1993 DODGE TRUCK ad blue
[x] Cancel search: ad bluePage 334 of 1502

•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 13 GENERATOR TEST PROCEDURES ON
VEHICLE
INDEX
page
Current
Output
Test
......................
14
Diagnostic Procedures
13
General
Information
13
Generator
Output
Wire Resistance Test
.......
13
page
How
to
Use
Malfunction
Indicator
(Check Engine) Lamp
for
Fault
Codes
17
Operational Check
with
Voltmeter
............
13
Using
On-Board Diagnostic System
15
GENERAL
INFORMATION
The generator
is
belt-driven
by the
engine.
All en
gines
use
serpentine drive. The amount
of DC
current produced
by the
gener
ator
is
controlled
by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
All vehicles
are
equipped with
On
Board Diagnos
tics (OBD).
All OBD
sensing systems
are
monitored
by
the PCM. The PCM
will store
in
electronic mem ory
any
detectable failure within
the
monitored cir
cuits.
Refer
to
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
in
this group
for
more information.
OPERATIONAL CHECK
WITH
VOLTMETER
When
the
ignition switch
is
turned
to the RUN po
sition, battery potential will register
on the
voltme
ter. During engine cranking
a
lower voltage will appear
on the
meter. With
the
engine running,
a
voltage reading higher than
the
first reading (igni
tion
in RUN)
should register.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
If
the
indicator does
not
operate properly,
or if an
undercharged
or
overcharged battery condition
oc
curs,
the
following procedures
may be
used
to
diag
nose
the
charging system. Remember that
an
undercharged battery
is
often
caused
by:
• accessories being left
on
overnight
•
or by a
defective switch which allows
a
bulb, such
as a
trunk
or
glove
box
light,
to
stay
on
(refer
to
Ignition
Off
Draw).
WISUAL
INSPECTION
• Inspect condition
of
battery cable terminals, bat
tery posts, connections
at
engine block, starter motor solenoid
and
relay. They should
be
clean
and
tight.
Repair
as
required.
• Inspect
all
fuses
in the
fuse block
for
tightness
in
receptacles. They should
be
properly installed
and
tight. Repair
or
replace
as
required.
• Inspect generator mounting bolts
for
tightness.
Re
place
or
torque bolt
as
required (refer
to
Torque Specifications).
• Inspect generator drive belt condition
and
tension.
Tension
or
replace belt
as
required. Refer
to
Belt
Tension Specifications. • Inspect connection
at
generator
B+
output.
It
should
be
clean
and
tight. Repair
as
required.
GENERATOR
OUTPUT
WIRE RESISTANCE TEST
(FIG.
1)
Generator output wire resistance test will show
amount
of
voltage drop across generator output wire
between generator
BAT
terminal
and
battery posi tive post.
PREPARATION
(1) Before starting test make sure vehicle
has a
fully charged battery. Test
and
procedures
on how to
check
for a
fully charged battery
are
shown
in
Bat
tery section
of
this Group.
(2) Turn
OFF
ignition switch.
(3)
Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4)
Disconnect generator output wire from genera
tor output Battery terminal. (5) Connect
a 0-150
ampere scale
D.C.
ammeter
in
series between generator
BAT
terminal
and
discon
nected generator output wire. Connect Positive lead
to generator
BAT
terminal
and
Negative lead
to
dis connected generator output wire. (6) Connect Positive lead
of a
test voltmeter
(Range
0-18
volts minimum)
to
disconnected genera
tor output wire. Connect negative lead
of
test voltme
ter
to
battery positive cable
at
positive post. (7) Connect
one end of a
Jumper Wire
to
ground
and with other
end
probe green
K20
lead wire
at
back
of
generator
(Fig. 1).
(This will generate
a
fault
code).
CAUTION:
Do not
connect blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground. Refer
to
Group
8W
-
Wiring Diagrams
for
more information.
(8) Connect
an
engine tachometer
and
connect neg
ative cable
to
battery.
(9) Connect
a
variable carbon pile rheostat
be
tween battery terminals.
Be
sure carbon pile
is in
"Open"
or "Off
position before connecting leads.
See
Battery Section, Load Testing
for
instructions.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting,
re
duce engine speed
to
idle.
