2010 JAGUAR XFR aux
[x] Cancel search: auxPage 1111 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Cooling - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Cooling - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
The engine cooling system maintains the engine within an optimum temperature range under changing ambient and engine
operating conditions. The system is a pressurized expansion tank system with continuous bleeds to separate air from the
coolant and prevent the formation of air locks. The engine cooling system also provides:
Heating for:
- The passenger compartment. For additional information, refer to 412-01 Climate Control.
- The throttle body.
Cooling for:
- The engine oil cooler. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine - 5.0L, Vehicles With: Supercharger or
303-01E Engine - 5.0L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger.
- The transmission fluid cooler. For additional information, refer to 307-02B Transmission/Transaxle Cooling -
5.0L/3.0L Diesel.
The primary components of the engine cooling system are the:
Coolant pump.
Thermostat.
Radiator.
Auxiliary radiator (SC (supercharger) vehicles only).
Cooling fan.
Expansion tank.
Engine oil cooler.
Outlet tube and heater manifold.
Connecting hoses and pipes.
Page 1114 of 3039
14 Radiator 15 Auxiliary radiator 16 Connection with supercharger cooling system
System Operation
When the engine is running, the coolant is circulated around the engine cooling system by the coolant pump. From the coolant
pump, coolant flows through the cylinder heads and the engine oil cooler into the cylinder block and the heater manifold.
In the cylinder block, the coolant flows forwards to the outlet tube. When the coolant is cold, the thermostat is closed and the
coolant flows direct from the outlet tube back to the coolant pump. Once the coolant reaches operating temperature the
thermostat begins to open, to control system temperature, and coolant flows from the outlet tube to the coolant pump via the
radiator and, on SC (supercharger) vehicles, the auxiliary radiator. When the thermostat is open, the coolant flow through the
radiator(s) also generates a coolant flow through the transmission fluid cooler.
From the heater manifold the coolant flows through the electronic throttle and the heater core, in parallel circuits that are
unaffected by the position of the thermostat. From the electronic throttle, the coolant merges with bleed coolant from the
coolant pump and the outlet tube and flows to the expansion tank. From the heater core, the coolant flows back to the inlet of
the coolant pump.
Expansion and contraction of the coolant is accommodated by an air space in the expansion tank and the compliance of the
flexible hoses.
If the coolant level in the expansion tank decreases below a predetermined value, the level sensor connects a ground to the
instrument cluster, which activates the appropriate warning. For additional information, refer to 413-01 Instrument Cluster.
The cooling fan is operated by a fan control module integrated into the cooling fan motor. The fan control module regulates the
voltage, and thus speed, of the cooling fan motor in response to a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM (engine
control module).
The cooling fan receives a battery feed and an ignition feed from the EJB (engine junction box). The ignition feed is supplied
from the main relay in the EJB, which is controlled by the ECM.
The ECM calculates the required fan speed from the engine temperature, A/C (air conditioning) system pressure and transmission fluid temperature. Under hot operating conditions, the fan may continue to operate for 4 minutes after the engine
has been switched off.
