1987 MAZDA 626 oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 879 of 1865

TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL) 7B
By following the above seven steps, the cause of the problem should be located.
As another guide to faster location of the causes of problems, the Quick Diagnosis Chart is included
at pages 7B—13, 14.
In this chart, a circle is used to indicate the components that might be the cause of trouble for 23
types of problems. It is only necessary to check those components indicated by circles, at each step
cf the troubleshooting process, in order to quickly locate the cause of the problem.
Quick Diagnosis Chart
The Quick Diagnosis Chart shows various problems and the relationship of various components that
might be the cause of the problem.
1. Components indicated in the "Self-Diag." column are diagnosed by the EC-AT control unit self-
diagnosis function.
The EC-AT Tester can be used for easy retrieval of these signals.
2. Components indicated in the "Adjustment" column indicate that there is a possibility that the prob-
lem may be the result of an incorrect adjustment.
Check the adjustment of each component, and readjust if necessary.
3. Input and outout signals of the EC-AT control unit for the components indicated in the "EC-AT
TESTER" column can be easily checked by using of the EC-AT Tester.
4. Components indicated in the "Stall Test" column can be checked for malfunction by the results
of the stall test.
5. Components indicated in the "Time Lag Test" column can be checked for malfunction by the results
of the time lag test.
6. Components indicated in the "Oil Pressure Test" column can be checked for malfunction by the
results of the oil pressure test.
7. Components indicated in the "Road Test" column can be checked for malfunction by the results
of the road test.
8. The checking, adjusting, repair or replacement procedures for each component is described in the
page(s) noted in the "Reference Page" column.
7B—13
Page 880 of 1865

7B TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL)
ON VEHICLE-
-f-
—OFF VEHICLE
\ Inspection point
and
\ reference page
Condition
•
Electronic control system Prelim-
inary
Hydraulic
control
system
Power train \ Inspection point
and
\ reference page
Condition
•
7B-66
m CO I m r--
7B-63
i
cn to I m
Section
4B
|
Section
4B
|
ID to i m
CO CO 1 CD
7B-68
|
en CO 1 IX)
to 1 00 r-.
cn CD 1 CO
7B-69
|
1 CD r--
cn s-1 m
Section
4B
r*-cn
S-1 CD h-
"=1-
rJ CO
7 CD r-
(XI o
1 m
cn CM 1 CD
7B-107
|
CD
7 CD 7 m
I
7B-113
I
CO CM
