1988 PONTIAC FIERO air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 341 of 1825
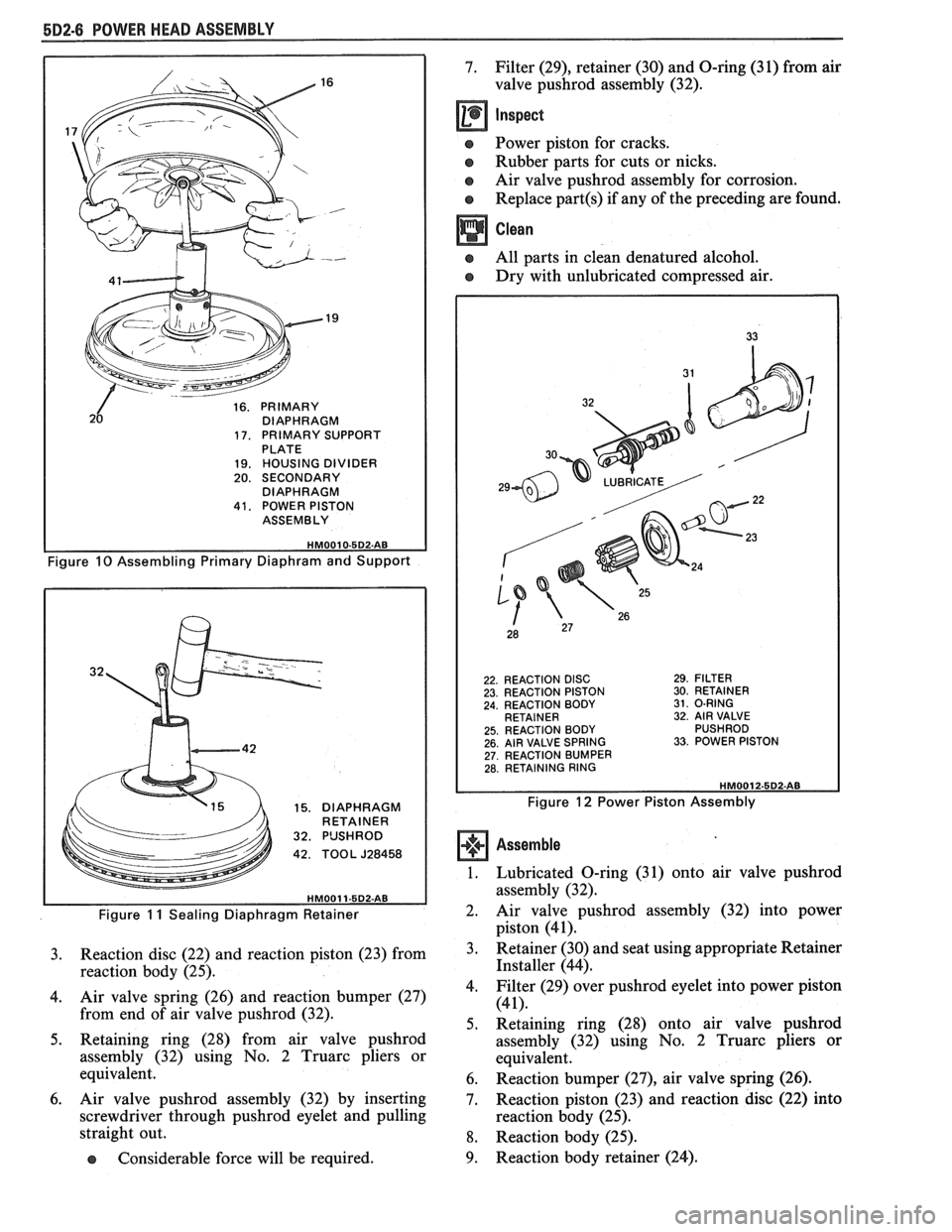
682-6 POWER HEAD ASSEMBLY
16. PRIMARY DIAPHRAGM
17. PRIMARY SUPPORT PLATE 19. HOUSING DIVIDER 20. SECONDARY
DIAPHRAGM
41. POWER PISTON ASSEMBLY
Figure 10 Assembling Primary Diaphram and Support
A, '15 h 15. DIAPHRAGM RETAINER 32. P'JSHROD
42. TOOL J28458
Figure 11 Sealing Diaphragm Retainer
3. Reaction disc (22) and reaction piston (23) from
reaction body
(25).
