1973 DATSUN B110 check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 13 of 513

Low
in
the
range
I
is
led
to
the
low
and
reverse
clutch
from
the
line
pressure
5
through
the
line
pressure
12
and
at
the
same
time
the
same
is
led
to
the
left
end
spring
unit
Consequently
although
the
go
vernor
pressure
increases
the
valve
is
still
depressed
toward
the
right
and
the
SFV
is
fixed
in
the
Low
posi
tion
When
kicked
down
at
the
2nd
speed
the
SDV
operates
and
the
line
pressure
13
depresse
the
FSV
to
ward
the
right
Although
the
governor
pressure
15
is
considerably
high
the
valve
is
depressed
completely
toward
the
right
and
the
FSV
is
returned
to
the
Low
position
This
operation
is
called
Kick
down
shift
2nd
3rd
shift
valve
SSV
The
SSV
is
a
transfer
vaIve
which
shifts
speed
from
2nd
to
3rd
When
the
vehicle
is
stopped
the
SSV
is
depressed
toward
the
right
by
the
spring
and
is
in
the
2nd
position
It
is
provided
however
that
the
FSV
decides
the
shifting
either
to
Low
or
2nd
When
the
vehicle
is
running
the
governor
pressure
15
is
applied
to
the
right
end
surface
and
the
SSV
is
depressed
toward
the
left
Contrarily
the
spring
force
line
pressure
3
and
throttle
pressure
19
depress
the
SSV
toward
the
right
When
the
vehicle
speed
exceeds
a
certain
level
the
governor
pressure
exceeds
the
sum
of
the
spring
force
line
pressure
and
throttle
pressure
the
valve
is
depressed
toward
the
left
and
the
line
pressure
3
is
closed
Conse
quently
the
forces
are
rapidly
un
balanced
the
force
to
depress
the
SSV
toward
the
right
reduces
and
thus
the
SSV
is
depressed
to
the
Ie
ft
end
for
a
moment
With
the
SSV
depressed
to
ward
the
left
end
the
line
pressure
3
is
connected
with
the
line
pressure
10
the
band
servo
is
released
the
front
clutch
is
engaged
and
speed
is
shifted
to
3rd
When
the
accelerator
pedal
is
de
pressed
both
the
line
pressure
3
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
are
high
and
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
therefore
the
SSV
is
retained
in
2nd
unless
ihe
governor
pressure
IS
exceeds
the
line
pressure
3
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
In
the
3rd
position
force
to
depress
the
SSV
toward
the
right
is
remained
only
on
the
throttle
pressure
16
and
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
slightly
lower
than
that
toward
the
right
which
is
applied
while
shifting
from
2nd
to
3rd
Consequently
the
SSV
is
returned
to
the
2nd
position
at
a
slightly
low
speed
side
Shifting
from
3rd
to
2nd
occurs
at
a
speed
slightly
lower
than
that
for
2nd
to
3rd
shifting
When
kicked
down
at
the
3rd
line
pressure
13
is
led
from
the
SDV
and
the
SSV
is
depressed
toward
the
right
Although
the
governor
pressure
is
considerably
high
the
valve
is
de
pressed
completely
toward
the
right
and
thus
the
SSV
is
returned
to
2nd
position
This
operation
is
called
Kick
down
shift
When
the
shift
lever
is
shifted
to
2
or
I
range
at
the
3rd
speed
the
line
pressure
3
is
drained
at
the
MNV
Consequently
the
front
clutch