Page 336 of 1502
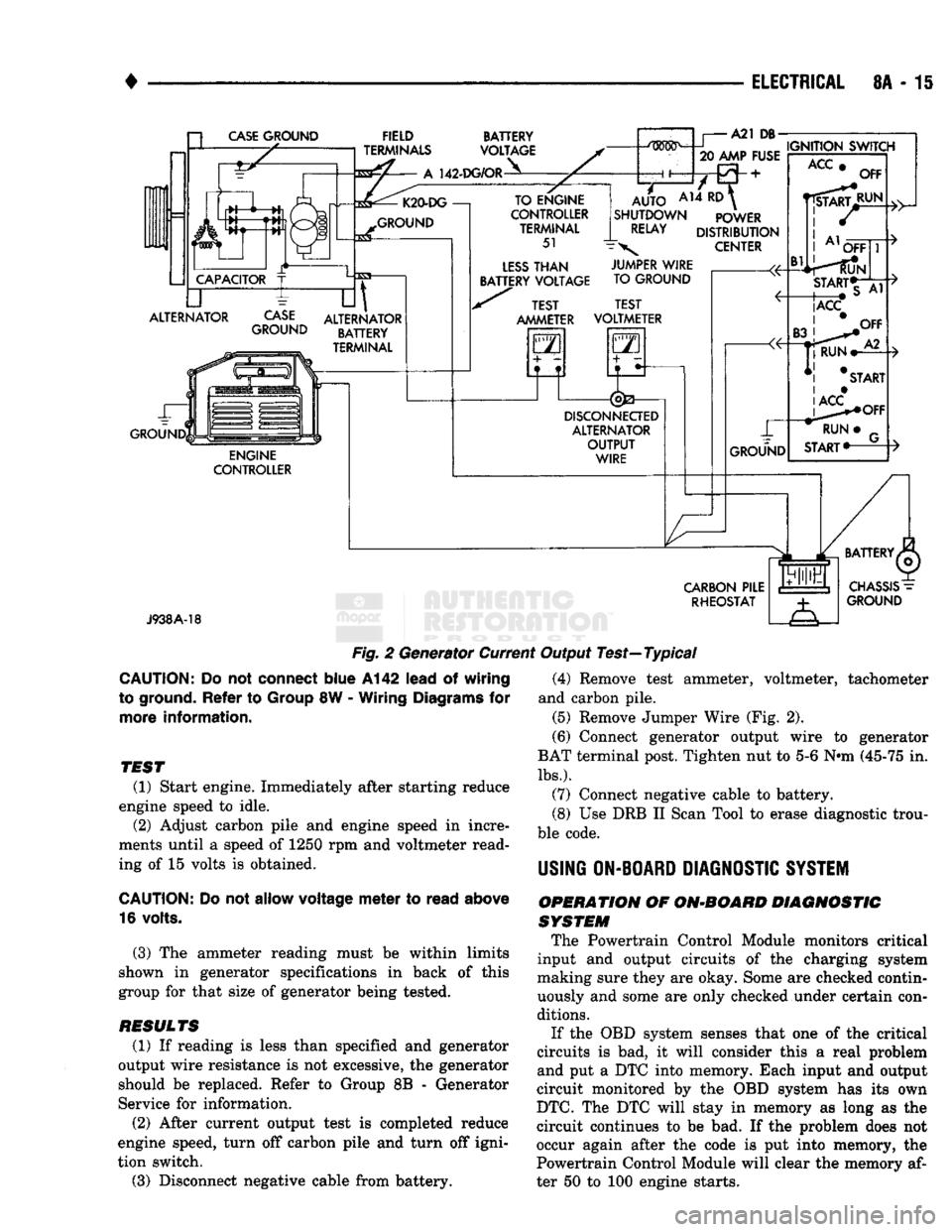
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 15 a
CASE
GROUND
CAPACITOR
ALTERNATOR ~L FIELD
TERMINALS
A
142-DG/OR BATTERY
VOLTAGE K20-DG
—!
GROUND
CASE
GROUND
til
ALTERNATOR BATTERY
TERMINAL ENGINE
CONTROLLER TO ENGINE
CONTROLLER TERMINAL
51
LESS
THAN
BATTERY VOLTAGE A21
DB-
.....
IGNITION SWITCH
20 AMP FUSE
AUTO
AH ^
SHUTDOWN POWER
RELAY
DISTRIBUTION
\
CENTER TEST
AMMETER JUMPER WIRE
TO GROUND
TEST
VOLTMETER
GO
5—n
DISCONNECTED
ALTERNATOR OUTPUT WIRE GROUND
ACC
Bl
OFF
RUN OFF
START*T
|ACC
CARBON
PILE RHEOSTAT
J938A-18
Fig.
2 Generator Current Output Test—Typical
CAUTION:
Do not
connect
blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground.
Refer
to
Group
8W -
Wiring
Diagrams
for
more
information.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting reduce
engine speed to idle. (2) Adjust carbon pile and engine speed in incre
ments until a speed of 1250 rpm and voltmeter read
ing of 15 volts is obtained.
CAUTION:
Do not
allow
voltage
meter
to
read
above
16 volts.