4.
Air valve spring (26) and reaction bumper (27)
from end of air valve pushrod (32).
5. Retaining ring (28) from air valve pushrod
assembly (32) using No. 2 Truarc pliers or
equivalent.
6. Air valve pushrod assembly (32) by inserting
screwdriver through
pushrod eyelet and pulling
straight out.
e Considerable force will be required.
7. Filter (29), retainer (30) and O-ring (3 1) from air
valve
pushrod assembly (32).
e Power piston for cracks.
e Rubber parts for cuts or nicks.
Air valve
pushrod assembly for corrosion.
Replace
part(s) if any of the preceding are found.
Clean
All parts in clean denatured alcohol.
e ~r~-with unlubricated compressed air.
22. REACTION DISC 29. FILTER 23. REACTION PISTON 30. RETAINER 24. REACTION BODY 31. O-RING RETAINER 32. AIR VALVE 25. REACTION BODY PUSHROD 26. AIR VALVE SPRING 33. POWER PISTON 27. REACTION BUMPER 28. RETAINING RING
HMO01 2.5D2-A6
Figure 12 Power Piston Assembly
Assemble
Lubricated O-ring (31) onto air valve pushrod
assembly (32).
Air valve pushrod assembly (32) into power
piston
(41).
Retainer (30) and seat using appropriate Retainer
Installer
(44).
Filter (29) over pushrod eyelet into power piston
(41).
Retaining ring (28) onto air valve pushrod
assembly (32) using No. 2 Truarc pliers or
equivalent.
Reaction bumper
(27), air valve spring (26).
Reaction piston (23) and reaction disc (22) into
reaction body
(25).
Reaction body (25).
Reaction body retainer (24).
Page 348 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-3
B, Section 6E2 - Fuel Injection (TBI)
B, Section 6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported)
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS
The following diagnostic information covers common problems and possible causes. When
the proper diagnosis is made, the problem should be corrected by adjustment, repair or part
replacement as required. Refer to the appropriate section of the manual for these procedures.
EXCESSIVE OIL LOSS
B, External oil leaks. Tighten bolts and/or replace o Continuous high speed driving, and/or severe
gaskets and seals as necessary. usage
such as trailer hauling, will normally cause
decreased oil mileage.
e Improper reading of dipstick. Check oil with car PCV system malfunctioning. on a level surface and allow adequate drain-down Valve guides and/or valve stem seals worn, or time.
seals omitted. Ream guides and install oversize
service valves and/or new valve stem seals.
Improper Use S.A'E' Piston rings broken, worn, or not seateded. Allow viscosity for prevailing temperatures. See
adequate time for rings to seat. Replace broken
Owner's Manual for proper specifications.
or worn rings, as necessary.
Piston improperly installed or misfitted.
LOW OIL PRESSURE
Slow idle speed. Set idle speed to correct
specification, if not ECM controlled.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure switch.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure gage.
Replace with proper gage.
.*
Improper oil viscosity, or diluted oil. install oil of
proper viscosity for expected temperature, or
install new oil if diluted with moisture or
unburned fuel mixtures.
o Oil pump worn or dirty.
e Plugged oil filter.
e Oil pickup screen loose or plugged.
B, Hole in oil pickup tube.
e Excessive bearing clearance. Replace if necessary.
o Cracked, porous or plugged oil galleys. Repair or
replace block.
o Galley plugs missing or misinstalled. Install
plugs, or repair as necessary.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
e Low oil pressure. Repair as necessary. (See o Broken valve spring.
preceding diagnosis for low oil pressure.)
o Sticking valves.
o Loose rocker arm attachments. Inspect and B, Lifters worn, dirty, or defective. Clean, inspect,
test and replace as necessary.
repair as necessary.
o Camshaft worn, or poor machining. Replace
o Worn rocker arm and/or pushrod. camshaft.
B, Worn valve guides.
