2010 JAGUAR XFR height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 302 of 3039

and drive half shaft failure, which could cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. Failure to follow these
instructions may result in personal injury.
CAUTION: The suspension should not be allowed to hang free. When the CV joint is run at a very high angle, extra
vibration as well as damage to the seals and joints can occur.
The rear suspension lower arm should be supported as far outboard as possible. To bring the vehicle to its correct ride height,
the full weight of the vehicle should be supported in the rear by floor jacks. REFER to: (100-02 Jacking and Lifting)
Jacking (Description and Operation), Lifting (Description and Operation).
1. Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to: (100-02 Jacking and Lifting)
Jacking (Description and Operation), Lifting (Description and Operation).
2. Explore the speed range of interest using the Road Test Quick Checks as previously described.
3. Carry out a coast down in neutral. If the vehicle is free of vibration when operating at a steady indicated speed and
behaves very differently in drive and coast, a transmission concern is likely.
Note, however, that a test on the lift may produce different vibrations and noises than a road test because of the effect of the
lift. It is not unusual to find vibrations on the lift that were not found in the road test. If the condition found on the road can
be duplicated on the lift, carrying out experiments on the lift may save a great deal of time.
Exhaust Neutralization Procedure
1. Raise vehicle on lift and slacken all exhaust fixings.
2. With all fixings loose, neutralize the exhaust system.
3. Tighten all fixings to correct torque, starting at the rear-most point working towards the front of the vehicle.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Cause Action High-speed shake
Wheel end vibration
Engine/transmission
Driveline GO to Pinpoint Test A. Tip-in moan
Air cleaner
Power steering
Powertrain
Engine mounts
Exhaust system GO to Pinpoint Test B. Idle boom/shake/vibration, or shudder
Cable(s)/hoses(s)
Intake air distribution and filtering system
Engine mounts
Exhaust system
Belt/pulleys GO to Pinpoint Test C. Wheel end vibration analysis
Suspension/rear drive halfshaft and CV joints
Tires/wheels
Wheel bearings
CV joint boots GO to Pinpoint Test D. Non-axle noise
Trim/mouldings
A/C system
Accessories GO to Pinpoint Test E. Pinpoint Tests
NOTE: These Pinpoint Tests are designed to take the technician through a step-by-step diagnosis procedure to determine
the cause of a condition. It may not always be necessary to follow the chart to its conclusion. Carry out only the Pinpoint Test
steps necessary to correct the condition. Then check operation of the system to make sure the condition is corrected.
After verifying that the condition has been corrected, make sure all components removed have been installed.
PINPOINT TEST A : HIGH-SPEED SHAKE TEST DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS www.JagDocs.com
Page 306 of 3039

Suspension System - General Information -
Vehicle Ride Height Published: 27-Aug-2013
NOTE: All figures are at "Kerb" height - For additional information, refer to Vehicle Ride Height below.
Description Measurement Description Front/Rear Kerb mm (inch) Tolerance mm (inch) Vehicles without supercharger Front 388 (15.28) ±12 (0.5) Rear 391 (15.39) ±12 (0.5) Vehicles with supercharger Front 385 (15.16) ±12 (0.5) Rear 384 (15.12) ±12 (0.5) Vehicles with All wheel drive Front 404 (15.90) ±12 (0.5) Rear 391 (15.39) ±12 (0.5)
Ride height is measured from the centre of the wheel to the apex of the wheel arch, through the wheel centre line.
Kerb - with all fluids at full and a full tank of fuel, no occupants/luggage.
Tires must be inflated to normal pressure -
For additional information, refer to: Specifications (204-04 Wheels and Tires, Specifications). Wheel Alignment - Front Camber
NOTE: *1 Camber Balance = left-hand camber - right-hand camber.
Description Left-hand Right-hand Balance*1 Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All right-hand drive and Japan Degrees/Minutes -0° 36' ±45' -0° 12' ±45' -0° 24' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.6° ±0.75° -0.2° ±0.75° -0.4° ±0.75° USA, Canada, Mexico and Dominican Republic
(Federal) Degrees/Minutes -0° 12' ±45' -0° 33' ±45' 0° 21' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.2° ±0.75° -0.55° ±0.75° 0.35° ±0.75° Rest of world Degrees/Minutes -0° 12' ±45' -0° 24' ±45' 0° 12' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.2° ±0.75° -0.4° ±0.75° 0.2° ±0.75° Vehicles with All wheel drive Degrees/Minutes -0° 11' ±45' -0º 32' ±0.45' 21' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.19° ±0.75º -0.54º ±0.75º 0.35º ±0.75° Wheel Alignment - Front Caster
NOTE: *2 Caster Balance = left-hand caster - right-hand caster.