(3) The ammeter reading must be within limits
shown in generator specifications in back of this
group for that size of generator being tested.
RESULTS
(1) If reading is less than specified and generator
output wire resistance is not excessive, the generator
should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B - Generator
Service for information.
(2) After current output test is completed reduce
engine speed, turn off carbon pile and turn off igni
tion switch.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery. (4) Remove test ammeter, voltmeter, tachometer
and carbon pile. (5) Remove Jumper Wire (Fig. 2).
(6) Connect generator output wire to generator
BAT terminal post. Tighten nut to 5-6 Nnn (45-75 in.
lbs.).
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
(8) Use DRB II Scan Tool to erase diagnostic trou
ble code.
USING
ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC
SYSTEM
OPERATION
OF
ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC
SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module monitors critical
input and output circuits of the charging system
making sure they are okay. Some are checked contin
uously and some are only checked under certain con
ditions.
If the OBD system senses that one of the critical
circuits is bad, it will consider this a real problem
and put a DTC into memory. Each input and output
circuit monitored by the OBD system has its own
DTC.
The DTC will stay in memory as long as the
circuit continues to be bad. If the problem does not
occur again after the code is put into memory, the
Powertrain Control Module will clear the memory af
ter 50 to 100 engine starts.
Page 378 of 1502
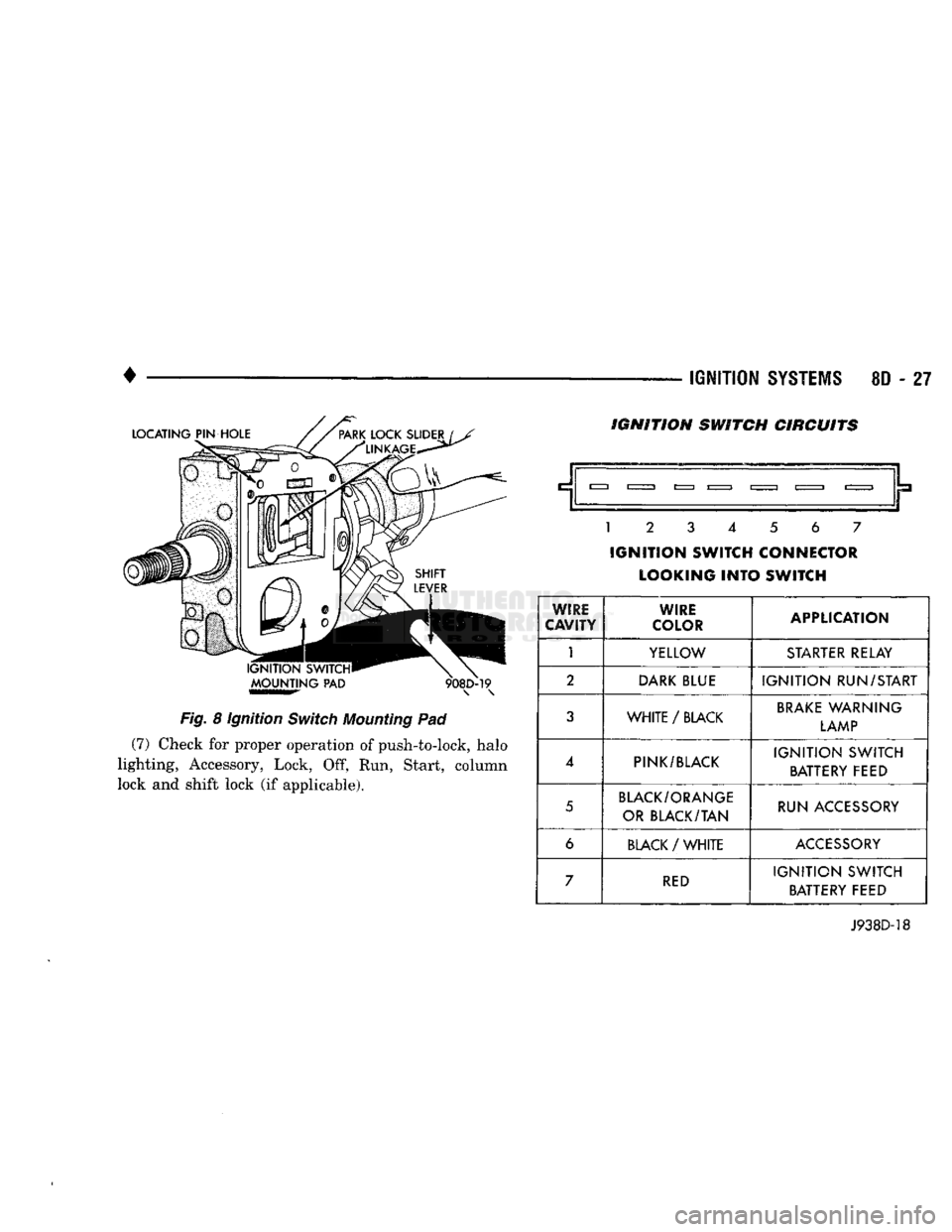
•
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
80 - 27
Fig.