ENGINE KNOCK DIAGNOSIS
KNOCKS COLD AND CONTINUES FOR TWO TO THREE MINUTES
INCREASES
WITH TORQUE
o Vacuum operated EFE engines may have valve o Excessive piston to bore clearance. Replace
knock. Replace EFE valve. piston.
e Flywheel contacting splash shield. Reposition
splash shield.
e Loose or broken balancer or drive pulleys.
Tighten, or replace as necessary. Cold engine piston knock usually
disappears when the cylinder is grounded
out. Cold engine piston knock which
disappears in 1.5 minutes should be
considered acceptable.
Page 381 of 1825

6A3-2 V-8 ENGINE
VALVE TRAIN
A very simple ball pivot-type train is used.
Motion is transmitted from the camshaft through the
hydraulic lifter and push rod to the rocker arm. The
rocker arm pivots on its ball and transmits the
camshaft motion to the valve. The rocker-arm ball is
retained by a nut.
HYDRAULIC VALVE LIFTERS
Hydraulic Valve Lifters are used to keep all parts
of the valve train in constant contact.
The hydraulic lifter assembly consists of: a roller,
the lifter body, which rides in the cylinder block boss,
a plunger, a push rod seat, a metering valve, a plunger
spring, a check ball and spring, a check ball retainer
and a push rod seat retainer.
When the lifter is riding on the low point of the
cam, the plunger spring keeps the plunger and push rod
seat in contact with the push rod.
When the lifter body begins to ride up the cam
lobe, the check ball cuts off the transfer of oil from the
reservoir below the plunger. The plunger and lifter
body then rise as a unit, pushing up the push rod and
opening the valve.
As the lifter body rides down the other side of the
cam, the plunger follows with it until the valve closes.
The lifter body continues to follow the cam to its low
point, but the plunger spring keeps the plunger in
contact with the push rod. The ball check valve will then
move off its seat and the lifter reservoir will
remain full.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold for those engines with
carburetors are made of cast iron or aluminum double
level design for efficient fuel distribution. An Exhaust
Gas Recirculation (EGR) port is also cast into the
manifold for the mixture of exhaust gases with the fuel
air mixture.
The intake manifold for those vehicles equipped
with
PFI is a cast aluminum unit. It centrally supports
a fuel rail with
8 fuel injectors.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS
Two cast iron exhaust manifolds are used to
direct exhaust gases from the combustion chambers to
the exhaust system. The left hand side manifold
receives a heat shield that is used to route heated air
to the air cleaner. for better fuel vaporization during
warm-up.
COMBUSTION CHAMBERS
Combustion Chambers are cast to insure uniform
shape for all cylinders. Spark plugs are located between
the intake and exhaust valves. The contoured wedge
shape of the combustion chamber minimizes the
possibility of detonation, facilitates breathing and
provides swirling turbulence for smooth, complete
combustion.
ENGINE LUBRICATION
Full pressure lubrication through a full flow oil through drilled passages, to the camshaft and
filter, is furnished by a gear-type oil pump. The crankshaft to lubricate the bearings. The valve lifter oil
distributor, driven by a helical gear on the camshaft,
gallery feeds the valve lifters which, through hollow
drives the oil pump. The main oil gallery feeds oil,
push rods, feed the individually mounted rocker arms.
