2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine mount
[x] Cancel search: engine mountPage 2333 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–163
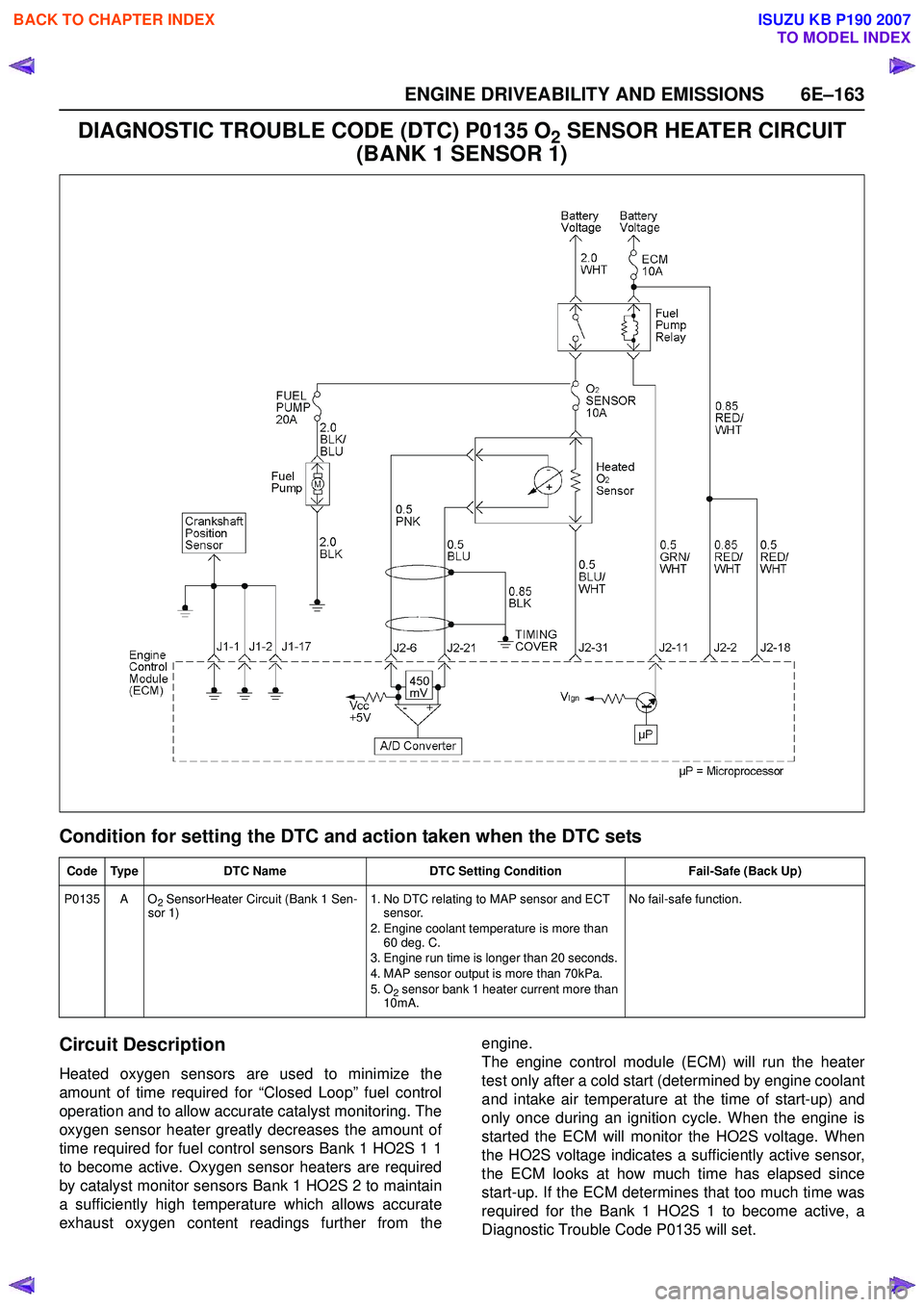
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135 O2 SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for “Closed Loop” fuel control
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The
oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of
time required for fuel control sensors Bank 1 HO2S 1 1
to become active. Oxygen sensor heaters are required
by catalyst monitor sensors Bank 1 HO2S 2 to maintain
a sufficiently high temperature which allows accurate
exhaust oxygen content readings further from the engine.
The engine control module (ECM) will run the heater
test only after a cold start (determined by engine coolant
and intake air temperature at the time of start-up) and
only once during an ignition cycle. When the engine is
started the ECM will monitor the HO2S voltage. When
the HO2S voltage indicates a sufficiently active sensor,
the ECM looks at how much time has elapsed since
start-up. If the ECM determines that too much time was
required for the Bank 1 HO2S 1 to become active, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0135 will set.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0135 A O
2 SensorHeater Circuit (Bank 1 Sen-
sor 1) 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor and ECT
sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 60 deg. C.
