Page 1068 of 1449
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -Disc Brake35A-26
LUBRICATION POINTS
Piston seal
Grease: Repair kit grease
Caution
The piston seal inside the
seal and boot kit is coated
with special grease, so do
not wipe this grease off.
Brake fluid: DOT3 or DOT4
Grease: Repair kit greaseGrease: Repair kit grease
Page 1069 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -Disc Brake35A-27
DISASSEMBLY SERVICE POINTS
Caution: Brembo disc brake
Take care not to contact the parts or tools to the caliper
because the paint of caliper will be scratched. And if
there is brake fluid on the caliper, wipe out quickly.
AA"PISTON BOOT/PISTON REMOVAL
Remove the piston boot by pumping in air slowly from the
brake hose connection. Be sure to use the handle of a plastic
hammer and adjust the height of the two pistons while so
that the pistons protrude evenly.
Caution
Do not remove one piston completely before trying to
remove the other piston, because it will become
impossible to remove the second piston.
Use a piece of wood to protect the caliper body outer side,
and then apply compressed air through the brake hose
connection hole to withdraw the piston and piston boot.
Caution
If air is blown into the caliper body suddenly, the piston
will pop out, causing damage to the caliper body. Be
sure to apply compressed air gradually.
AB"PISTON SEAL REMOVAL
1. Remove the piston seal with finger tip.
Caution
Do not use a flat-tipped screwdriver or other tool to
prevent damage to inner cylinder.
2. Clean piston surface and inner bore with trichloroethylene,
alcohol or the specified brake fluid.
Specified brake fluid: DOT3 or DOT4
REASSEMBLY SERVICE POINT
Caution: Brembo disc brake
Take care not to contact the parts or tools to the caliper
because the paint of caliper will be scratched. And if
there is brake fluid on the caliper, wipe out quickly.
Page 1070 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -Disc Brake35A-28
"AALOCK PIN/GUIDE PIN INSTALLATION
As shown in the illustration, align the identification mark on
the caliper body and the head mark of the guide pin/lock
pin, then install the guide pin/lock pin.
INSPECTION
DCheck the cylinder for wear, damage or rust.
DCheck the piston surface for wear, damage or rust.
DCheck the caliper body or sleeve for wear.
DCheck pad for damage or adhesion of grease, check
the backing metal for damage.
PAD WEAR CHECK
Measure thickness at the thinnest and worn area of the pad.
Replace the pad assembly if the pad thickness is less than
the limit value.
Standard value:
10.0 mm ,
9.0 mm
Limit: 2.0 mm
Caution
1. Always replace the brake pads as an axle set.
2. If an excessive difference is found in the thickness
between the right and left brake pads, check moving
parts.
Identification
mark ”L”
Front of
vehicle
Rear of
vehicle
Lock pin Lock pin
Guide pin Guide pin
Identification
mark ”G”
Identification
mark ”B”
Identification mark ”A”
Page 1071 of 1449

35B-1
ANTI-SKID
BRAKING SYSTEM
(ABS) <4WD>
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION 2..................
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 3.................
LUBRICANTS Refer to GROUP 35A..........
SEALANT Refer to GROUP 35A..............
SPECIAL TOOLS 4...........................
TROUBLESHOOTING 4.......................
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 26....................
Brake Pedal Check and Adjustment
Refer to GROUP 35A ..........................
Brake Booster Operating Test
Refer to GROUP 35A ..........................
Check Valve Operation Check
Refer to GROUP 35A ..........................
Bleeding Refer to GROUP 35A..................
Brake Fluid Level Sensor Check
Refer to GROUP 35A ..........................
Disc Brake Pad Check and
Replacement Refer to GROUP 35A..............Disc Brake Rotor Check Refer to GROUP 35A...
Brake Disc Thickness Check
Refer to GROUP 35A ..........................
Brake Disc Run-out Check and Correction
Refer to GROUP 35A ..........................
Wheel Speed Sensor Output Voltage Check
26 ............................................
Hydraulic Unit Check 28........................
Remedy for a Flat Battery 29...................
BRAKE PEDAL Refer to GROUP 35A........
MASTER CYLINDER AND BRAKE
BOOSTER Refer to GROUP 35A............
DISC BRAKE Refer to GROUP 35A..........
HYDRAULIC UNIT AND ABS-ECU 30.........
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR 33..................
G SENSORS AND STEERING WHEEL
SENSOR 35..................................
Page 1072 of 1449

ABS <4WD> -General Information35B-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
ABS has been adopted as optional equipment in
RS-IIto maintain directional stability and steering
performance during sudden braking or braking on
slippery road surfaces.
