Page 780 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System
Vacuum tank
Alternator
Purge control solenoid valve
17-10
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The evaporative emission control system prevents
fuel vapours generated in the fuel tank from
escaping into the atmosphere.
Fuel vapours from the fuel tank flow through the
fuel tank pressure control valve and vapour
pipe/hose to be stored temporarily in the canister.
When driving the vehicle, fuel vapours stored in
the canister flow through the purge solenoid and
purge port and go into the intake manifold to be
sent to the combustion chamber.When the engine coolant temperature is low or
when the intake air quantity is small (when the
engine is at idle, for example), the engine control
unit turns the purge solenoid off to shut off the
fuel vapour flow to the intake manifold.
This does not only insure the driveability when the
engine is cold or running under low load but also
stabilize the emission level.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
BatteryIntake air
temperature sensor
Barometric pressure
sensor
Check
valve
Canister
Control
relay
Purge control
solenoid valve
(ON: Open)
Engine-ECUEngine coolant
temperature sensor Air flow sensor
COMPONENT LOCATION
Page 781 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-11
PURGE CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripe) from throttle
body and connect it to a hand vacuum pump.
2. Plug the nipple from which the vacuum hose was removed.
3. When the engine is cold or hot, apply a vacuum of 53
kPa, and check the condition of the vacuum.
When engine is cold
(Engine coolant temperature: 40_C or less)
Engine conditionNormal condition
At idleVacuum is maintained
3,000 r/min
When engine is hot
(Engine coolant temperature: 80_C or higher)
Engine conditionNormal condition
At idleVacuum is maintained
3,000 r/min (within 3
minutes after engine starts)Vacuum will leak.
PURGE PORT VACUUM CHECK
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripe) from the throttle
body purge vacuum nipple and connect a hand vacuum
pump to the nipple.
2. Confirm that the vacuum is approximately constant
regardless of the engine rotation speed.
NOTE
If vacuum changes, it is possible that the throttle body
purge port maybe clogged and require cleaning.
Red stripe
Plug
Throttle body
Red stripe
Throttle body
Vac-
uum
Engine speed (r/min)
Page 782 of 1449
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-12
PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE CHECK
NOTE
When disconnecting the vacuum hose, always make a mark
so that it can be reconnected at original position.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the solenoid valve.
2. Disconnect the harness connector.
3. Connect a hand vacuum pump to nipple (A) of the solenoid
valve (refer to the illustration at left).
4. Check airtightness by applying a vacuum with voltage
applied directly from the battery to the purge control
solenoid valve and without applying voltage.
Battery voltageNormal condition
AppliedVacuum leaks
Not appliedVacuum maintained
5. Measure the resistance between the terminals of the
solenoid valve.
Standard value: 30 - 34Ω(at 20_C)
CHECK VALVE CHECK
Connect a hand vacuum pump to the check valve, apply
vacuum and check the airtightness.
Connected nipple colourNormal condition
BlackVacuum leaks
BrownVacuum is maintained
Battery A
Page 783 of 1449
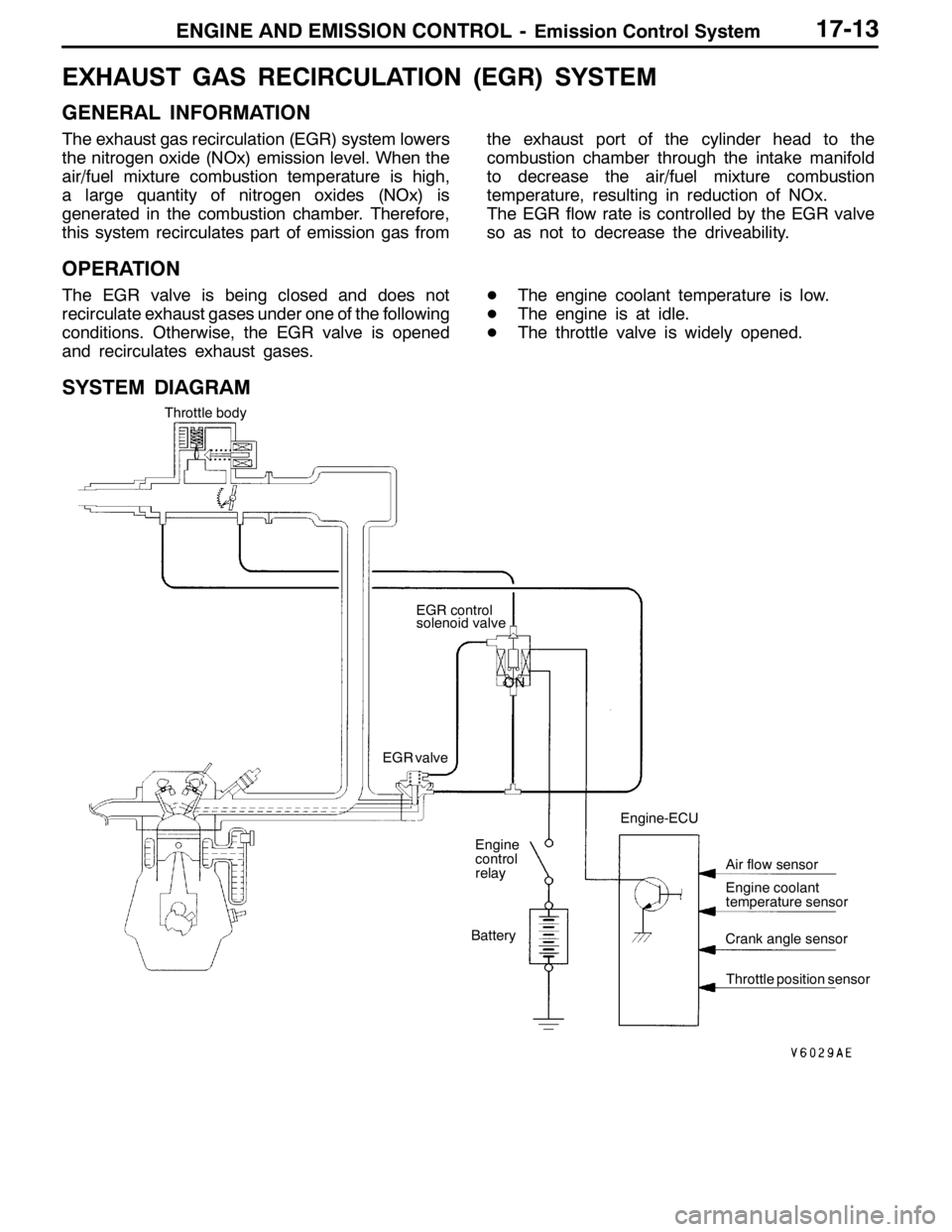
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-13
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system lowers
the nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission level. When the
air/fuel mixture combustion temperature is high,
a large quantity of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is
generated in the combustion chamber. Therefore,
this system recirculates part of emission gas fromthe exhaust port of the cylinder head to the
combustion chamber through the intake manifold
to decrease the air/fuel mixture combustion
temperature, resulting in reduction of NOx.