7 CO r-.
m cn
7 CO r-.
cn
7 DO r-
CM CM
7 CO
|
7B-126
CO
1*-r*-
7 m r-
\ Inspection point
and
\ reference page
Condition
•
Brake
light
switch
|
Inhibitor
switch
|
Mode
switch
|
1
CO. •o o X
Idle
switch
Throttle
sensor
|
Water
temp,
switch
|
0 tn c 0) cn
s
ffi
Q tn 01 o Hi >
Pulse
generator
|
"a o c 0) a to CM
TJ O CL ID s CO C\l 3-4
solenoid
|
Lock-up
solenoid
I
ATF
level
and
condition
|
Selector
lever
m Xj CO CJ 03
1 sz
Idle
speed
and
Ignition
timing
Control
valves
Accumulators
Oil
pump
Hydraulic
circuit
Torque
converter
Forward
clutch
Coasting
clutch
Reverse
clutch
JT O
u TT ro 2-4
brake
band
and
servo
$ 2
B cn cii > £ "O C CO
o
XI y
o >. CO S cb a O
One-way
clutch
2
s CI Cn tz JC 5 0-
Planetary
gear
Differential
assembly
Accelerating
Vehicle does
not
move
in
D,
S,
L,
or R
range
O O O O O O O O O O 0
Accelerating
Vehicle moves
in N
range -0 0 -—
Accelerating
Excessive creep
-0 O O -—
Accelerating
No creep
at all
O o o o
o
G 0 O O
Shifting
|
No shift
O O o
o
0 O 0 0
o
o O
Shifting
|
Abnormal shift sequence
0 o O O 0
o
o 0 O o o 0 O
Shifting
|
Frequent shifting 0 o 0 0 o 0 O O 0
Shifting
|
Excessively high
or
low
shift point 0 o 0 O 0 0 o 0 O 0 0
Shifting
|
No lock-up
0 o 0 0 o 0 O O o O
Shifting
|
No kick-down o o o o
Slipping
Engine
run
away
or
slip when
starting vehicle 0 o 0 O o O
Slipping
Engine
run
away
or
slip when
up-
or
down-shifting o o o 0 o O 0 0 O
8 n cn 4S SI V)
Excessive
N to D or N to R
shift shock o O o o o O
8 n cn 4S SI V)
Excessive shift shock when
up-
shifting
or
downshifting o o o o 0 0 0 8 n cn 4S SI V) Excessive shift shock when
changing range 0 0 o 0 o
j
Noise
Transaxle noisy
in N or P
range o o 0 O
j
Noise
Transaxle noisy
in D, S, L,
or
R range o 0 0 O
I
Others
j
No engine braking o O o 0 o o
I
Others
j
No mode change o 0 o o o o o o o
O
o
0
I
Others
j
Transaxle overheats
o o
0 o 0 o 0
I
Others
j
Vehicle moves
in
"P",
or
park-ing gear
not
disengaged when
"P"
is
dis-
engaged
0 O
I
Others
j
Hold indicator flashes o
0
o
0
o
O
o — — —
I
Others
j
Engine will
not
start
o
o
O — — —
76G07B-014
7B—14
Page 889 of 1865
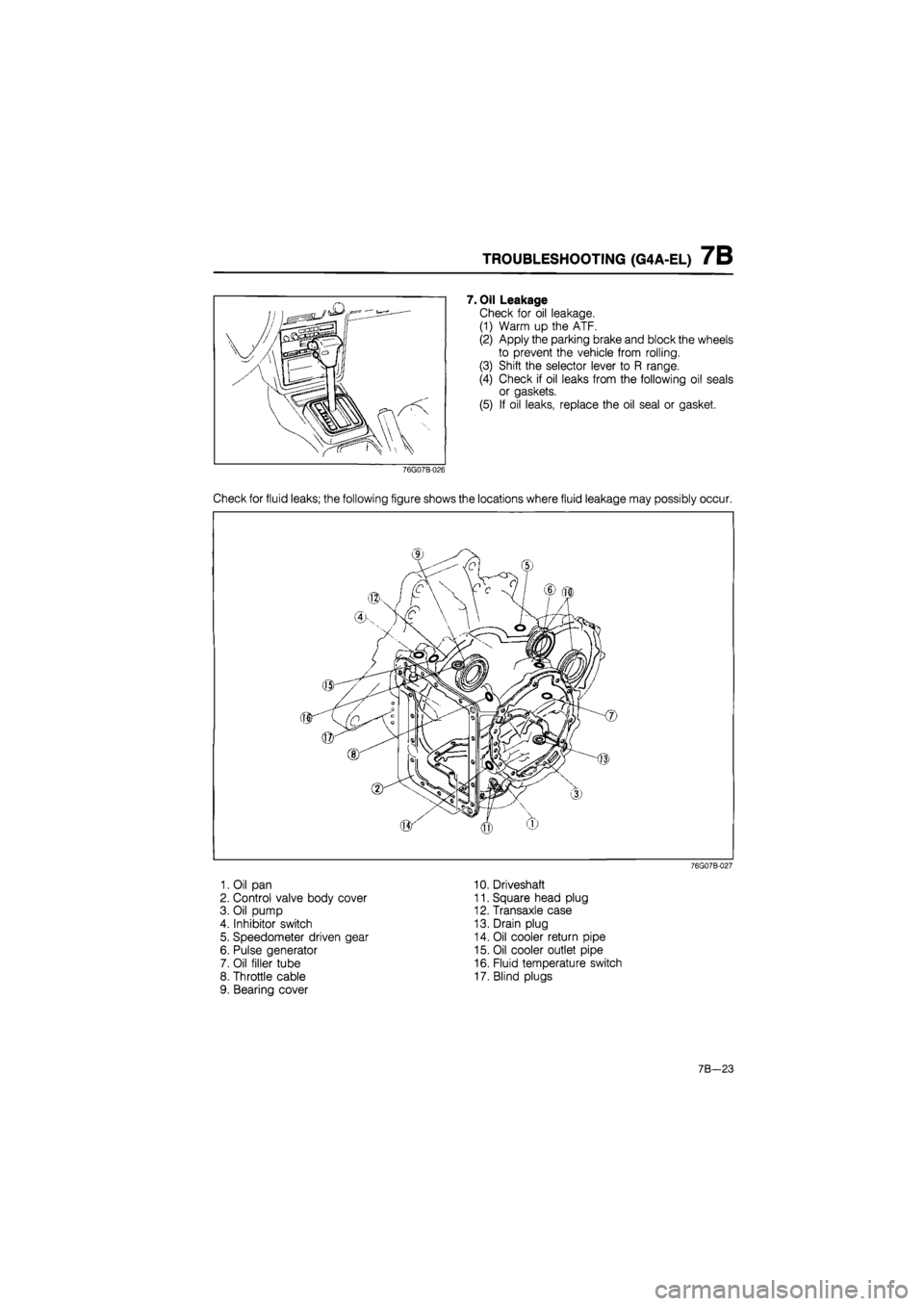
TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL) 7B
7. Oil Leakage
Check for oil leakage.
(1) Warm up the ATF.
(2) Apply the parking brake and block the wheels
to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
(3) Shift the selector lever to R range.
(4) Check if oil leaks from the following oil seals
or gaskets.
(5) If oil leaks, replace the oil seal or gasket.
76G07B-026