8 Ignition
Switch
Mounting
Pad (7) Check for proper operation of push-to-lock, halo
lighting, Accessory, Lock, Off, Run, Start, column
lock and shift lock (if applicable). IGNITION SWITCH CIRCUITS
.__|.
1
2 3 4 5 6 7
IGNITION
SWITCH CONNECTOR LOOKING
INTO
SWITCH
WIRE
CAVITY WIRE
COLOR APPLICATION
1
YELLOW
STARTER
RELAY
2
DARK
BLUE
IGNITION
RUN/START
3
WHITE
/
BLACK
BRAKE
WARNING
LAMP
4
PINK/BLACK
IGNITION
SWITCH
BATTERY FEED
5
BLACK/ORANGE
OR BLACK/TAN RUN ACCESSORY
6
BLACK
/
WHITE
ACCESSORY
7
RED
IGNITION
SWITCH
BATTERY FEED
J938D-18
Page 423 of 1502
8H - 8
VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
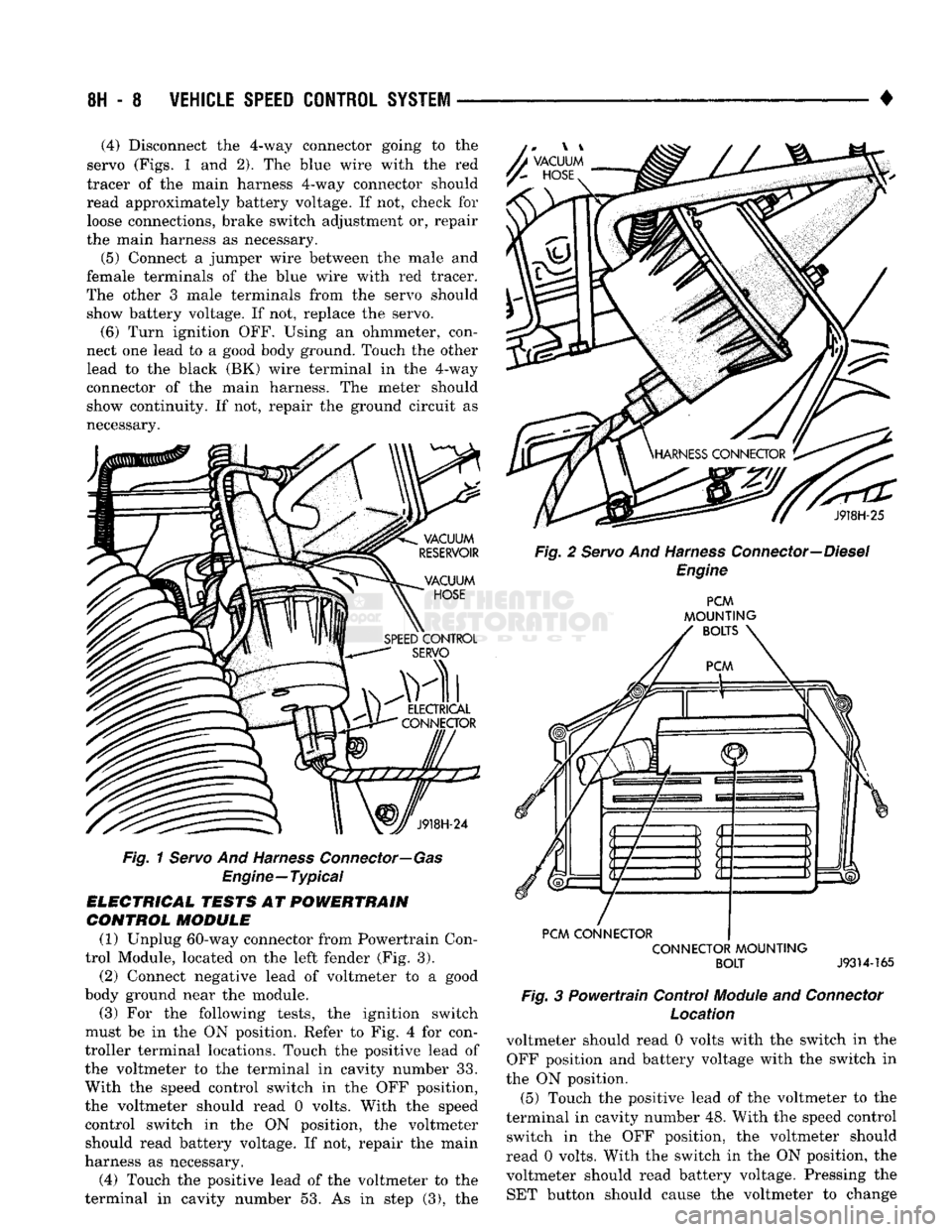
• (4) Disconnect the 4-way connector going to the
servo (Figs. 1 and 2), The blue wire with the red
tracer of the main harness 4-way connector should
read approximately battery voltage. If not, check for loose connections, brake switch adjustment or, repair
the main harness as necessary.
