1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 512 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 512
5. Make sure the ring gaps are pr
operly spaced around the circumference
of the piston. Fit a piston ring co mpressor around the piston and slide the
piston and connecting rod assembly do wn into the cylinder bore, pushing
it in with the wooden hammer handle. Pu sh the piston down until it is only
slightly below the top of the cylinder bore. Guide the connecting rod onto
the crankshaft bearing journal carefully, to avoid damaging the
crankshaft.
6. Check the bearing clearance of all the rod bearings, fitting them to the
crankshaft bearing journals. Follow the procedure in the crankshaft
installation above.
7. After the bearings have been fitted, apply a light coating of assembly oil
to the journals and bearings.
8. Turn the crankshaft until the appropria te bearing journal is at the bottom
of its stroke, then push the piston a ssembly all the way down until the
connecting rod bearing seat s on the crankshaft journal. Be careful not to
allow the bearing cap screws to stri ke the crankshaft bearing journals
and damage them.
9. After the piston and connecting rod assemblies have been installed, check the connecting rod side clearance on each crankshaft journal.
10. Prime and install t he oil pump and the oil pump intake tube.
CAMSHAFT, LIFTERS AND TIMING ASSEMBLY 1. Install the camshaft.
2. Install the lifters/followers into their bores.
3. Install the timing gears/chain assembly.
CYLINDER HEAD(S) 1. Install the cylinder head(s) using new gaskets.
2. Assemble the rest of the valve tr ain (pushrods and rocker arms and/or
shafts).
ENGINE COVERS AND COMPONENTS
Install the timing cover(s) and oil pan. Re fer to your notes and drawings made
prior to disassembly and install all of the components that were removed. Install
the engine into the vehicle.
ENGINE START-UP AND BREAK-IN
STARTING THE ENGINE
Now that the engine is inst alled and every wire and hose is properly connected,
go back and double check that all cool ant and vacuum hoses are connected.
Check that you oil drain plug is instal led and properly tightened. If not already
done, install a new oil filt er onto the engine. Fill the crankcase with the proper
amount and grade of engine oil. Fill the cooling system with a 50/50 mixture of
coolant/water.
Page 513 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 513
1. Connect the vehicle battery.
2. Start the engine. Keep y
our eye on your oil pressure indicator; if it does
not indicate oil pressure within 10 se conds of starting, turn the vehicle
off.
WARNING - Damage to the engine can result if it is allowed to run with no oil
pressure. Check the engine oil level to make sure that it is full. Check for any
leaks and if found, repair the leaks be fore continuing. If there is still no
indication of oil pressure, y ou may need to prime the system.
3. Confirm that there are no fluid leaks (oil or other).
4. Allow the engine to reach nor mal operating temperature (the upper
radiator hose will be hot to the touch).
5. If necessary, set the ignition timing.
6. Install any remaining components such as the air cleaner (if removed for
ignition timing) or body panels which were removed.
BREAKING IT IN
Make the first miles on the new engine , easy ones. Vary the speed but do not
accelerate hard. Most importantly, do not lug the engine, and avoid sustained
high speeds until at least 100 miles. Ch eck the engine oil and coolant levels
frequently. Expect the engine to use a littl e oil until the rings seat. Change the
oil and filter at 500 miles, 1500 mile s, then every 3000 miles past that.
KEEP IT MAINTAINED
Now that you have just gone through all of that hard work, keep yourself from
doing it all over again by thoroughly maintaining it. Not that you may not have
maintained it before, heck you c ould have had one to two hundred thousand
miles on it before doing this. However, you may have bought the vehicle used,
and the previous owner did not keep up on maintenance. Which is why you just
went through all of that hard work. See?
Page 626 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 626
ENGINE PERFORMANCE AND TUNE-UP
TUNE-UP PROCEDURES
In order to extract the full measure of performance and economy from your
engine it is essential that it is properly tuned at regul ar intervals. A regular tune-
up will keep your Camaro's engine running smoothly and will prevent the
annoying breakdowns and poor perform ance associated with an untuned
engine.
A complete tune-up should be performed every 30,000 miles (48,000 km). This
interval should be halved if the car is operated under severe conditions such as
trailer towing, prolonged idling, start-and- stop driving, or if starting or running
problems are noticed. It is assumed that the routine maintenance described in
General Information & Maintenance has been kept up, as this will have a
decided effect on the result s of a tune-up. All of the applicable steps of a tune-
up should be followed in order, as the result is a cumulative one.
