1993 DODGE TRUCK torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 75 of 1502
2
- 22
FRONT SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
——
J9202-79
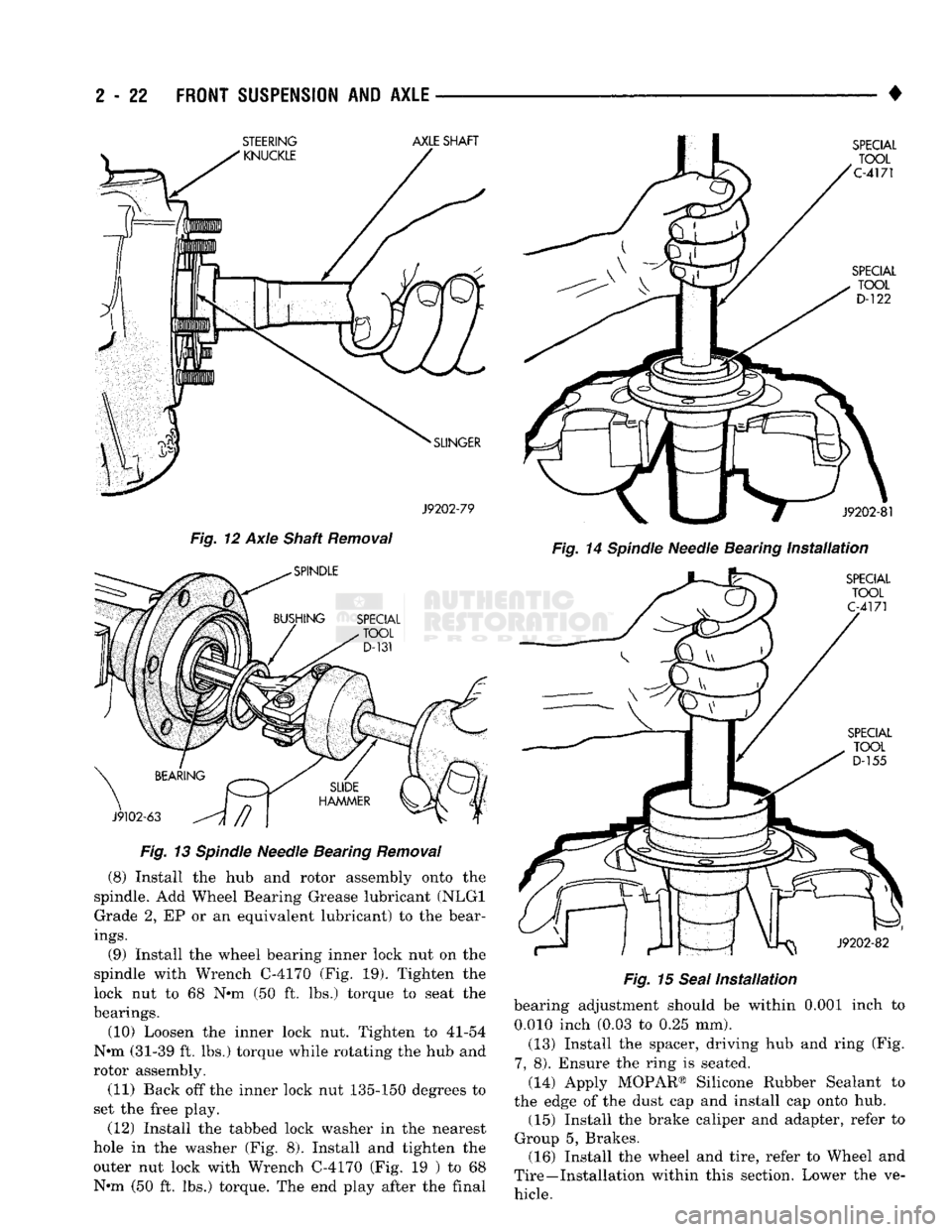
Fig. 12 Axle Shaft Removal
Fig. 13 Spindle Needle Bearing Removal (8) Install the hub and rotor assembly onto the
spindle. Add Wheel Bearing Grease lubricant (NLGI Grade 2, EP or an equivalent lubricant) to the bear
ings.
(9) Install the wheel bearing inner lock nut on the
spindle with Wrench C-4170 (Fig. 19). Tighten the
lock nut to 68 N*m (50 ft. lbs.) torque to seat the
bearings.
(10) Loosen the inner lock nut. Tighten to 41-54
N*m (31-39 ft. lbs.) torque while rotating the hub and
rotor assembly.
(11) Back off the inner lock nut 135-150 degrees to
set the free play.