operating
and
band
servo
releasing
oils
are
drained
As
the
res
lIt
the
trans
mission
is
shifted
to
the
2nd
or
low
speed
although
the
SSV
is
in
the
3rd
position
When
the
speed
is
shifted
to
the
3rd
a
one
way
orifice
24
on
the
top
of
the
SSV
relieves
oil
transmitting
velocity
from
the
line
pressure
3
to
the
line
pressure
10
and
reduces
a
shock
generated
from
the
shifting
Contrarily
when
shifted
from
3rd
to
2
or
range
and
the
speed
is
shifted
to
the
2nd
spring
of
the
orifice
24
is
depressed
the
throttle
becomes
ineffective
the
line
pressure
10
is
drained
quickly
and
thus
delay
in
the
speed
shifting
is
elimi
nated
Throttle
of
the
line
pressure
6
relieves
the
oil
transmitting
velocity
from
the
line
pressure
6
to
the
line
pressure
10
when
the
lever
is
shifted
to
the
R
range
and
relieves
drain
velocity
from
the
line
pressure
10
to
the
line
pressure
6
when
shifting
from
3rd
to
2nd
at
the
D
range
Thus
the
throttle
of
the
line
pressure
6
reduces
a
shock
generated
from
the
shifting
A
plug
in
the
SSV
left
end
readjust
the
throttle
pressure
16
which
varie
depending
on
the
engine
throttle
con
dition
to
a
throttle
pressure
19
suited
to
the
speed
change
control
Moreover
the
plug
is
a
valve
which
applies
line
pressure
13
in
lieu
of
the
throttle
pressure
to
the
SSV
and
the
FSV
when
kick
down
is
performed
When
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
applied
to
the
left
side
of
this
plug
and
the
plug
is
depressed
toward
the
right
a
slight
space
is
made
from
the
throttle
pressure
16
to
19
A
throt
tIe
pressure
19
which
is
lower
by
the
pressure
loss
equivalent
to
this
space
is
generated
the
pressure
loss
is
added
to
the
spring
force
and
thus
the
plug
is
depressed
back
from
the
right
to
the
left
When
this
pressure
19
increases
excessively
the
plug
is
further
de
pressed
toward
the
left
space
from
the
throttle
pressure
19
to
the
drain
circuit
13
increases
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
lowers
Thus
the
plug
is
balanced
and
the
throttle
pressure
19
is
reduced
in
a
certain
value
b
3
Orifice
t
checking
valve
24
15
2
2
i
I
1
c
V
Y
ii
pr
W
jt1
iff
I
W
q
I
nHH
J
L19
H
10
15
AT
9
A
T098
Fig
AT
13
2nd
3rd
shiflvalue
Page 38 of 513

Fig
A
T
49
Torque
converter
aligning
cut
3
When
connecting
torque
con
verter
to
transmission
measure
dis
tance
A
to
be
certain
that
they
are
correctly
assembled
See
Figure
AT
50
Distance
A
More
than
16
5
IllIll
0
650
in
A
AT117
Fig
A
T
50
Installing
torque
converter
CHASSIS
4
Bolt
converter
to
drive
plate
Tightening
torque
0
8
to
1
0
kg
Ill
5
8
to
7
2
ft
Ib
Note
Align
chalk
marks
painted
a
cross
both
parts
during
disas
sembling
processes
5
After
converter
is
installed
rotate
crankshaft
several
turns
and
check
to
be
sure
that
transmission
rotates
freely
without
binding
6
Pour
recommended
automatic
transmission
fluid
up
to
correct
level
through
oil
charge
pipe
7
Connect
manual
lever
to
shift
rod
Operation
should
be
carried
out
with
manual
and
selector
levers
in
N
8
Connect
inhibitor
switch
wires
Notes