3. Engine run time is longer than 20 seconds.
4. MAP sensor output is more than 70kPa.
5. O
2 sensor bank 1 heater current more than
10mA. No fail-safe function.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2347 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–177
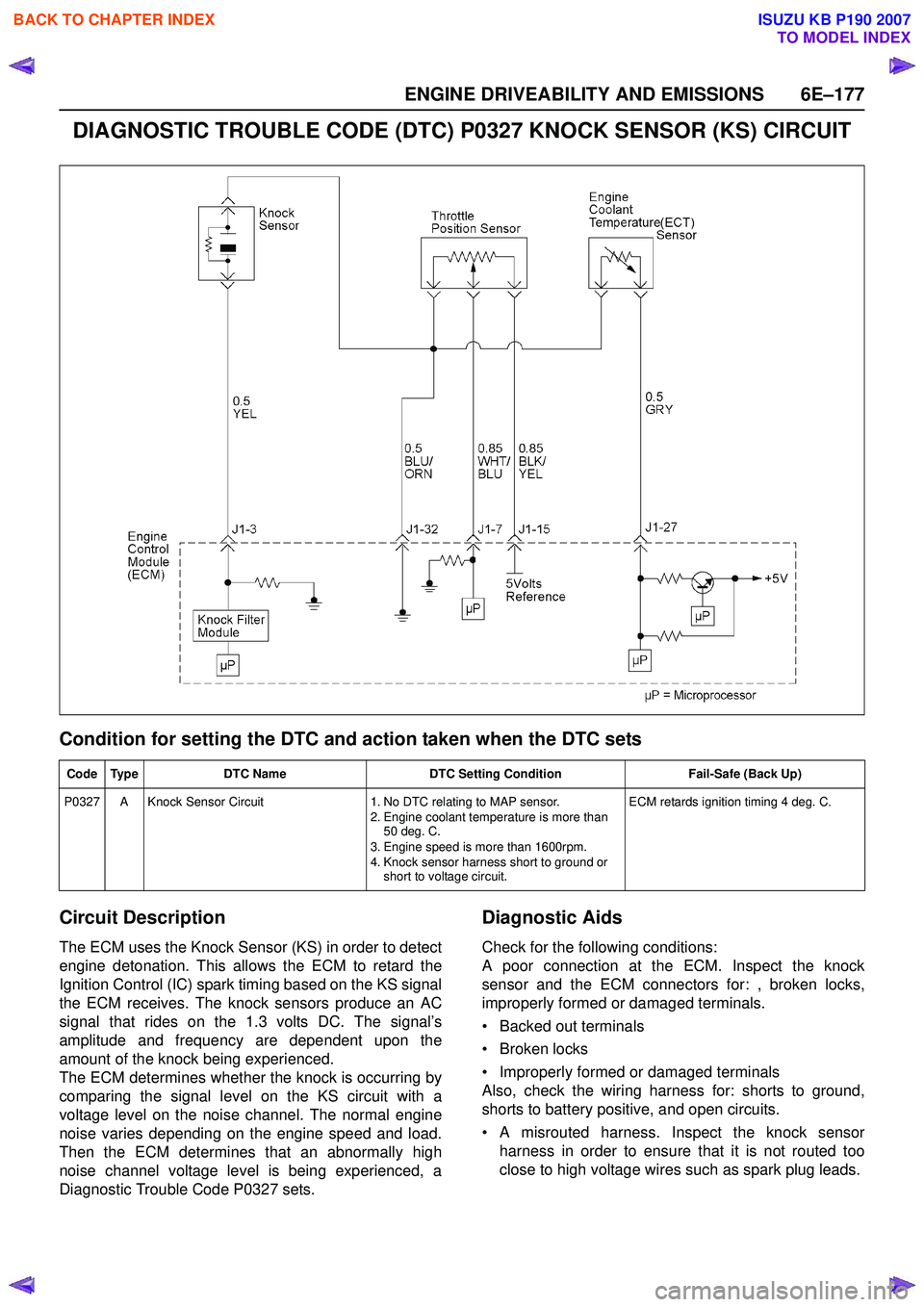
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The ECM uses the Knock Sensor (KS) in order to detect
engine detonation. This allows the ECM to retard the
Ignition Control (IC) spark timing based on the KS signal
the ECM receives. The knock sensors produce an AC
signal that rides on the 1.3 volts DC. The signal’s
amplitude and frequency are dependent upon the
amount of the knock being experienced.