(5) Connect a jumper wire between the male and
female terminals of the blue wire with red tracer.
The other 3 male terminals from the servo should show battery voltage. If not, replace the servo. (6) Turn ignition OFF. Using an ohmmeter, con
nect one lead to a good body ground. Touch the other
lead to the black (BK) wire terminal in the 4-way
connector of the main harness. The meter should
show continuity. If not, repair the ground circuit as
necessary. A
VACUUM
y~
HOSE
J918H-24
Fig.
1 Servo And Harness Connector—Gas
Engine—Typical
ELECTRICAL TESTS AT POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(1) Unplug 60-way connector from Powertrain Con
trol Module, located on the left fender (Fig. 3).
(2) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to a good
body ground near the module. (3) For the following tests, the ignition switch
must be in the ON position. Refer to Fig. 4 for con
troller terminal locations. Touch the positive lead of
the voltmeter to the terminal in cavity number 33.
With the speed control switch in the OFF position,
the voltmeter should read 0 volts. With the speed
control switch in the ON position, the voltmeter should read battery voltage. If not, repair the main
harness as necessary.
(4) Touch the positive lead of the voltmeter to the
terminal in cavity number 53. As in step (3), the J918H-25
Fig. 2 Servo And Harness Connector—Diesel Engine PCM
MOUNTING
BOLTS
PCM CONNECTOR CONNECTOR MOUNTING BOLT
J9314-165
Fig.
3 Powertrain Control
Module
and
Connector
Location
voltmeter should read 0 volts with the switch in the OFF position and battery voltage with the switch in
the ON position. (5) Touch the positive lead of the voltmeter to the
terminal in cavity number 48. With the speed control switch in the OFF position, the voltmeter should
read 0 volts. With the switch in the ON position, the voltmeter should read battery voltage. Pressing the SET button should cause the voltmeter to change
Page 424 of 1502
![DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL SYSTEM
8H - 9
rain
oooooooooo
1 10,
.oooooooooo
\21 30
„. \£] 50 x
OOOOOOOOOO OOOOOOOOOO^
11
20
OOOOOOOOOO
51
31 1 6ooooooooo60y/ Tratr
TJKT
RR8HC DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL SYSTEM
8H - 9
rain
oooooooooo
1 10,
.oooooooooo
\21 30
„. \£] 50 x
OOOOOOOOOO OOOOOOOOOO^
11
20
OOOOOOOOOO
51
31 1 6ooooooooo60y/ Tratr
TJKT
RR8HC](/manual-img/12/56922/w960_56922-423.png)
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL SYSTEM
8H - 9
rain
oooooooooo
1 10,
.oooooooooo
\21 30
„. \£] 50 x
OOOOOOOOOO OOOOOOOOOO^
11
20
OOOOOOOOOO
51
31 1 6ooooooooo60y/ Tratr
TJKT
RR8HC7
Fig.
4 Powertrain Control Module 60-Way Connector
Shown from Terminal End
from battery voltage to 0 volts for as long as the switch is held. If not, perform the speed control
switch test. If the switch is not at fault, then check
the main harness and repair as necessary.
(6) Touch the positive lead of the voltmeter to the
terminal in cavity number 50. The voltmeter should read 0 volts with the speed control switch in either
the OFF or ON position. With switch in either RE SUME or SET position, the voltmeter should read
battery voltage. If not, perform the speed control switch test. If the switch is not at fault, then check
the main harness and repair as necessary.
(7) Touch the positive lead of the voltmeter to the
terminal in cavity number 49. The voltmeter should read 0 volts with the switch in the OFF position.
With the switch in the ON position, the voltmeter should read battery voltage. The voltmeter will con
tinue to read battery voltage when either the SET or
RESUME switch is pressed. If not, perform the speed control switch test. If the switch is not at fault, then
check the main harness and repair as necessary . (8) Turn key OFF. Using an ohmmeter, connect
one lead to a good body ground and touch the other
lead to the terminal in cavity number 29. With the
brake pedal released, the meter should show continu ity. When the pedal is depressed, the meter should
show open circuit.