Description Left-hand Right-hand Balance*2 Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All right-hand drive and Japan Degrees/Minutes 6° 53' ±45' 6° 20' ±45' 0° 33' ±45' Decimal Degrees 6.88° ±0.75° 6.33° ±0.75° 0.55° ±0.75° USA, Canada, Mexico and Dominican Republic
(Federal) Degrees/Minutes 6° 36' ±45' 6° 45' ±45' -0° 8' ±45' Decimal Degrees 6.61° ±0.75° 6.74° ±0.75° -0.14° ±0.75° Rest of world Degrees/Minutes 6° 36' ±45' 6° 36' ±45' 0° 0' ±45' Decimal Degrees 6.61° ±0.75° 6.61° ±0.75° 0° ±0.75° Vehicles with All wheel drive Degrees/Minutes 6° 2' ± 45' 6° 11' ± 45' - 9' ± 45' Decimal Degrees 6.04º ±0.75° 6.19° ± 0.75° -0.15° ± 0.75° Wheel Alignment - Front Toe
Description Total Toe Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance All right-hand drive and Japan Degrees/Minutes 0° 13' ±12' Decimal Degrees 0.22° ±0.20° USA, Canada, Mexico and Dominican Republic (Federal) Degrees/Minutes 0° 13' ±12' Decimal Degrees 0.22° ±0.20° Rest of world Degrees/Minutes 0° 13' ±12' Decimal Degrees 0.22° ±0.20° Vehicles with All wheel drive Degrees/Minutes 16' ± 12' Decimal Degrees 0.27° ± 0.20° Wheel Alignment - Rear Camber (Vehicles without supercharger)
Description Left-hand Right-hand Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All Markets Degrees/Minutes -0° 47' ±45' -0° 47' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.78° ±0.75° -0.78° ±0.75° Wheel Alignment - Rear Camber (Vehicles with supercharger)
Description Left-hand Right-hand Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All Markets Degrees/Minutes -0° 59' ±45' -0° 59' ±45'
Page 310 of 3039

Shock Absorber and Spring Assembly (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). * Loose front stabilizer bar or rear
stabilizer bar. * Check and tighten the stabilizer bar to specification.
REFER to:
Specifications (204-01 Front Suspension, Specifications), Specifications (204-02 Rear Suspension, Specifications). * Worn lower suspension arm stabilizer
bar insulators. * Install new lower suspension arm stabilizer bar as
necessary. REFER to:
Front Stabilizer Bar - 2.7L Diesel (204-01, Removal and
Installation),
Front Stabilizer Bar - V6 3.0L Petrol (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation),
Front Stabilizer Bar - 4.2L (204-01, Removal and
Installation),
Rear Stabilizer Bar (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). * Shock absorber(s). * Check and install new shock absorber(s) as necessary.
REFER to:
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation),
Shock Absorber and Spring Assembly (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). Vehicle Leans to One
Side * Unevenly loaded or overloaded vehicle. * Notify the customer of incorrect vehicle loading. * Front or rear suspension components.
* Inspect the front and rear suspension systems. Repair or
install new suspension components as necessary. * Shock absorber(s). * Check and install new shock absorber(s) as necessary.
REFER to:
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation),
Shock Absorber and Spring Assembly (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). * Coil spring(s).
* Check and install new spring(s) as necessary. REFER to:
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation),
Shock Absorber and Spring Assembly (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). * Incorrect ride height. Lateral tilt out of
specification. * Check the ride height. Install new spring(s) as
necessary. REFER to:
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation),
Shock Absorber and Spring Assembly (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). Vibration/Noise * Tires/wheels.
* Wheel bearings.
* Wheel hubs.
* Brake components.
* Suspension components.
* Steering components. * Check and install new components as necessary. Wander * Unevenly loaded or overloaded vehicle. * Notify the customer of incorrect vehicle loading. * Ball joint(s). * Check the Ball Joint(s). * Front wheel bearing(s). * Check the wheel bearings. * Loose, worn or damaged suspension components. * Check and install new suspension components as necessary. * Loose suspension fasteners.