Check for fluid leaks; the following figure shows the locations where fluid leakage may possibly occur.
1. Oil pan
2. Control valve body cover
3. Oil pump
4. Inhibitor switch
5. Speedometer driven gear
6. Pulse generator
7. Oil filler tube
8. Throttle cable
9. Bearing cover
10. Driveshaft
11. Square head plug
12. Transaxle case
13. Drain plug
14. Oil cooler return pipe
15. Oil cooler outlet pipe
16. Fluid temperature switch
17. Blind plugs
76G07B-027
7B—23
Page 893 of 1865

TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL) 7B
STEP 4 (STALL TEST)
This step is performed to determine if there is slippage of the friction elements or malfunction of the
hydraulic components.
Preparation
Check the following items prior to testing:
1. Engine coolant, engine oil and ATF levels.
2. Warm the engine thoroughly to raise the ATF temperature to operating level (50—80°C, 122—176°F).
3. Engage the parking brake and use wheel chocks at the front and rear wheels.
Pull the parking brake Water temperature
ATF
79G07C-084
7B-27
Page 895 of 1865

TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL) 7B
7. Perform the stall test for the following ranges in the same manner.
(1) D range (4) L range
(2) D range (Hold) (5) L range (Hold)
(3) S range (Hold)
Caution
Be sure to allow sufficient cooling time between each stall test.
Engine stall speed: D.S.L range 2170—2270 rpm
R range 2130—2230 rpm
Note
The stall test can be performed with the EC-AT Tester in place of a tachometer.
Drum stall speed indication: 0 rpm
76G0/B-029
Evaluation
Condition Possible cause
Above specification
In all ranges Insufficient line
pressure
Worn oil pump
Above specification
In all ranges Insufficient line
pressure Oil leakage from oil pump, control valve, and/or transmission case
Stuck pressure regulator valve
Above specification
In forward ranges Forward clutch slipping One-way clutch 1 slipping
Above specification
In D range One-way clutch 2 slipping
Above specification
In S (Hold) and L (Hold) ranges Coasting clutch slipping
Above specification In D (Hold) and S (Hold) ranges 2-4 brake band slipping Above specification
In R, L and L (Hold) ranges Low and reverse brake slipping
Above specification
In R range
Low and reverse brake slipping Reverse cluch slipping Perform road test to determine whether problem is low and reverse brake or reverse clutch
a) Engine brake applied in 1st ...Reverse clutch
b) Engine brake not applied in 1st ...Low and reverse brake
Within specification All shift control elements within transmission are func-
tioning normally.