Page 397 of 1825
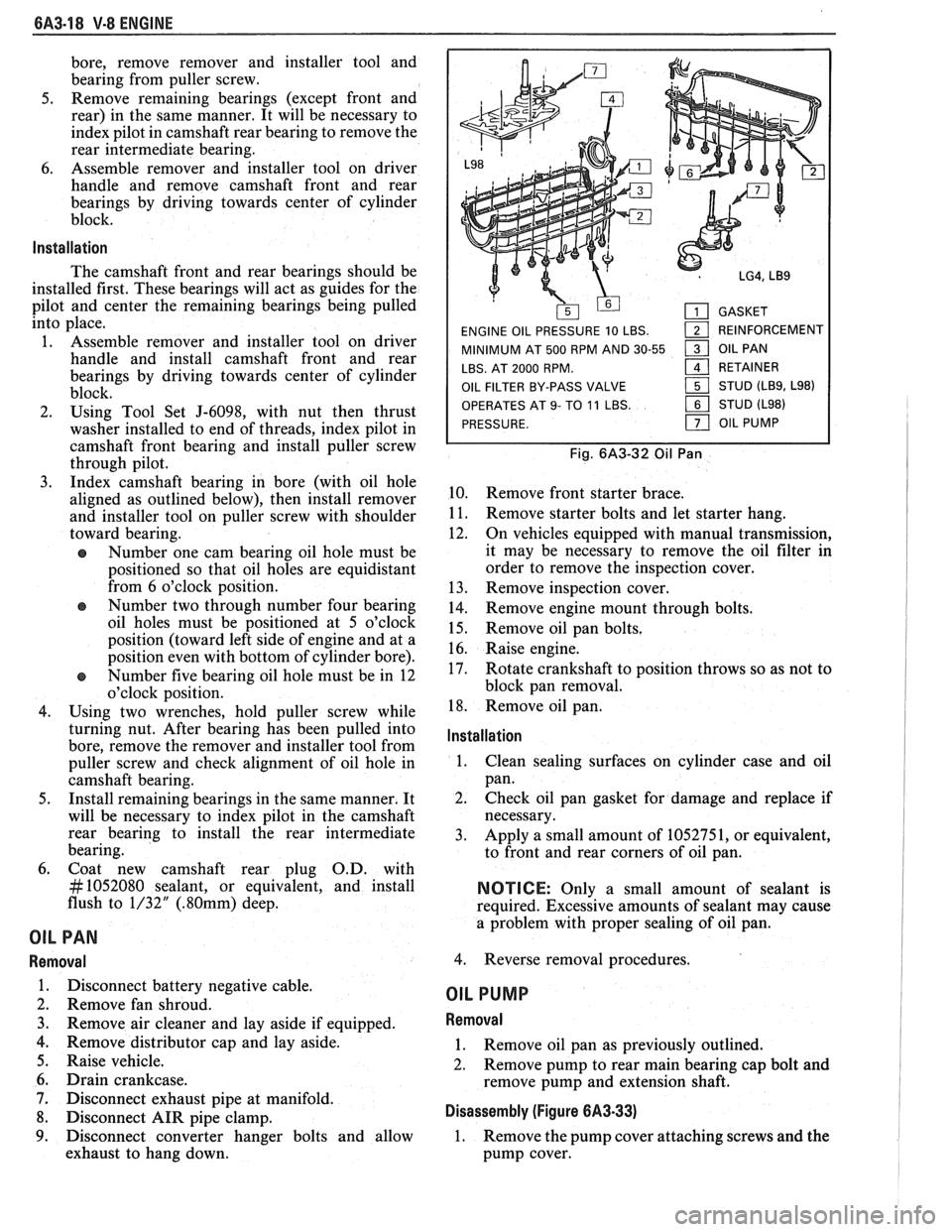
6A3-18 V-8 ENGINE
bore, remove remover and installer tool and
bearing from puller screw.
5. Remove remaining bearings (except front and
rear) in the same manner. It will be necessary to
index pilot in camshaft rear bearing to remove the
rear intermediate bearing.
6. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and remove camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
lnstallation
The camshaft front and rear bearings should be
installed first. These bearings will act as guides for the
pilot and center the remaining bearings being pulled
into place.
1. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and install camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
2. Using Tool Set J-6098, with nut then thrust
washer installed to end of threads, index pilot in
camshaft front bearing and install puller screw
through pilot.
3. Index camshaft bearing in bore (with oil hole
aligned as outlined below), then install remover
and installer tool on puller screw with shoulder
toward bearing.
e Number one cam bearing oil hole must be
positioned so that oil holes are equidistant
from 6 o'clock position.
e Number two through number four bearing
oil holes must be positioned at 5 o'clock
position (toward left side of engine and at a
position even with bottom of cylinder bore).
e Number five bearing oil hole must be in 12
o'clock position.
4. Using two wrenches, hold puller screw while
turning nut. After bearing has been pulled into
bore, remove the remover and installer tool from
puller screw and check alignment of oil hole in
camshaft bearing.
5. Install remaining bearings in the same manner. It
will be necessary to index pilot in the camshaft
rear bearing to install the rear intermediate
bearing.
