1973 DATSUN B110 oil level
[x] Cancel search: oil levelPage 8 of 513
I
transmission
output
shaft
They
op
erate
in
the
same
speed
as
that
of
the
output
shaft
In
other
wotds
they
operate
at
a
speed
in
proportion
to
the
vehicle
speed
To
those
valves
the
line
pressure
is
applied
as
the
input
ftom
the
control
valve
through
the
transmission
case
rear
flange
and
oil
distributor
The
governor
pressure
in
proportion
to
the
output
shaft
speed
vehicle
speed
is
led
to
the
shift
valve
of
the
control
valve
through
inverse
rou
te
as
the
output
and
thus
the
speed
change
and
the
line
pressure
are
controlled
Operation
of
secondary
governor
valve
The
secondary
valve
is
a
control
valve
which
receives
line
pressure
I
and
controls
the
governor
pressure
When
the
manual
valve
is
selected
D
2
or
1
range
line
pres
sure
is
applied
to
the
ring
shape
area
of
f
this
valve
from
circuit
I
and
this
valve
is
depressed
toward
the
center
side
Movement
of
this
valve
to
a
certain
position
closes
the
circuit
from
I
to
15
simultaneously
while
mak
ing
a
space
from
the
15
to
the
center
drain
port
and
pressure
in
the
circuit
IS
is
lowered
When
the
vehicle
is
stopped
and
the
centrifugal
force
of
this
valve
is
zero
the
valve
is
balanced
In
this
a
gover
nor
pressure
which
is
balanced
with
the
spring
force
occurs
on
the
15
When
the
vehicle
is
started
and
the
centrifugal
force
increases
this
valve
slightly
moves
to
the
outside
and
when
the
space
from
I
to
15
increases
space
from
the
15
to
the
drain
port
reduces
simultaneously
As
the
result
governor
pressure
of
the
15
increases
and
the
governor
pres
sure
is
balanced
with
the
sum
of
centrifugal
force
and
the
spring
force
The
governor
pressure
thus
changt
s
in
response
to
the
vehicle
speed
change
centrifugal
force
Operation
of
primary
governor
valve
The
valve
is
an
ON
OFF
valve
which
closes
the
governor
pressure
15
regulated
by
the
secondary
gover
CHASSIS
nor
valve
when
the
vehicle
speed
reaches
the
minimum
speed
and
when
the
vehicle
speed
exceeds
a
certain
level
open
the
governor
and
forwards
the
governor
pressure
15
to
the
control
valve
When
the
vehicle
is
stopped
the
governor
pressure
is
zero
However
when
the
vehicle
is
running
slowly
this
valve
is
depressed
to
the
center
side
and
the
groove
to
the
IS
is
closed
since
the
governor
pressure
applied
to
the
ring
shape
area
is
higher
than
the
centrifugal
force
of
this
valve
When
the
governor
speed
exceeds
cer
tain
revolution
the
governor
pressure
in
the
circuit
15
also
increases
How
ever
as
the
centrifugal
force
increases
and
exceeds
the
governor
pressure
this
valve
moves
toward
the
outside
and
the
governor
pressure
is
transmitted
to
the
circuit
15
Two
different
valves
are
employed
in
the
governor
so
that
it
will
inde
pendently
control
the
speed
at
high
speed
and
at
low
speed
That
is
within
the
low
speed
range
the
governor
pressure
is
not
generated
owing
to
the
primary
valve
whereas
at
the
high
speed
range
above
the
break
point
a
governor
pressure
regula
ted
by
the
sec0Hdary
valve
is
introduced
The
break
point
is
the
point
at
which
the
function
of
one
of
the
govp
rnors
is
transferred
to
the
other
whee
the
speed
changes
from
the
w
speed
range
to
the
high
speed
range
To
con
trol
valve
Governor
pressure
tiS
y
ID
t
4
From
control
valve
Line
pressure
I
J
I
Primary
governor
2
Secondar
governor
3
Governor
valve
body
AT090
4
Oil
distributor
5
Output
shaft
