1990 MITSUBISHI SPYDER light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 464 of 2103
I E N G I N E
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE (FOR YOUR
ItemsSymptom
StartingWon’tThe starter is used to crank the engine, but there is no combustion
within the cylinders, and the engine
Fires up and diesThere is combustion within the cylinders, but then the
stalls..
Engine starts after cranking a while.Hard starting
Idling
stability
HuntingEngine speed doesn’t constant; idle.
Usually, a judgement can be
upon the of
tachometer pointer, and the vibration transmitted to the
wheel, shift lever, body, etc. This is rough idle.
Rough idle
The engine doesn’t idle at the usual correct Speed. ”
The engine stalls when the foot is taken ‘from
pedal,
regardless of whether
vehicle is moving or not.
Incorrect idle speed
Engine stall (Die out)
The engine stalls when the accelerator pedal is dep ressed
is being used.
Engine stall (Pass out)
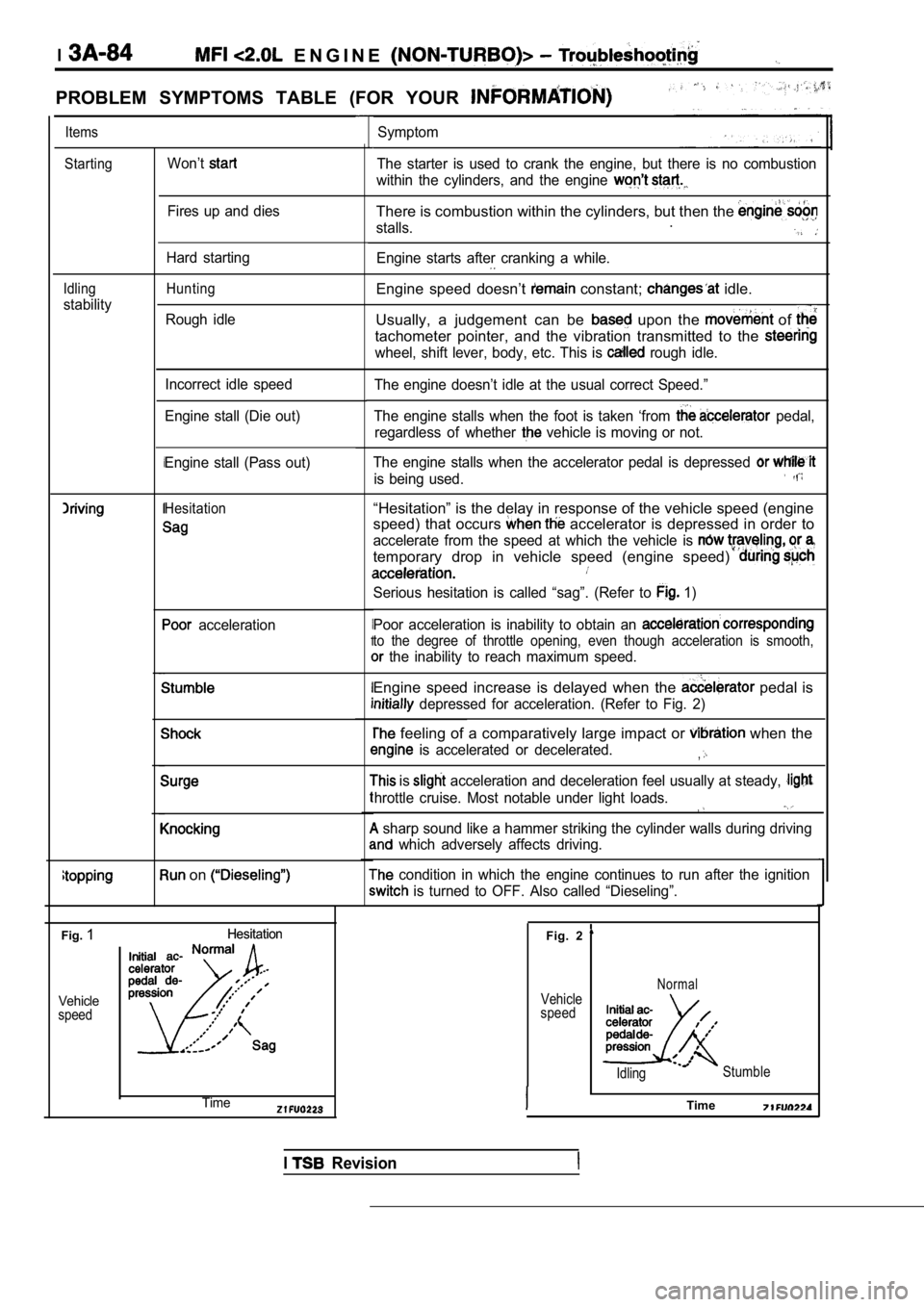
Hesitation“Hesitation” is the delay in response of the vehicle speed (engine
speed) that occurs
accelerator is depressed in order to
accelerate from the speed at which the vehicle is
temporary drop in vehicle speed (engine speed)
Serious hesitation is called “sag”. (Refer to 1)
Poor acceleration is inability to obtain an
to the degree of throttle opening, even though acce leration is smooth,
the inability to reach maximum speed.
acceleration
Engine speed increase is delayed when the pedal is
depressed for acceleration. (Refer to Fig. 2)
feeling of a comparatively large impact or when the
is accelerated or decelerated.,
is acceleration and deceleration feel usually at steady,
hrottle cruise. Most notable under light loads.
sharp sound like a hammer striking the cylinder wa lls during driving
which adversely affects driving.
condition in which the engine continues to run after the ignition
is turned to OFF. Also called “Dieseling”.
on
Fig.1Hesitation
Hesitation
Vehicle
speed
Fig. 2
Vehicle
speedNormal
Idling Stumble
ITimeTime
I Revision
Page 468 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)=,
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 6
Fires up and dies.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]l of the ignition system
In such cases as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark plugs are MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (NON-TURBO)=,