* Check and tighten the suspension fasteners to
specification.
REFER to: Specifications (204-00 Suspension System - General Information, Specifications). * Steering components. * Check and install new steering components. * Wheel alignment (excessive total front
toe-out). * Check and adjust the wheel alignment. REFER to:
(204-00 Suspension System - General Information)
Front Toe Adjustment (General Procedures), Rear Toe Adjustment (General Procedures), Camber and Caster Adjustment (General Procedures). Component Tests
Ball Joint Inspection
NOTE: The front suspension is shown in the following procedures. The inspection of the rear suspension upper ball joint
is similar.
1. Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to: (100-02 Jacking and Lifting)
Jacking (Description and Operation), Lifting (Description and Operation).
2. Prior to carrying out any inspection of the ball joints, inspect the front wheel bearings.
Page 396 of 3039

Frontandrearspringanddamperassembliesarefittedwith spacerstoraiserideheightinIndia-specificvehicles.Thefront
andtherearspacersarethesame,theircolorisblack.
Page 479 of 3039
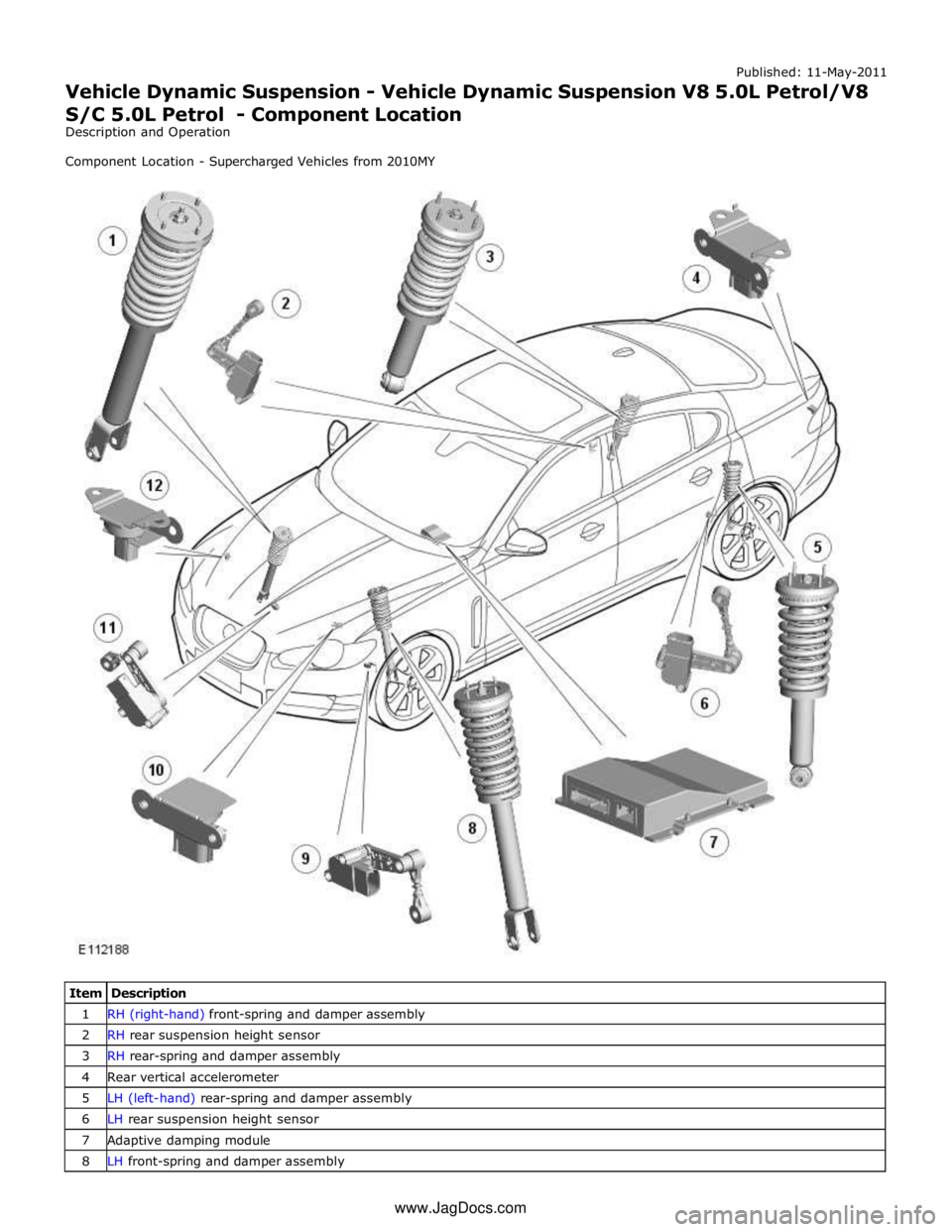
1 RH (right-hand) front-spring and damper assembly 2 RH rear suspension height sensor 3 RH rear-spring and damper assembly 4 Rear vertical accelerometer 5 LH (left-hand) rear-spring and damper assembly 6 LH rear suspension height sensor 7 Adaptive damping module 8 LH front-spring and damper assembly www.JagDocs.com
Page 480 of 3039

10 LH front vertical accelerometer 11 RH front suspension height sensor 12 RH front vertical accelerometer
Page 481 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - Vehicle Dynamic Suspension V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
Adaptive Dynamics - Supercharged Vehicles from 2010MY
The adaptive dynamics system, is an electronically controlled suspension system which constantly adjusts the damping
characteristics of the suspension dampers in reaction to the existing driving conditions. The adaptive dynamics system is
available on specified models.