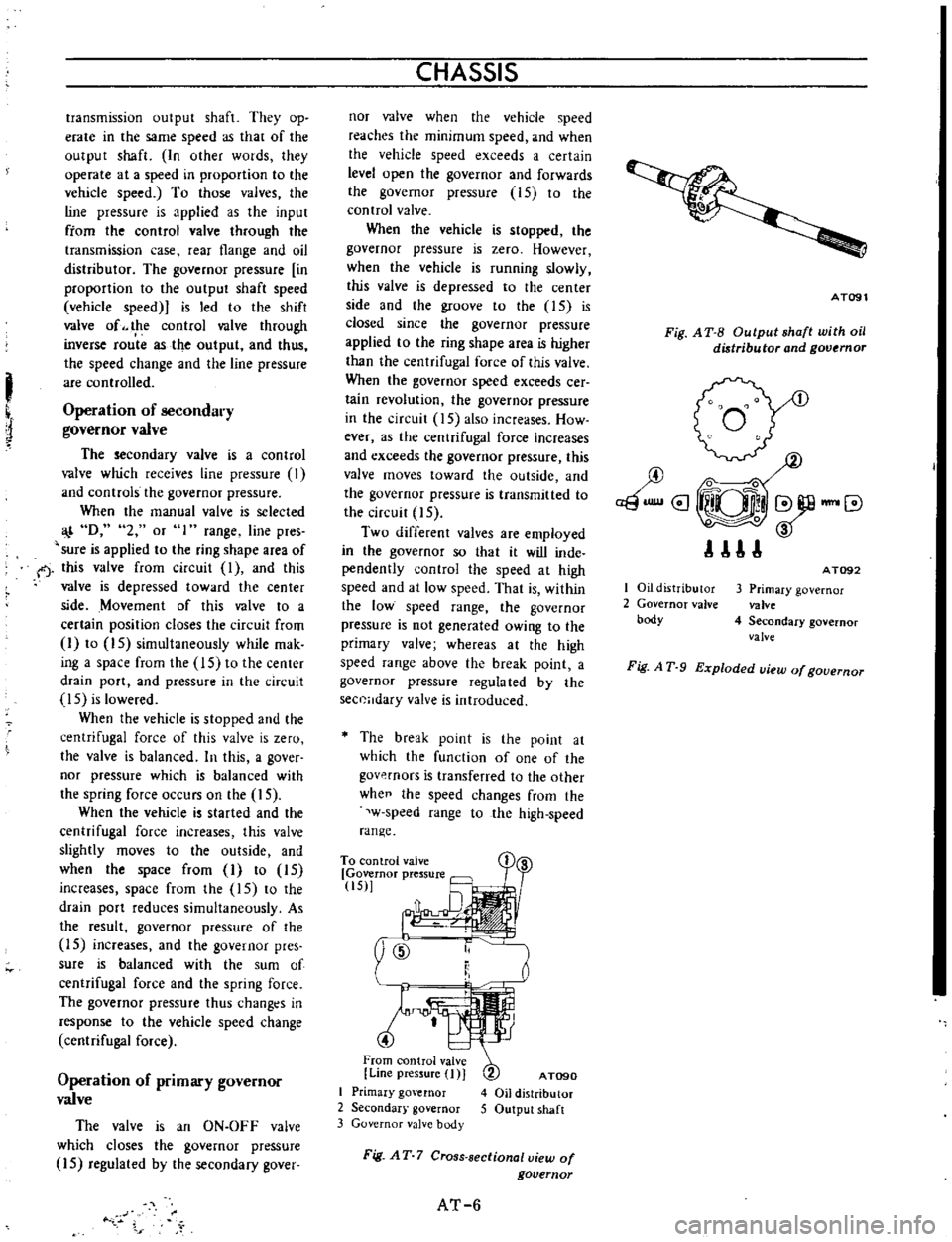
Fig
AT
7
Cross
sectional
view
of
governor
AT
6
AT091
Fig
A
T
B
Output
shaft
with
oil
distributor
and
governor
I
Oil
distributor
2
Governor
valve
body
AT092
3
Primary
governor
valve
4
Secondary
governor
valve
Fig
A
T
9
Exploded
uiew
of
gouernor
Page 13 of 513

Low
in
the
range
I
is
led
to
the
low
and
reverse
clutch
from
the
line
pressure
5
through
the
line
pressure
12
and
at
the
same
time
the
same
is
led
to
the
left
end
spring
unit
Consequently
although
the
go
vernor
pressure
increases
the
valve
is
still
depressed
toward
the
right
and
the
SFV
is
fixed
in
the
Low
posi
tion
When
kicked
down
at
the
2nd
speed
the
SDV
operates
and
the
line
pressure
13
depresse
the
FSV
to
ward
the
right
Although
the
governor
pressure
15
is
considerably
high
the
valve
is
depressed
completely
toward
the
right
and
the
FSV
is
returned
to
the
Low
position
This
operation
is
called
Kick
down
shift
2nd
3rd
shift
valve
SSV
The
SSV
is
a
transfer
vaIve
which
shifts
speed
from
2nd
to
3rd
When
the
vehicle
is
stopped
the
SSV
is
depressed
toward
the
right
by
the
spring
and
is
in
the
2nd
position
It
is
provided
however
that
the
FSV
decides
the
shifting
either
to
Low
or
2nd
When
the
vehicle
is
running
the
governor
pressure
15
is
applied
to
the
right
end
surface
and
the
SSV
is
depressed
toward
the
left
Contrarily
the
spring
force
line
pressure
3
and
throttle
pressure
19
depress
the
SSV
toward
the
right
When
the
vehicle
speed
exceeds
a
certain
level
the
governor
pressure
exceeds
the
sum
of
the
spring
force
line
pressure
and
throttle
pressure
the
valve
is
depressed
toward
the
left
and
the
line
pressure
3
is
closed
Conse
quently
the
forces
are
rapidly
un
balanced
the
force
to
depress
the
SSV
toward
the
right
reduces
and
thus
the
SSV
is
depressed
to
the
Ie
ft
end
for
a
moment
With
the
SSV
depressed
to
ward
the
left
end
the
line
pressure
3
is
connected
with
the
line
pressure
10
the
band
servo
is
released
the
front
clutch
is
engaged
and
speed
is
shifted
to
3rd
When
the
accelerator
pedal
is
de
pressed
both
the
line
pressure
3
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
are
high
and
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
therefore
the
SSV
is
retained
in
2nd
unless
ihe
governor
pressure
IS
exceeds
the
line
pressure
3
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
In
the
3rd
position
force
to
depress
the
SSV
toward
the
right
is
remained
only
on
the
throttle
pressure
16
and
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
slightly
lower
than
that
toward
the
right
which
is
applied
while
shifting
from
2nd
to
3rd
Consequently
the
SSV
is
returned
to
the
2nd
position
at
a
slightly
low
speed
side
Shifting
from
3rd
to
2nd
occurs
at
a
speed
slightly
lower
than
that
for
2nd
to
3rd
shifting
When
kicked
down
at
the
3rd
line
pressure
13
is
led
from
the
SDV
and
the
SSV
is
depressed
toward
the
right
Although
the
governor
pressure
is
considerably
high
the
valve
is
de
pressed
completely
toward
the
right
and
thus
the
SSV
is
returned
to
2nd
position
This
operation
is
called
Kick
down
shift
When
the
shift
lever
is
shifted
to
2
or
I
range
at
the
3rd
speed
the
line
pressure
3
is
drained
at
the
MNV
Consequently
the
front
clutch
operating
and
band
servo
releasing
oils
are
drained
As
the
res
lIt
the
trans
mission
is
shifted
to
the
2nd
or
low
speed
although
the
SSV
is
in
the
3rd
position
When
the
speed
is
shifted
to
