2010 JAGUAR XFR Engine
[x] Cancel search: EnginePage 1317 of 3039
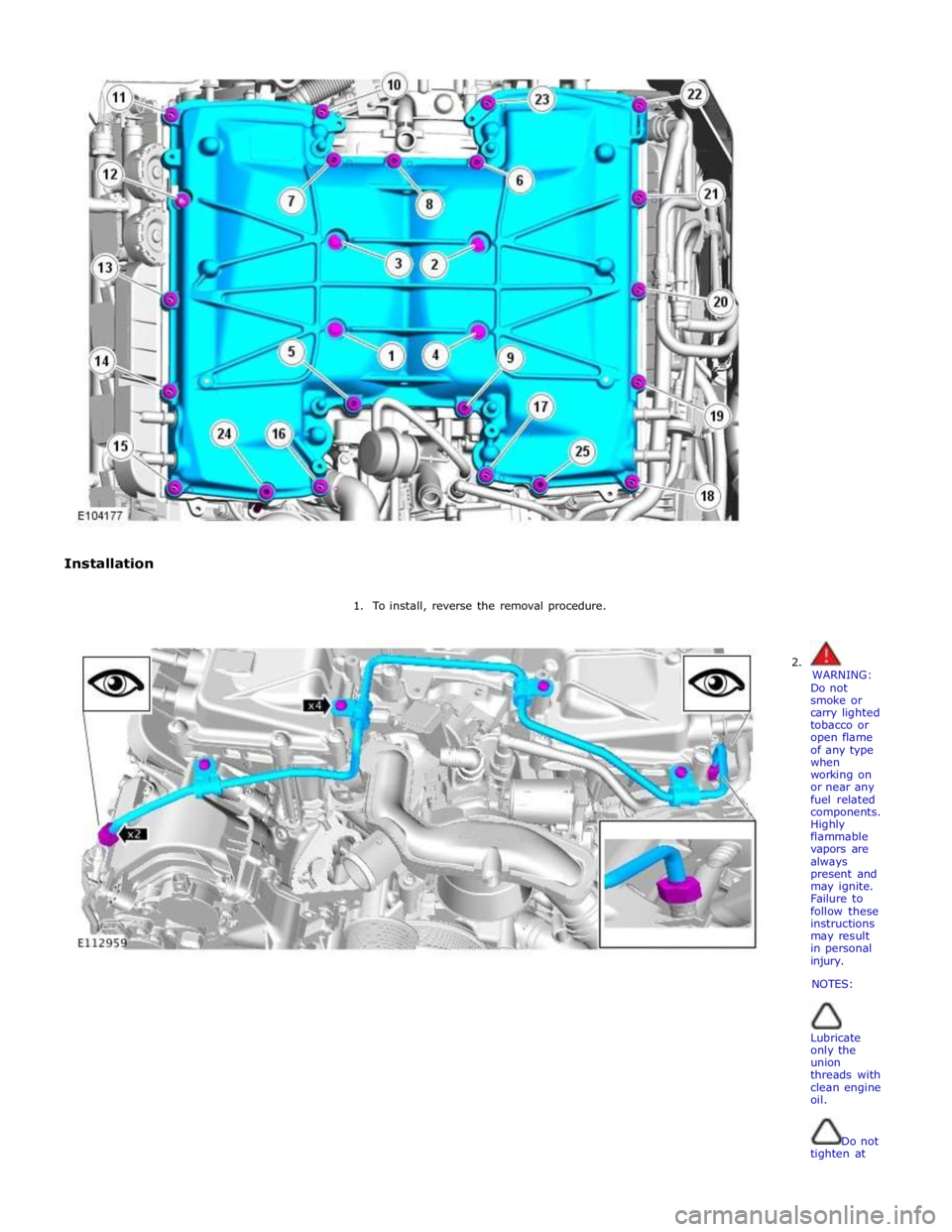
Installation
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2.
WARNING:
Do not
smoke or
carry lighted
tobacco or
open flame
of any type
when
working on
or near any
fuel related
components.