The ECM determines whether the knock is occurring by
comparing the signal level on the KS circuit with a
voltage level on the noise channel. The normal engine
noise varies depending on the engine speed and load.
Then the ECM determines that an abnormally high
noise channel voltage level is being experienced, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0327 sets.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
A poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the knock
sensor and the ECM connectors for: , broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals.
• Backed out terminals
• Broken locks
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals
Also, check the wiring harness for: shorts to ground,
shorts to battery positive, and open circuits.
• A misrouted harness. Inspect the knock sensor harness in order to ensure that it is not routed too
close to high voltage wires such as spark plug leads.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0327 A Knock Sensor Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor harness short to ground or short to voltage circuit. ECM retards ignition timing 4 deg. C
.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2381 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–211
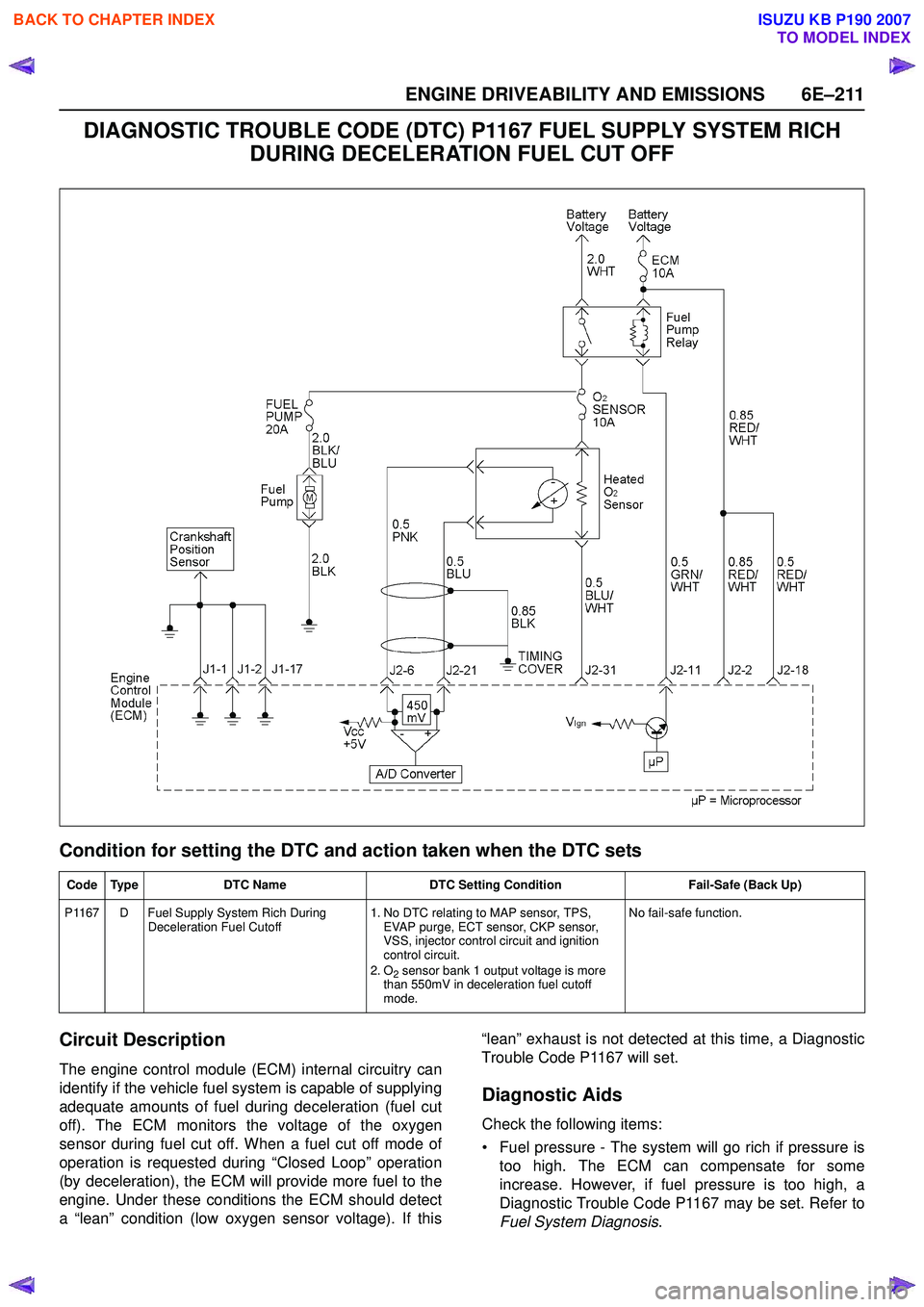
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1167 FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM RICH DURING DECELERATION FUEL CUT OFF
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) internal circuitry can
identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of supplying
adequate amounts of fuel during deceleration (fuel cut
off). The ECM monitors the voltage of the oxygen
sensor during fuel cut off. When a fuel cut off mode of
operation is requested during “Closed Loop” operation
(by deceleration), the ECM will provide more fuel to the
engine. Under these conditions the ECM should detect
a “lean” condition (low oxygen sensor voltage). If this “lean” exhaust is not detected at this time, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code P1167 will set.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the following items:
• Fuel pressure - The system will go rich if pressure is too high. The ECM can compensate for some
increase. However, if fuel pressure is too high, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1167 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis .
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1167 D Fuel Supply System Rich During Deceleration Fuel Cutoff 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is more
than 550mV in deceleration fuel cutoff
mode. No fail-safe function.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2384 of 6020
6E–214 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
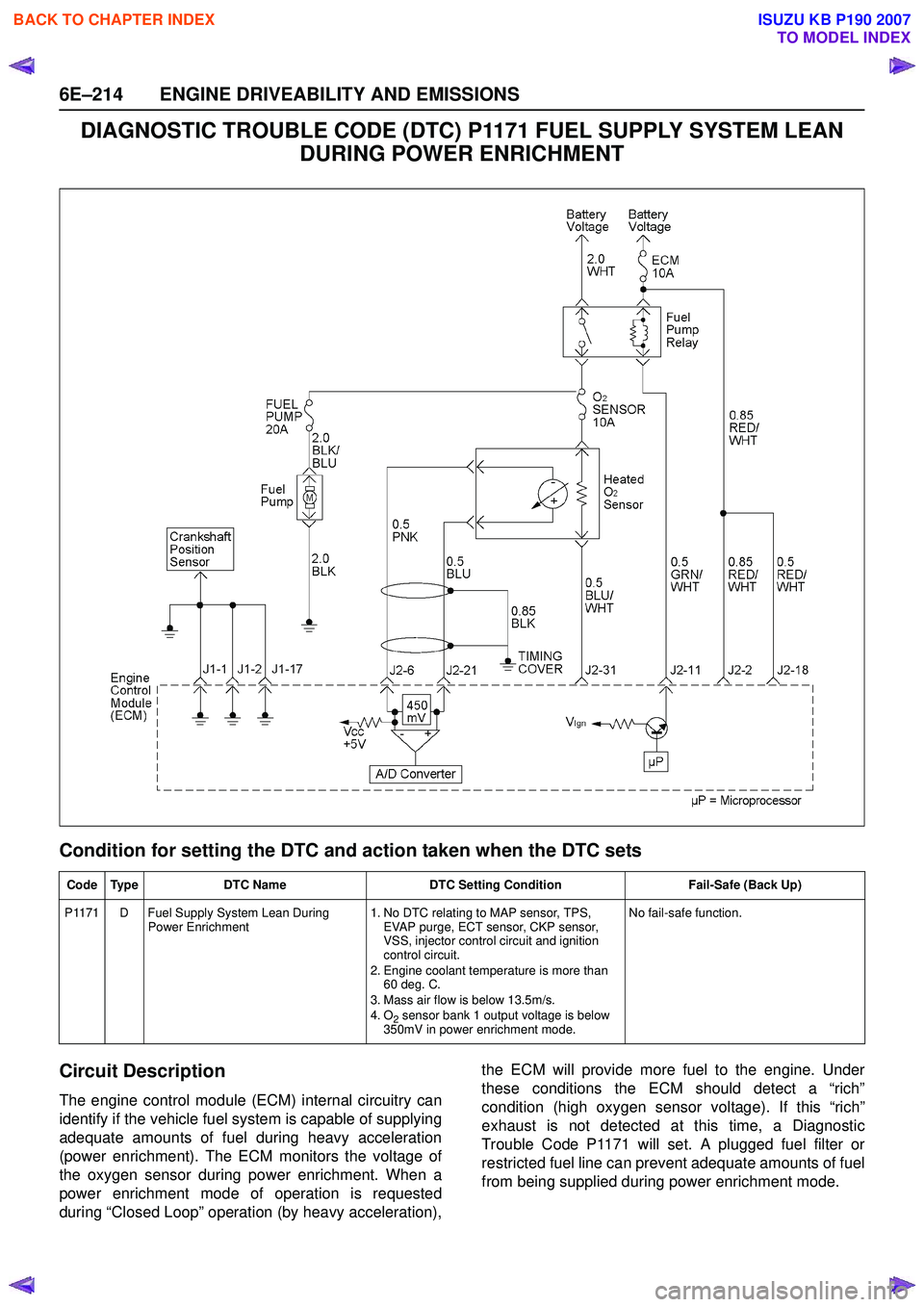
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1171 FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM LEAN DURING POWER ENRICHMENT
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) internal circuitry can
identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of supplying
adequate amounts of fuel during heavy acceleration
(power enrichment). The ECM monitors the voltage of
the oxygen sensor during power enrichment. When a
power enrichment mode of operation is requested
during “Closed Loop” operation (by heavy acceleration), the ECM will provide more fuel to the engine. Under
these conditions the ECM should detect a “rich”
condition (high oxygen sensor voltage). If this “rich”
exhaust is not detected at this time, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code P1171 will set. A plugged fuel filter or
restricted fuel line can prevent adequate amounts of fuel
from being supplied during power enrichment mode.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1171 D Fuel Supply System Lean During Power Enrichment 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 60 deg. C.