the
3rd
a
one
way
orifice
24
on
the
top
of
the
SSV
relieves
oil
transmitting
velocity
from
the
line
pressure
3
to
the
line
pressure
10
and
reduces
a
shock
generated
from
the
shifting
Contrarily
when
shifted
from
3rd
to
2
or
range
and
the
speed
is
shifted
to
the
2nd
spring
of
the
orifice
24
is
depressed
the
throttle
becomes
ineffective
the
line
pressure
10
is
drained
quickly
and
thus
delay
in
the
speed
shifting
is
elimi
nated
Throttle
of
the
line
pressure
6
relieves
the
oil
transmitting
velocity
from
the
line
pressure
6
to
the
line
pressure
10
when
the
lever
is
shifted
to
the
R
range
and
relieves
drain
velocity
from
the
line
pressure
10
to
the
line
pressure
6
when
shifting
from
3rd
to
2nd
at
the
D
range
Thus
the
throttle
of
the
line
pressure
6
reduces
a
shock
generated
from
the
shifting
A
plug
in
the
SSV
left
end
readjust
the
throttle
pressure
16
which
varie
depending
on
the
engine
throttle
con
dition
to
a
throttle
pressure
19
suited
to
the
speed
change
control
Moreover
the
plug
is
a
valve
which
applies
line
pressure
13
in
lieu
of
the
throttle
pressure
to
the
SSV
and
the
FSV
when
kick
down
is
performed
When
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
applied
to
the
left
side
of
this
plug
and
the
plug
is
depressed
toward
the
right
a
slight
space
is
made
from
the
throttle
pressure
16
to
19
A
throt
tIe
pressure
19
which
is
lower
by
the
pressure
loss
equivalent
to
this
space
is
generated
the
pressure
loss
is
added
to
the
spring
force
and
thus
the
plug
is
depressed
back
from
the
right
to
the
left
When
this
pressure
19
increases
excessively
the
plug
is
further
de
pressed
toward
the
left
space
from
the
throttle
pressure
19
to
the
drain
circuit
13
increases
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
lowers
Thus
the
plug
is
balanced
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
is
reduced
in
a
certain
value
b
3
Orifice
t
checking
valve
24
15
2
2
i
I
1
c
V
Y
ii
pr
W
jt1
iff
I
W
q
I
nHH
J
L19
H
10
15
AT
9
A
T098
Fig
AT
13
2nd
3rd
shiflvalue
Page 14 of 513

against
the
throttle
pressure
16
When
performing
the
kick
down
the
SOV
moves
a
high
line
pressure
is
led
to
the
circuit
19
from
the
line
pressute
circuit
13
which
had
been
drained
the
plug
is
depressed
toward
the
left
and
the
circuit
19
becomes
equal
to
the
line
pressure
13
Thus
the
kick
down
is
performed
Preasure
modifier
valve
PMV
In
comparison
with
the
operating
pressure
required
in
starting
the
vehi
ele
power
transmitting
capacity
of
the
clutch
in
other
words
required
op
erating
pressure
may
be
lower
when
the
vehicle
is
once
started
When
the
line
pressure
is
retained
in
a
high
level
up
to
a
high
vehicle
speed
a
shock
generated
from
the
shifting
increases
and
the
oil
pump
loss
also
increases
In
order
to
prevent
the
above
described
defective
occurrences
with
the
opera
lion
of
the
governor
pressure
15
the
throttle
pressure
must
be
changed
over
to
reduce
the
line
pressure
The
PMV
is
used
for
this
purpose
When
the
governor
pressure
15
which
is
applied
to
the
right
side
of
the
PMV
is
low
the
valve
is
depressed
toward
the
right
by
the
throttle
pres
sure
16
applied
to
the
area
differ
ence
of
the
value
and
the
spring
force
and
the
circuit
from
the
circuit
16
to
the
circuit
18
is
closed
However
when
the
vehicle
speed
increases
and
the
governor
pressure
15
exceeds
a
certain
level
the
governor
pressure
toward
the
left
which
is
applied
to
the
right