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 6
Fires up and dies.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]l of the ignition system
In such cases as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark plugs are](/manual-img/19/57345/w960_57345-467.png)
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)=,
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 6
Fires up and dies.P r o b a b l e
[Comment]l of the ignition system
In such cases as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark plugs are generating sparkslbut the sparks are weak, or the initial mixture for starting is not appropriate.Malfunction of the injector system
l Foreign fuel
l Poor compression
l
of the PCM
Check the battery. (Refer to GROUP 54
OK:8 or higher
Scan tool: Inspection when incomplete combustion oc curs.(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 30.)
OK
Canany sound be heard (Refer to
Yes
Check the injector control circuit. Carry out procedures in “INSPECTION PROCEDURE
FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES”.
Is starting good if the engine is cranked with the acceleratorpedal slightly depressed?
No
motor circuit INSPECTION
PROCEDURE FOR
TROUBLECODE
Check the following items.
l Check the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug ca bles.
l Clean the injectors.
l Check the compression pressure.
l Check fuel lines for
l Check if foreign (water, alcohol, etc.) got into fuel.
TSB Revision
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 7
Hard startingIProbable cause I
[Comment]l Malfunction of the ignition systemIn cases such as the above, the cause is probably t hat the spark is weak and ignition is difficult,lMalfunction of the injector system
the initial mixture for starting is not appropriate , or sufficient compression pressure is not beinglInappropriate gasoline useobtained.l P o o r
Check battery positive vo
OK: 8 or higherOK
Scan tool: Inspection when incomplete combustion oc curs.
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 30.)Check the battery. (Refer to GROUP 54
Battery)1
Can any sound be heard fro
No Check the injector control circuit. Carry out proc
edures 19, 20, 21,
(Refer to in “INSPECTION PROCEDURE
YesFOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES”.