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL SWITCH TEST
To check the switch, remove the switch from its
mounting position. Use an ohmmeter and refer to the
Switch Continuity Chart to determine if continuity is
correct. If there is no continuity at any one of the
switch positions, replace the switch.
STOP
LAMP SWITCH TEST
(1) Disconnect connector at stop lamp switch. Us
ing an ohmmeter, continuity may be checked at
switch side of connector as follows (Fig. 5): (a) With brake pedal released, there should be:
• continuity between black (BK) and white with
pink tracer (WT/PK) wires
• continuity between yellow with red tracer (YL/RD) and dark blue with red tracer (DB/RD) wires
• No continuity between pink (PK) and white (WT)
wires.
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH CONTINUITY
CHART
CONNECTOR
TERMINAL
END
JE
El
SWITCH
SPEED
CONTROL
SWITCH
CONTINUITY
SWITCH!
rea?!®^
CONTINUITY
BETWEEN
OFF PIN 1
AND PIN 4
ON PIN
1 AND PIN 4
PIN 1
AND PIN 2
PIN
2 AND PIN 4
ON
AND
SET PIN
1
AN D
PIN 2
ON
AND
RESUME PIN
1 AND PIN 3
J928H-4
(b) With brake pedal depressed, there should be:
• continuity between pink (PK) and white (WT)
wires.
• No continuity between black (BK) and white with
pink tracer (WT/PK) wires.
• No continuity between yellow with red tracer (YL/
RD) and dark blue with red tracer (DB/RD) wires. (2) If the above results are not obtained, the stop
lamp switch is defective or out of adjustment.
Stop lamp switch adjustment is detailed in Group 5 -
Brakes.
VACUUM SUPPLY TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at the servo and in
stall a vacuum gauge in the hose (Fig. 6). (2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vac
uum gauge should read at least ten inches of mer
cury. (3) If vacuum does not meet this requirement,
check for vacuum leaks or poor engine performance.
SPEED
CONTROL
CABLE
ADJUSTMENT-DIESEL
ENGINE
(1) The gap between the end of the slot on the ca
ble and the bellcrank pin must be as small as possi
ble (0 to 1mm) without moving the throttle. If gap is not correct, remove adjustment clip. Push protective
Page 477 of 1502

8W
- 2
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
•
WIRE CODE
IDENTIFICATION
Each wire shown in the diagrams contains a code
(Fig. 3) which identifies the main circuit, part of the
main circuit, gauge of wire, and color. The color is shown as a two letter code which can be identified by
referring to the Wire Color Code Chart (Fig. 4). If
the wire has a tracer and it is a standard color an asterisk will follow the main wire color. If the tracer
is non-standard the main wire color will have a slash (/) after it followed by the tracer color. 18
LB/YL*
COLOR
OF
WIRE
(Light
Blue
with
Yellow
Tracer)
.
GAUGE
OF
WIRE
(18
Gauge)
PART
OF
AAAIN CIRCUIT
(Varies
Depending
on
Equipment)
AAAIN CIRCUIT
IDENTIFICATION
918W-16
Fig.
3
Wire
Color
Code
Identification
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
All circuits in the diagrams use an alpha/numeric
code to identify the, wire and its function. To identify
which circuit code applies to a system, refer to the
Circuit Identification Code Chart. This chart shows
the main circuits only and does not show the second ary codes that may apply to some models.
COLOR
CODE COLOR
STANDARD
TRACER
COLOR COLOR
CODE
COLOR
STANDARD
TRACER
CODE
BL BLUE WT
OR ORANGE
BK
BK
BLACK
WT PK
PINK
BK
OR WT
BR
BROWN
WT RD
RED WT
DB DARK
BLUE WT
TN
TAN WT
DG DARK
GREEN WT
VT
VIOLET
WT
GY GRAY
BK
WT
WHITE
BK
LB
LIGHT
BLUE
BK
YL YELLOW
BK
LG
LIGHT
GREEN
BK
*
WITH
TRACER
918W-136
Fig.
