s) and catalytic converter. If any
components can touch the body or
suspension parts, secure the exhaust system
with new mountings.
5Check the running condition of the engine
by inspecting inside the end of the tailpipe;
the exhaust deposits here are an indication of
the engine’s state of tune. The inside of the
tailpipe should be dry, and should vary in
colour from dark grey to light grey/brown; if it
is black and sooty, or coated with white
deposits, the engine is in need of a thorough
fuel system inspection.
1With the vehicle raised and supported on
axle stands or over an inspection pit,
thoroughly inspect the underbody and wheel
arches for signs of damage and corrosion. In
particular, examine the bottom of the side
sills, and any concealed areas where mud can
collect. Where corrosion and rust is evident,press and tap firmly on the panel with a
screwdriver, and check for any serious
corrosion which would necessitate repairs. If
the panel is not seriously corroded, clean
away the rust, and apply a new coating of
underseal. Refer to Chapter 11 for more
details of body repairs.
2At the same time, inspect the PVC-coated
lower body panels for stone damage and
general condition.
3Inspect all of the fuel and brake lines on the
underbody for damage, rust, corrosion and
leakage. Also make sure that they are
correctly supported in their clips. Where
applicable, check the PVC coating on the
lines for damage.
Note:For detailed photographs of the brake
system, refer to Chapter 9.
1The work described in this Section should
be carried out at the specified intervals, or
whenever a defect is suspected in the braking
system. Any of the following symptoms could
indicate a potential brake system defect:
(a) The vehicle pulls to one side when the
brake pedal is depressed.
(b) The brakes make scraping or dragging
noises when applied.
(c) Brake pedal travel is excessive.
(d) The brake fluid requires repeated topping-
up.
2A brake pad wear warning light is fitted, and
it is illuminated when the thickness of the front
(or rear) disc brake pad linings reach the
minimum amount. However, a physical check
should be made to confirm the thickness of
the linings, as follows.
Disc brakes
3Jack up the front or rear of the vehicle, as
applicable, and support it on axle stands.
Where rear brake pads are fitted, also jack up
the rear of the vehicle and support on axle
stands.
4For better access to the brake calipers,
remove the wheels.
5Look through the inspection window in thecaliper, and check that the thickness of the
friction lining material on each of the pads is
not less than the recommended minimum
thickness given in the Specifications. Note:
Bear in mind that the lining material is normally
bonded to a metal backing plate.
6If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the pad linings, or if you are at all
concerned about the condition of the pads,
then remove them from the calipers for further
inspection (refer to Chapter 9).
7Check the remaining brake caliper(s) in the
same way.
8If any one of the brake pads has worn down
to, or below, the specified limit, all fourpads
at that end of the car must be renewed as a
set (ie all the front pads or all the rear pads).
9Measure the thickness of the discs with a
micrometer, if available, to make sure that
they still have service life remaining. If any
disc is thinner than the specified minimum
thickness, renew it (refer to Chapter 9). In any
case, check the general condition of the
discs. Look for excessive scoring and
discolouration caused by overheating. If these
conditions exist, remove the relevant disc and
have it resurfaced or renewed (refer to
Chapter 9).
10Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). In
particular, check the flexible hoses in the
vicinity of the calipers, where they are
subjected to most movement. Bend them
between the fingers (but do not actually bend
them double, or the casing may be damaged)
and check that this does not reveal
previously-hidden cracks, cuts or splits (see
illustration).
Rear drum brakes
11Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle and support on axle stands.
12For better access, remove the rear
wheels.
13To check the brake shoe lining thickness
without removing the brake drums, prise the
rubber plugs from the backplates, and use an
electric torch to inspect the linings of the
leading brake shoes (see illustration). Check
that the thickness of the lining material on the
23 Brake check
22 Underbody and fuel/brake
line check
1•19
121.2 If any of the exhaust system rubber
mountings are to be renewed, ensure that
the replacements are of the correct type -
their colour is a good guide. Those nearest
to the catalytic converter are more heat-
resistant than the others23.10 Checking the condition of a flexible
brake hose23.13 Prise the rubber plugs from the
backplates to inspect the leading brake
shoe linings
Every 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 273 of 279

REF•14Glossary of Technical Terms
Catalytic converterA silencer-like device in
the exhaust system which converts certain
pollutants in the exhaust gases into less
harmful substances.
CirclipA ring-shaped clip used to prevent
endwise movement of cylindrical parts and
shafts. An internal circlip is installed in a
groove in a housing; an external circlip fits into
a groove on the outside of a cylindrical piece
such as a shaft.