a
Refer
to
covering
topic
under
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
on
page
AT
51
b
Inspect
and
adjust
switch
as
above
whenever
it
has
to
be
removed
for
service
9
Check
inhibitor
switch
for
op
eration
AT
34
Starter
should
be
brought
into
op
eration
only
when
selector
lever
is
in
P
and
N
positions
it
should
not
be
started
when
lever
is
in
D
2
1
and
R
positions
Back
up
lamp
should
also
light
when
selector
lever
is
placed
in
R
position
10
Check
level
of
oil
in
transmis
sion
For
detailed
procedure
see
page
AT
49
II
Move
selector
lever
through
all
positions
to
be
sure
that
transmission
operates
correctly
With
hand
brake
applied
rotate
engine
at
idling
Without
disturbing
the
above
setting
move
selector
lever
through
N
to
D
to
2
to
I
and
to
R
A
slight
shock
should
be
felt
by
hand
gripping
selector
each
time
transmission
is
shifted
Note
See
page
AT
50
for
checking
enigne
idling
12
Check
to
be
sure
that
line
pres
sure
is
correct
To
do
this
refer
to
relative
topic
under
Testing
line
pres
sure
on
page
AT
53
13
Perform
stall
test
as
per
the
instructions
on
page
AT
51
Page 55 of 513

c
Inspection
and
adJu
Stmenf
trouble
first
check
the
linhge
f
no
1
i
jI
fect
is
found
in
the
lin1
age
check
of
manu
a
l
liiiJ
i
the
inhibitor
switch
Th
d
1F
aI
S
t
th
I
I
f
e
a
JU
i
J
u
epara
e
e
range
se
eet
ever
rom
Iy
important
ii
s3
ns
etion
of
oil
the
lower
shift
rod
and
turn
the
range
1
level
for
the
automatiC
tran
smission
select
lever
to
N
Therefore
great
care
should
be
exer
Note
In
the
position
N
the
slot
of
cised
because
defective
adjustment
will
the
manual
shaft
is
vertical
result
in
the
breakdown
of
the
trans
By
the
use
of
the
tester
check
the
two
bIack
yellow
BY
wires
from
the
inhibitor
switch
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
and
the
two
red
bIack
RB
wires
in
the
range
R
for
continuity
Turn
range
select
lever
to
both
directions
from
each
lever
set
position
and
check
each
continuity
range
It
is
normal
if
the
electricity
is
on
while
the
lever
is
within
an
angle
of
about
3
0
on
both
sides
from
each
lever
set
line
How
ever
if
its
continuity
range
is
obvi
ously
unequal
on
both
sides
the
adjustment
is
required
f
any
malfunction
is
found
un
screw
the
fastening
nut
of
the
range
selector
lever
and
two
fastening
bolts
of
the
switch
body
and
then
remove
the
machine
screw
under
the
switch
body
Adjust
the
manual
shaft
correct
ly
to
the
position
N
by
means
of
the
selector
lever
When
the
slot
of
the
shaft
becomes
vertical
the
detent
works
to
position
the
shaft
correctly
with
a
click
sound
Move
the
switch
slightly
aside
so
that
the
screw
hole
will
be
aligned
with
the
pin
hole
of
the
internal
rotor
combined
with
the
manual
shaft
and
check
their
alignment
by
inserting
a
1
5
0101
0
0591
in
diameter
pin
into
the
holes
If
the
alignment
is
made
correct
1
5ten
the
switch
body
with
the
bolts
pull
out
the
pin
and
tighten
up
the
screw
again
into
the
hole
and
fasten
the
selector
lever
as
before
Check
over
again
the
continuity
with
the