side
exceeds
the
spring
force
and
the
throttle
pressure
16
toward
the
right
the
valve
is
depressed
toward
the
left
and
the
throttle
pressure
is
led
from
the
circuit
16
to
the
circuit
18
This
throttle
pressure
18
is
applied
to
the
top
of
the
PRY
and
pressure
of
the
line
pressure
source
7
is
reduced
Contrarily
when
the
vehi
cle
speed
lowers
and
the
governor
pressure
15
lowers
the
force
toward
the
right
exceeds
the
governor
pres
CHASSIS
sure
the
valve
is
depressed
back
to
ward
the
right
the
throttle
pressure
18
is
drained
to
the
spring
unit
This
valve
is
switched
when
the
throttle
pressure
and
the
governor
pressure
are
high
or
when
the
throttle
pressure
is
low
and
the
governor
pres
sure
is
low
II
18
16
1JU
k
I
15
AT099
Fig
AT
14
Pressure
modifier
valve
Vacuum
throttle
valve
VTV
The
vacuum
throttle
valve
is
a
regulator
valve
which
uses
the
line
pressure
7
for
the
pressure
source
and
regulates
the
throttle
pressure
16
which
is
proportioned
to
the
force
of
the
vacuum
diaphragm
The
vacuum
diaphragm
varies
depending
on
the
engine
throttle
condition
negative
pressure
in
the
intake
line
When
the
line
pressure
7
is
ap
plied
to
the
bottom
through
the
valve
hole
and
the
valve
is
depressed
up
ward
space
from
the
line
pressure
7
to
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
closed
and
the
space
from
the
throttle
pres
sure
16
to
the
drain
circuit
17
is
about
to
open
In
this
the
throttle
pressure
16
becomes
lower
than
the
line
pressure
7
by
the
pressure
equivalent
to
the
pressure
loss
of
the
space
and
the
force
to
depress
through
the
rod
of
the
vacuum
dia
phragm
is
balanced
with
the
throttle
pressure
16
applied
upward
to
the
bottom
When
the
engine
torque
is
high
the
negative
pressure
in
the
intake
line
rises
similar
to
the
atmospheric
pres
sure
and
the
force
of
the
rod
to
depress
the
valve
increases
As
the
result
the
valve
is
depressed
down
ward
the
space
from
the
throttle
pressure
16
to
the
drain
17
re
AT
lO
duces
and
the
space
from
the
line
pressure
7
to
the
throttle
pressure
16
increases
Consequently
the
throttle
pressure
16
increases
and
the
valve
is
baI
anced
Contrarily
when
the
engine
torque
lowers
and
the
negative
pres
sure
in
the
intake
line
lowers
similar
to
vacuum
force
of
the
rod
to
de
press
the
valve
lowers
and
the
throttle
pressure
16
also
lowers
When
a
pressure
regulated
by
the
throttle
back
up
valve
described
in
the
subse
quent
paragraph
is
led
to
the
circuit
17
a
high
pressure
is
applied
through
the
space
from
the
circuit
17
to
the
throttle
pressure
16
Consequently
the
VTV
is
unbalanced
the
throttle
pressure
16
becomes
equal
to
the
back
up
ptessure
17
and
the
valve
is
locked
upward
bi
II
I
ATlOa
Fig
AT
15
Vacuum
throttle
valve
Throttle
back
up
valve
TBV
Usually
this
valve
is
depressed
downward
by
the
spring
force
and
the
circuit
17
is
drained
upward
As
soon
as
the
lever
is
shfted
either
to
2
or
range
line
pressure
is
led
from
the
circuit
4
the
line
pressure
is
applied
to
the
area
differ
ence
of
the
valve
the
valve
is
depres
sed
upward
the
space
from
the
circuit
Page 15 of 513

4
to
the
circuit
17
is
timely
closed
and
with
the
space
from
the
circuit
17
to
the
upper
drain
being
about
to
open
the
back
up
pressure
17
which
is
lower
than
the
line
pressure
4
by
the
pressure
loss
due
to
the
space
from
the
circuit
4
to
the
circuit
17
is
balanced
with
the
spring
force
Further
when
speed
is
shifted
from
2nd