Highly
flammable
vapors are
always
present and
may ignite.
Failure to
follow these
instructions
may result
in personal
injury.
NOTES:
Lubricate
only the
union
threads with
clean engine
oil.
Do not
tighten at
Page 1319 of 3039

Published: 30-Jan-2014
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Supercharger
Removal and Installation
Special Tool(s)
303-1449-01
Supercharger Installation Guide Pins - Threaded
303-1449-02
Supercharger Installation Guide Pins - Unthreaded Removal
CAUTION: If a new cylinder head has been installed, then new taptite bolts must be used to install the supercharger.
NOTES:
New taptite bolts when used cut their own threads on the first application.
Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
2. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Charge Air Cooler (303-12D Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
4. Refer to: Throttle Body (303-04E Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
5. Refer to: Supercharger Belt (303-05 Accessory Drive - 5.0L, Removal and
Installation).
6. Refer to: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
Page 1326 of 3039
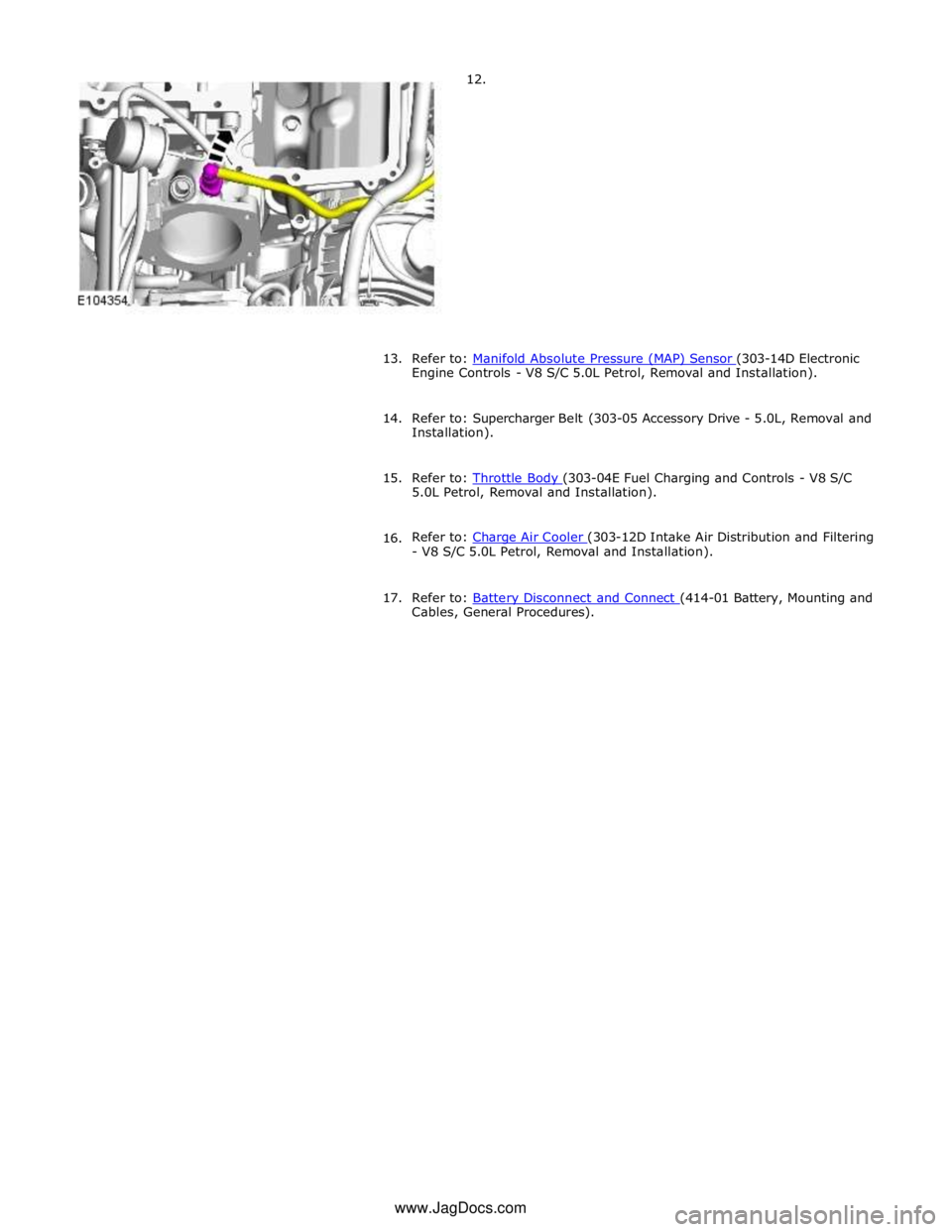
Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
14. Refer to: Supercharger Belt (303-05 Accessory Drive - 5.0L, Removal and
Installation).