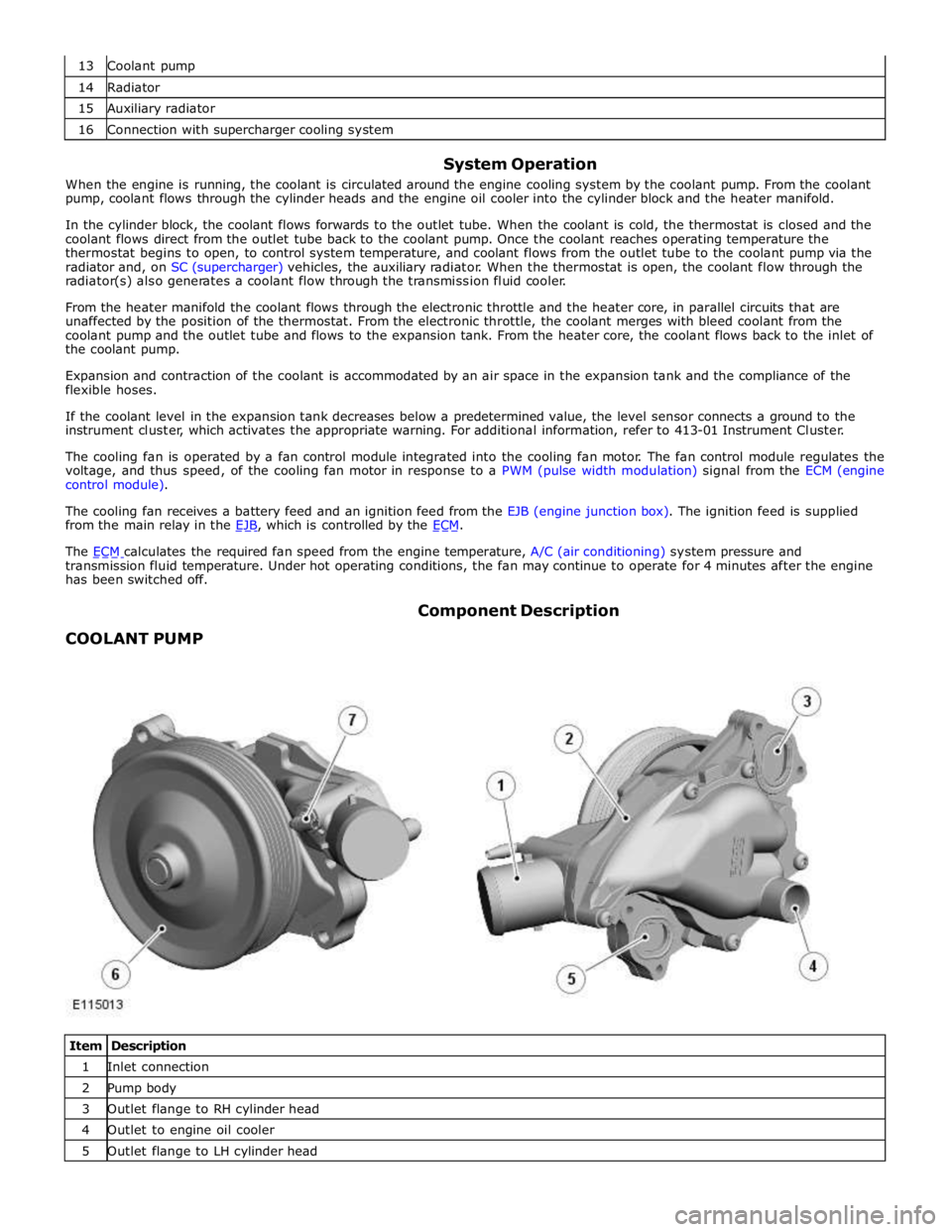
COOLANT PUMP Component Description
Item Description 1 Inlet connection 2 Pump body 3 Outlet flange to RH cylinder head 4 Outlet to engine oil cooler 5 Outlet flange to LH cylinder head
Page 1116 of 3039
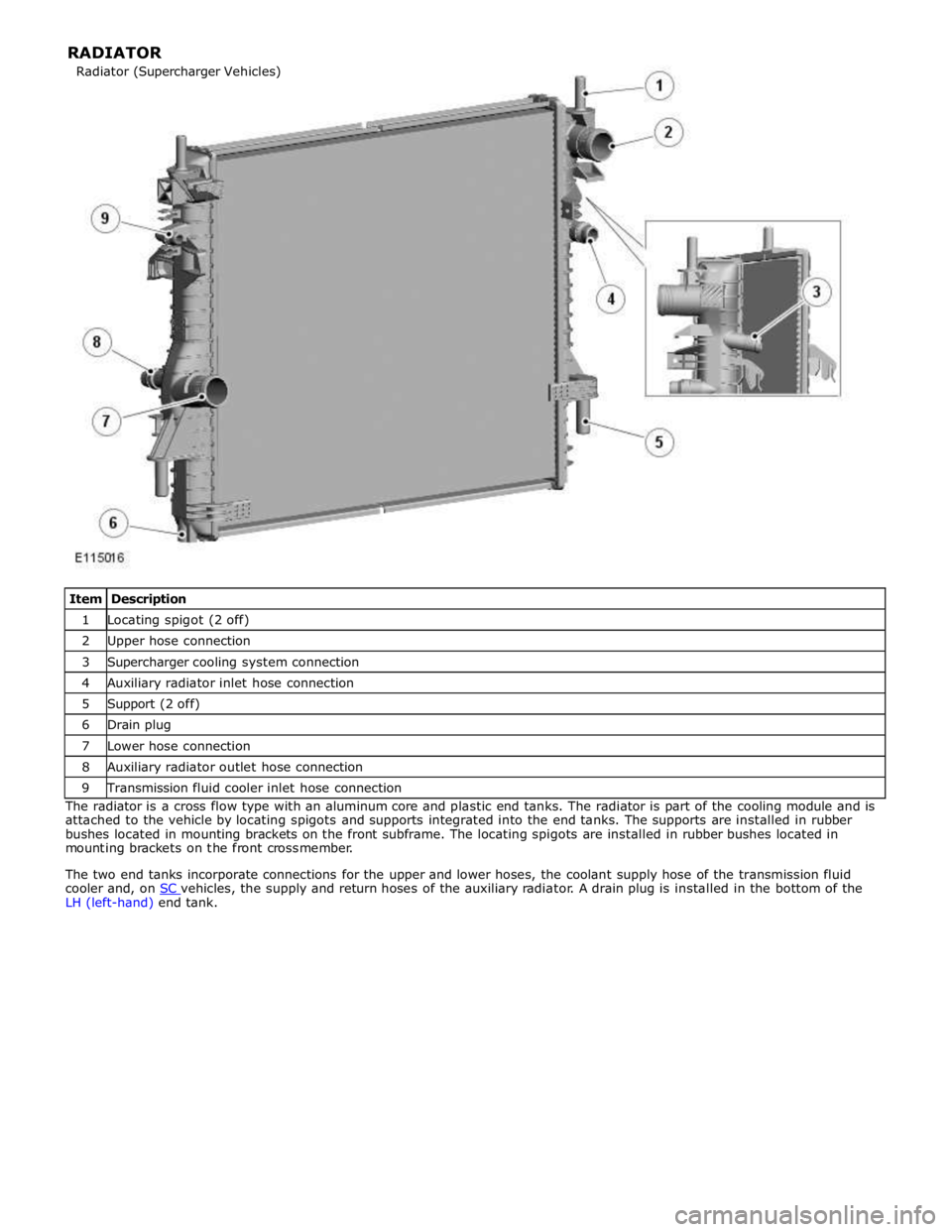
1 Locating spigot (2 off) 2 Upper hose connection 3 Supercharger cooling system connection 4 Auxiliary radiator inlet hose connection 5 Support (2 off) 6 Drain plug 7 Lower hose connection 8 Auxiliary radiator outlet hose connection 9 Transmission fluid cooler inlet hose connection The radiator is a cross flow type with an aluminum core and plastic end tanks. The radiator is part of the cooling module and is
attached to the vehicle by locating spigots and supports integrated into the end tanks. The supports are installed in rubber
bushes located in mounting brackets on the front subframe. The locating spigots are installed in rubber bushes located in
mounting brackets on the front crossmember.