to
Low
at
the
range
I
line
pressure
is
led
from
the
circuit
12
and
the
line
pressure
is
applied
upward
to
the
bottom
of
the
valve
through
the
valve
hole
Consequently
the
valve
is
depressed
upward
and
locked
As
the
result
the
space
from
the
line
pressure
4
to
the
back
up
pressure
17
is
closed
completely
and
the
back
up
pressure
17
is
drained
upward
AT101
Fig
AT
16
Throttle
back
up
valve
Solenoid
downshift
valve
SDV
This
valve
is
a
transfer
valve
which
leads
the
line
pressure
7
to
13
and
transmits
the
same
to
the
FSV
and
SSV
when
a
kick
down
signal
is
re
ceived
from
the
downshift
solenoid
Usually
the
solenoid
push
rod
and
valve
are
locked
upward
by
the
spring
in
the
lower
end
and
circuit
from
the
line
pressure
4
to
the
line
pressure
13
is
opened
When
kick
down
is
performed
the
push
rod
operates
the
valve
is
depres
sed
downward
and
the
circuit
from
the
line
pressure
7
to
the
line
pres
sure
13
opens
The
line
pressure
13
opposes
the
governor
pressure
15
at
the
SSV
and
FSV
and
thus
performs
the
downshift
operation
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
AT102
Fig
AT
17
Solenoid
downshift
value
Second
lock
valve
SLV
This
valve
is
a
transfer
valve
which
assists
the
shift
valve
in
order
to
decide
the
fixed
2nd
speed
at
the
2
range
In
the
D
range
the
sum
of
the
spring
force
and
line
pressure
3
applied
upward
exceeds
the
line
pres
sure
2
which
is
applied
to
the
valve
area
difference
as
the
downward
force
As
the
result
the
valve
is
locked
upward
and
the
circuit
from
the
line
pressure
8
to
the
line
pressure
9
is
opened
Consequently
the
FSV
becomes
the
2nd
speed
condition
and
line
pressure
is
led
to
the
band
servo
engaging
circuit
9
only
when
the
line
pressure
1
is
released
to
the
line
pressure
8
In
the
2
range
the
upward
force
is
retained
only
on
the
spring
and
the
downward
line
pressure
2
exceeds
the
upward
force
As
the
result
the
valve
is
locked
downward
the
line
pressure
2
is
released
to
9
regardless
of
the
operat
ing
condition
of
the
FSV
and
the
band
servo
is
engaged
2nd
3rd
timing
valve
TMV
This
valve
is
a
transfer
valve
which
switches
the
by
pass
circuit
of
the
AT
ll
J
2
3
ATl03
Fig
A
T
18
Second
lock
ualue
orifice
22
in
the
front
clutch
pres
sure
circuit
II
in
response
to
the
vehicle
speed
and
the
throttle
con
dition
A
force
created
when
the
go
vernor
pressure
15
applies
to
the
bottom
of
the
TMV
is
used
for
the
upward
force
and
a
force
created
when
the
spring
force
and
the
throttle
pressure
apply
to
the
top
of
the
TMV
is
used
for
the
downward
force
When
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
lower
than
the
governor
pressure
15
the
upward
force
exceeds
the
down
ward
force
the
valve
is
locked
upward
and
passage
from
the
circuit
10
2nd
from
the
Top
to
the
circuit
II
is
closed
Consequently
the
line
pressure
10
is
led
to
the
front
clutch
circuit
1
I
through
the
orifice
22
and
thus
the
oil
pressure
is
trans
mitted
slowly
However
under
the
normal
shifting
the
throttle
pressure
16
has
a
pressure
exceeding
a
certain
level
and
the
downward
force
exceeds
the
upward
force
As
the
result
the
valve
is
locked
downward
the
passage
from
the
circuit
10
to
the
circuit
1
I
is
opened
and
the
orifice
22
is
disregarded
1
i
16
I
O
11
l1
1
r
X
lp
I
15
J
AT104
Fig
AT
19
2nd
3rd
timing
ualue
Page 38 of 513

Fig
A
T
49
Torque
converter
aligning
cut
3
When
connecting
torque
con
verter
to
transmission
measure
dis