If the specifications on the underhoo d tune-up sticker in the engine
compartment of your car disagree with th e "Tune-Up Specifications" chart in this
Section, the figures on the sticker must be used. The sticker often reflects
changes made during t he production run.
SPARK PLUGS
A typical spark plug consists of a metal shell surrounding a ceramic insulator. A
metal electrode extends downward through the center of the insulator and
protrudes a small distance. Located at the end of the plug and attached to the
side of the outer metal shell is the side el ectrode. The side electrode bends in at
a 90 angle so that its tip is just pas t and parallel to the tip of the center
electrode. The distance between these two electrodes (measured in
thousandths of an inch or hundredths of a millimeter) is called the spark plug
gap.
The spark plug does not pr oduce a spark, but instead provides a gap across
which the current can arc. The coil produces anywhere from 20,000 to 50,000
volts (depending on the type and application) which travels through the wires to
the spark plugs. The current passes along the center electrode and jumps the
gap to the side electrode, and in doing so, ignites the air/fuel mixture in the
combustion chamber.
Page 628 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 628
SPARK PLUG HEAT RANGE
Spark plug heat range is
the ability of the plug to dissipate heat. The longer the
insulator (or the farther it extends in to the engine), the hotter the plug will
operate; the shorter the insulator (the cl oser the electrode is to the block's
cooling passages) the cooler it will operate. A plug that absorbs little heat and
remains too cool will quickly accumulate deposits of oil and carbon since it is
not hot enough to burn them off. This leads to plug fouling and consequently to
misfiring. A plug that absorbs too much heat will have no deposits but, due to
the excessive heat, the electrodes will burn away quickly and might possibly
lead to preignition or other ignition probl ems. Preignition takes place when plug
tips get so hot that they gl ow sufficiently to ignite the air/fuel mixture before the
actual spark occurs. This early igniti on will usually cause a pinging during low
speeds and heavy loads.
Fig. 3: Spark plug heat range
The general rule of thumb for choosing the correct heat range when picking a
spark plug is: if most of your driving is long distanc e, high speed travel, use a
colder plug; if most of your driving is stop and go, use a hotter plug. Original
equipment plugs are general ly a good compromise between the 2 styles and
most people never have the need to change their plugs from the factory-
recommended heat range.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
A set of spark plugs usually requi res replacement after about 20,000-30,000
miles (32,000-48,000 km), depending on y our style of driving. In normal
operation plug gap increases about 0.001 in. (0.025mm) for every 2500 miles
(4000 km). As the gap increases, the plug' s voltage requirement also increases.
It requires a greater voltage to jump t he wider gap and about two to three times
Page 629 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 629
as much voltage to fire the plug at hi
gh speeds than at idle. The improved
air/fuel ratio control of modern fuel injection combin ed with the higher voltage
output of modern ignition systems will often allow an engine to run significantly
longer on a set of standard spark plugs, but keep in mind that efficiency will
drop as the gap widens (along wit h fuel economy and power).
When you're removing spark plugs, work on one at a time. Don't start by
removing the plug wires all at once, because, unless you number them, they
may become mixed up. Take a minute before you begin and number the wires
with tape.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cabl e, and if the vehicle has been run
recently, allow the engine to thoroughly cool.
2. Carefully twist the spark plug wire boot to loosen it, then pull upward and
remove the boot from the plug. Be su re to pull on the boot and not on the
wire, otherwise the connector locat ed inside the boot may become
separated.
3. Using compressed air, blow any water or debris from the spark plug well
to assure that no harmful contam inants are allowed to enter the
combustion chamber when the spark plug is removed. If compressed air
is not available, use a rag or a brush to clean the area.
Remove the spark plugs when the engine is cold, if possible, to prevent damage
to the threads. If removal of the plugs is difficult, apply a few drops of
penetrating oil or silicone spray to t he area around the base of the plug, and
allow it a few minutes to work.
4. Using a spark plug socket that is equipped with a rubber insert to
properly hold the plug, turn the spar k plug counterclockwise to loosen
and remove the spark pl ug from the bore.
WARNING - Be sure not to use a flexible extension on the socket. Use of a
flexible extension may allow a shear fo rce to be applied to the plug. A shear
force could break the plug off in the cylinder head, leading to costly a\
nd
frustrating repairs.