Below specification
Engine out of tune
Below specification One-way clutch slipping within torque converter
86U07B-036
7B-29
Page 897 of 1865

TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL) 7B
STEP 6 (OIL PRESSURE TEST)
This step checks line pressures for checking the hydraulic components and for oil leakage.
Line Pressure Test
Preparation
1. Perform the preparation procedure shown in STEP 4 (STALL TEST).
2. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
3. Connect the SST to the line pressure inspection hole (square head plug L)
Procedure
76G07B-031
1. Start the engine and check the idle speed in P range
Idle speed: 900 -so rpm
2. Shift the selector lever to D range and read the line pressure at idle.
3. Depress the brake pedal firmly with the left foot and gradually depress the accelerator pedal with
the right foot.
4. Read the line pressure as soon as the engine speed becomes constant, then release the accelera-
tor pedal.
Caution
Steps 3 to 4 must be performed within 5 seconds.
5. Shift the selector lever to N range and run the engine at idle for at least one minute.
6. Read the line pressure at idle and engine stall speeds for each range in the same manner.
7B—31
Page 898 of 1865
7B TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-EL)
Specified line pressure:
Line pressure kPa, (kg/cm2, psi)
Range DSL R
When idling 353-432 (3.6-4.4, 51-63) 598—942 (6.1-9.6, 87—137)
At stall speed 873-1040 (8.9-10.6, 127-151) 1668-2011 (17.0-20.5, 242-292)
76G07B-032
Evaluation
Line pressure Possible location of problem
Low pressure in every position
Worn oil pump
Fluid leaking from oil pump, control valve body, or transaxle case
Pressure regulator valve sticking
Low pressure in D and S only Fluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of forward clutch
Low pressure in R only Fluid leaking from hydraulic circuit of low and reverse brake
Higher than specification
Throttle valve sticking
Throttle modulator valve sticking
Pressure regulator valve sticking
76G07B-033
7B—32
Page 907 of 1865

TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-HL) 7B
TROUBLESHOOTING (G4A-HL)
GENERAL NOTE
In the event of a problem with the automatic transaxle, the cause may be in the engine, power train,
hydraulic control system, or electrical control system.
When troubleshooting, therefore, it is recommended to begin from those points that can be judged
quickly and easily. The recommended troubleshooting sequence is described below.
STEP 4: TIME LAG TEST
Check time lag of oil pressure supply
STEP 6: OIL PRESSURE TEST Check line, throttle, and governor pressures
This step checks conditions surrounding the automatic
transaxle.
This step checks the electrical control system.
• Function of the electrical control system
• Components
This step checks the power train. • Friction element slipping • Torque converter capacity
This step checks operation of the hydraulic control system. • Accumulators • Friction elements slipping • Regulating valves
This step checks functions of the electric control system and
hydraulic control system.
This step checks major points of the hydraulic control system.
• Oil pump • Line pressure control • Throttle pressure control
• Governer pressure control
STEP 5: ROAD TEST Check items on road test
• Shift point • Shift schedule
• Kick-down • Shift shock • Lock-up and overdrive inhibition
By following the above 6 steps, the cause of the problem should be located.
As another guide to faster location of the causes of problems, the Quick Diagnosis Chart is included
at pages 7B—42, 43.
In this chart, a circle is used to indicate the components that might be the cause of trouble for 20
types of problems. It is only necessary to check those components indicated by circles, at each step
of the troubleshooting process, in order to quickly locate the cause of the problem.
76G07B-040
7B—41