tance
A
to
be
certain
that
they
are
correctly
assembled
See
Figure
AT
50
Distance
A
More
than
16
5
IllIll
0
650
in
A
AT117
Fig
A
T
50
Installing
torque
converter
CHASSIS
4
Bolt
converter
to
drive
plate
Tightening
torque
0
8
to
1
0
kg
Ill
5
8
to
7
2
ft
Ib
Note
Align
chalk
marks
painted
a
cross
both
parts
during
disas
sembling
processes
5
After
converter
is
installed
rotate
crankshaft
several
turns
and
check
to
be
sure
that
transmission
rotates
freely
without
binding
6
Pour
recommended
automatic
transmission
fluid
up
to
correct
level
through
oil
charge
pipe
7
Connect
manual
lever
to
shift
rod
Operation
should
be
carried
out
with
manual
and
selector
levers
in
N
8
Connect
inhibitor
switch
wires
Notes
a
Refer
to
covering
topic
under
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
on
page
AT
51
b
Inspect
and
adjust
switch
as
above
whenever
it
has
to
be
removed
for
service
9
Check
inhibitor
switch
for
op
eration
AT
34
Starter
should
be
brought
into
op
eration
only
when
selector
lever
is
in
P
and
N
positions
it
should
not
be
started
when
lever
is
in
D
2
1
and
R
positions
Back
up
lamp
should
also
light
when
selector
lever
is
placed
in
R
position
10
Check
level
of
oil
in
transmis
sion
For
detailed
procedure
see
page
AT
49
II
Move
selector
lever
through
all
positions
to
be
sure
that
transmission
operates
correctly
With
hand
brake
applied
rotate
engine
at
idling
Without
disturbing
the
above
setting
move
selector
lever
through
N
to
D
to
2
to
I
and
to
R
A
slight
shock
should
be
felt
by
hand
gripping
selector
each
time
transmission
is
shifted
Note
See
page
AT
50
for
checking
enigne
idling
12
Check
to
be
sure
that
line
pres
sure
is
correct
To
do
this
refer
to
relative
topic
under
Testing
line
pres
sure
on
page
AT
53
13
Perform
stall
test
as
per
the
instructions
on
page
AT
51
Page 40 of 513

Removal
and
installation
I
Disconnect
control
knob
from
hand
lever
by
removing
a
screw
Remove
console
box
Disconnect
shift
rod
from
cross
shaft
4
Remove
hand
lever
hand
lever
shaft
and
shift
rod
assembly
with
bracket
To
install
reverse
the
order
of
removal
CHASSIS
Adjustment
The
adjustment
of
linkage
is
as
important
as
Inspection
of
Oil
Level
for
the
automatic
transmission
Therefore
great
care
should
be
exercised
because
defective
adjustment
will
result
in
the
breakdown
of
the
transmission
Loosen
adjust
nuts
@
See
Figure
AT
51
2
Set
hand
lever
CD
and
selector
range
lever
@
at
N
position
See
Figure
AT
51
AT
36
3
Set
lower
shift
rod
@
to
trunnion
@
by
turning
in
or
out
adjust
nuts
See
Figure
AT
I
After
adjusting
make
sure
that
hand
lever
can
be
set
in
any
position
correctly
and
that
hand
lever
operates
properly
without
any
binding
If
levers
do
not
operate
satisfactori
ly
readjust
or
replace
parts
as
neces
sary
Page 53 of 513

AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSIO
N
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
ADJUSTMENT
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
BEFORE
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
Testing
instrument
for
inspection
Checking
oil
level
Inspection
and
repair
of
oil
leakage
Checking
engine
idling
rpm
Checking
and
adjusting
kick
down
switch
and
downshift
solenoid
Inspection
and
adjustment
of
manual
linkage
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
STALL
TEST
Stall
test
procedures
Judgement
As
the
troubles
on
the
automatic
transmission
can
be