6. Coat new camshaft rear plug O.D. with
# 1052080 sealant, or equivalent, and install
flush to 1/32"
(.80mm) deep.
OIL PAN
Removal
1. Disconnect battery negative cable.
2. Remove fan shroud.
3. Remove air cleaner and lay aside if equipped.
4. Remove distributor cap and lay aside.
5. Raise vehicle.
6. Drain crankcase.
7. Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
8. Disconnect AIR pipe clamp.
9. Disconnect converter hanger bolts and allow
exhaust to hang down.
GASKET
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE 10 LBS.
1 REINFORCEMENT
MINIMUM AT 500 RPM AND 30-55
1 OIL PAN
LBS. AT 2000 RPM.
161 RETAINER
OIL FILTER BY-PASS VALVE STUD
(LB9, L98)
OPERATES
AT 9- TO 11 LBS. STUD (L98)
PRESSURE.
OIL PUMP
Fig. 6A3-32 Oil Pan
10. Remove front starter brace.
11. Remove starter bolts and let starter hang.
12. On vehicles equipped with manual transmission,
it may be necessary to remove the oil filter in
order to remove the inspection cover.
13. Remove inspection cover.
14. Remove engine mount through bolts.
15. Remove oil pan bolts.
16. Raise engine.
17. Rotate crankshaft to position throws so as not to
block pan removal.
18. Remove oil pan.
lnstallation
1.
Clean sealing surfaces on cylinder case and oil
pan.
2. Check oil pan gasket for damage and replace if
necessary.
3. Apply a small amount of 1052751, or equivalent,
to front and rear corners of oil pan.
NOTICE: Only a small amount of sealant is
required. Excessive amounts of sealant may cause
a problem with proper sealing of oil pan.
4. Reverse removal procedures.
OIL PUMP
Removal
1. Remove oil pan as previously outlined.
2. Remove pump to rear main bearing cap bolt and
remove pump and extension shaft.
Disassembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. Remove the pump cover attaching screws and the
pump cover.
Page 406 of 1825

V-8 ENGINE 6A3-27
3. When finish honing
a cylinder bore to fit a piston,
the hone should be moved up and down at a
sufficient speed to obtain very fine uniform
surface finish marks in a cross-hatch pattern of
approximately
45" to 65" included angle. The
finish marks should be clean but not sharp, free
from imbedded particles and torn or folded
metal.
4. Permanently mark
the piston for the cylinder to
which it has been fitted and proceed to hone
cylinders and fit the remaining pistons.
NOTICE: Handle the pistons with care and do not
attempt to force them through the cylinder until
the cylinder has been honed to correct size as this
type piston can be distorted through careless
handling.
5. Thoroughly
clean the bores with hot water and
detergent. Scrub well with a stiff bristle brush and
rinse thoroughly with hot water. It is extremely
essential that a good cleaning operation be
performed. If any of the abrasive material is
allowed to remain in the cylinder bores, it will
rapidly wear the new rings and cylinder bores in
addition to the bearings lubricated by the
contaminated oil, the bores should be swabbed
and then wiped with a clean dry cloth. Cylinder
should not be cleaned with kerosene or gasoline.
Clean the remainder of the cylinder block to
remove the excess material spread during the
honing operation.
Piston Selection
1. Check USED piston to cylinder bore clearance as
follows:
a. Measure
the "Cylinder Bore Diameter"
with a telescope gage
"2-1/2" (64mm) from
top of cylinder bore").
b. Measure
the
"Piston Diameter" (at skirt
across center line of piston pin).
c. Subtract
piston diameter from cylinder bore
diameter to determine "Piston to Bore
Clearance".
d. Determine if piston to bore clearance is in
the acceptable range.
2. If
used piston is not acceptable, check Piston Size
Chart and determine if a new piston can be
selected to fit cylinder bore within the acceptable
range.
3. If
cylinder bore must be reconditioned, measure
new piston diameter (across center line of piston
pin) then hone cylinder bore to correct clearance
(preferable range).
4. Mark the piston to identify the cylinder for which
it was fitted.
OIL FILTER BYPASS VALVE
Inspection and Replacement
With the oil filter removed, check the spring and
fibre valve for operation. Inspect for a cracked or
broken valve. If replacement is necessary, the oil filter
adapter and bypass valve assembly must be replaced as an
assembly. Clean valve chamber in cylinder block
thoroughly. Torque retaining screws to specifications.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
Removal
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Remove air cleaner.
3. Remove hood.
4. Drain radiator.
5. Remove lower radiator hose.
6. Remove upper fan shroud.
7. Remove upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
8. Remove transmission cooler lines.
9. Remove radiator.
10. Remove fan assembly.
1 1. Remove heater hoses.
12. Disconnect
carburetor linkage, includes cruise
control detent cable.
13. Remove vacuum brake booster line.
14. Remove
distributor cap and lay wiring aside.
15. Disconnect necessary wires and hoses.
16. Remove power steering
pump and lay aside.
17. Raise vehicle.
18. Remove exhaust
pipes at exhaust manifold.
19. Remove dust cover.
20. Remove converter bolts.
2 1. Disconnect starter wires.
22. Remove bell housing bolts.
23. Remove
motor mount through bolts.
24. Disconnect fuel lines
at fuel pump.
25. Lower vehicle.
26. Support transmission.
27. Remove
A.I.R./Converter pipe bracket.
28. Remove engine, include removing wire
from
bracket at rear left of engine.
Installation
1. Position engine
assembly in vehicle.
2. Attach
motor mount to engine brackets and
lower engine in place.
3. Remove engine lifting device.
4. Remove transmission floor jack.
5. Raise vehicle on hoist.
6. Install mount "through" bolts. Torque to
specifications.
7. Install bell housing bolts. Torque to
specifications.
8. On vehicles with automatic transmissions, install
I
converter to flywheel attaching bolts. Torque to
specifications.
9. Install flywheel splash shield of converter
housing cover as applicable. Torque attaching
bolts to specifications.
I
10. Install starter wires.
1 1. Connect fuel lines.
12. Connect exhaust pipe at manifold.
13. Lower vehicle on hoist.
14. Reinstall power steering pump, if so equipped.
15. Connect necessary wires and hoses.
Page 432 of 1825

ENGINE FUEL BC-1
SECTION 6C
NE FUEL
CONTENTS
General Description ..................................... 6C-1 Fuel
Cap ........................................................... 6C-3
.................................................. ............................................. Alcohol-In-Fuel 6C- 1 Fuel Filter Neck 6C-3
................... ............ Fuel Metering .................................................. 6C-2 Fuel Gage Sending Unit .. 6C-4
....................... ............................... Throttle Body Injection (TBI) .... 6C-2 Diagnosis ,. 6C-4 ................... Service
Procedures ............................................. 6C-4
Port Fuel Injection ...................................... 6C-2
Pressure Relief ........................................... 6C-4
Fuel Feed and Return Pipe
............................... 6C-2
Flow Test .................................................... 6C-4
Fuel Pipes (MPFI)
.......................................... 6C-3
Pressure Test - TBI ................................... 6C-4
Fuel and Vapor Hoses
....................................... 6C-3
Pressure Test - MPFI .................................... 6C-4
Fuel Pump ........................................................ 6C-3 ...................................................... Fuel Pump Relay .............................................. 6C-3 Fuel Tank 6C-4
Fuel Filter
......................................................... 6C-3 Accelerator Controls ...................................... 6C-5
Fuel Tank
....................................................... 6C-3
All new General Motors vehicles are certified by
the United States Environmental Protection Agency as
conforming to the requirements of the regulations for
the control of air pollution from new motor vehicles.
This certification is contingent on certain adjustments
being set to factory standards. In most cases, these
adjustment points either have been permanently
sealed and/or made inaccessible to prevent
indiscriminate or routine adjustment in the field. For
this reason, the factory procedure for temporarily
removing plugs, caps, etc., for purposes of servicing the
product must be strictly followed and, wherever
practicable, returned to the original intent of the
design.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All gasoline engines are designed to use only
unleaded gasoline. Unleaded gasoline must be used for
proper emission control system operation. Its use will
also minimize spark plug fouling and extend engine oil
life. Using leaded gasoline can damage the emission
control system and could result in loss of emission
warranty coverage.