The system is controlled by an Adaptive Damping Module (ADM), located beneath the right-hand front seat. The module
receives signals from three dedicated vertical accelerometers; two at the front of the vehicle and one at the rear, which,
together with four suspension height sensors, determine the state of the body and wheel motions. In addition to these inputs,
further signals from other vehicle electronic system components to determine vehicle state and driver inputs are monitored by
the adaptive damping module. These combined signals are used by the adaptive damping module to continuously adjust the
damping characteristics of each of the suspension dampers in reaction to the current driving conditions to give the optimum
body control and vehicle ride.
Page 483 of 3039

7 Rear accelerometer 8 Instrument cluster 9 JaguarDrive selector module 10 ABS (anti-lock brake system) module 11 TCM (transmission control module) 12 ECM (engine control module) 13 RH (right-hand) rear damper 14 RH front damper 15 LH (left-hand) front damper 16 LH rear damper 17 LH rear suspension height sensor 18 RH rear suspension height sensor 19 LH front suspension height sensor 20 RH front accelerometer 21 RH front suspension height sensor 22 Adaptive damping module 23 LH front accelerometer
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION System Operation
The adaptive damping module uses a combination of information from other system modules and data from the accelerometers
and suspension height sensors to measure the vehicle and suspension states and driver inputs. Using this information, the
adaptive damping module applies algorithms to control the dampers for the current driving conditions.
The adaptive damping module receives signals on the high speed CAN bus from the following system components: Brake Pressure - ABS module. Brake Pressure Quality Factor - ABS module. Car Configuration Parameters - AJB. Center Differential Range Actual - ECM. Engine Speed - ECM. Engine Speed Quality Factor - ECM. Engine Torque Flywheel Actual - ECM. Engine Torque Flywheel Actual Quality Factor - ECM. Gear Position Target - TCM. Lateral Acceleration - ABS module. Power Mode (Ignition Signal) - CJB. Power Mode Quality Factor - CJB. Roll Stability Control Mode - ABS module. Steering Wheel Angle - ABS module. Steering Wheel Angle Speed - ABS module. Steering Wheel Angle Status - ABS module. Terrain Mode Requested - JaguarDrive selector.
Torque Converter Slip - TCM. Vehicle Information Parameters HS - AJB Vehicle Speed - ABS module. Vehicle Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Front Left Wheel Speed - ABS module. Front Left Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Front Right Wheel Speed - ABS module. Front Right Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Rear Left Wheel Speed - ABS module. Rear Left Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Rear Right Wheel Speed Quality Factor - ABS module. Rear Right Wheel Speed - ABS module. The adaptive damping module also outputs information on the high speed CAN bus for use by other systems as follows: Fault Message - instrument cluster.
Terrain Mode Change Status - JaguarDrive selector.
Terrain Mode - JaguarDrive selector.
The adaptive damping module monitors the input signals and operates the damper solenoids. The input signals are used in
control modes and a force required for each damper for that mode is calculated. An arbitration mode monitors the force
requirements from each mode and apportions a force to a damper. The force is converted to the appropriate current and sent to
the damper.
The control modes are as follows: