Page 325 of 364

CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
ACTIVE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)35C-15
C1863G and yaw rate sensor
power supply voltage
malfunction (low
voltage) OffOffIlluminatesIlluminates
U1073Bus-offIlluminatesIlluminatesIlluminatesIlluminates
U1100Engine-related CAN
Timeout errorOffOffIlluminatesIlluminates
U1104Steering wheel sensor
CAN Timeout errorOffOffIlluminatesIlluminates
U1105G and yaw rate sensor
time-outOffOffIlluminatesIlluminates
U1406Failure information on
engine-A-M/T-ECU
(related to engine)OffOffIlluminatesIlluminates
U1426Failure information on
engine-A-M/T-ECU
(related to engine)OffOffIlluminatesIlluminates
U1427Failure information on
engine-A-M/T-ECU
(related to engine)
U1428Failure information on
engine-A-M/T-ECU
(related to engine)
U1429Failure information on
engine-A-M/T-ECU
(related to engine)
U1430Failure information on
engine-A-M/T-ECU
(related to engine)
Diagnosis
code No.Item Brake warning
lampABS warning lamp Active stability
control system
(ASC) indicator
lamp ASC OFF indicator
lamp
Page 326 of 364

CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
ACTIVE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)35C-16
DIAGNOSIS CODE READING METHOD
There are 55 diagnosis items. The diagnosis code
can be checked using M.U.T.-III.
HOW TO ERASE DIAGNOSIS CODE
MEMORY
Diagnosis code can be erased using M.U.T.-III.
Data list output
The following items input to ASC-ECU can be read
using M.U.T.-III.
NOTE: For service data items, refer to Workshop
Manual.
Actuator test
By forcibly operating the actuator using M.U.T.-III,
the following operations can be performed.
•Forced ABS activation for each wheel
•Forced TCL (brake control) activation for each
wheel
•Forced TCL (engine control) activation
NOTE: .
•When ASC-ECU is disabled, the actuator test
cannot be performed.
•M.U.T.-III uses the ABS data list.
•For the actuator test specification, refer to Work-
shop Manual.
CALIBRATION
When the following operations are performed, the
steering wheel sensor needs to be calibrated using
the M.U.T.-III*.
•Front wheel alignment adjustment
•Steering wheel sensor replacement
NOTE: .
•M.U.T.-III uses the ABS data list.
•*: For calibration, refer to Workshop Manual.
Page 328 of 364
DESCRIPTION OF CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
ACTIVE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)35C-18
When the brake fluid pressure is increased at ABS deactivation (normal brake
control)/ABS activation (Example: When the front-left/rear-right wheel system
pressure is increased)
AC600863 AB
MP
Master cylinder
Cut valve
Motor Inlet valve (RR)
Outlet valve
(RR)
Wheel cylinder (RR) Hydraulic unit
Pressure sensor
Suction valve
Pump Inlet valve
(FL)
Outlet valve (FL)
Wheel cylinder (FL)
The fluid p r essure ge nerated from the maste r cylin-
de r is supplied to each wheel cylinder through the cut
valve an
d outlet valve (FL/RR).
VA L VE CONDITION
ItemPower statusOpen/Close
Suction valveOFFClosed
Cut valveOFFOpen
Inlet valve (FL)OFFOpen
Inlet valve (RR)OFFOpen
Outlet valve (FL)OFFClosed
Outlet valve (RR)OFFClosed
Page 329 of 364
DESCRIPTION OF CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
ACTIVE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)35C-19
When the brake fluid pressure is held by the ABS control/stability control (Example:
When the front-left/rear-right whee l system pressure is held)
AC600863
AC
MP
Master cylinder
Cut valve
Motor Inlet valve (RR)
Outlet valve
(RR)
Wheel cylinder (RR) Hydraulic unit
Pressure sensor
Suction valve
Pump Inlet valve
(FL)
Outlet valve (FL)
Wheel cylinder (FL)
By closing the inlet va lve (FL/RR) and o u tle t valve
(FL/RR), the br
ake f l uid pressure in the wh eel cylin
-
der can be main t a ined.