Check the following items.
l Check the ignition coil, spark plugs, spark plug ca bles.
l Clean the
l Check the pressure.
l Check if foreign materials (water, alcohol, etc.) g ot into fuel.
Page 496 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> , ,
OUTPUT STATE TESTS (DATA LIST) REFERENCE TABLE
Item Inspection
No. itemInspection contentsNormal condition ,
No.
TorqueWhen running at constant speed
reduction,
linkWhen shiftingUP, DOWN
A/C switch: OFFOFF
A/C clutch
relayEngine: IdleA/C switch: ON (A/C ON
compressor activated)
relayIgnition switch: ON
OFF
Engine: Cranking or idle
Engine: WarmRight after starting en-
gine
tive purge
solenoid
Engine: Warm1 0 s e c o n d s o r m o r e
after starting engine
Engine: Warm, idleON
E G R s o l e -OFFSlight racing (Engine: 2,000 or more)( m o m e n t a r i l y ). ..
Radiator fan: Not activated [Engine coolant
Radiator temperature: Less than approx. (176” F)]
fan lowRadiator operates at low speed [Engine coolantspeed relaye m p e r a t u r e i s or less, A/C ON
switch: ON]
Radiator fan: Not activated [Engine OFF
Radiatortemperature: Less than approx.
fan high
speed relay Radiator operates at high speed.
ngine coolant temperature is (220” F)ON
or more, A/C switch: ON]
Fuel pumpIgnition switch: ON
OFF
relayEngine: Cranking or idleON
(CheckIgnition switch: OFF ON
ON OFF
engine)(Everything is OK and DTC is not memorized) (Severa l minutes
lamp later)
TSB Revision
Page 519 of 2103

ENGINE (TURBO)
ENGINE>
DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODEl When an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to emis-
sion control, the CHECK
FUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP illuminates
as a warning to the driver.
l When an abnormality is detected in one
of the’ sensors or actuators, a
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
1. Fuel Pump Control
Turns the fuel pump relay ON current
is supplied to the fuel pump while the engine
is cranking or running.
2. A/C Compressor Clutch Relay Control Turns the A/C compressor clutch ON and
OFF.
3. Fan Relay Control
The radiator fan and condenser fan speeds
are controlled in response to the engine
coolant temperature and vehicle speed.
4. Fuel
Control
Supplies current to fuel pressure solenoid
coil to raise the fuel pressure so that the
fuel does not vaporize when the engine
is started while it is warm.
trouble code ‘the,,
normality is output.
lThe RAM data inside the that
to the sensors and actuators can be read’
by
scan’ tool.
addition, the actuators can be controlled
under certain
5. Charge Control
Controls the intake charge pressure by con-
trolling the duty of the turbocharger
gate solenoid!
6. Intake Pressure Gauge’ Control Indicates the intake charge pressure on
the
7. Generator Output Current Control
Prevents generator output current from in-
creasing idle speed from
dropping at times such as when the head-
lights are turned on.
8.Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Con-
trol Engine (TURBO)>
Refer to
17.
Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Con-
trol GROUP 17.
9. EGR Solenoid’ Control
Refer to GROUP
,,
,
TSB Revision
Page 535 of 2103
ENGINE (TURBO)
AND
ENGINE> Troubleshooting .