The ABS control method is a 4-sensor, 4-channel
method which provides independent control for all
wheels.
Following system for Lancer EVOLUTION-VII has
been modified from Lancer EVOLUTION-VI Tommi
Makinen Edition.DBy adding lateral G sensor, longitudinal G
sensor and steering wheel sensor, optimized
ABS control at the time of cornering.
DBy inputting parking brake switch signal to
ABS-ECU with pulling parking brake lever, ABS
control has been optimized.
DABS-ECU outputs ABS signal to 4WD-ECU.
DG sensor (lateral), steering wheel sensor and
parking brake switch have been added to the
diagnosis and service data.
DABS-ECU connector has been changed.
EBD CONTROL
In ABS, electronic control method is used by which
the rear wheel brake hydraulic pressure during
braking is regulated by rear wheel control solenoid
valves in accordance with the vehicle’s rate of
deceleration and the front and rear wheel slippage
which are calculated from the each wheel speed
sensor’s signal. EBD control is a control system
which provides a high level of control for both vehicle
braking force and vehicle stability. The system has
the following features:
DBecause the system provides the optimum rear
wheel braking force regardless of the vehicleladen condition and the condition of the road
surface, the system reduces the required pedal
depression force, particularly when the vehicle
is heavily laden or driving on road surfaces
with high frictional coefficients.
DBecause the duty placed on the front brakes
has been reduced, the increases in pad
temperature can be controlled to improve the
wear resistance characteristics of the pad,
during front brakes applying.
DControl valves such as the proportioning valve
are no longer required.
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemSpecifications
ABS control method4-sensor, 4-channel
No. of ABS rotor teethFront43
Rear43
ABS speed sensorTypeMagnet coil typep
Gap between sensor and rotor mm0.85 / 0.60 (non-adjustable type)
Page 1073 of 1449
ABS <4WD> -General Information/Service Specifications35B-3
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
Stop lamp
switch*Parking brake
switch
Diagnosis
connector*
Wheel speed sensorWheel speed sensor Hydraulic unit
assembly*
(integrated with
the ABS-ECU) ABS warning lamp
Lateral G sensor
Longitudinal G sensor Steering
wheel
sensor*
NOTE
For R.H. drive vehicles, only the position indicated by the * is symmetrical.
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsStandard value
Wheel speed sensor internal resistance kΩ1.24 - 1.64
Wheel speed sensor insulation resistance kΩ100 or more
Lateral G sensor/Longitudinal G
sensoroutputvoltageV
On stationary vehicle2.4 - 2.6
sensor outputvoltageV
With front mark downward3.4 - 3.6
Page 1074 of 1449
ABS <4WD> -Special Tools/Troubleshooting35B-4
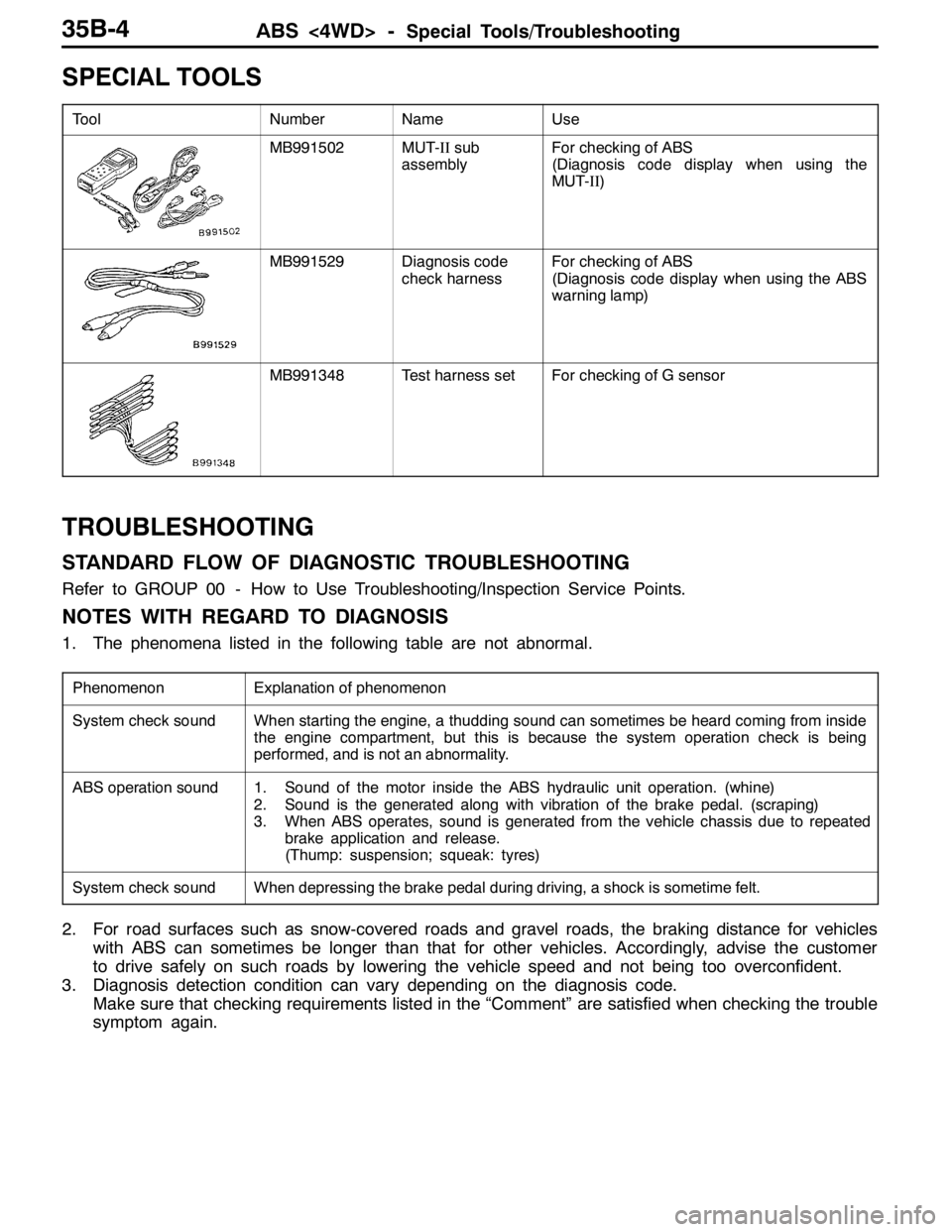
SPECIAL TOOLS
ToolNumberNameUse
MB991502MUT-IIsub
assemblyFor checking of ABS
(Diagnosis code display when using the
MUT-II)
MB991529Diagnosis code
check harnessFor checking of ABS
(Diagnosis code display when using the ABS
warning lamp)
MB991348Test harness setFor checking of G sensor
TROUBLESHOOTING
STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING
Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Use Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points.
NOTES WITH REGARD TO DIAGNOSIS
1. The phenomena listed in the following table are not abnormal.
PhenomenonExplanation of phenomenon
System check soundWhen starting the engine, a thudding sound can sometimes be heard coming from inside
the engine compartment, but this is because the system operation check is being
performed, and is not an abnormality.
ABS operation sound1. Sound of the motor inside the ABS hydraulic unit operation. (whine)
2. Sound is the generated along with vibration of the brake pedal. (scraping)
3. When ABS operates, sound is generated from the vehicle chassis due to repeated
brake application and release.
(Thump: suspension; squeak: tyres)
System check soundWhen depressing the brake pedal during driving, a shock is sometime felt.
2. For road surfaces such as snow-covered roads and gravel roads, the braking distance for vehicles
with ABS can sometimes be longer than that for other vehicles. Accordingly, advise the customer
to drive safely on such roads by lowering the vehicle speed and not being too overconfident.
3. Diagnosis detection condition can vary depending on the diagnosis code.
Make sure that checking requirements listed in the “Comment” are satisfied when checking the trouble
symptom again.
Page 1076 of 1449
ABS <4WD> -Troubleshooting35B-6
When not using the MUT-II
NOTE
If the ABS-ECU function has been stopped because of fail-safe
operation, it will not be possible to erase the diagnosis codes.
1. Stop the engine.
2. Use the special tool to earth terminal (1) (diagnosis control
terminal) of the diagnosis connector.
3. Turn on the stop lamp switch. (Depress the brake pedal.)
4. After carrying out steps 1. to 3., turn the ignition switch
to “ON”. Within 3 seconds after turning the ignition switch
to “ON”, turn off the stop lamp switch (release the brake
pedal). Then, turn the stop lamp switch on and off a
total of 10 times.
1st2nd3rd4th5th6th7th8th9th10th
Within
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
secondWithin
1
second
1 second
Ignition switchON
LOCK (OFF)
Stop lamp switchON
OFF
ABS warning lampON
OFF
ABS-ECU memory
Within 3
seconds
Erasing of ABS-ECU
diagnosis codes complete.
MB991529