(12) Install the tabbed lock washer in the nearest
hole in the washer (Fig. 8). Install and tighten the outer nut lock with Wrench C-4170 (Fig. 19 ) to 68
N«m (50 ft. lbs.) torque. The end play after the final •
Fig. 14 Spindle Needle Bearing Installation Fig. 15 Seal Installation bearing adjustment should be within 0.001 inch to
0.010 inch (0.03 to 0.25 mm).
(13) Install the spacer, driving hub and ring (Fig.
7,
8). Ensure the ring is seated.
(14) Apply MOPAR® Silicone Rubber Sealant to
the edge of the dust cap and install cap onto hub. (15) Install the brake caliper and adapter, refer to
Group 5, Brakes. (16) Install the wheel and tire, refer to Wheel and
Tire—Installation within this section. Lower the ve hicle. STEERING
AXLE
SHAFT
Page 79 of 1502
2
- 26
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
•
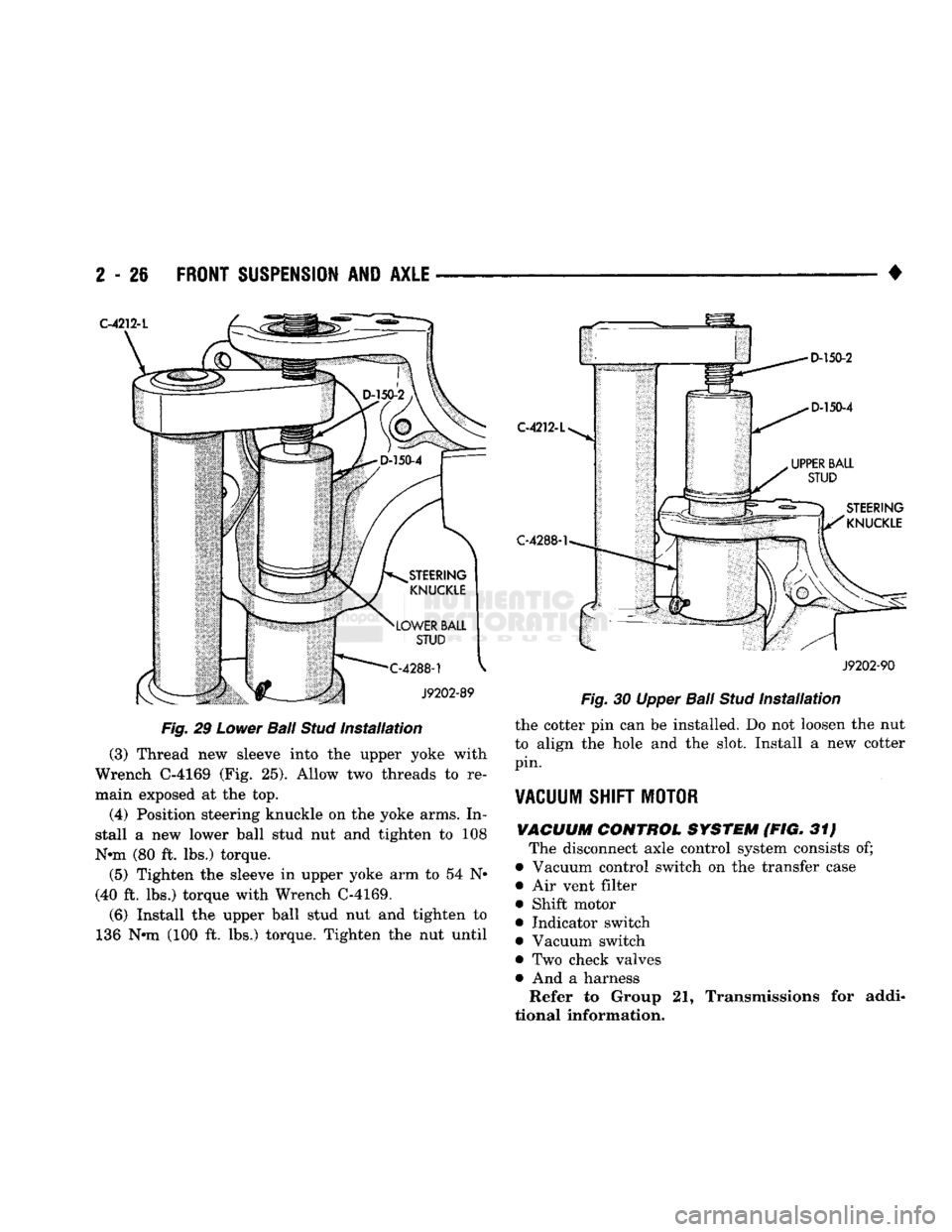
Fig.