The two end tanks incorporate connections for the upper and lower hoses, the coolant supply hose of the transmission fluid
cooler and, on SC vehicles, the supply and return hoses of the auxiliary radiator. A drain plug is installed in the bottom of the LH (left-hand) end tank. Radiator (Supercharger Vehicles) RADIATOR
Page 1117 of 3039

1 Return hose connection 2 Supply hose connection 3 Bottom bracket 4 Top bracket The auxiliary radiator is connected in parallel with the (main) radiator to increase the engine cooling capacity on SC vehicles. The auxiliary radiator is installed in an air duct, to the right of the cooling module, which takes cooling air from the RH (right-
hand) grille in the front bumper. Two spigots on the top of the auxiliary radiator provide the coolant supply and return
connections with the main radiator.
Page 1140 of 3039
Published: 19-Nov-2013
Engine Cooling - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Auxiliary Radiator
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
2. Refer to: Air Cleaner RH (303-12C Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
3. CAUTION: Be prepared to collect escaping coolant.
4. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
5. Refer to: Cooling System Partial Draining, Filling and Bleeding - V8 5.0L Petrol (303-03C Engine Cooling - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
6. Refer to: Fender Splash Shield (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation). www.JagDocs.com
Page 1182 of 3039
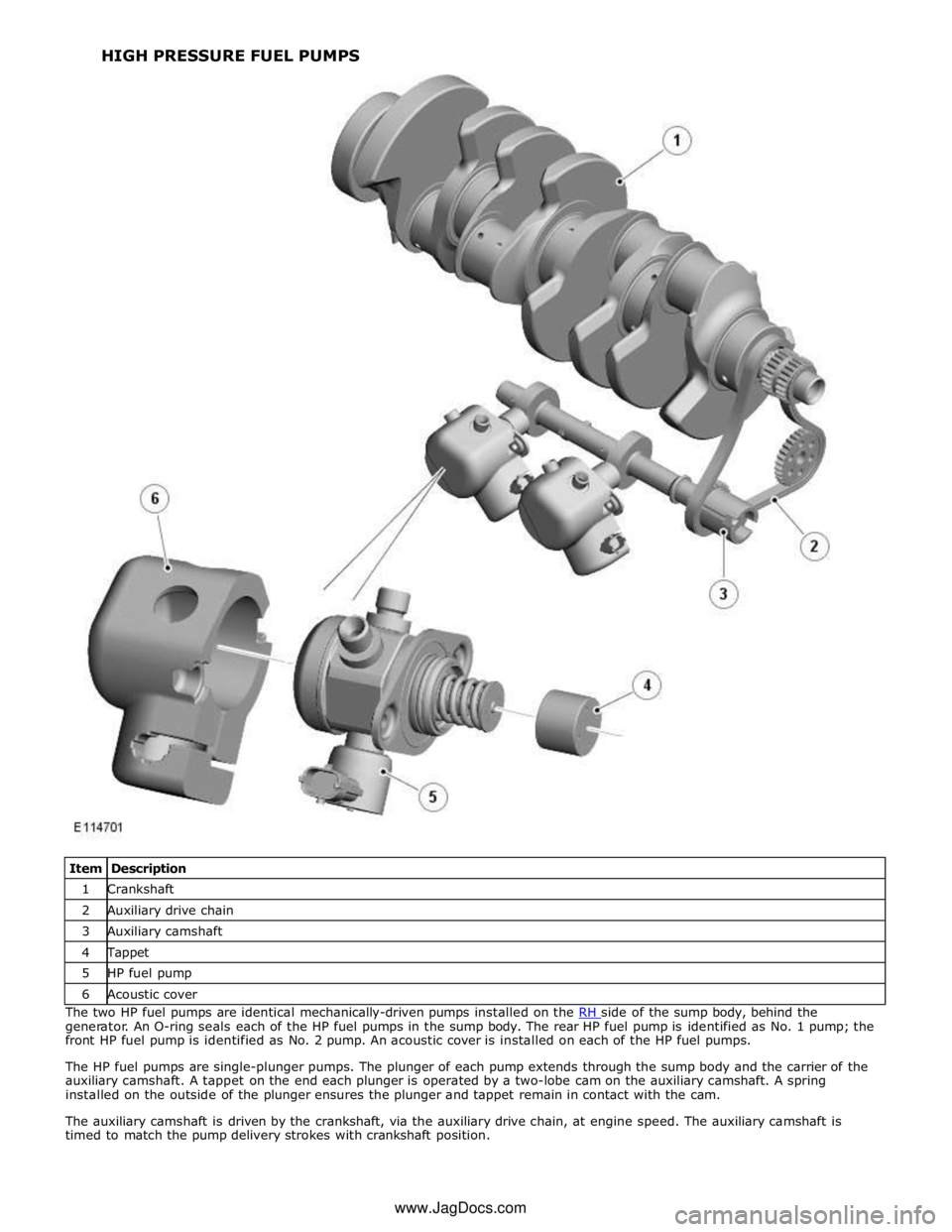
1 Crankshaft 2 Auxiliary drive chain 3 Auxiliary camshaft 4 Tappet 5 HP fuel pump 6 Acoustic cover The two HP fuel pumps are identical mechanically-driven pumps installed on the RH side of the sump body, behind the generator. An O-ring seals each of the HP fuel pumps in the sump body. The rear HP fuel pump is identified as No. 1 pump; the
front HP fuel pump is identified as No. 2 pump. An acoustic cover is installed on each of the HP fuel pumps.
The HP fuel pumps are single-plunger pumps. The plunger of each pump extends through the sump body and the carrier of the
auxiliary camshaft. A tappet on the end each plunger is operated by a two-lobe cam on the auxiliary camshaft. A spring
installed on the outside of the plunger ensures the plunger and tappet remain in contact with the cam.
The auxiliary camshaft is driven by the crankshaft, via the auxiliary drive chain, at engine speed. The auxiliary camshaft is
timed to match the pump delivery strokes with crankshaft position. HIGH PRESSURE FUEL PUMPS
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1664 of 3039

Published: 11-Jul-2014
Climate Control System - General Information - Climate Control System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the Climate Control System, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
Workshop Manual. REFER to:
Air Distribution and Filtering (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Distribution and Filtering (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Distribution and Filtering (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Heating and Ventilation (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Heating and Ventilation (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Heating and Ventilation (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Conditioning (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Conditioning (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Conditioning (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Control Components (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Control Components (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Control Components (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Electric Booster Heater (412-02 Auxiliary Climate Control, Description and Operation), Electric Booster Heater (412-02 Auxiliary Climate Control, Description and Operation), Electric Booster Heater (412-02 Auxiliary Climate Control, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNING: Servicing must be carried out by personnel familiar with both vehicle system and the charging and testing
equipment. All operations must be carried out in a well ventilated area away from open flame and heat sources.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Coolant level
Hose(s)
Coolant pump
Control flap(s)
Duct(s)
Vent(s)
Cabin air filter
Drive belt
Air conditioning compressor
Thermostatic expansion valve
Evaporator
Receiver drier
Air conditioning condenser
Refrigerant pipes Auxiliary
drive belt
Fuel fired booster heater
Fuel fired booster heater fuel pump
Fuel fired booster heater fuel pipes
Fuse(s)
Wiring harness
Electrical connectors
Blower
Air conditioning compressor
Electric cooling fan
Automatic Temperature Control Module (ATCM)
Refrigerant pressure sensor
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index
5. Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
Page 1690 of 3039
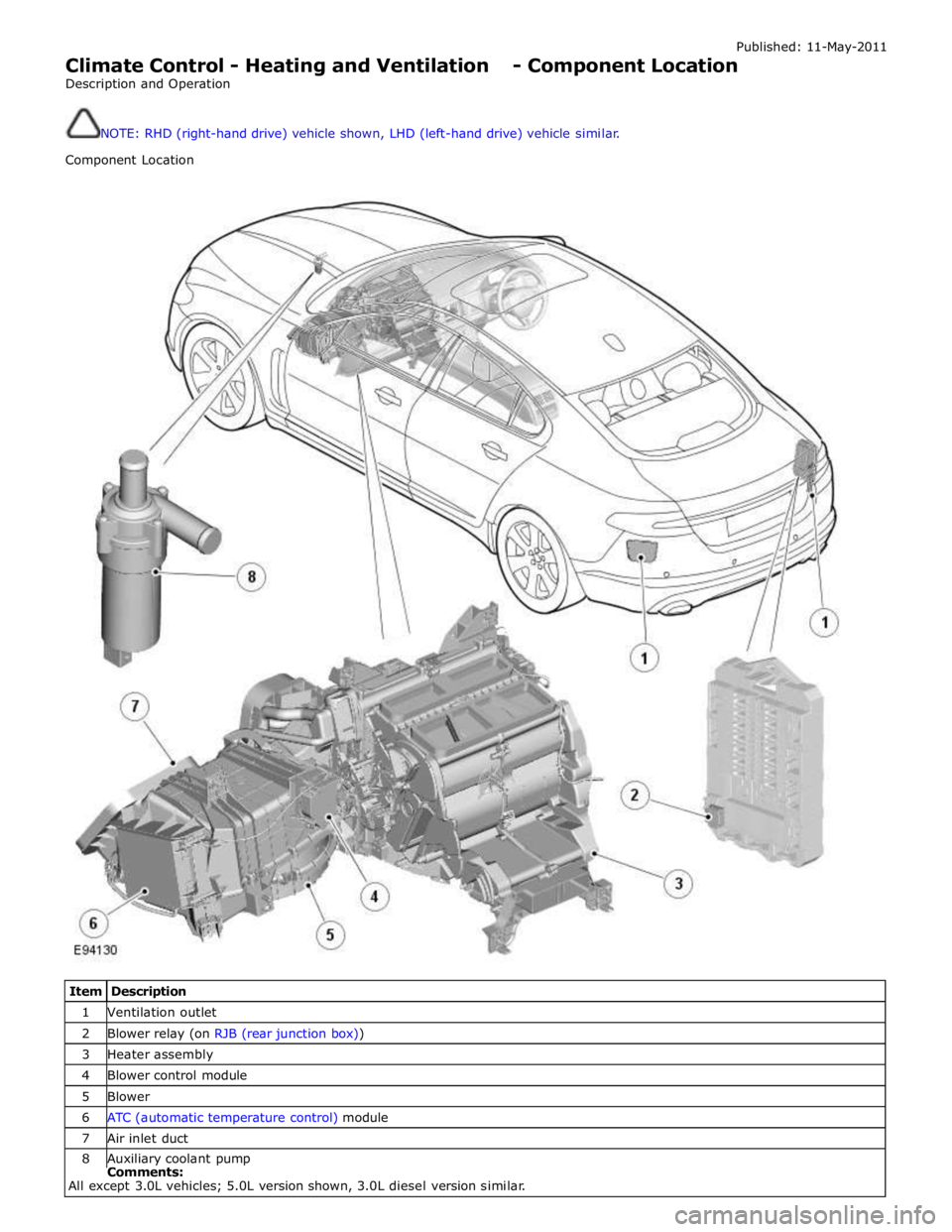
Published: 11-May-2011
Climate Control - Heating and Ventilation - Component Location
Description and Operation
NOTE: RHD (right-hand drive) vehicle shown, LHD (left-hand drive) vehicle similar.
Component Location
Item Description 1 Ventilation outlet 2 Blower relay (on RJB (rear junction box)) 3 Heater assembly 4 Blower control module 5 Blower 6 ATC (automatic temperature control) module 7 Air inlet duct 8 Auxiliary coolant pump Comments:
All except 3.0L vehicles; 5.0L version shown, 3.0L diesel version similar.