3. Mass air flow is below 13.5m/s.
4. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
350mV in power enrichment mode. No fail-safe function.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2385 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–215
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
• Heated oxygen sensor wiring - The sensor pigtail may be routed incorrectly and contacting the exhaust
system.
• Poor ECM to engine block ground.
• Fuel pressure - The system will go lean if pressure is too low. The ECM can compensate for some
decrease. However, if fuel pressure is too low, a
diagnostic Trouble Code P1171 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis .
• Lean injector(s) - Perform “Injector Balance Test.” • Vacuum leaks - Check for disconnected or damaged
vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake
manifold, throttle body, and PCV system.
• Exhaust leaks - An exhaust leak may cause outside air to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the
HO2S, causing the system to appear lean. Check for
exhaust leaks that may cause a false lean condition
to be indicated.
• Fuel contamination - Water, even in small amounts, can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can
cause a lean exhaust to be indicated, Excessive
alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition.
Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis for the procedure to
check for fuel contamination.
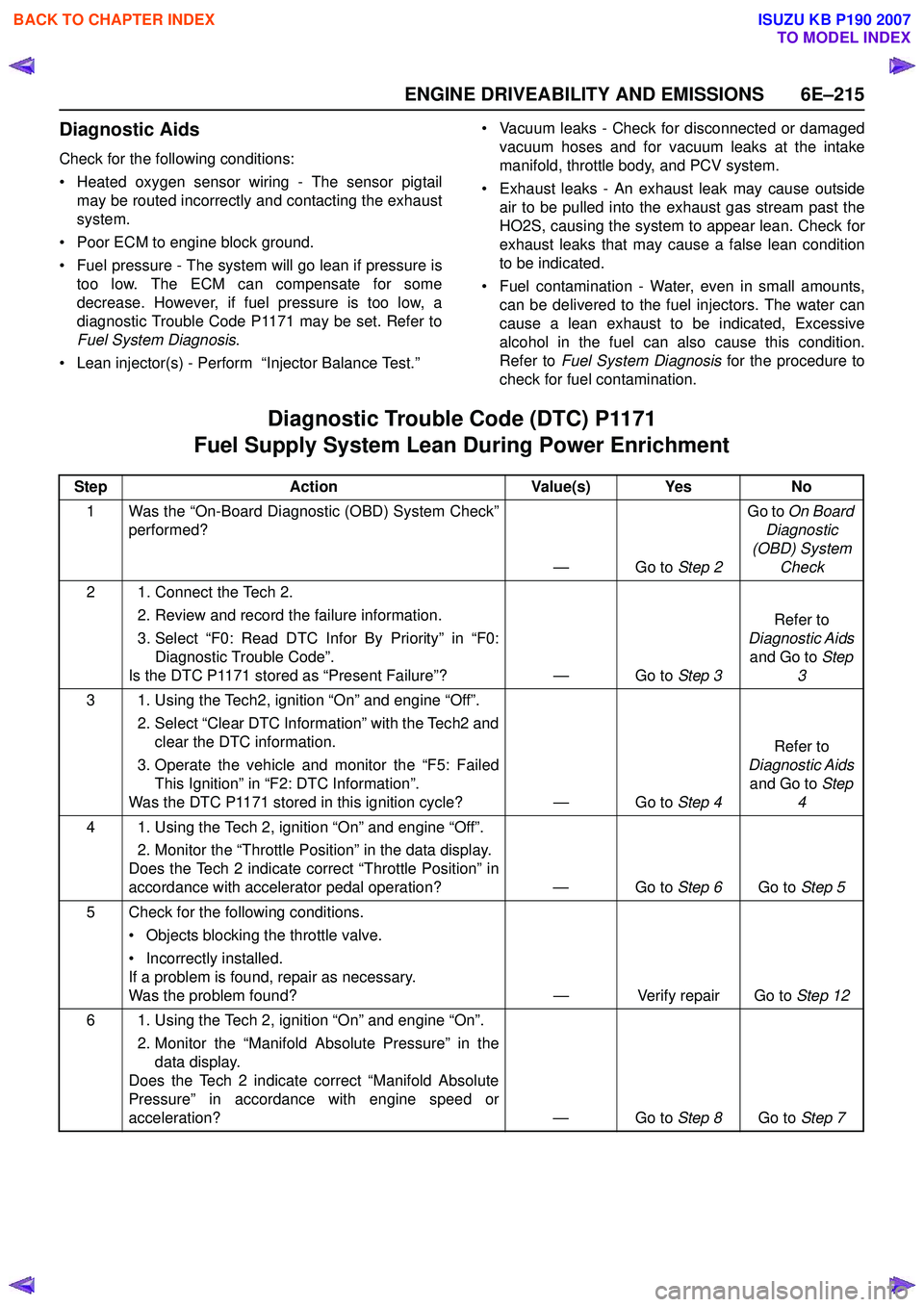
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1171
Fuel Supply System Lean During Power Enrichment
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P1171 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P1171 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Monitor the “Throttle Position” in the data display.
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct “Throttle Position” in
accordance with accelerator pedal operation? — Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5 Check for the following conditions. • Objects blocking the throttle valve.
• Incorrectly installed.
If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
6 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Manifold Absolute Pressure” in thedata display.
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct “Manifold Absolute
Pressure” in accordance with engine speed or
acceleration? — Go to Step 8Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2402 of 6020

6E–232 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Before using this section, perform the “On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” and verify all of the
following items:
• The engine control module (ECM) and malfunction indicator lamp (MIL = Check Engine Lamp) are
operating correctly.
• There are no Diagnostic Trouble Code(s) stored.
• Tech 2 data is within normal operating range. Refer to Typical Scan Data Values.
• Verify the customer complaint and locate the correct symptom in the table of contents. Perform the
procedure included in the symptom chart.
VISUAL/PHYSICAL CHECK
Several of the symptom procedures call for a careful
visual/physical check. This can lead to correcting a
problem without further checks and can save valuable
time. This check should include the following items:
• ECM grounds for cleanliness, tightness and proper location.
• Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper connection, shown on the “Emission Control System
Schematics”. Check thoroughly for any type of leak or
restriction.
• Air intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas.
• Air leaks at throttle body mounting area, manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor and intake manifold
sealing surfaces.
• Ignition wires for cracking, harness, and carbon tracking.
• Wiring for proper connections, pinches and cuts.
INTERMITTENT
Important: An intermittent problem may or may not turn
on the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) or store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code. Do NOT use the Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) charts for intermittent problems.
The fault must be present to locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are cased by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical
check for the following conditions.
• Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not fully seated in the connector (backed out).
• Improperly formed or damaged terminal.
• All connector terminals in the problem circuit should be carefully checked for proper contact tension.
• Poor terminal-to-wire connection. This requires removing the terminal form the connector body to
check.
• Ignition coils shorted to ground and arcing at ignition wires or plugs. • MIL (Check Engine Lamp) wire to ECM shorted to
ground.
• Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams.
Road test the vehicle with a Digital Multimeter
connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a fault in the circuit being monitored.
Using Tech 2 to help detect intermittent conditions. The
Tech 2 has several features that can be used to located
an intermittent condition.
An intermittent MIL (Check Engine Lamp) with no stored
Diagnostic Trouble Code may be caused by the
following:
• Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at ignition wires or plugs.
• MIL (Check Engine Lamp) wire to ECM short to ground.
• Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams.
Check for improper installation of electrical options such
as light, cellular phones, etc. Check all wires from ECM
to the ignition control module for poor connections.
Check for an open diode across the A/C compressor
clutch and check for other open diodes (refer to wiring
diagrams in Electrical Diagnosis).
If problem has not been found, refer to ECM connector
symptom tables.
• Check the “Broadcast Code” of the ECM, and compare it with the latest Isuzu service bulletins and/
or Isuzu EEPROM reprogramming equipment to
determine if an update to the ECM’s reprogrammable
memory has been released.
To check the “Broadcast Code”, connect the Tech 2,
then look for “ID info.” then select “Broadcast Code”.
This should display a 4 character code, such as “XBYA”
(example only).
This identifies the contents of the reprogrammable
software and calibration contained in the ECM.
If the “Broadcast Code” is not the most current
available, it is advisable to reprogram the ECM’s
EEPROM memory, which may either help identify a
hard-to find problem or may fix the problem.