29
Lower
Ball
Stud
Installation
(3) Thread new sleeve into the upper yoke with
Wrench C-4169 (Fig. 25). Allow two threads to re
main exposed at the top.
(4) Position steering knuckle on the yoke arms. In
stall a new lower ball stud nut and tighten to 108
Nnn (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Tighten the sleeve in upper yoke arm to 54 N*
(40 ft. lbs.) torque with Wrench C-4169.
(6) Install the upper ball stud nut and tighten to
136 Nnn (100 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the nut until C-4212-L
C-4288-1
J9202-90
Fig.
30 Upper
Ball
Stud
Installation
the cotter pin can be installed. Do not loosen the nut
to align the hole and the slot. Install a new cotter
pin.
VACUUM
SHIFT
MOTOR
VACUUM
CONTROL
SYSTEM
(FIG. 31) The disconnect axle control system consists of;
• Vacuum control switch on the transfer case • Air vent filter
• Shift motor
• Indicator switch
• Vacuum switch
• Two check valves • And a harness Refer to Group 21, Transmissions for addi
tional information.
Page 80 of 1502
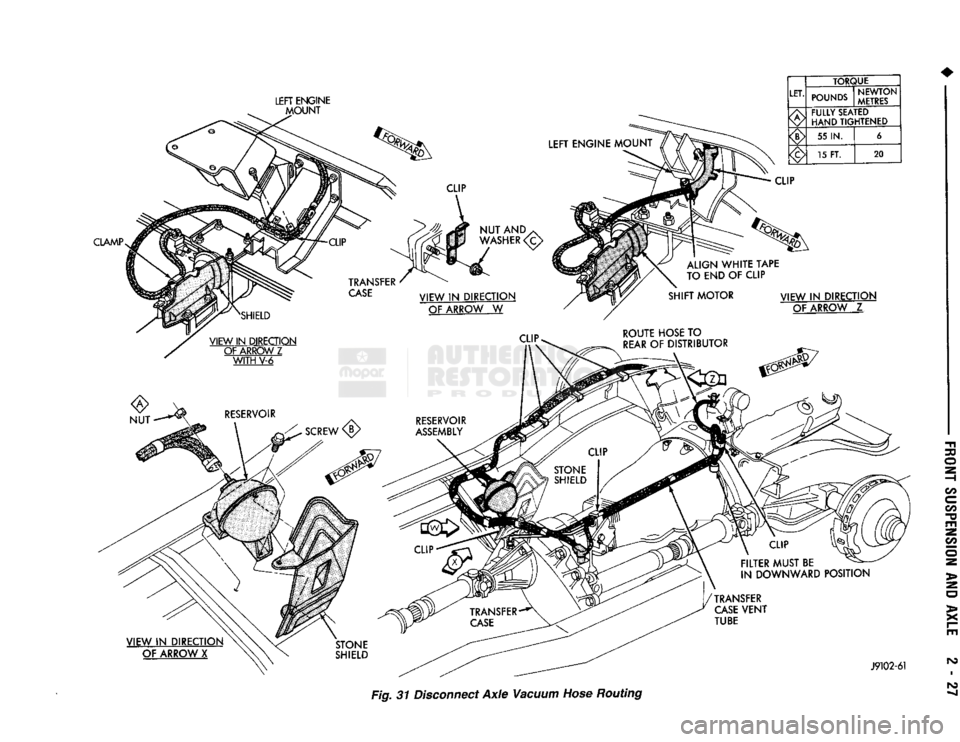
NUT
LEFT
ENGINE
MOUNT
LEFT
ENGINE
MOUNT
NUT
ANDyv
WASHER
VIEW
IN DIRECTION
OF ARROW
W
TORQUE
LET. POUNDS NEWTON
METRES
FULLY SEATED
HAND TIGHTENED
55
IN.
6
15 FT. 20
CLIP
ALIGN
WHITE
TAPE
TO END OF CLIP
VIEW
IN DIRECTION
OF
ARROW Z
WITH
V-6
CLIP.
SHIFT
MOTOR
ROUTE HOSE
TO
REAR
OF
DISTRIBUTOR
VIEW
IN DIRECTION
OF ARROW
Z
VIEW
IN
DIRECTION OF ARROW X
J9102-61
Fig. 31 Disconnect
Axle
Vacuum Hose Routing
Page 83 of 1502
2
- 30
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
• REMOVAUDISASSEMBL
Y
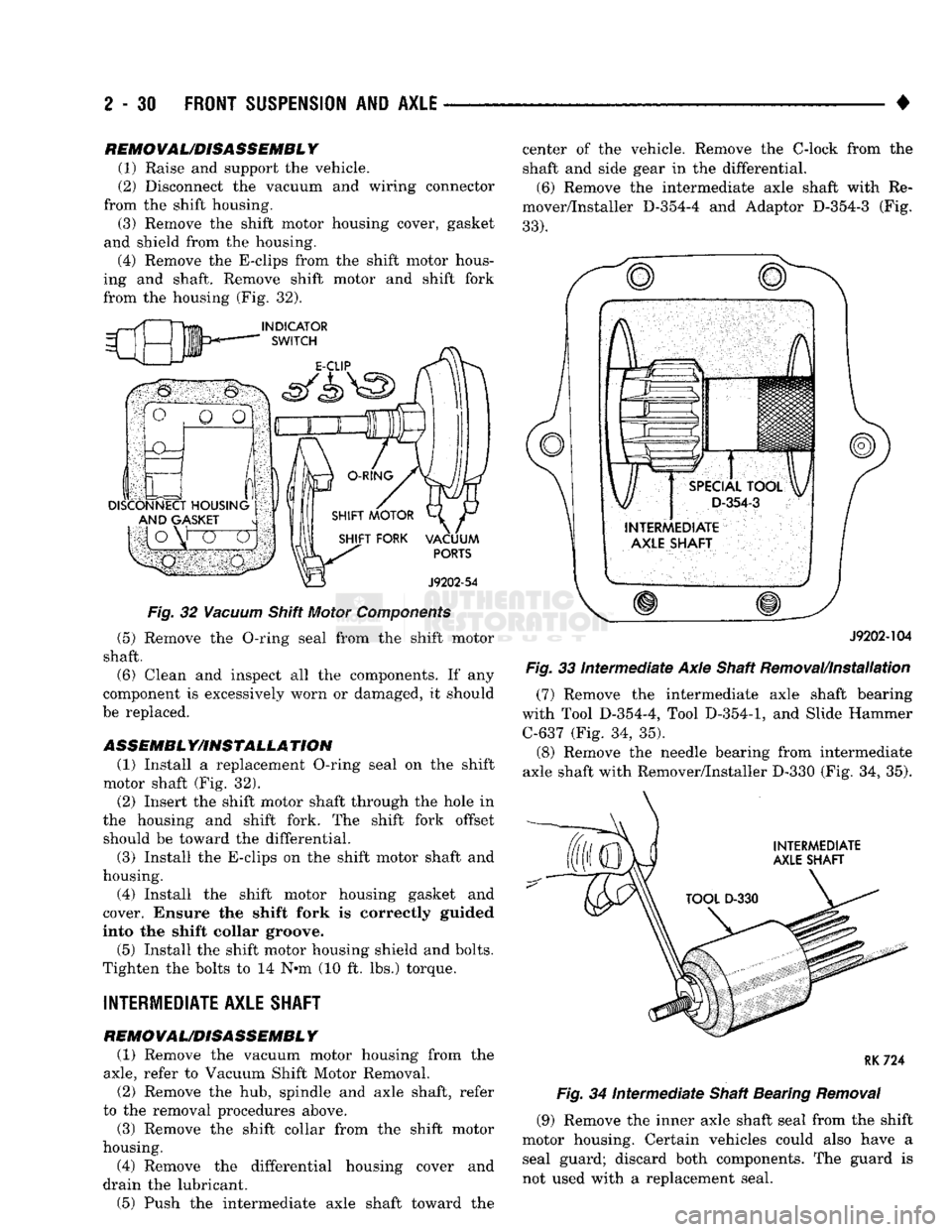
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing. (3) Remove the shift motor housing cover, gasket
and shield from the housing.
(4) Remove the E-clips from the shift motor hous
ing and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork
from the housing (Fig. 32).
Fig.
32
Vacuum
Shift Motor
Components
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the shift motor
shaft. (6) Clean and inspect all the components. If any
component is excessively worn or damaged, it should
be replaced.
ASSEMBL Y/IHSTALLA TION (1) Install a replacement O-ring seal on the shift
motor shaft (Fig. 32). (2) Insert the shift motor shaft through the hole in
the housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset should be toward the differential.
(3) Install the E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
(4) Install the shift motor housing gasket and
cover. Ensure the shift fork is correctly guided
into the shift collar groove.
(5) Install the shift motor housing shield and bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 14 N*m (10 ft. lbs.) torque.
INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFT
REMOVAL/DISASSEMBLY (1) Remove the vacuum motor housing from the
axle,
refer to Vacuum Shift Motor Removal.
(2) Remove the hub, spindle and axle shaft, refer
to the removal procedures above.
(3) Remove the shift collar from the shift motor
housing.
(4) Remove the differential housing cover and
drain the lubricant.
(5) Push the intermediate axle shaft toward the center of the vehicle. Remove the C-lock from the
shaft and side gear in the differential.
(6) Remove the intermediate axle shaft with Re
mover/Installer D-354-4 and Adaptor D-354-3 (Fig.
33).
J9202-104
Fig.
33
intermediate
Axle Shaft Removal/Installation
(7) Remove the intermediate axle shaft bearing
with Tool D-354-4, Tool
D-354-1,
and Slide Hammer C-637 (Fig. 34, 35).
(8) Remove the needle bearing from intermediate
axle shaft with Remover/Installer D-330 (Fig. 34, 35).
RK724
Fig.
34
Intermediate
Shaft Bearing
Removal
(9) Remove the inner axle shaft seal from the shift
motor housing. Certain vehicles could also have a
seal guard; discard both components. The guard is
not used with a replacement seal.
Page 84 of 1502

•
FRONT SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 31
Fig. 35 Disconnect Axle Service Tools ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Install the needle bearing in the end of the in
termediate shaft with Installer D-328 and Driver Handle C-4171 (Fig. 36).
RK
727
Fig. 36 Intermediate Shaft Bearing installation (2) Install the intermediate axle shaft bearing with
Tool D-354-4, Tool 354-2 and Slide Hammer C-637 (Fig. 34, 35).
(3) Install the intermediate axle shaft with Tool
D-354-4 and Adaptor Tool D-354-3.
(4) Install the C-lock in the axle shaft and side
gear.
(5) Clean the tube bore and remove any rust from
the seal area.
(6) Place the axle shaft seal on Tool 5041-1 and po
sition in housing. Thread Tool 5041-2 through the
seal into Tool
5041-1.
Install Tool 5041-3 and nut on
the end of the threaded bar tool. Tighten the nut un
til the tool contacts the threaded bar shoulder.
(7) Install the shift collar on the splined end of the
intermediate axle shaft.
(8) Lubricate the splined end of the intermediate
axle shaft with multi-purpose lubricant.
(9) Install the axle shaft, spindle and hub, refer to
the installation procedures above. (10) Install the shift motor housing, refer to Vac
uum Shift Motor Installation.
STEERING
KNUCKLE
ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Install Puller C-4150 on each drag-link ball
stud. Apply sufficient force with the tool to loosen
the drag-link ball stud from the steering arm.
(2) Remove the lock nuts that attach the steering
arm to the knuckle (Fig. 37). Tap the steering arm to
loosen it from the knuckle. Pry upward to remove. Fig. 37 Steering Knuckle Arm Removal
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering arm on the knuckle. In
stall the nuts. Tighten the nuts to 122 N«m (90 ft.
lbs.).
(2) Position the drag link at steering knuckle arm.
(3) Install and tighten the ball stud nut to 81 N*m
(60 ft. lbs.) torque. Install new cotter pins.
COMPLETE
AXLE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
SERVICE
INFORMATION
It is not necessary to remove the complete front
axle from the vehicle for routine service. If the hous
ing or axle shaft tubes are damaged, the complete axle can be removed and installed via the following
procedures.
REMOVAL (1) Remove the front wheels/tires.
(2) Mark the front drive shaft and the pinion yoke
for installation alignment reference.
(3) Disconnect the front drive shaft from the axle
yoke. Attach the drive shaft to the frame rail with
wire.
(4) Remove the cotter pin, nut, and disconnect the
drag link from the steering knuckle arm (left side
only).
Discard the cotter pin.
Page 85 of 1502

2
- 32
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
• (5) Disconnect flexible brake fluid hose fittings at
the frame crossmember. Plug the hoses at the fit
tings.
(6) Remove the shock absorber lower nut and stud
from the axle shaft tube bracket. Remove the nuts and disconnect the stabilizer bar links from the
spring brackets.
(7) Disconnect the vacuum hoses and wiring con
nections from the shift motor housing.
(8) Remove nuts and the washers from the spring
U-bolts. Remove the complete front axle from the ve
hicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the front axle under the front of the
vehicle with the axle spring pads under the springs.
Place the spring brackets over the springs. Make sure the stabilizer bar link bolt holes face toward the
rear of the vehicle.
(2) Install the spring U-bolts, washers and nuts.