15. Refer to: Throttle Body (303-04E Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
16. Refer to: Charge Air Cooler (303-12D Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
17. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures). www.JagDocs.com
Page 1343 of 3039

vehicles, a DMTL pump and filter. The vapor pipes are connected to the system components using quick release connectors.
Fuel vapor is generated by the fuel in the tank and the amount of vapor produced increases as the fuel heats up. Fuel vapor
can flow freely to the EVAP canister via the tank venting system. On NAS vehicles the vapor generated in the fuel tank during refueling flows without restriction to the EVAP canister.
On all vehicles except NAS, the vapor is restricted in its path to the EVAP canister, but can flow freely during the refueling operation to atmosphere via the fuel filler pipe opening.
The vapor passes into the EVAP canister where it is absorbed and stored by the charcoal. Because there is a limit to the amount of vapor the canister can contain, the fuel vapor is purged from the canister when the engine is running and burned in
the engine.
Page 1344 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Evaporative Emissions - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Evaporative Emissions - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
System Operation DIAGNOSTIC MODULE - TANK LEAKAGE PUMP (NAS ONLY)
To check the fuel tank and the EVAP (evaporative emission) system for leaks, the ECM (engine control module) operates the
DMTL pump and monitors the current draw. Initially, the ECM establishes a reference current by pumping air through the reference orifice and back to atmosphere. Once the reference current is determined, the ECM closes the change-over valve, which seals the EVAP system. The EVAP canister purge valve remains de-energized and is therefore closed. The output from the air pump is diverted from the reference orifice and into the EVAP system.
When the change-over valve is closed, the load on the air pump falls to zero. Providing there are no leaks, the air pump will
begin to pressurize the EVAP system and the load and current draw in the pump increases. By monitoring the rate and level of the current increase, the ECM can determine if there is a leak in the EVAP system.
During normal vehicle operation, 15 seconds after the engine has started, the ECM energizes the heating element in the pump to prevent condensation formation and possible incorrect readings. The heater remains energized until either the engine and
ignition are off (if no DMTL test is running) or until after the DMTL test is completed.
Leaks are classified as:
Minor - equivalent to a hole diameter of 0.5 to 1.0 mm (0.02 to 0.04 in.).
Major - equivalent to a hole diameter of 1.0 mm (0.04 in.) or greater.
The ECM performs a check for major leaks each time the ignition is switched off, providing the following conditions are met: The vehicle speed is zero.
The engine speed is zero.
The atmospheric pressure is above 70 kPa (10.15 lbf/in2
), i.e. the altitude is less than approximately 3047 m (10000
feet).
The ambient temperature is between 0 and 40 °C (32 and 104 °F).
The EVAP canister vapor concentration factor is 5 or less (where 0 is no fuel vapor, 1 is stoichiometric fuel vapor and greater than 1 is rich fuel vapor).
The fuel tank level is valid and between 15 and 85% of nominal capacity.
The engine running time during the previous cycle was more than 10 minutes.
The battery voltage is between 10 and 15 volts.
The last engine off time was more than 180 minutes.
No errors are detected with the EVAP components, the ambient air temperature and the fuel level.
NOTE: A leak test can be performed using a Jaguar recognized diagnostic tool. This overrides the above conditions and is
useful for checking correct system and component operation.