6. Other monitoring
lMisfire
l Evaporative emission control system
l Idle air control system
l Manifold differential pressure sensor
lExcessive time to enter closed loop fuel control
l Throttle position sensor
l Barometric pressure sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
l Serial communication link
l Crankshaft position sensor
l Camshaft position sensor
Volume air flow sensor
Test conditions/procedure
l Engine coolant temperature sensor
l Closed throttle position switch
l Generator terminal circuit
l sensor circuit
l sensor heater circuit
Turbocharger waste gate solenoid
l EGR solenoid
lEvaporative emission purge solenoid
l Evaporativeemissionventilation
solenoid Engine>
l Fuel pressure solenoid
lInjector circuit
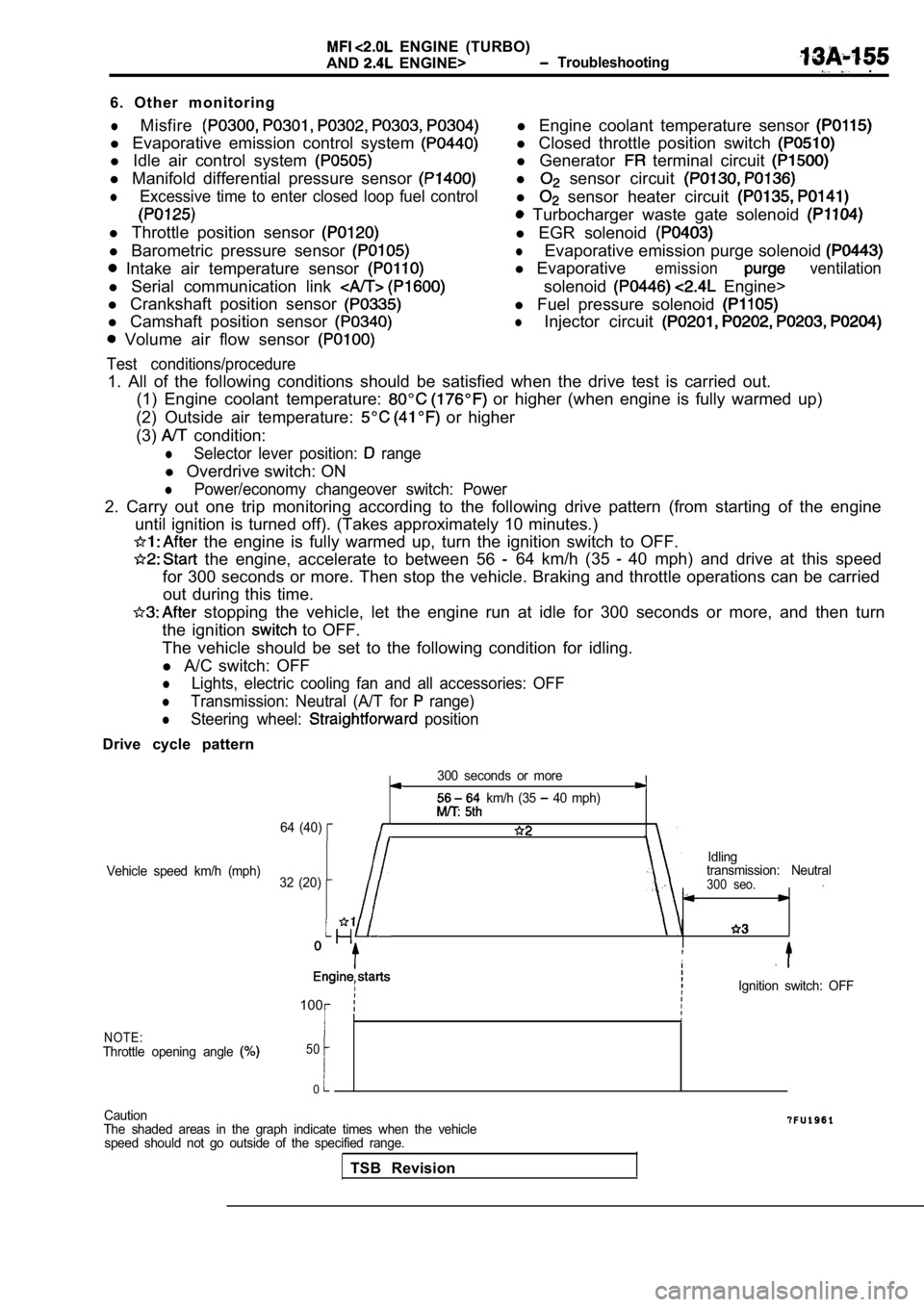
1. All of the following conditions should be satisf ied when the drive test is carried out.
(1) Engine coolant temperature:
or higher (when engine is fully warmed up)
(2) Outside air temperature:
or higher
(3)
condition:
lSelector lever position: range
l Overdrive switch: ON
lPower/economy changeover switch: Power
2. Carry out one trip monitoring according to the f ollowing drive pattern (from starting of the engine
until ignition is turned off). (Takes approximately 10 minutes.)
the engine is fully warmed up, turn the ignition s witch to OFF.
the engine, accelerate to between 56 64 km/h (35 40 mph) and drive at this speed
for 300 seconds or more. Then stop the vehicle. Bra king and throttle operations can be carried
out during this time.
stopping the vehicle, let the engine run at idle f or 300 seconds or more, and then turn
the ignition
to OFF.
The vehicle should be set to the following conditio n for idling.
l A/C switch: OFF
lLights, electric cooling fan and all accessories: O FF
lTransmission: Neutral (A/T for range)
lSteering wheel: position
Drive cycle pattern
300 seconds or more
km/h (35 40 mph)
64 (40)
Idling
Vehicle speed km/h (mph) transmission: Neutral
32 (20)
300 seo.
,
Ignition switch: OFF
100
NOTE:Throttle opening angle 50
0
Caution
The shaded areas in the graph indicate times when t he vehicle
speed should not go outside of the specified range.
TSB Revision