4
Wire
Color
Code
Chart
LOCATING
A
SYSTEM
OR
COMPONENT
To locate a system or component in the diagrams,
refer to the alphabetical index at the front of the di agrams. Determine the diagram sheet number. Sheet
numbers are located at the lower right or left hand
corner of each sheet. Page numbers at the top of
the page do not apply to diagram sheets. The diagram index identifies the main system and
all components that relate to that system. There are
also sections of the index that identify specific com
ponents only (for example modules, lamps, etc.). Re-
MAIN
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
A
Battery
Feed: Fused and Unfused
P
Power
Assist
System:
Locks,
Mirrors
B
ABS
System Q Power
Assist
System: Windows
C
Air Conditioning System
R
Airbag System
D
CCD
(+),
CCD
(-)
S
Air Suspension, Automatic Load Leveling
E
Interior
Lamp
Illumination
T Electronic Automatic Transaxle
F
Battery
Feed: Fused and Unfused
V
Windshield Wipers and Washers,
G
Sensors,
Sending Units, Switches Vehicle Speed Control System
K
Powertrain
Central
Module W Power
Assist
System: Windows
L
Exterior
Lighting, Stop Lamp Switch
X
Horn, Radio, Radio Speakers, Power Locks
M
Interior
Lamps
Z
Ground Circuits: Includes power and signal
Interior
Lamps
grounds
for PCM
938W-17
Page 478 of 1502

•
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
8W - 3 fer to a components name in the index if you are
unclear as to what a system may be called.
Diagram pages are arranged starting with the bat
tery and fuses. Then working into charging, starting, and ignition systems. After this they start at the
front of the vehicle and work to rear of the vehicle.
The diagrams end with connector identification
pages.
COMPONENT
IDENTIFICATION
To find a components actual location on the vehicle
refer to the wiring and components section index. This section shows the wire harness routing and the compo
nents location in the vehicle. When using this section
refer to the wiring diagrams for the general location of
the component. Then use the component identification index to locate the proper figure number.
SPLICE
LOCATIONS
Splices are indicated in the wiring diagrams by a
diamond with splice circuit code within it (Fig. 5 ex ample 1). If there is more than one splice per circuit
splice code a small box will be connected to the dia
mond with the splice number in it (Fig. 5 example 2). To locate a splice in the wire harness determine
the splice number from the wiring diagrams, then re
fer to the splice location index. This section shows
the general location of the splice in the harness.
EXAMPLE
1
EXAMPLE
2 918W-18
Fig.
5 Wiring
Splice
Examples
CONNECTORS
The connectors shown in the diagram are viewed from
the terminal end unless otherwise specified. For view ing bulkhead and engine controller connectors refer to
the back of the wiring diagrams. This area shows major connectors for pin and cavity identification.
TROUBLESHOOTING
WIRING
PROBLEMS
When troubleshooting wiring problems there are
six steps which can aid in the procedure. The steps
are listed and explained below. (1) Verify the problem.
(2) Verify any related symptoms. Perform opera
tional checks on components in the same circuit as the problem area. Refer to the wiring diagram fuse
application chart for circuit information. (3) Analyze the symptoms. Use the wiring dia
grams to determine what the circuit is doing, where
the problem most likely is occurring and where the diagnosis will continue. (4) Isolate the problem area. (5) Repair the problem.
(6) Verify proper operation. For this step check for
proper operation of all items on the circuit repaired. Refer to the wiring diagram fuse application chart.
FUSIBLE
LINKS
Vehicle wiring harnesses are equipped with fusible
links.
For protection against harness damage in the
event of a short. Fusible links are color coded as to
wire gauge size. Refer to the fusible link chart for color and gauge identification (Fig. 6).
Wire and
Gauge
Color
Code
Color
12 Ga.
BK
Black
14 Ga.
RD
Red
16 Ga.
DB
Dark
Blue
18 Ga.
GY
Gray
20 Ga.
OR
Orange
22 Ga.
WT
White
918W-19
Fig.
6 Fusible
Link
Chart
HARNESS
REPAIR
FUSIBLE
LINK
REPLACEMENT
CAUTION:
Do not replace blown fusible
links
with
a
standard
wire.
Only
use fusible type
wire
with
hyp-
alon
insulation or
damage
to the electrical
system
could
occur.
Also
make
sure
correct
gauge
of
wir
ing
is
used.
Refer to the wiring
diagrams
for proper
gauge
and
color.
When a fusible link blows it is important to find
out what the problem is. They are placed in the elec
trical system for protection against shorts to ground
that can be caused by a component or various wiring
failures. Do not just replace the fusible link to correct the problem.
When diagnosing a faulty fusible link it is impor
tant to check the wire carefully. In some instances
the link may be blown and it will not show through the insulation, the wire should be checked over its
entire length for internal breaks.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Cut out the blown portion of the fusible link.
(3) Strip 1 inch of insulation from each end of the
existing fusible link.
(4) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the fusible link. Make sure the tubing will be
long enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(5) Cut a replacement piece of fusible link approx
imately two inches longer than the piece removed. (6) Remove one inch of insulation from each end of
the replacement fusible link.