The ECM performs a check for minor leaks after every 2nd major leak check.
When the leak check is complete, the ECM stops the DMTL pump and opens (de-energizes) the change-over valve.
If the fuel filler cap is opened or refueling is detected during the leak check, by a sudden drop in the current draw or a rise in
the fuel level, the ECM aborts the leak check.
If a leak is detected during the check, the ECM stores an appropriate fault code in its memory. If a leak is detected on two consecutive checks, the ECM illuminates the MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) in the instrument cluster on the next drive cycle. The duration of a leak check can be between 60 and 900 seconds depending on the results and fuel tank level.
EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVE
The ECM waits until the engine is running above 55 °C (131 °F) coolant temperature with closed loop fuel operational before the purging process is activated. Under these conditions the engine should be running smoothly with no warm up enrichment.
The EVAP canister purge valve duty (and flow) is initially ramped slowly because the vapor concentration is unknown (a sudden increase in purge could cause unstable engine running or cause it to stall due to an extremely "rich" air/fuel mixture). The
concentration is then determined from the amount of adjustment that the closed loop fueling is required to make to achieve
the target AFR (air fuel ratio). Once the concentration has been determined, the purge flow can be increased rapidly and the
injected fuel can be pro-actively adjusted to compensate for the known purge vapor and the target AIR control is maintained.
When the purging process is active, fresh air is drawn into the EVAP canister via the DMTL filter and pump on NAS vehicles, or via the vent port on the EVAP canister of non NAS vehicles.
Page 1345 of 3039
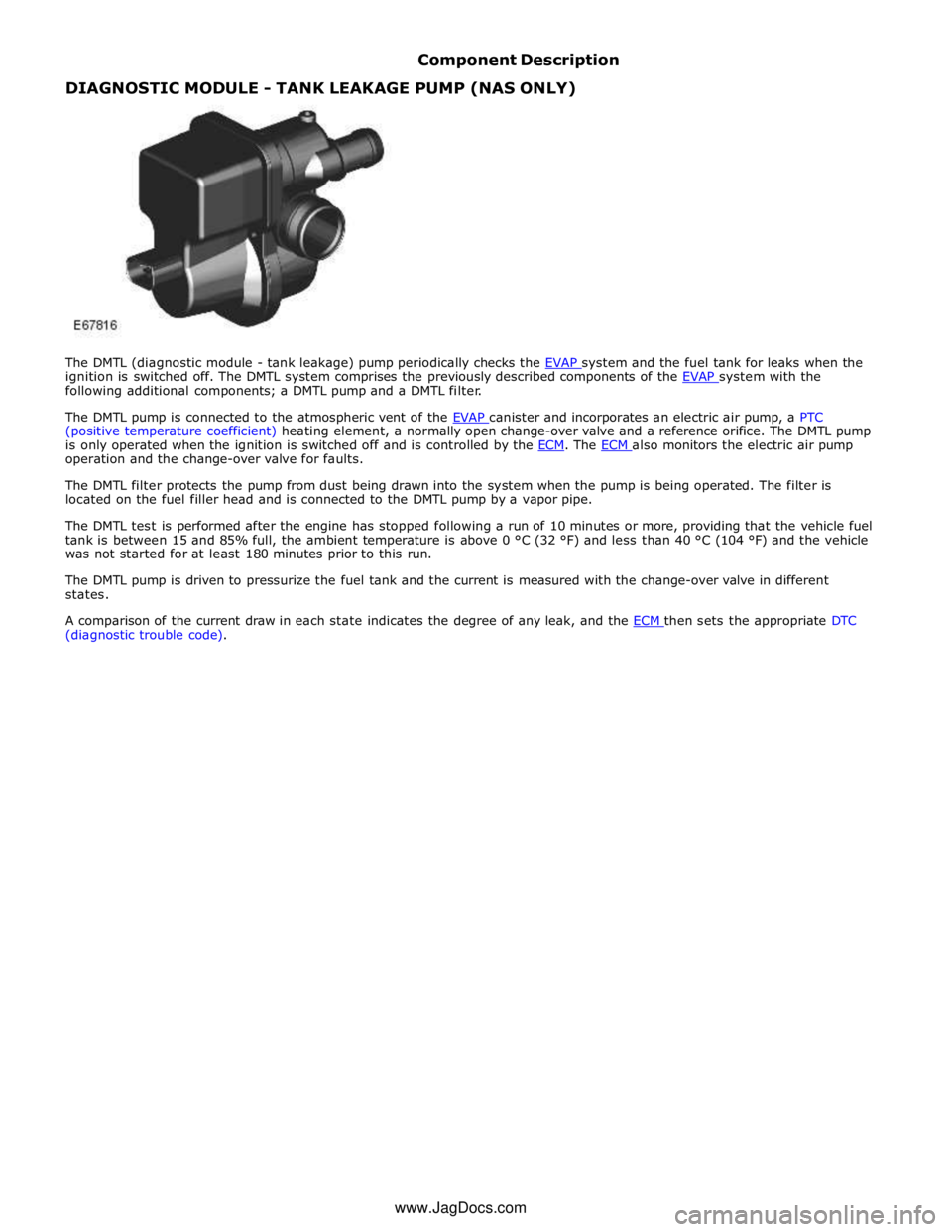