VA L VE CONDITION
ItemPower statusOpen/Close
Suction valveOFFClosed
Cut valveOFFOpen
Inlet valve (FL)ONClosed
Inlet valve (RR)ONClosed
Outlet valve (FL)OFFClosed
Outlet valve (RR)OFFClosed
Page 330 of 364
DESCRIPTION OF CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
ACTIVE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM (ASC)35C-20
When the brake fluid pressure is reduced by the ABS control/stability control
(Example: Front-left/rear-right wheel system)
AC600863 AD
MP
Master cylinder
Cut valve
Motor Inlet valve (RR)
Outlet valve
(RR)
Wheel cylinder (RR) Hydraulic unit
Pressure sensor
Suction valve
Pump Inlet valve
(FL)
Outlet valve (FL)
Wheel cylinder (FL)
The out let valve (FL/RR) is ope ned to drive the
pump
, and th e brake fluid in the wh eel cylinde r is
returned
to the master cylinder so tha t the fluid level
in the
wheel cylinde r is reduced.
VA L VE CONDITION
ItemPower statusOpen/Close
Suction valveOFFClosed
Cut valveOFFOpen
Inlet valve (FL)ONClosed
Inlet valve (RR)ONClosed
Outlet valve (FL)ONOpen
Outlet valve (RR)ONOpen
Page 342 of 364

GENERAL INFORMATION
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
M2350000100848
FEATURES
Brake system with high reliability and durability have
achieved distinguished braking performance.
BRAKING PERFORMANCE
•Brake booster with 9-inch variable amplification
ratio mechanism by which greater braking force
can be obtained with a less pedal pressure has
been installed (with brake assist function).
•14-inch disc brake is installed on the front
wheels.
•15-inch disc brake is installed on the front
wheels.
•8-inch leading trailing type drum brake is installed
on the rear wheels.
•14-inch disc brake is installed on the rear wheels.
STABILITY
•4-wheel anti-lock braking system (4ABS) is
adopted to prevent slipping caused by the vehicle
wheels locking up, in order to maintain appropri
-
ate braking distance, and also to maintain vehicle
stability and steering function.
•Electronic brake-force distribution (EBD) is
adopted to maintain the maximum amount of rear
braking force even when the vehicle's load is var
-
ied.
•Diagonal split (X-type) brake fluid line is adopted.
•Ventilated discs have been adopted to front
brakes to improve anti-fading performance.
•A brake pedal retraction suppression structure
that restrains the retraction of the brake pedal
and reduces the shock to the feet of the driver in
the event of a frontal collision has been adopted.
SERVICEABILITY
•Diagnosis function is adopted for the ABS system
in order to make inspection easier.
•For the front disc brakes, brake disc separated
front hub is adapted to make removal and instal
-
lation easier.
•ABS-ECU and hydraulic unit have been inte-
grated to make them more compact and lighter.
Page 343 of 364
GENERAL INFORMATION
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-3
CONFIGURATION DIAGRAM
AC601653
Brake booster (with variable
boosting mechanism)
Hydraulic unit
(Integrated with ABS-ECU)
Master cylinder
Front disc brake Rear drum brake
Brake booster (with variable
boosting mechanism)
Hydraulic unit
(Integrated with ABS-ECU)
Master cylinder
Front disc brake Rear disc brake
AB
Page 351 of 364
CVT
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)23-3
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
EEPROM
M2231012000024
Because EEPROM has been used, even if the bat-
tery terminals or control unit connectors are discon-
nected, the necessary learned values are stored in
the engine-CVT-ECU to prevent a loss of shift qual
-
ity. (Initialisation is available by M.U.T.-III).
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN)
COMMUNICATION
M2231017000018
CAN* communication has been adopted for commu-
nication with other ECUs in order to decrease the
number of wires and ensure information transmis
-
sion. For CVT control, the engine-CVT-ECU receives
the following signals.
CAN COMMUNICATION INPUT SIGNAL TABLE
Input signalTransmitter ECU
Average vehicle speed signal from drive wheelsABS-ECU
Motor current signalEPS-ECU
EPS warning lamp illumination request signal
Compressor signalMeter and A/C-ECU
NOTE: *: For more information about CAN (Control-
ler Area Network), refer to GROUP 54C P.54C-2.
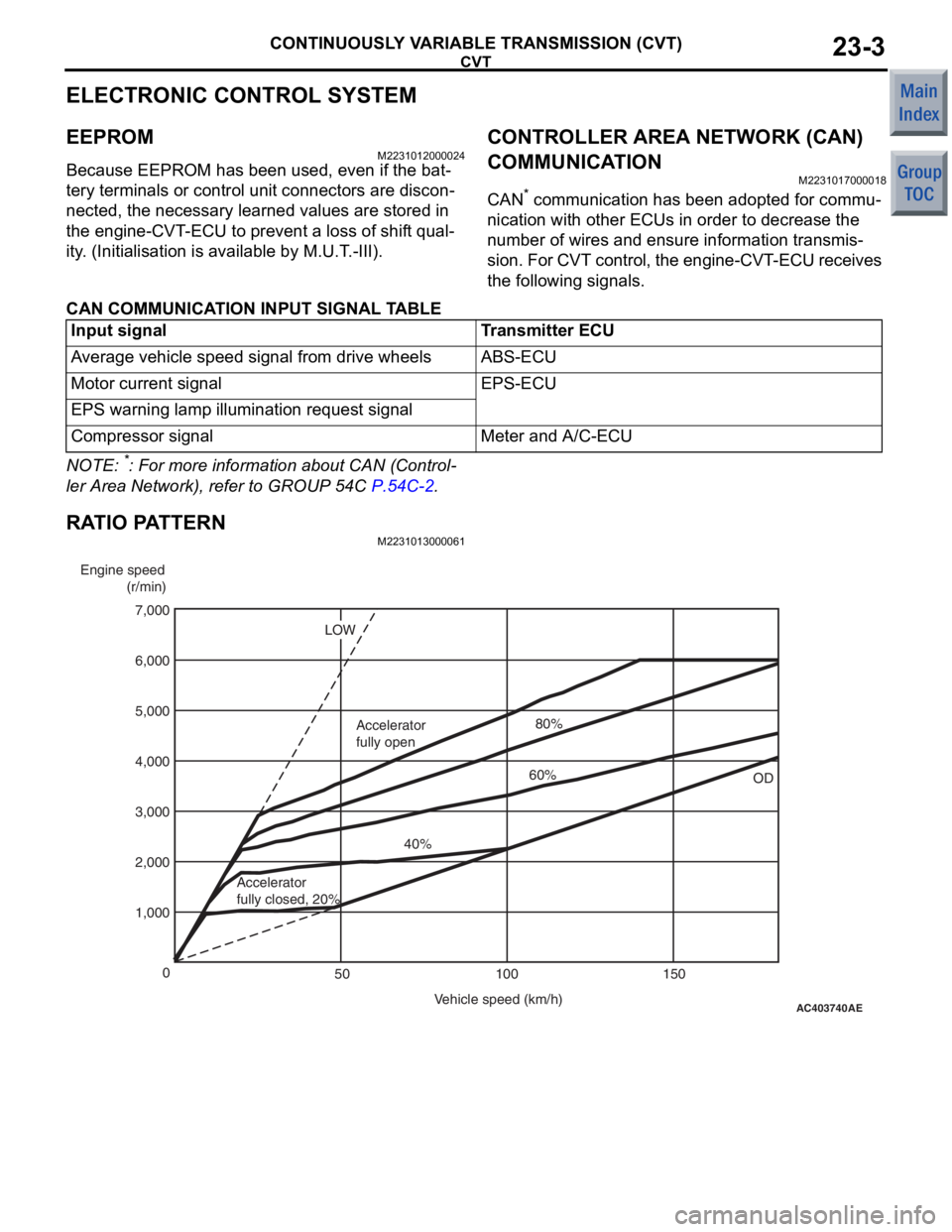
RATIO PATTERN
M2231013000061
AC403740
AE
Engine speed
(r/min)
Vehicle speed (km/h)
0
100 150
50
1,000 2,000 4,000
3,000 5,000
7,000
6,000
OD
LOW
Accelerator
fully closed, 20% 40%
Accelerator
fully open
60%80%