To install:
5. Inspect the spark plug boot for t ears or damage. If a damaged boot is
found, the spark plug wire must be replaced.
6. Using a wire feeler gauge, check and adjust the spark plug gap. When
using a gauge, the proper size shoul d pass between the electrodes with
a slight drag. The next larger size should not be able to pass while the\
next smaller size should pass freely.
7. Carefully thread the plug into the bor e by hand. If resistance is felt before
the plug is almost completely th readed, back the plug out and begin
threading again. In small, hard to r each areas, an old spark plug wire and
boot could be used as a th reading tool. The boot will hold the plug while
you twist the end of the wire and t he wire is supple enough to twist
before it would allow t he plug to crossthread.
Page 637 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 637
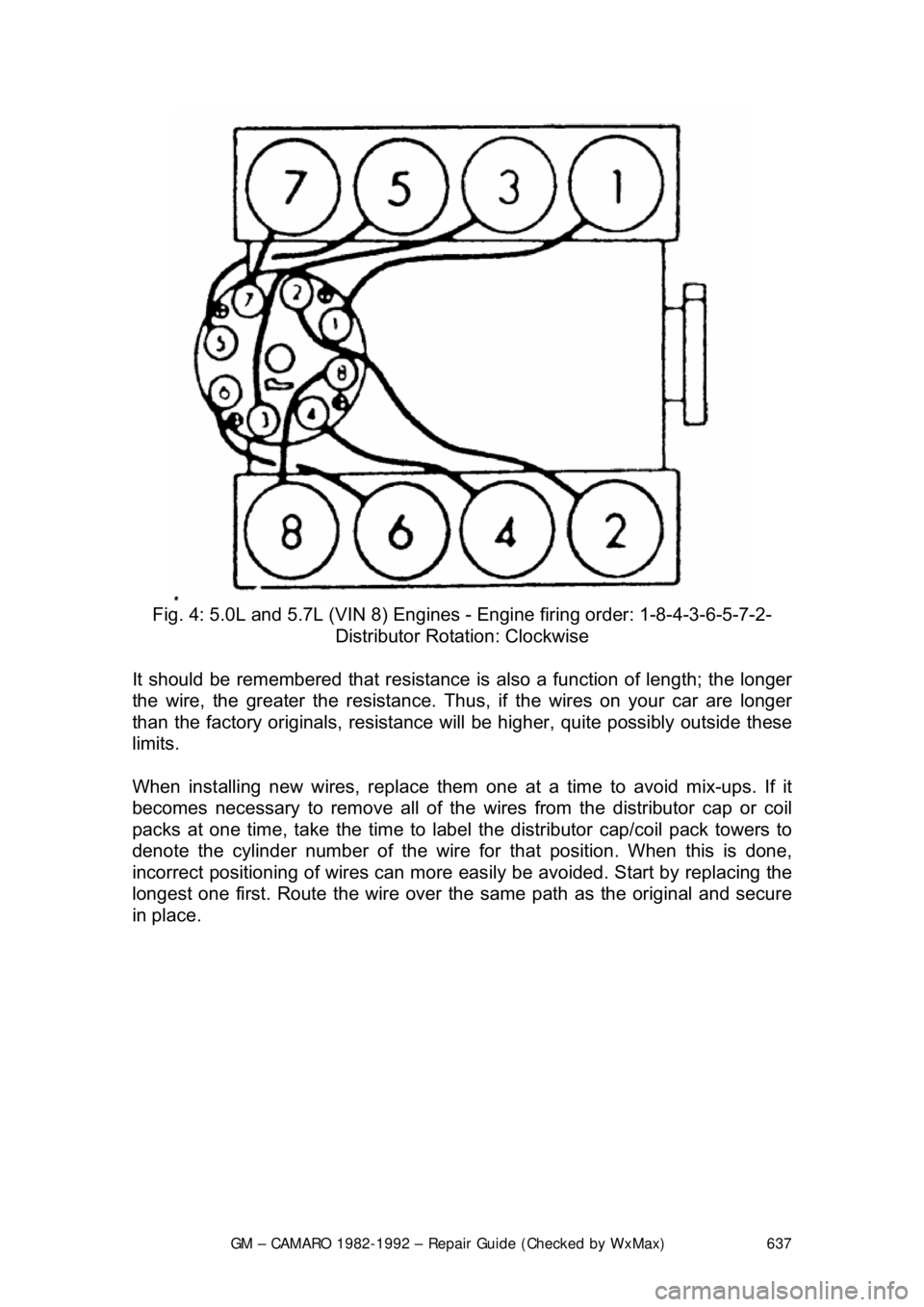
Fig. 4: 5.0L and 5.7L (VIN 8) Engines - Engine firing order: 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2-
Distributor Rotation: Clockwise
It should be remembered that resistance is also a function of length; the longer
the wire, the greater the re sistance. Thus, if the wires on your car are longer
than the factory originals, resistance will be higher, qui te possibly outside these
limits.
When installing new wires, r eplace them one at a time to avoid mix-ups. If it
becomes necessary to remove all of the wires from the distributor cap or coil
packs at one time, take the time to label the distributor cap/coil pack towers to
denote the cylinder number of the wire fo r that position. When this is done,
incorrect positioning of wires can more eas ily be avoided. Start by replacing the
longest one first. Route the wire over the same path as the original and secure
in place.
Page 638 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 638
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The High Energy Ignition (HEI) system
controls the fuel combustion by
providing a spark to ignite the compress ed air/fuel mixture at the correct time.
To provide improved engine performance, fuel economy, and control of exhaust
emissions, the engine contro l module (ECM) controls distributor spark advance
(timing) with an ignition control system.
The distributor may have an internal, or ex ternal ignition coil. To be certain of
the type coil used for your vehicle, vis ually inspect the ignition system. If the
ignition coil is inside the distributor c ap, it connects through a resistance brush
to the rotor. If your vehicle is equipped with an external ignition coil, it connects
to the rotor through a high tension wire.
Fig. 1: Distributor with exterior ignition coil - 1987 vehicle shown
The distributor contains the ignition c ontrol module, and the magnetic triggering
device. The magnetic pickup assembly contains a permanent magnet, a pole
piece with internal "teeth", and a pickup co il (not to be confused with the ignition
coil).
All spark timing changes are done electr onically by the engine control module
(ECM) which monitors information from various engine sensors. The ECM
computes the desired spark timing and t hen signals the distributor ignition
module to change the timing accordingly. No vacuum or mechanical advance
systems are used.
Page 639 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 639
In the HEI system, as in other electr
onic ignition systems, the breaker points
have been replaced wit h an electronic switch - a tr ansistor - which is located
within the ignition module. This switching transistor pe rforms the same function
the points did in a conventi onal ignition system; it simply turns the coil's primary
current on and off at the correct time. Essentially, electronic and conventional
ignition systems operate on t he same principle.
The module which houses the switching transistor is controlled (turned on and
off) by a magnetically gener ated impulse induced in the pickup coil. When the
teeth of the rotating timer align with t he teeth of the pole piece, the induced
voltage in the pickup coil signals the elec tronic module to open the coil primary
circuit. The primary current then decreases, and a high voltage is induced in the
ignition coil secondary windings, which is then directed through the rotor and
high voltage leads (spark plug wires) to fire the spark plugs.
In essence, the pickup coil module system simply replaces the conventional
breaker points and condenser. The condenser found within the distributor is for
radio suppression purposes only and has nothing to do with the ignition
process. The ignition module automatically controls the dwell period, increasing
it with increasing en gine speed. Since dwell is co ntrolled in this manner, it
cannot be adjusted. The module itse lf is non-adjustable/non-repairable and
must be replaced if found defective.
SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS
Before proceeding with troubleshooting, ta ke note of the following precautions:
TIMING LIGHT USE
Care should be exercised when connec ting a timing light or other pick-up
equipment. Do not force anything between the boots and wiring, or through the
silicone jacket. Connections should be made in parallel using an adapter.
Inductive pickup timing lights are the bes t kind to use with the ignition systems
covered by this information.
SPARK PLUG WIRES
The plug wires used with these systems are of a different construction than
conventional wires. When replacing them, make sure you get the correct wires,
since conventional wires will not carry the voltage. Also, handle the wires
carefully to avoid cracking or splitti ng them, and NEVER pierce the wires.
TACHOMETER USE
Not all tachometers will operate or indi cate correctly when used on an HEI or
C
3I system. While some tachometers ma y give a reading, this does not
necessarily mean the reading is correct. In addition, some tachometers hook up
differently from others. If you cannot fi gure out whether or not your tachometer
will work on your car, check with the tachometer manufacturer.