Refer to Front Suspension — 4WD Vehicles within
this group. (3) Install the shock absorber. Refer to Front Sus
pension — 4WD Vehicles within this group. (4) Connect the stabilizer bar links to the spring
brackets. Refer to Front Suspension-4WD Vehicles
within this group.
(5) Remove plugs and connect the brake hose fit
tings.
Refer to Group 5, Brakes. (6) Connect the drag-link ball stud to the steering
knuckle arm. Refer to Group 19, Steering. (7) Connect the drive shaft to the pinion yoke with
the installation reference marks aligned. Install the
washers and the nuts and tighten to 19 N*m (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Connect the vacuum hoses and wiring connec
tions to the shift motor housing. (9) Remove the supports, lower the vehicle and re
move the block from the brake pedal.
(10) Raise the vehicle.
• Bleed and adjust the brakes
• Lubricate all the ball stud fittings
• Inspect the differential housing lubricant level. Re
fer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. (11) Lower the vehicle and test the axle and sus
pension operation.
DIFFERENTIAL
DISASSEMBLY
REMOVAL/DISASSEMBLY (1) Note the installation reference letters
stamped on the bearing caps and housing ma
chined sealing surface (Fig. 38). (2) Remove the differential bearing caps.
(3) Position Spreader W-129-A with the tool dowel
pins seated in the locating holes (Fig. 39). Install the
holddown clamps and tighten the tool turnbuckle fin ger-tight.
INSTALLATION
EFERENCE
LETTERS
J9003-92
Fig.
38 Bearing Cap
Identification
SPECIAL
TOOL
MODEL
44-W-129-A
MODEL
60-D-167
DIAL
INDICATOR
«ar"P—
J9202-113
Fig.
39
Differential
Housing
Separation
(4) Install a pilot stud at the left side of the differ
ential housing. Attach Dial Indicator to housing pilot stud. Load the indicator plunger against the opposite
side of the housing (Fig. 39) and zero the indicator.
CAUTION:
Do not
spread
over the specified
dis
tance.
If the
housing
is over-separated, it
could
be distorted or
damaged.
(5) Separate the housing enough to remove the
case from the housing. Separate housing a maxi
mum distance of 0.38 mm (0.015 in) with the spreader tool. Measure the distance with the dial
indicator (Fig. 39).