Page 482 of 1502
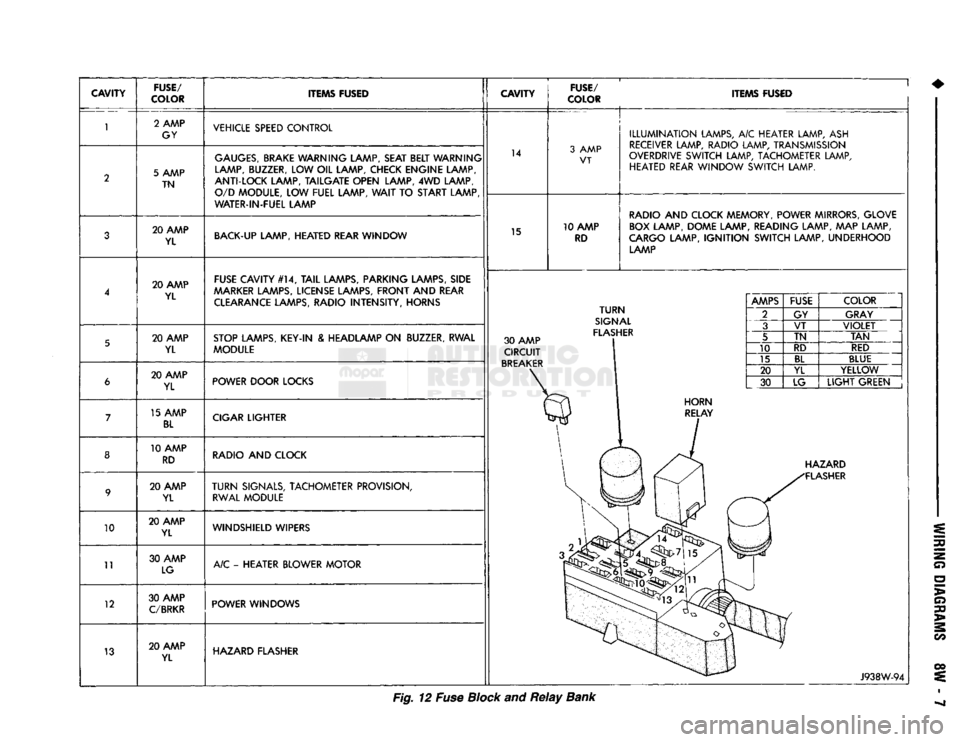
CAVITY
FUSE/
COLOR ITEMS FUSED
CAVITY
FUSE/
COLOR ITEMS FUSED
10
11
12
13 2 AMP
GY VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL
5 AMP TN
GAUGES,
BRAKE WARNING LAMP, SEAT BELT WARNING
LAMP, BUZZER, LOW OIL LAMP, CHECK ENGINE LAMP,
ANTI-LOCK LAMP, TAILGATE OPEN LAMP, 4WD LAMP, O/D MODULE, LOW FUEL LAMP,
WAIT
TO START LAMP
WATER-IN-FUEL LAMP 14
3 AMP
VT
20 AMP YL BACK-UP LAMP, HEATED REAR WINDOW
15 10 AMP
RD
ILLUMINATION
LAMPS, A/C HEATER LAMP, ASH
RECEIVER LAMP, RADIO LAMP, TRANSMISSION
OVERDRIVE SWITCH LAMP, TACHOMETER LAMP, HEATED REAR WINDOW SWITCH LAMP.
RADIO AND CLOCK MEMORY, POWER MIRRORS, GLOVE BOX LAMP, DOME LAMP, READING LAMP, MAP LAMP,
CARGO LAMP,
IGNITION
SWITCH LAMP, UNDERHOOD LAMP
20 AMP YL FUSE CAVITY #14,
TAIL
LAMPS, PARKING LAMPS, SIDE
AAARKER
LAMPS, LICENSE LAMPS, FRONT AND REAR CLEARANCE LAMPS, RADIO INTENSITY, HORNS
20 AMP YL STOP LAMPS, KEY-IN & HEADLAMP ON BUZZER, RWAL
MODULE 30 AMP
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
TURN
SIGNAL
FLASHER 20 AMP
YL POWER DOOR LOCKS
15 AMP
BL
CIGAR LIGHTER
10 AMP RD RADIO AND CLOCK
20 AMP YL
TURN
SIGNALS, TACHOMETER PROVISION,
RWAL MODULE
20 AMP YL WINDSHIELD WIPERS
30 AMP LG A/C - HEATER BLOWER MOTOR
30 AMP
C/BRKR
POWER WINDOWS
20 AMP YL HAZARD FLASHER
AMPS
FUSE
COLOR
2 GY GRAY
3 VT
VIOLET
5 TN
TAN
10 RD
RED
15
BL
BLUE
20 YL YELLOW
30 LG
LIGHT
GREEN HAZARD
FLASHER
J938W-94
Fig. 12 Fuse Block and
Relay
Bank