tester
If
the
malfunction
still
remains
replace
the
inhibitor
switch
mission
Inspection
Pull
the
selector
lever
toward
you
and
turn
it
so
far
as
p
to
1
range
where
clicks
will
be
felt
by
hand
This
is
the
detent
of
manual
valve
in
the
body
and
indicates
the
correct
posi
tion
of
the
lever
Inspect
whether
the
pointer
of
selector
dial
corresponds
to
this
point
and
also
whether
the
lever
comes
in
alignment
with
the
stepping
of
posi
tion
plate
when
it
is
released
Adjustment
This
procedure
can
be
accom
plished
by
referring
to
Removal
and
nstallation
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
The
inhibitor
switch
serves
to
light
the
reverse
lamp
in
the
range
R
of
the
transmission
operation
and
also
to
rotate
the
starter
motor
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
j
r@
I
If
r
f
B
@
I
Jt
@
@
c
v@
i
r
fji
AT109
1
Inhibitor
switch
2
Manual
shaft
3
Washer
4
Nut
5
Manual
plate
Fig
AT
II
0
Con
truction
of
inhibitor
witch
6
Washer
7
Nut
8
Inhibitor
switch
9
Range
select
lever
Check
whether
the
reverse
lamp
and
the
starter
motor
operate
normal
ly
in
these
ranges
If
there
is
any
t
ki
A
mm
ATIC
TRANSMISSION
STALL
TEST
The
purpose
of
this
test
is
to
check
the
transmission
and
engine
for
trou
ble
by
measuring
the
maximwn
num
bers
of
revolutions
of
the
engine
while
vehicle
is
held
in
a
stalled
condition
and
the
carburetor
is
in
full
throttle
operation
with
the
selector
lever
in
AT
51
rang
s
D
2
and
I
respectively
and
by
com
pairing
the
measured
re
sults
with
the
standard
values
Standard
stall
revolution
1
750
to
2
000
rpm
Components
to
be
tested
and
test
items
1
Clutches
brake
and
band
in
trans
mission
for
slipping
2
Torque
converter
for
function
3
Engine
for
overall
property
Stall
test
procedures
Before
testing
check
the
enigne
oil
and
torque
converter
oil
warm
up
the
engine
cooling
water
to
the
suitable
temperature
by
warming
up
ope
ration
at
1
200
rpm
with
the
selector
lever
in
the
range
P
for
several
minutes
and
warm
up
the
torque
converter
oil
to
the
suitable
temperature
60
to
IOOoC
140
to
2120F
1
Mount
the
engine
tachometer
at
a
location
that
allows
good
visibility
from
the
driver
s
seat
and
put
a
mark
on
specified
revolutions
on
the
meter
2
Secure
the
front
and
rear
wheels
completely
with
chocks
and
apply
the
hand
brake
Be
sure
to
depress
the
brake
pedal
firmly
with
the
left
foot
before
depressing
down
the
accelerator
pedal
3
Throw
the
selector
lever
into
the
range
D
4
Slowly
depress
the
accelerator
pedal
down
till
the
throttle
valve
is
fully
opened
Quickly
read
and
record
the
engine
revolution
when
the
engine
begins
to
rotate
steadily
and
then
release
the
accelerator
pedal
5
Turn
the
selector
lever
into
N
and
operate
the
enigne
at
approxi
mately
1
200
rpm
for
more
than
one
minute
to
cool
down
the
torque
con
verter
oil
and
coolant
6
Make
similar
stall
tests
in
the
ranges
2
I
and
R
Note
The
stall
test
operation
as
spec
ified
in
the
item
4
should
be
made
within
five
seconds
If
it
takes
too
long
the
oil
deterio
rates