The Service Programming System (SPS) will not allow
incorrect software programming or incorrect calibration
changes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2410 of 6020
6E–240 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
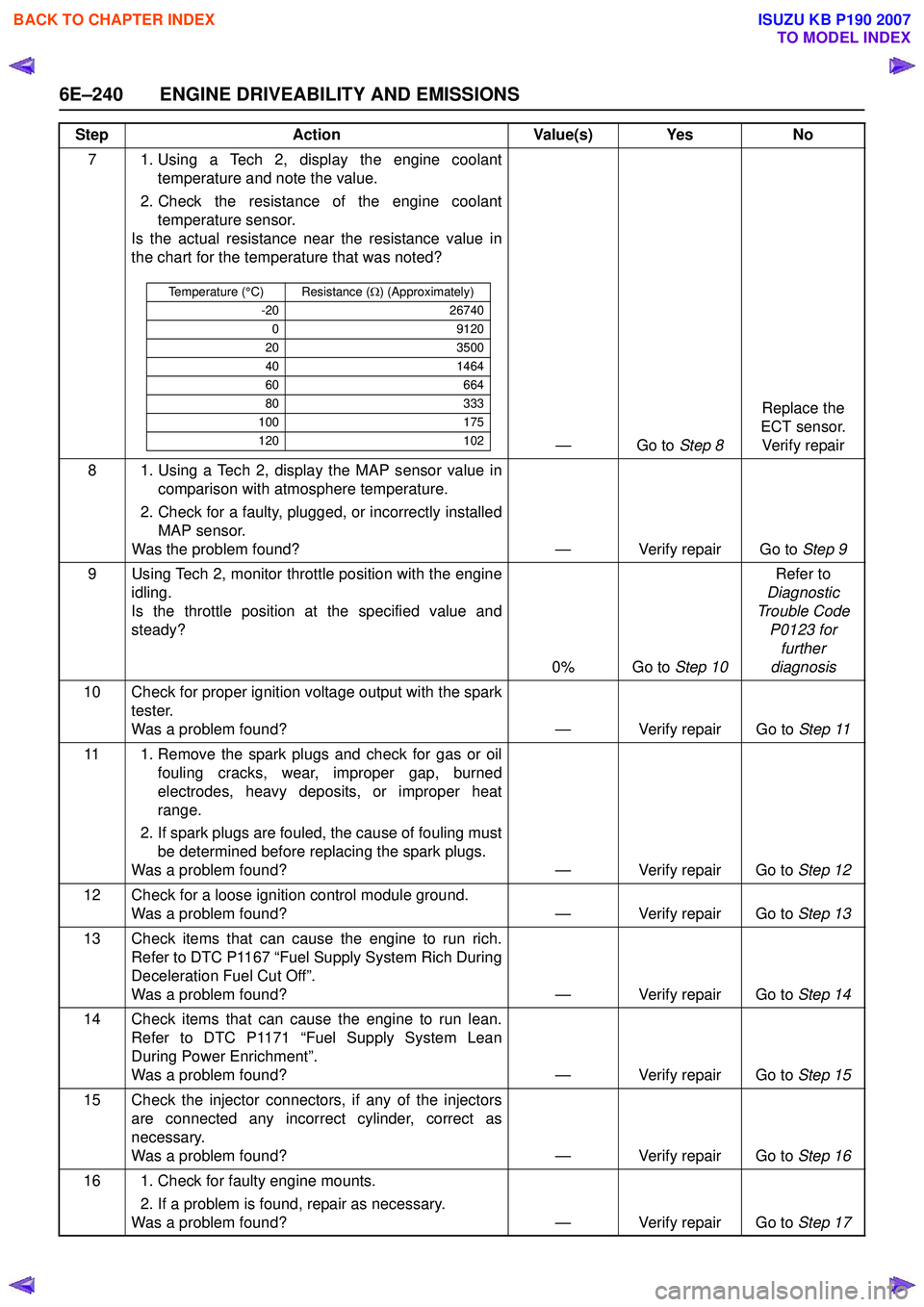
7 1. Using a Tech 2, display the engine coolanttemperature and note the value.
2. Check the resistance of the engine coolant temperature sensor.
Is the actual resistance near the resistance value in
the chart for the temperature that was noted?
—Go to Step 8Replace the
ECT sensor. Verify repair
8 1. Using a Tech 2, display the MAP sensor value in comparison with atmosphere temperature.
2. Check for a faulty, plugged, or incorrectly installed MAP sensor.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Using Tech 2, monitor throttle position with the engine idling.
Is the throttle position at the specified value and
steady?