Page 546 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
Code No. Throttle Position Circuit MalfunctionProbable cause’
[Comment]lThrottle position sensor failed or Backgroundl lThe throttle pos MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual ENGINE (TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
Code No. Throttle Position Circuit MalfunctionProbable cause’
[Comment]lThrottle position sensor failed or Backgroundl lThe throttle pos](/manual-img/19/57345/w960_57345-545.png)
ENGINE (TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
Code No. Throttle Position Circuit MalfunctionProbable cause’
[Comment]lThrottle position sensor failed or Backgroundl lThe throttle position sensor outputs a voltage whic h corresponds to the throttle valve
or loose connector
opening angle.
l The engine control module checks whether the voltag e is within a specified range. InClosed switch l Closed throttle position switch addition, it checks that the voltage output does no t become too large while the engineshortedis at idle. Engine control module failed
Check Area, Judgement Criteria
1. Check Area, Judgement Criteria l
Withtheclose throttle position switch set to ON, the senso r output voltage has continuedto be 2 or higher for 4 sec.orI ,
l Sensor output has continued to be 0.2 or lower for 4 sec.
2. Check Area
l Engine speed is at between 500 and 3000 Volumetric efficiency is 30% or lower.
Judgement Criterial Sensor output voltage has continued to be 4.6 or higher for 4 sec.
3. Check Area
l Engine speed is higher than 2000 l Volumetric efficiency is 60% or higher.
Judgement Criterial Sensor output voltage is or less for 4 seconds.
26 Cosed throttle position switchsystemOK:With the throttle valve at the idleposition: ON
With the throttle valve slightly
ooen: OFF (Refer to
INSPECTION
Check the throttle position sensor. Replace
Measure at the position sensorconnectorl
Disconnect the connector, and
measure at the harness side.
l Voltage between
and ground
(Ignition switch: ON)
O K :
l Continuity between 4 and ground
OK: Continuity
TSB Revision
ECM and the throttle position sensor
Check the throttle position sensor Replace the ECM.