and
the
clutches
brake
Page 131 of 513

Tightening
torque
3
way
connector
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lh
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lh
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lb
0
7
to
0
9
kg
m
5
1
to
6
5
ft
1b
Master
cylinder
Brake
hose
Air
bleeder
5
Fill
the
master
cylinder
brake
fluid
reservoir
with
brake
fluid
and
perform
air
bleeding
complele1y
Note
a
Do
not
use
brake
fluid
other
than
specified
b
The
specified
brake
fluid
is
used
for
both
single
and
tandem
type
master
cylinders
6
Upon
completion
of
air
bleeding
make
sure
that
the
brake
operates
correctly
and
check
the
brake
tube
and
hose
connectors
for
fluid
leaking
Fully
depress
the
brake
pedal
continue
to
depress
the
brake
pedal
for
several
seconds
and
make
sure
that
no
brake
fluid
leaks
from
any
part
of
the
brake
line
Replace
defective
part
if
required
Brake
line
pressure
differential
warning
light
switch
A
warning
light
is
located
on
the
instrument
panel
to
warn
the
driver
when
a
pressure
difference
of
13
to
17
kg
cm2
185
to
2421bJsq
in
exists
between
the
front
and
rear
b
rake
systems
A
hydraulically
actuated
warning
light
switch
is
located
in
the
engine
compartment
Both
front
and
rear
brake
systems
are
connected
to
this
switch
assembly
When
a
pressure
difference
of
13
to
17
kgJcm2
185
to
242
lbJsq
in
occurs
between
the
front
and
rear
brake
systems
the
valves
will
shuttle
toward
the
side
with
the
low
pressure
The
valve
contacts
with
the
switch
terminal
BRAKE
the
ground
circuit
for
the
warning
light
is
completed
and
thus
the
warning
light
lights
In
this
case
correct
the
hydraulic
brake
problem
and
bleed
the
brakes
Check
the
warning
light
switch
assembly
for
a
proper
operation
Check
the
switch
assembly
for
fluid
leakage
Note
Do
not
attempt
to
repair
switch
for
any
reason
replace
switch
assembly
completely
1
To
front
brake
L
H
2
From
master
cylinder
F
3
From
master
cylinder
R
4
To
rear
brake
L
B
R
M
5
To
front
brake
R
H
Fig
BR
12
Warning
light
switch
r
I
@
I
I
3
I
Valve
assembly
4
Piston
load
spring
Wire
terminal
Brake
tube
Fig
BR
13
Sectional
view
of
warning
light
switch
BR
7
Page 225 of 513
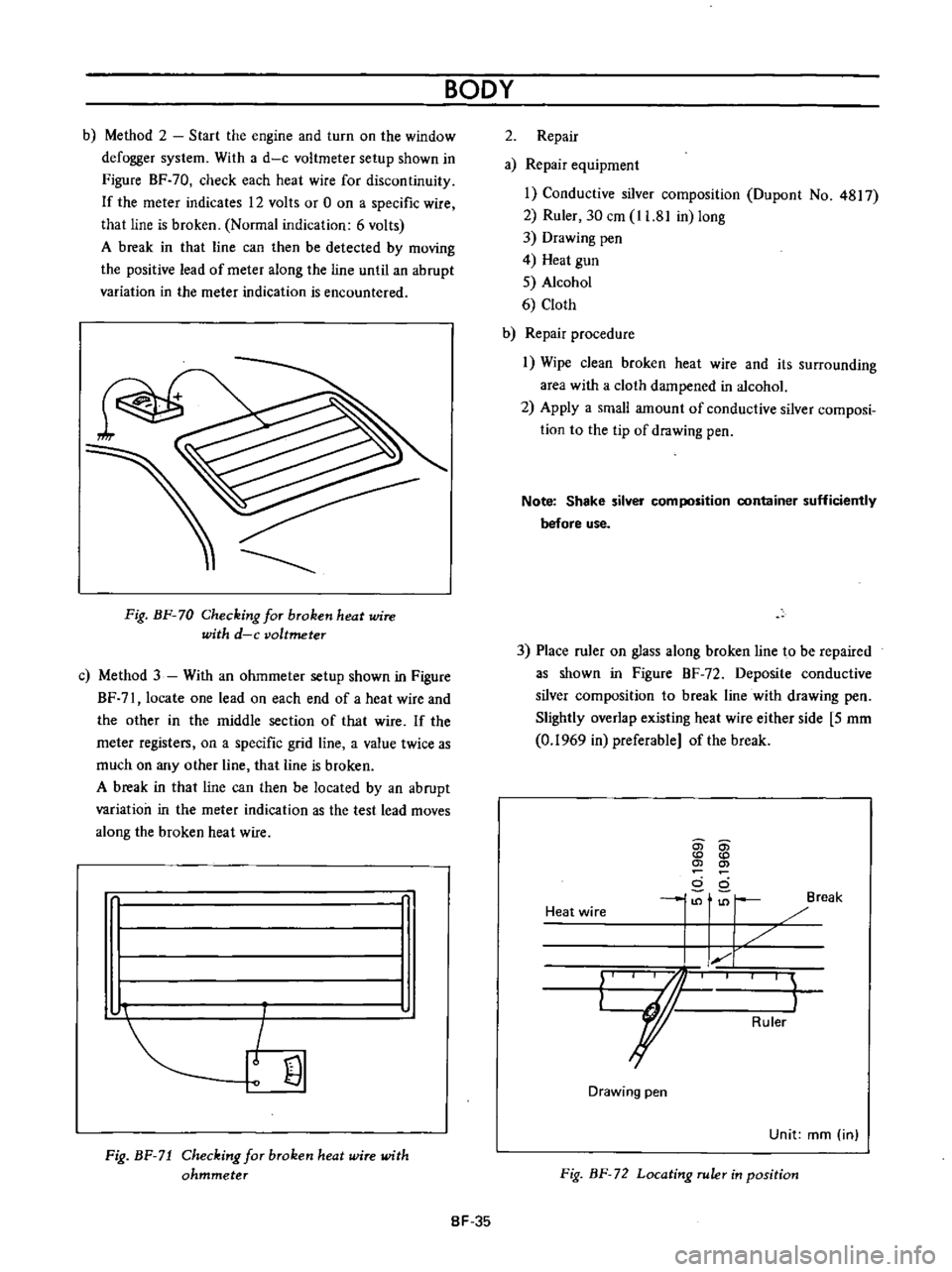
BODY
b
Method
2
Start
the
engine
and
turn
on
the
window
defogger
system
With
a
d
c
voltmeter
setup
shown
in
Figure
BF
70
check
each
heat
wire
for
discontinuity
If
the
meter
indicates
12
volts
or
0
on
a
specific
wire
that
line
is
broken
Normal
indication
6
volts
A
break
in
that
line
can
then
be
detected
by
moving
the
positive
lead
of
meter
along
the
line
until
an
abrupt
variation
in
the
meter
indication
is
encountered
Fig
BF
70
Checking
for
broken
heat
wire
with
d
c
voltmeter
c
Method
3
With
an
ohmmeter
setup
shown
in
Figure
BF
7l
locate
one
lead
on
each
end
of
a
heat
wire
and
the
other
in
the
rniddle
section
of
that
wire
If
the
meter
registers
on
a
specific
grid
line
a
value
twice
as
much
on
any
other
line
that
line
is
broken
A
break
in
that
line
can
then
be
located
by
an
abrupt