0% Go to Step 10Refer to
Diagnostic
Trouble Code P0123 for further
diagnosis
10 Check for proper ignition voltage output with the spark tester.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat
range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Check for a loose ignition control module ground. Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check items that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer to DTC P1167 “Fuel Supply System Rich During
Deceleration Fuel Cut Off”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to DTC P1171 “Fuel Supply System Lean
During Power Enrichment”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Check the injector connectors, if any of the injectors are connected any incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Check for faulty engine mounts. 2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
Temperature (°C) Resistance (Ω) (Approximately)
-20 26740
0 9120
20 3500
40 1464
60 664
80 333
100 175
120 102
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2420 of 6020
6E–250 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
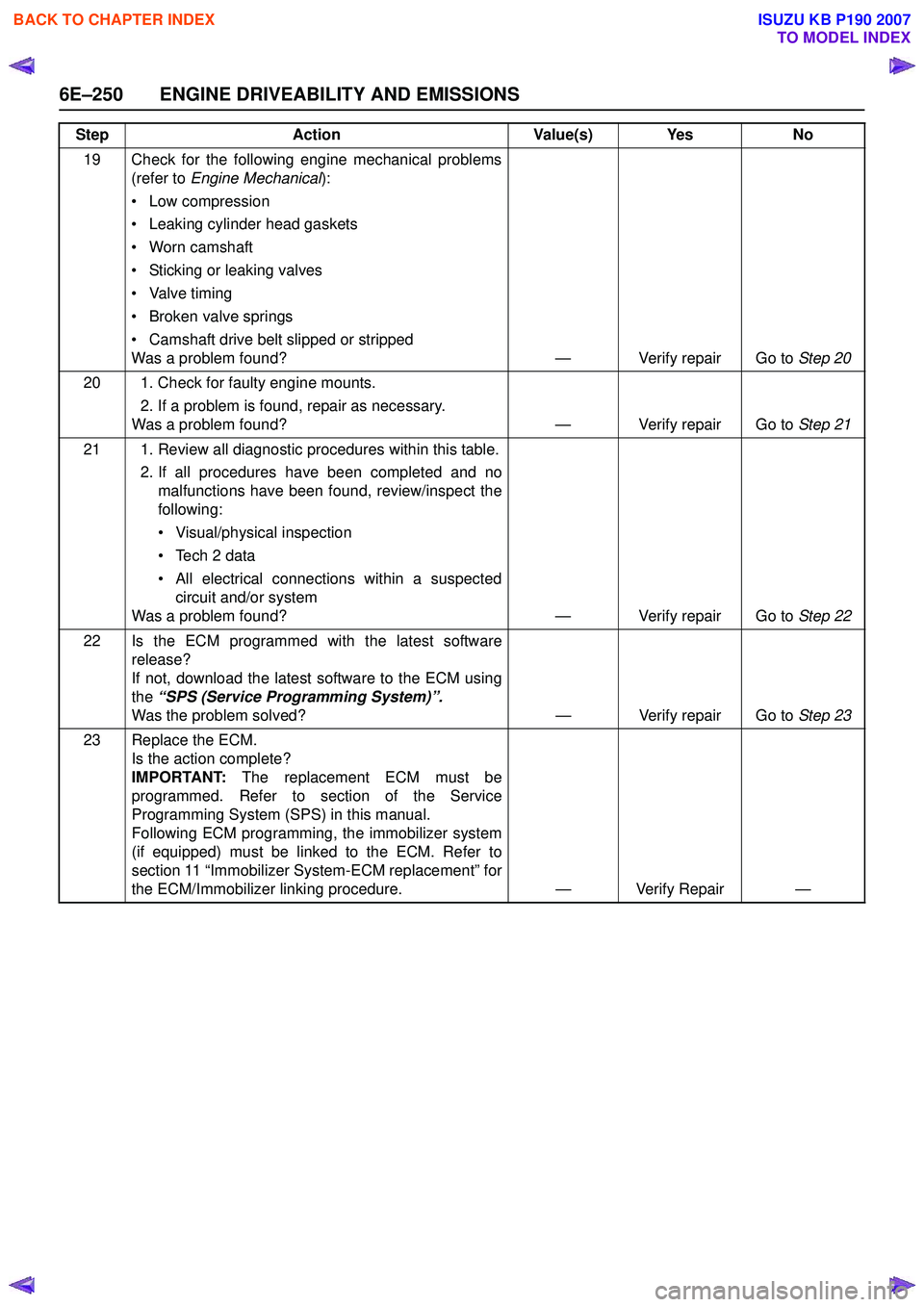
19 Check for the following engine mechanical problems(refer to Engine Mechanical ):
• Low compression
• Leaking cylinder head gaskets
• Worn camshaft
• Sticking or leaking valves
• Valve timing
• Broken valve springs
• Camshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
20 1. Check for faulty engine mounts. 2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 21
21 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table. 2. If all procedures have been completed and nomalfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
• Visual/physical inspection
• Tech 2 data
• All electrical connections within a suspected circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 22
22 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 23
23 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify Repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007