Page 576 of 2103
![MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual (TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
Code No. Generator Terminal Circuit Malfunction
[Comment]
Background
lWhen the generator field coil is controlled, the generator terminal inpu MITSUBISHI SPYDER 1990 Service Repair Manual (TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
Code No. Generator Terminal Circuit Malfunction
[Comment]
Background
lWhen the generator field coil is controlled, the generator terminal inpu](/manual-img/19/57345/w960_57345-575.png)
(TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
Code No. Generator Terminal Circuit Malfunction
[Comment]
Background
lWhen the generator field coil is controlled, the generator terminal inputs a signal to
the engine control module.
lThe engine control module detects the generator out put with the input signal, and controlsthe idle air control motor according to the generator output.
Check Area
l Engine speed is higher than 50
Judgement CriterialInput voltage from the generator terminal has continued to be not lower than 4.5 for 20 sec.
Measure at the generator connector
l Connect the connector.
l Voltage between 4 and ground
Engine: Idle
Radiator fan: stopped
Headlight: off
on
Stop Lamp: off on
Rear defogger switch: off on
OK: voltage drops
NG
Measure at the generator connector lDisconnect the connector, and measure at the harnes s side.
l Voltage between 4 and ground (Ignition switch: ON)
O K :
Probable cause
lOpen circuit in generator terminal circuitl Enginecontrol module failed
,
Replace the ECM.
,
. ,
Check trouble symptom.
NG
NG
Repairbetween theECMand the
OK
connector:
NG Repair
OK
Check trouble symptom. generator
NG
Check the NG Repair Replace the ECM.I
TSB Revision
Replace the generator.1
Code No. Serial Communication Link Malfunction
Probable cause
(with
[Comment]l Automatic transaxle control system Backgroundl Open or short circuit in communication linelThe engine control module receives message signals from the transaxle control modulebetween engine module and transaxlevia the communication line. control module, or poor connector contactlThe engine control module monitors abnormalities in message signals resulting froml
Transaxle control module failed.
a broken communication line or transaxle control mo dule problems.l Engine control module failed.
Check Areal 2 seconds or more have passed since starting was co mpleted.
Judgement CriterialAbnormality in communication line (TCM to ECM) with transaxle control module l Problem with transaxle control module (TCM).
Page 580 of 2103

ENGINE (TURBO)
AND Troubleshooting
Items
Starting
Idling stabilityWon’t start Fires up and dies
Hard starting
Hunting
Rough idle
Incorrect idle
speed
Engine stall
(Die out)
Engine stall
(Pass out)
Hesitation
Poor acceleration
Stumble
Shock
Surge
Knocking
Run on
Symptom
The starter is usedto crank the engine, but there is no combustion wit hin the
cylinders, and the engine won’t start.
There is combustion within the cylinders, but then the engine
Engine starts after cranking a while.
Engine speed doesn’t remain constant; changes at id le.
Usually, a judgement can be based upon the movement of the tachometer
pointer, and the vibration transmitted to the steer ing wheel,
lever, body,
etc. This is called rough idle.
The engine doesn’t idle at the usual correct speed.
The engine stalls when the foot is taken from the
pedal, regardless
of whether the vehicle is moving or not.
The engine stalls when the accelerator pedal is dep ressed or being
used.
“Hesitation” is the delay in response of the vehicle speed (engine speed) that
occurs when the accelerator is depressed in order t o, accelerate from the
speed at which the vehicle is now traveling, or a drop in
speed (engine speed) during such acceleration.
Serious hesitation is called to
Poor acceleration is inability to obtain an acceleration corresponding to the
degree of throttle opening, even though acceleratio n is smooth, or the
to reach maximum speed.
Engine speed increase is delayed when the pedal is initially
depressed for
to
The feeling of a comparatively large impact or when the engine is
accelerated or decelerated.
This is slight acceleration and deceleration feel u sually at steady, light
throttle cruise. Most notable under light loads.
A sharp sound like a hammer striking the cylinder w alls during driving
which adversely affects driving.
The condition in which the engine continues to run after
ignition switch
turned to OFF. Also called “Dieseling”.
Vehicle
speedHesitation
Hesitation
Time
Vehicle
speed
Idling Stumble
Revision