variation
in
the
meter
indication
as
the
test
lead
moves
along
the
broken
heat
wire
r
I
I
I
J
I
I
v
Ejl
Fig
BF
71
Checking
for
broken
heat
wire
with
ohmmeter
2
Repair
a
Repair
equipment
1
Conductive
silver
composition
Dupont
No
4817
2
Ruler
30
em
11
81
in
long
3
Drawing
pen
4
Heat
gun
5
Alcohol
6
Cloth
b
Repair
procedure
1
Wipe
clean
broken
heat
wire
and
its
surrounding
area
with
a
cloth
dampened
in
alcohol
2
Apply
a
small
amount
of
conductive
silver
composi
tion
to
the
tip
of
drawing
pen
Note
Shake
silver
composition
container
sufficiently
before
use
3
Place
ruler
on
glass
along
broken
line
to
be
repaired
as
shown
in
Figure
BF
72
Deposite
conductive
silver
composition
to
break
line
with
drawing
pen
Slightly
overlap
existing
heat
wire
either
side
5
mm
0
1969
in
preferable
of
the
break
Heat
wire
0
en
0
0
d
ci
1
I
Break
I
1
I
kr
I
I
Ruler
Drawing
pen
Unit
mm
in
Fig
BF
72
Locating
ruler
in
position
8F
35
Page 248 of 513
BODY
ELECTRICAL
Main
high
beam
Defective
dimmer
switch
cannot
be
switch
ed
to
dimmer
low
beam
or
vice
versa
Head
lamps
dim
Defective
light
circuit
Head
lamps
dim
Partly
discharged
battery
when
the
engine
is
stopped
or
op
era
ted
under
idling
speed
Defective
battery
Head
lamps
still
Faulty
sealed
beam
unit
dim
with
engine
run
above
idling
speed
Faulty
charging
system
Head
light
in
only
one
side
lights
Faulty
head
lamp
terrnianl
con
tact
Defective
lamp
Turn
signal
lamps
Probable
Condition
cause
All
turn
signal
Blown
fuse
or
faulty
contact
lamps
do
not
light
When
red
yellow
cable
is
con
nected
to
red
white
cable
or
red
black
cable
and
the
main
beam
or
dimmer
beam
lights
the
circuit
is
nonnal
The
dimmer
switch
is
defective
Check
the
head
light
circuit
for
cable
being
about
to
break
and
faulty
contact
or
check
fuse
for
faulty
contact
Measure
specific
gravity
of
elec
trolyte
Voltage
between
head
lamp
red
white
cable
and
red
cable
ter
minals
is
12
8V
or
higher
Voltage
is
less
than
12
8V
through
above
test
Method
of
inspection
Check
the
fuse
for
fusing
and
faulty
contact
BE
13
Conduct
continuity
test
and
if
the
dirn
mer
switch
is
defec
tive
replace
Repair
or
replace
if
required
Charge
battery
if
required
Replace
battery
Replace
sealed
beam
units
Check
the
generator
regulator
and
light
circuit
Repair
as
required
Replace
lamp
Corrective
action
When
the
fuse
is
fused
detect
and
repair
the
cause
and
replace
the
fuse
Page 260 of 513

BODY
ELECTRICAL
Improper
cable
contact
Oil
pressure
and
ignition
warning
lamps
Condition
Oil
pressure
Want
ing
lamp
The
lamp
does
not
ligh
t
when
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
Probable
cause
Blown
off
fuse
or
faulty
contact
Broken
lamp
bulb
fIlarnent
or
faulty
cable
contact
Defective
oil
pressure
switch
The
lamp
does
not
Oil
pressure
is
too
low
go
out
while
the
engine
is
being
operated
Lack
of
engine
oil
Defective
oil
pressure
switch
Ignition
warning
lamp
The
lamp
does
not
light
when
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
Blown
off
fuse
or
faulty
contact