mostly
repaired
by
doing
simple
adjustment
so
do
not
disassemble
immediately
if
the
auto
m
tic
transmission
is
in
trouble
Firstly
inspect
and
adjust
the
auto
matic
transmission
with
mounting
on
vehicle
by
observing
the
trouble
shooting
chart
If
the
trouble
could
not
be
solved
by
this
procedure
then
remove
and
disassemble
the
automatic
transmis
sion
It
is
advisable
to
check
overhaul
and
repair
each
point
in
the
order
itemized
in
the
trouble
shooting
chart
l
In
the
trouble
shooting
chart
the
diagnosis
items
are
arranged
in
the
order
from
easy
to
difficult
and
there
fore
please
follow
these
items
The
transmission
should
not
be
removed
unless
necessary
2
The
test
and
adjustment
for
trou
ble
diagnosis
should
be
made
on
the
basis
of
standard
values
and
the
data
should
be
recorded
ROAD
TEST
Car
speed
at
gear
shift
Checking
speed
changing
condition
Checking
items
during
speed
change
Shift
schedule
LINE
PRESSURE
TEST
Line
pressure
governor
feed
pressure
Judgement
in
measuring
line
pressure
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
CHART
Inspecting
items
Trouble
shooting
chart
for
3N71
B
Automatic
Transmission
Trouble
shooting
guide
for
3N718
Automatic
Transmission
CONTENTS
AT
49
AT
49
AT
49
AT
50
AT
50
AT
50
AT
51
AT
51
AT
51
AT51
AT
52
INSPECTION
AND
AD
JUSTMENT
BEFORE
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
Testing
instrument
for
inspection
1
Engine
tachometer
2
Vacuum
gauge
3
Oil
pressure
gauge
It
is
convenient
to
install
these
instruments
in
a
way
that
allows
meas
urements
to
be
made
from
the
driver
s
seat
Checking
oil
level
In
checking
the
automatic
transmis
sion
the
oil
level
and
the
condition
of
oil
around
the
oil
level
gauge
should
be
examined
every
5
000
km
3
000
miles
These
steps
are
easy
and
effec
live
in
trouble
shooting
as
some
change
of
oil
conditions
are
linked
with
developed
troubles
in
many
cases
AT
49
AT
52
AT
52
AT
53
AT
53
AT
53
AT
53
AT
53
AT
54
AT
54
AT
54
AT
55
AT
5B
For
instance
Lack
of
oil
causes
defective
opera
tion
by
making
the
clutches
and
brakes
slip
developing
severe
wear
The
cause
of
this
operation
is
that
the
oil
pump
has
begun
to
suck
air
which
caused
oil
foaming
thus
rapidly
deteriora
ting
the
oil
quality
and
pro
ducing
sludge
and
varnish
Meanwhile
excessive
oil
is
also
bad
as
in
the
case
of
a
lack
of
oil
because
of
oil
foaming
by
being
stirred
up
by
the
gears
Moreover
in
high
speed
driving
with
excessive
oil
in
the
trans
mission
the
oil
often
blows
out
from
the
breather
I
Measuring
oil
level
When
checking
the
fluid
level
start
the
engine
and
run
it
until
normal
operating
temperatures
oil
tempera
ture
50
to
800e
122
to
176
F
Approximately
ten
minute
operation
will
elevate
the
temperature
to
this
range
and
enigne
idling
conditions
are
stabilized
Then
apply
the
brakes
and
move
the
transmission
shift
lever
Page 54 of 513

through
all
drive
positions
and
place
the
lever
in
park
P
position
In
this
inspection
the
car
must
be
placed
on
a
level
surface
The
amount
of
the
oil
varies
with
the
temperature
As
a
rule
the
oil
level
must
be
measured
after
its
tempera
ture
becomes
sufficiently
high
I
Fill
the
oil
to
the
line
H
The
difference
of
capacities
between
both
H
and
L
is
approximately
0
4
liter
7
8
U
S
pt
3
4
Imper
pt
and
therefore
take
care
not
to
fill
beyond
the
line
H
2
At
the
time
of
the
above
topping
up
and
changing
of
oil
care
should
be
taken
of
to
prevent
mixing