ClearanceThe amount of space between
two parts. For example, between a piston and
a cylinder, between a bearing and a journal,
etc.
Coil springA spiral of elastic steel found in
various sizes throughout a vehicle, for
example as a springing medium in the
suspension and in the valve train.
CompressionReduction in volume, and
increase in pressure and temperature, of a
gas, caused by squeezing it into a smaller
space.
Compression ratioThe relationship between
cylinder volume when the piston is at top
dead centre and cylinder volume when the
piston is at bottom dead centre.
Constant velocity (CV) jointA type of
universal joint that cancels out vibrations
caused by driving power being transmitted
through an angle.
Core plugA disc or cup-shaped metal device
inserted in a hole in a casting through which
core was removed when the casting was
formed. Also known as a freeze plug or
expansion plug.
CrankcaseThe lower part of the engine
block in which the crankshaft rotates.
CrankshaftThe main rotating member, or
shaft, running the length of the crankcase,
with offset “throws” to which the connecting
rods are attached.
Crocodile clipSee Alligator clipDDiagnostic codeCode numbers obtained by
accessing the diagnostic mode of an engine
management computer. This code can be
used to determine the area in the system
where a malfunction may be located.
Disc brakeA brake design incorporating a
rotating disc onto which brake pads are
squeezed. The resulting friction converts the
energy of a moving vehicle into heat.
Double-overhead cam (DOHC)An engine
that uses two overhead camshafts, usually
one for the intake valves and one for the
exhaust valves.
Drivebelt(s)The belt(s) used to drive
accessories such as the alternator, water
pump, power steering pump, air conditioning
compressor, etc. off the crankshaft pulley.
DriveshaftAny shaft used to transmit
motion. Commonly used when referring to the
axleshafts on a front wheel drive vehicle.
Drum brakeA type of brake using a drum-
shaped metal cylinder attached to the inner
surface of the wheel. When the brake pedal is
pressed, curved brake shoes with friction
linings press against the inside of the drum to
slow or stop the vehicle.
EEGR valveA valve used to introduce exhaust
gases into the intake air stream.
Electronic control unit (ECU)A computer
which controls (for instance) ignition and fuel
injection systems, or an anti-lock braking
system. For more information refer to the
Haynes Automotive Electrical and Electronic
Systems Manual.
Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)A computer
controlled fuel system that distributes fuel
through an injector located in each intake port
of the engine.
Emergency brakeA braking system,
independent of the main hydraulic system,
that can be used to slow or stop the vehicle if
the primary brakes fail, or to hold the vehicle
stationary even though the brake pedal isn’t
depressed. It usually consists of a hand lever
that actuates either front or rear brakes
mechanically through a series of cables and
linkages. Also known as a handbrake or
parking brake.EndfloatThe amount of lengthwise
movement between two parts. As applied to a
crankshaft, the distance that the crankshaft
can move forward and back in the cylinder
block.
Engine management system (EMS)A
computer controlled system which manages
the fuel injection and the ignition systems in
an integrated fashion.
Exhaust manifoldA part with several
passages through which exhaust gases leave
the engine combustion chambers and enter
the exhaust pipe.
F
Fan clutchA viscous (fluid) drive coupling
device which permits variable engine fan
speeds in relation to engine speeds.
Feeler bladeA thin strip or blade of hardened
steel, ground to an exact thickness, used to
check or measure clearances between parts.
Firing orderThe order in which the engine
cylinders fire, or deliver their power strokes,
beginning with the number one cylinder.
Flywheel A heavy spinning wheel in which
energy is absorbed and stored by means of
momentum. On cars, the flywheel is attached
to the crankshaft to smooth out firing
impulses.
Free playThe amount of travel before any
action takes place. The “looseness” in a
linkage, or an assembly of parts, between the
initial application of force and actual
movement. For example, the distance the
brake pedal moves before the pistons in the
master cylinder are actuated.
FuseAn electrical device which protects a
circuit against accidental overload. The typical
fuse contains a soft piece of metal which is
calibrated to melt at a predetermined current
flow (expressed as amps) and break the
circuit.
Fusible linkA circuit protection device
consisting of a conductor surrounded by
heat-resistant insulation. The conductor is
smaller than the wire it protects, so it acts as
the weakest link in the circuit. Unlike a blown
fuse, a failed fusible link must frequently be
cut from the wire for replacement.Catalytic converter
Crankshaft assembly
Accessory drivebelts
Feeler blade
procarmanuals.com