All cars are equipped with an Evaporative
Emission System. The purpose of the system is to
minimize the escape of fuel vapors to the atmosphere.
Information on this system will be found in Section
6E2, or 6E3.
When working on the fuel system, there are
several things to keep in mind.
@ Any time fuel system is being worked on,
disconnect the negative battery cable
except for those tests where battery
Adhere to all Notices and Cautions.
Always keep a dry chemical (Class B) fire
extinguisher near the work area.
-
Always use a backup wrench when loosening or
tightening a screw couple fitting.
The torque on a screw fitting is
30 N-m (22 lb.
ft.).
Pipe is used on all MPFI, TPI, SFI, and TBI
applications. Fittings require the use of an
"0"
Ring. Replace all pipe with the same type of pipe
and fittings that were removed.
All fuel pipes must meet GM Specification
124-M, or its equivalent.
All fuel hoses must meet GM Specification
6163-M, or its equivalent.
Do not replace fuel pipe with fuel hose.
voltage is required.
@ On MPFI, TPI, SF1 and TBI systems, always A1cohol-ln-Fuel
relieve the line pressure before servicing any fuel Certain driveability complaints such as
system components. hesitation, lack of power, stall, no start, etc., may be
@ Do not repair the fuel system until you have read caused
by an excessive amount of alcohol-in-fuel. The
the copy and checked the illustrations relating to complaints
may be due to fuel system corrosion and
that repair. subsequent
fuel filter plugging, deterioration of rubber
Page 436 of 1825

ENGINE FUEL CC-5
FUEL TANK
Draining Fuel Tank
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. Also have
a dry chemical (Class B) fire extinguisher near the
work area.
2. Use a hand operated pump device when possible
to drain as much fuel through the filler tube as
possible.
3. If
a hand operated pump device cannot be used
to complete the draining process, use a siphon at
the main (not return) fuel pipe at the fuel pump
or the fuel tank gage unit.
CAUTION: Never drain or store
gasoline in an open container due to
the possibility of fire or explosion.
4. Reinstall any removed hoses, lines and cap.
Removing Fuel Tank
1. Remove all fuel, see "Draining Fuel Tank".
2. Support
fuel tank and disconnect the two fuel
tank retaining straps.
3. Lower tank enough to disconnect sending unit
wire, hoses, and ground strap, if so equipped.
4. Remove tank from vehicle.
5. Remove sending unit.
Installing Fuel Tank
1. Reverse removal procedure.
2. Always replace "0" ring when tank unit has been
removed.
3. When reinstalling fuel tank, be sure to reinstall
anti-squeak pieces on top of the tank to reduce
rattles and other annoying noises.
4. Tighten fuel tank retaining strap bolts or screws.
Fuel System Cleaning
CAUTION: This procedure will NOT
remove all fuel vapor. Do not attempt
any repair
on tank or filler neck where
heat or flame is required, as an
explosion resulting in personal injury
could occur.
If trouble is due to contaminated fuel or foreign
material that is in the tank, it can usually be cleaned.
If tank is rusted internally, it should be replaced.
1. Disconnect negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect ignition engine harness connector.
Have dry chemical (Class B) fire extinguisher
near the work area.
3. Relieve fuel system pressure.
4. Drain fuel tank (see "Draining Fuel Tank").
5. Remove fuel tank (see "Fuel Tank Removal").
6. Remove external fuel filter and inspect for
contamination. If filter is plugged, replace.
7. Locate tank away from heat, flame, or other
source of ignition. Remove fuel gage sending unit
and fuel pump assembly, if so equipped, and
inspect condition of strainer. If strainer is
contaminated, a new strainer should be installed.
8. Complete draining of tank by rocking it and
allowing fuel to run out of fuel sending unit
opening.
9. Flush fuel tank with running hot water for at least
five minutes. Pour water out of fuel sending unit
opening. (Rock tank to be sure that removal of
water is complete.)
10. Disconnect fuel feed pipe and use air pressure to
clean fuel line. Apply air pressure in the opposite
direction fuel normally flows through the line. On
vehicles equipped with a fuel return line, clean
line in similar manner. Disconnect pipe at
throttle body unit and apply air pressure to clean
return line. Reconnect and torque all pipes to 30
N-m (22 1b. ft.).