Burnt
out
light
bulb
filarnent
or
faulty
cable
contact
The
fuel
rneter
indicates
a
level
slightly
lower
than
the
actual
level
Method
of
inspection
Check
the
fuse
for
fusing
and
faulty
contact
The
warning
lamp
does
not
light
when
oil
pressure
switch
yellow
black
cable
is
grounded
The
warning
lamp
lights
through
the
above
inspection
Inspect
the
engine
oil
pressure
system
Check
oil
level
Continuity
exists
on
the
oil
pres
sure
switch
when
the
engine
is
being
operated
Check
the
fuse
for
fusing
and
faulty
contact
The
pilot
lamp
does
not
light
when
the
voltage
regulator
con
nector
is
disconnected
the
white
red
cable
is
grounded
and
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
BE
25
Check
the
cable
from
the
fuel
meter
to
the
tank
unit
for
cable
being
about
to
break
poor
contact
and
faulty
grounding
and
repair
as
required
Corrective
action
Replace
after
corree
ting
the
fuse
the
cause
if
fused
Check
the
light
bulb
for
burnt
out
fIla
ment
and
replace
as
required
Replace
the
oil
pres
sure
switch
Add
oil
Replace
the
oil
pres
sure
switch
Repair
or
replace
as
required
Check
the
bulb
for
burnt
out
fIlament
and
replace
as
re
quired
Page 308 of 513
EMISSION
CONTROL
AND
TUNE
UP
Capacity
Maximum
3
3
L
X
US
gal
y
Imp
gal
2
3
L
US
gal
f
Imp
gal
Minimum
Make
sure
that
engine
oil
is
not
deteriorated
with
cooling
water
or
gasoline
Drain
and
refill
the
oil
if
necessary
Notes
a
A
milky
oil
indicates
the
presence
of
cooling
water
Find
the
cause
for
necessary
corrective
action
b
Oil
with
extremely
low
viscosity
indicates
dilution
with
gasoline
2
Check
oil
level
If
found
below
L
mark
refill
to
H
mark
on
gauge
Fig
ET
3
Checking
engine
oil
level
Replacing
oil
filter
The
oil
ftIter
is
of
a
cartridge
type
The
oil
filter
can
be
removed
using
oil
ftIter
wrench
STl9320000
Check
for
oil
leaks
through
gasketed
flange
If
any
leakage
is
found
retighten
slightly
If
necessary
replace
filter
as
an
assembly
2
When
installing
an
oil
filter
tighten
by
hand
Note
Do
not
overtighten
oil
filter
or
oil
leakage
way
result
Changing
engine
coolant
L
L
C
Nissan
long
life
coolant
LLC
is
an
ethylene
glycol
base
product
containing
chemical
inhibitors
to
protect
the
cooling
system
from
rusting
and
corrosion
The
L
L
C
does
not
contain
any
glycerine
ethyl
or
methyl
alcohol
It
will
not
evaporate
or
boil
away
and
can
be
used
with
either
high
or
low
temperature
thermostat
It
flows
freely
transfers
heat
efficiently
and
will
not
clog
the
passages
in
the
cooling
system
The
LL
C
must
not
be
mixed
with
other
products
This
coolant
can
be
used
throughout
tlie
seasons
of
the
year
Whenever
any
coolant
is
changed
the
cooling
system
should
be
flushed
and
refilled
with
a
new
coolant
Check
the
level
J
Percent
Boiling
point
0
9
kgfcm2
Freeze
concen
tration
Sea
level
cooling
sys
protection
tern
pressure
30
1060
C
I
240C
15OC
221OF
255OF
5OF
50
IUY
C
1270C
35
C
2280
F
2610F
3IOF
DC
OF
0
321
10
14
20141
50
58
I
I
I
I
1
I
I
1
30
1
22
40
401
40
10
30
50
20
EGOOl
Fig
ET
4
Protection
concentration
ET
3