Component Description DIAGNOSTIC MODULE - TANK LEAKAGE PUMP (NAS ONLY)
The DMTL (diagnostic module - tank leakage) pump periodically checks the EVAP system and the fuel tank for leaks when the ignition is switched off. The DMTL system comprises the previously described components of the EVAP system with the following additional components; a DMTL pump and a DMTL filter.
The DMTL pump is connected to the atmospheric vent of the EVAP canister and incorporates an electric air pump, a PTC (positive temperature coefficient) heating element, a normally open change-over valve and a reference orifice. The DMTL pump
is only operated when the ignition is switched off and is controlled by the ECM. The ECM also monitors the electric air pump operation and the change-over valve for faults.
The DMTL filter protects the pump from dust being drawn into the system when the pump is being operated. The filter is
located on the fuel filler head and is connected to the DMTL pump by a vapor pipe.
The DMTL test is performed after the engine has stopped following a run of 10 minutes or more, providing that the vehicle fuel
tank is between 15 and 85% full, the ambient temperature is above 0 °C (32 °F) and less than 40 °C (104 °F) and the vehicle
was not started for at least 180 minutes prior to this run.
The DMTL pump is driven to pressurize the fuel tank and the current is measured with the change-over valve in different
states.
A comparison of the current draw in each state indicates the degree of any leak, and the ECM then sets the appropriate DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1348 of 3039
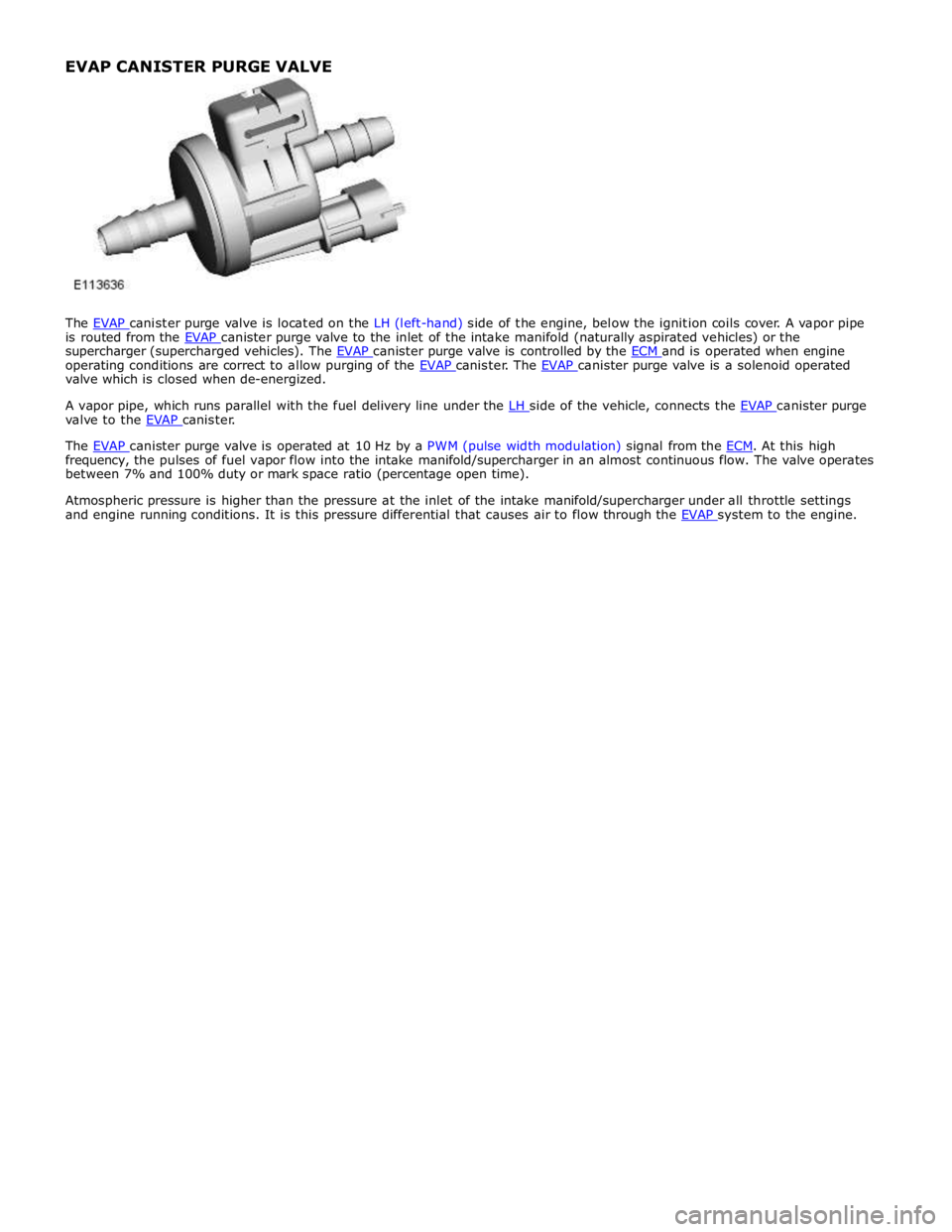
is routed from the EVAP canister purge valve to the inlet of the intake manifold (naturally aspirated vehicles) or the supercharger (supercharged vehicles). The EVAP canister purge valve is controlled by the ECM and is operated when engine operating conditions are correct to allow purging of the EVAP canister. The EVAP canister purge valve is a solenoid operated valve which is closed when de-energized.
A vapor pipe, which runs parallel with the fuel delivery line under the LH side of the vehicle, connects the EVAP canister purge valve to the EVAP canister.
The EVAP canister purge valve is operated at 10 Hz by a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM. At this high frequency, the pulses of fuel vapor flow into the intake manifold/supercharger in an almost continuous flow. The valve operates
between 7% and 100% duty or mark space ratio (percentage open time).
Atmospheric pressure is higher than the pressure at the inlet of the intake manifold/supercharger under all throttle settings
and engine running conditions. It is this pressure differential that causes air to flow through the EVAP system to the engine. EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVE
Page 1349 of 3039

Published: 03-Jun-2014
Evaporative Emissions - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Evaporative
Emissions
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the Evaporative Emissions system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
workshop manual.
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Fuel filler cap and seal
Fuel filler neck
Fuel pipes
Fuel tank
Evaporative emissions canister
Purge valve
Fuses
Wiring harnesses and connectors
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Purge valve
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index
5. Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Difficulty in filling
fuel tank
Restriction in the vapour line between the fuel tank and the
carbon canister outlet/atmospheric port
Check for
restrictions/damage Fuel smell
System leak
Purge valve inoperative
Check for leaks
Check the purge valve
operation DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.