11. Use low air pressure to clean pipes on fuel gage
sending unit.
112. Install new strainer on fuel gage sending unit, if
required. Install fuel gage sending unit and fuel
pump, with new gasket, into tank and install fuel
tank. Connect fuel gage wire harness to body
harness. Connect all fuel lines except feed line to
external fuel filter.
13. Disconnect fuel feed hose to chassis pipe at front.
Connect a hose to front end of chassis fuel feed
pipe and insert other end of hose into a one gallon
fuel can.
14. Connect battery cable.
15. Put six gallons of clean fuel into fuel tank and
apply 12 volts to Terminal
"G" of ALCL to
operate fuel pump. Pump two quarts of fuel into
fuel can. This will purge fuel pump.
16. Remove hose and connect fuel hose to chassis
pipe.
17. Check all connections
for leaks; tighten all hose
clamps.
Fuel Tank Purging Procedure
The following procedure is used prior to repairing
of fuel tank.
1. Remove fuel sending unit and fuel pump and
drain all remaining fuel from tank.
2. Visually inspect interior cavity of tank. If any fuel
is evident, drain again.
3. Move tank to flushing area (wash rack).
4. Fill tank completely with tap water, agitate
vigorously and drain.
5. Add gasoline emulsifying agent to the tank, refill
with water, agitate mixture for 10 minutes, and
drain tank completely.
For correct gasoline emulsifying agent-to-water
mixture, refer to the
manufacturer's
specifications. Use an available emulsifying
agent, such as "Product-Sol No.
913", or
equivalent.
6. When empty, refill the tank to overflowing with
water. Completely flush out remaining mixture
and empty tank.
7. If available, an explosion meter should be used Lo
check for negative reading.
8. Perform required service work.
Page 550 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-B-3
SURGES AND/OR CHUGGLE
Definition: Engine power variation, under steady
throttle or cruise. Feels like the car speeds up and slows
down, with no change in the accelerator pedal.
@ Use a "Scan" tool to make sure reading of VSS
matches vehicle speedometer. See "Special
Information", Section
"6E".
e CHECK:
- For intermittent EGR at idle. See appropriate
CHART C-7.
- Ignition timing. See Emission Control
Information label.
- Inline fuel filter for dirt or restriction.
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7.
- Generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9,
or more than
16 volts.
- TCC Operation. CHART C-8A.
@ Inspect oxygen sensor for silicon contamination
from fuel, or use of improper RTV sealant. The
sensor may have a white, powdery
coabing and
result in a high but false signal voltage (rich
exhaust indication). The ECM will then reduce
the amount of fuel delivered to the engine,
causing a severe driveability problem.
@ Remove spark plugs. Check for cracks, wear,
improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Also, check condition of the rest of the
ignition system.
LACK OF BOWER, SLUGGISH, OR SPONGY
Definition: Engine delivers less than expected power. Little or no
increase in speed, when accelerator pedal is pushed down part way.
@ Compare customer's car to similar unit. Make - For restricted fuel filter, contaminated fuel or
sure the customer's car has an actual problem. improper fuel pressure. See CHART A-7.
@ Remove air cleaner and check air filter for dirt, - ECM Grounds.
or for being plugged. Replace as necessary.
- EGR operation for being open, or partly open, all
If there is spray from only one injector, then, the time
- CHART C-7.
there is a malfunction in the injector assembly,
- Generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9, or
or in the signal to the injector assembly.
'I'he more than 16 volts.
malfunction can be isolated, by switching the
- Engine valve timing and compression.
injector connectors.
If the problem remains with - Engine, for proper or worn camshaft. See Section
the original injector, after switching the
"6A".
connector, then the injector is defective. Replace - Transmission torque converter operation. See
the injector. If the problem moves with the
Sectionw7A".
injector connector, then the problem is an - Secondary ignition voltage.
improper signal in the injector circuits, see
- Proper operation or ESC. See Section "C5".
CHART A-3. @ Check exhaust system for restriction. See
@ CHECK: CHART B- 1.
- Ignition timing. See Emission Control
Information label.