(6) Remove the dial indicator.
(7) Pry the differential case loose from the hous
ing. To prevent damage, pivot on housing with the end of the pry bar against case.
(8) Remove the case from housing. If they are re
usable, retain the differential bearing cups and bear ings together as matched sets.
Page 88 of 1502
•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 35
PINION
MATE SHAFT ADAPTERS
DRIFT
J9203-60
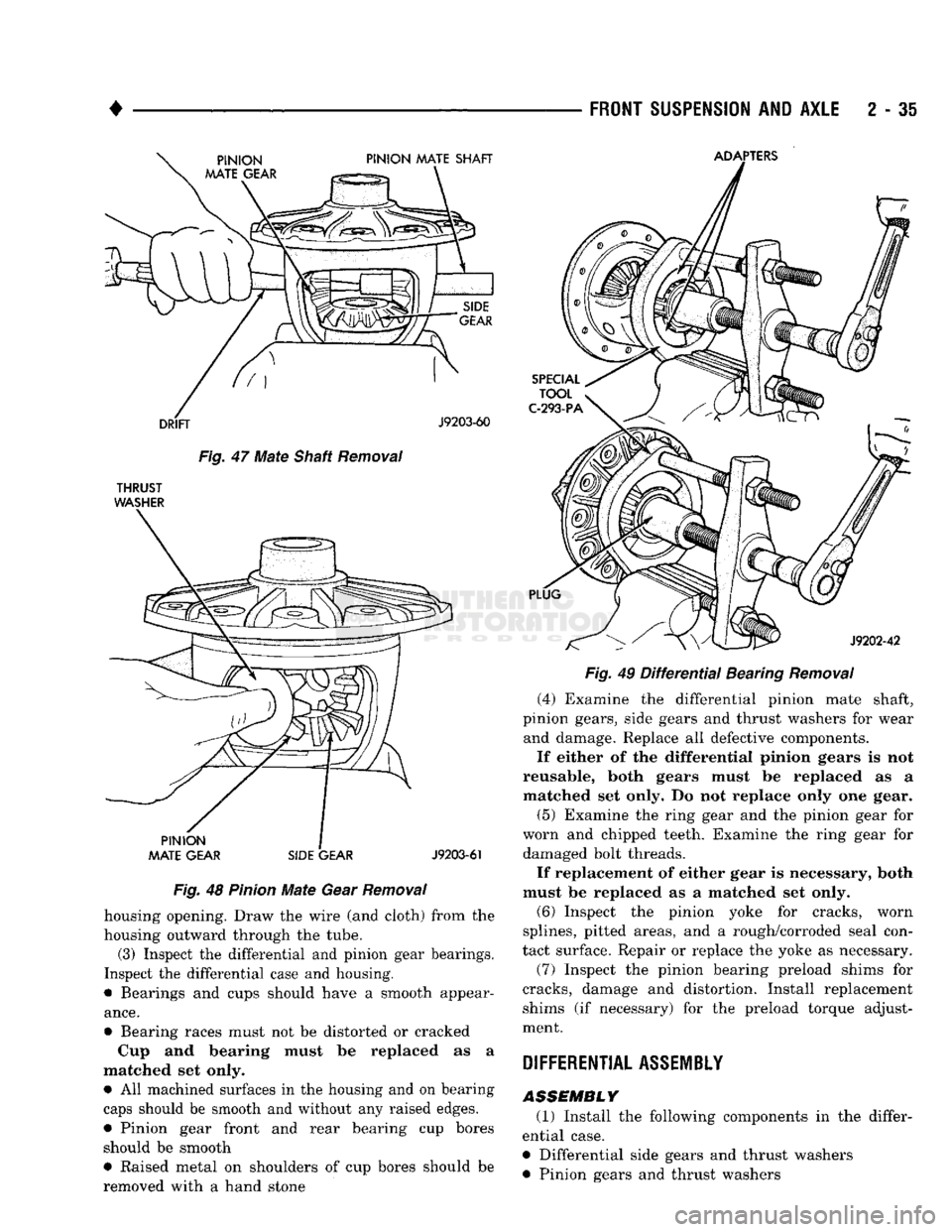
Fig.
47
Mate
Shaft
Removal
THRUST
WASHER
PINION
MATE GEAR SIDE GEAR
J9203-61
Fig.
48
Pinion
Mate
Gear
Removal
housing opening. Draw the wire (and cloth) from the
housing outward through the tube. (3) Inspect the differential and pinion gear bearings.
Inspect the differential case and housing.
• Bearings and cups should have a smooth appear
ance.
• Bearing races must not be distorted or cracked Cup and bearing must be replaced as a
matched set only. • All machined surfaces in the housing and on bearing
caps should be smooth and without any raised edges.
• Pinion gear front and rear bearing cup bores should be smooth
• Raised metal on shoulders of cup bores should be
removed with a hand stone
PLUG
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-293-PA
J9202-42
Fig.
49
Differential
Bearing
Removal
(4) Examine the differential pinion mate shaft,
pinion gears, side gears and thrust washers for wear and damage. Replace all defective components.
If either of the differential pinion gears is not
reusable, both gears must be replaced as a matched set only. Do not replace only one gear.
(5) Examine the ring gear and the pinion gear for
worn and chipped teeth. Examine the ring gear for damaged bolt threads.
If replacement of either gear is necessary, both
must be replaced as a matched set only.
(6) Inspect the pinion yoke for cracks, worn
splines, pitted areas, and a rough/corroded seal con
tact surface. Repair or replace the yoke as necessary.
(7) Inspect the pinion bearing preload shims for
cracks, damage and distortion. Install replacement shims (if necessary) for the preload torque adjust
ment.
DIFFERENTIAL
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY (1) Install the following components in the differ
ential case.