The EGR flow rate is controlled by the EGR valve
so as not to decrease the driveability.
OPERATION
The EGR valve is being closed and does not
recirculate exhaust gases under one of the following
conditions. Otherwise, the EGR valve is opened
and recirculates exhaust gases.DThe engine coolant temperature is low.
DThe engine is at idle.
DThe throttle valve is widely opened.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
ON Throttle body
EGR control
solenoid valve
Engine
control
relay
Battery EGR valve
Crank angle sensor
Throttle position sensor Engine-ECU
Engine coolant
temperature sensor Air flow sensor
Page 784 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System
EGR control solenoid valve
Vacuum tank
Alternator
EGR valve
Throttle body
17-14
COMPONENT LOCATION
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (green stripe) from the EGR
control solenoid valve, and then connect a hand vacuum
pump via the three-way terminal.
2. When the engine is hot or cold, check the condition of
vacuum by racing the engine.
When engine is cold
(Engine coolant temperature: 20_C or less)
Throttle valveNormal vacuum condition
Open quicklyNo vacuum will generate
(the same as barometric pressure.)
When engine is hot
(Engine coolant temperature: 80_C or higher)
Throttle valveNormal vacuum condition
Open quicklyIt will momentarily rise over 13 kPa
3. Disconnect the three-way terminal.
4. Connect the hand vacuum pump to the vacuum hose
(green stripe).
5. Check whether the engine stalls or the idling is unstable
when a vacuum of 27 kPa or higher is applied during
idling.
Three-way
terminal
EGR control
solenoid valveVacuum
tankAlternator
EGR control
solenoid valveVacuum
tank
Alternator
Green stripe
Page 785 of 1449

ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-15
EGR VALVE CHECK
1. Remove the EGR valve and inspect for sticking, carbon
deposits, etc. If found, clean with a suitable solvent so
that the valve seats correctly.
2. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the EGR valve.
3. Apply 67 kPa of vacuum, and check that the vacuum
is maintained.
4. Apply a vacuum and check the passage of air by blowing
through one side of the EGR passage.
VacuumPassage of air
5.3 kPa or lessAir is not blown out
27 kPa or moreAir is blown out
5. Replace the gasket, and tighten to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 20±2 N·m
EGR PORT VACUUM CHECK
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (White stripe) from the
throttle body EGR vacuum nipple and connect a hand
vacuum pump to the nipple.
2. Start the engine and check vacuum remains fairly constant
after racing the engine.
NOTE
If the vacuum fluctuates, the throttle body EGR port may
be clogged and need cleaning.
White stripe
Throttle body
Vacu-
um
Engine speed (r/min)
Page 786 of 1449
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-16
EGR CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE CHECK
NOTE
When disconnecting the vacuum hose, always make a mark
so that it can be reconnected at original position.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (yellow stripe, green stripe,
white stripe) from the solenoid valve.
2. Disconnect the harness connector.
3. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the nipple to which
the green-striped vacuum hose was connected.
4. Check airtightness by applying a vacuum with voltage
applied directly from the battery to the EGR control
solenoid valve and without applying voltage.
Battery voltageB nipple conditionNormal condition
Not appliedOpenVacuum maintained
AppliedOpenVacuum leaks
ClosedVacuum maintained
5. Measure the resistance between the terminals of the
solenoid valve.
Standard value: 29 - 35Ω(at 20_C)
Battery
A B
C
Page 787 of 1449
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL -Emission Control System17-17
EGR VALVE
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operation
Air Hose E Removal and Installation
(Refer to GROUP 15 - Inter Cooler.)
1 2
3
21±4N·m
Removal steps
1. Vacuum hose connection
2. EGR valve
3. EGR valve gasket