the
oil
with
dust
and
water
2
Inspecting
oil
condition
The
condition
of
oil
sticking
to
the
level
gauge
indicates
whether
to
over
haul
and
repair
the
transmission
or
look
for
the
defective
part
If
the
oil
has
deteriorated
into
a
varnish
like
quality
it
causes
the
con
trol
valve
to
stick
The
blackened
oil
gives
the
proof
of
the
burned
clutch
brake
band
etc
In
these
cases
the
transmission
must
be
replaced
Notes
a
In
oil
level
checking
use
special
paper
waste
to
handle
the
level
gauge
and
take
care
not
to
let
the
scraps
of
paper
and
cloth
tick
to
the
gauge
b
Insert
the
gauge
fully
and
take
it
out
quickly
before
splashing
oil
adheres
to
the
gauge
and
theu
observe
the
level
c
Use
automatic
transmission
fluid
having
DEXRON
iden
tIficatIon
only
in
the
3N71
B
automatic
transmission
d
Pay
atteutIon
because
the
oil
to
be
used
dIffers
from
that
i
used
in
the
Nissan
Full
Automatic
Transmission
3N7IA
Never
mix
the
oil
with
that
CHASSIS
Inspection
and
repair
of
oil
leakage
When
oil
leakage
takes
place
the
portion
near
the
leakage
is
covered
with
oil
presenting
difficulty
in
de
tecting
the
spot
Therefore
the
places
where
oil
seals
and
gaskets
are
equipped
are
enumerated
below
I
Converter
housing
The
rubber
ring
of
oil
pump
hous
ing
The
oil
eaI
of
oil
pump
housing
The
oil
seal
of
engine
crankshaft
The
bolts
of
converter
housing
to
case
2
Transmission
and
rear
extension
Junction
of
transmission
and
rear
extension
Oil
tube
connectors
Oil
pan
Oil
pressure
inspection
holes
Refer
to
Figure
AT
112
The
mounting
portion
of
vacuum
diaphragm
and
downshift
solenoid
Breather
and
oil
charging
pipe
Speedometer
pinion
sleeve
The
oil
seal
of
rear
extension
To
exactly
locate
the
place
of
oil
leakage
proceeds
as
follows
Place
the
vehicle
in
a
pit
and
by
sampling
the
leaked
oil
examine
whe
ther
it
is
the
torq
le
converter
oil
or
not
The
torque
converter
oil
assumes
color
like
red
wine
when
shipped
from
the
factory
so
it
is
ea
ily
distin
guished
from
engine
oil
or
gear
oil
Cleanly
wipe
off
the
leaking
oil
and
dust
and
detect
the
spot
of
oil
leakage
Use
nonflammable
organic
solvent
such
as
carbon
tetrachloride
for
wip
ing
Raise
the
oil
temperature
by
op
erating
the
engine
and
shift
the
lever
to
0
to
heighten
the
oil
pressure
The
spot
of
oil
leakage
will
then
be
found
more
easily
Note
A
the
oil
leakage
from
the
breather
does
not
take
place
except
when
running
at
high
speed
it
is
impossible
to
locate
the
spot
of
leakage
with
vehicle
stalled
AT
50
Checking
engine
idling
rprn
The
engine
idling
revolution
should
be
properly
adjusted
If
the
engine
revolution
is
too
low
the
engine
does
not
operate
smoothly
and
if
too
high
a
strong
shock
or
creep
develops
when
changing
over
from
N
to
D
or
R
Specified
idling
speed
650
rpm
at
D
position
800
rpm
at
N
position
Checking
and
adjusting
kick
down
switch
and
downshift
solenoid
When
the
kick
down
operation
is
not
made
properly
or
the
speed
chang
ing
point
is
too
high
check
the
kick
down
switch
downshift
solenoid
and
wiring
between
them
When
the
igni
tion
key
is
positioned
at
the
1st
stage
and
the
accelerator
pedal
is
depressed
deeply
the
switch
contact
should
be
closed
and
the
solenoid
should
click
If
it
does
not
click
it
indicates
a
defect
Then
check
each
part
with
the
testing
instruments
See
Figure
AT
I09
0
0
1
M
r
7
I
Y
ATl08
Fig
A
T
l
09
Downshift
solenoid
Note
Watch
for
oil
leakage
from
transmission
case