• Differential side gears and thrust washers
• Pinion gears and thrust washers
Page 89 of 1502
2
- 36
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
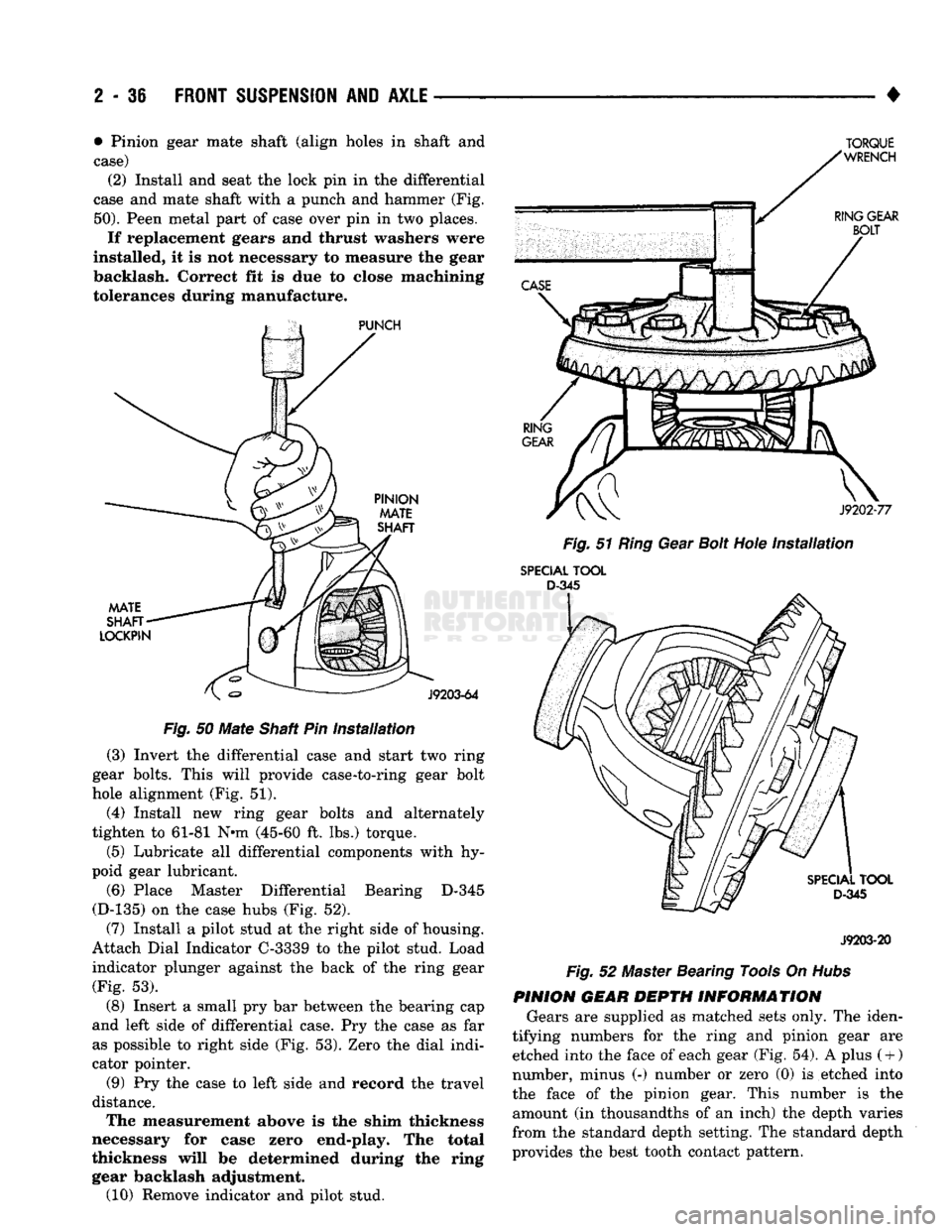
• • Pinion gear mate shaft (align holes in shaft and
case) (2) Install and seat the lock pin in the differential
case and mate shaft with a punch and hammer (Fig.
50).
Peen metal part of case over pin in two places.
If replacement gears and thrust washers were
installed, it is not necessary to measure the gear
backlash. Correct fit is due to close machining
tolerances during manufacture.
Fig.
50
Mate
Shaft Pin
installation
(3) Invert the differential case and start two ring
gear bolts. This will provide case-to-ring gear bolt
hole alignment (Fig. 51).
(4) Install new ring gear bolts and alternately
tighten to 61-81 N*m (45-60 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Lubricate all differential components with hy
poid gear lubricant.
(6) Place Master Differential Bearing D-345
(D-135) on the case hubs (Fig. 52).
(7) Install a pilot stud at the right side of housing.
Attach Dial Indicator C-3339 to the pilot stud. Load
indicator plunger against the back of the ring gear (Fig. 53).
(8) Insert a small pry bar between the bearing cap
and left side of differential case. Pry the case as far as possible to right side (Fig. 53). Zero the dial indi
cator pointer.
(9) Pry the case to left side and record the travel
distance. The measurement above is the shim thickness
necessary for case zero end-play. The total
thickness will be determined during the ring gear backlash adjustment. (10) Remove indicator and pilot stud.
TORQUE
Fig.
51
Ring
Gear
Bolt
Hole
Installation
SPECIAL
TOOL
D-345
J9203-20
Fig.
52 Master Bearing Tools On
Hubs
PINION GEAR DEPTH INFORMATION Gears are supplied as matched sets only. The iden
tifying numbers for the ring and pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig. 54). A plus
(
+ )
number, minus (-) number or zero (0) is etched into
the face of the pinion gear. This number is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth varies
from the standard depth setting. The standard depth
provides the best tooth contact pattern.