2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1747 of 2305

²Increased service life and reliability.
²Lower maintenance costs.
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The transmission can be generically identified
visually by the presence of a round 13-way connector
located near the front corner of the transmission oil
pan, on the right side. Specific transmission informa-
tion can be found stamped into a pad on the left side
of the transmission, above the oil pan rail.
TRANSMISSION GEAR RATIOS
The gear ratios for the NAG1 automatic transmis-
sion are as follows:
1st Gear............................3.59:1
2nd Gear............................2.19:1
3rd Gear............................1.41:1
4th Gear............................1.00:1
5th Gear............................0.83:1
Reverse.............................3.16:1
TRANSMISSION HOUSING
The converter housing and transmission are made
from a light alloy. These are bolted together and cen-
tered via the outer multi-disc carrier of multi-disc
holding clutch, B1. A coated intermediate plate pro-
vides the sealing. The oil pump and the outer multi-
disc carrier of the multi-disc holding clutch, B1, are
bolted to the converter housing. The stator shaft is
pressed into it and prevented from rotating by
splines. The electrohydraulic unit is bolted to the
transmission housing from underneath. A sheet
metal steel oil pan forms the closure.
MECHANICAL SECTION
The mechanical section consists of a input shaft,
output shaft, a sun gear shaft, and three planetary
gear sets which are coupled to each other. The plan-
etary gear sets each have four planetary pinion
gears. The oil pressure for the torque converter
lock-up clutch and clutch K2 is supplied through
bores in the input shaft. The oil pressure to clutch
K3 is transmitted through the output shaft. The
lubricating oil is distributed through additional bores
in both shafts. All the bearing points of the gear sets,
as well as the freewheeling clutches and actuators,
are supplied with lubricating oil. The parking lock
gear is connected to the output shaft via splines.
Freewheeling clutches F1 and F2 are used to opti-
mize the shifts. The front freewheel, F1, is supported
on the extension of the stator shaft on the transmis-
sion side and, in the locking direction, connects the
sun gear of the front planetary gear set to the trans-
mission housing. In the locking direction, the rear
freewheeling clutch, F2, connects the sun gear of the
center planetary gear set to the sun gear of the rear
planetary gear set.
ELECTROHYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
The electrohydraulic control unit comprises the
shift plate made from light alloy for the hydraulic
control and an electrical control unit. The electrical
control unit comprises of a supporting body made of
plastic, into which the electrical components are
assembled. The supporting body is mounted on the
shift plate and screwed to it.
Strip conductors inserted into the supporting body
make the connection between the electrical compo-
nents and a plug connector. The connection to the
wiring harness on the vehicle and the transmission
control module (TCM) is produced via this 13-pin
plug connector with a bayonet lock.
SHIFT GROUPS
The hydraulic control components (including actua-
tors) which are responsible for the pressure distribu-
tion before, during, and after a gear change are
described as a shift group. Each shift group contains
a command valve, a holding pressure shift valve, a
shift pressure shift valve, overlap regulating valve,
and a solenoid.
The hydraulic system contains three shift groups:
1-2/4-5, 2-3, and 3-4. Each shift group can also be
described as being in one of two possible states. The
active shift group is described as being in the shift
phase when it is actively engaging/disengaging a
clutch combination. The 1-2/4-5 shift group control
the B1 and K1 clutches. The 2-3 shift group controls
the K2 and K3 clutches. The 3-4 shift group controls
the K3 and B2 clutches.
OPERATION
The transmission control is divided into the elec-
tronic and hydraulic transmission control functions.
While the electronic transmission control is responsi-
ble for gear selection and for matching the pressures
to the torque to be transmitted, the transmission's
power supply control occurs via hydraulic elements
in the electrohydraulic control module. The oil supply
to the hydraulic elements, such as the hydrodynamic
torque converter, the shift elements and the hydrau-
lic transmission control, is provided by way of an oil
pump connected with the torque converter.
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) allows for
the precise adaptation of pressures to the correspond-
ing operating conditions and to the engine output
during the gearshift phase, resulting in a noticeable
improvement in shift quality. The engine speed limit
can be reached in the individual gears at full throttle
and kickdown. The shift range can be changed in the
forward gears while driving, but the TCM employs a
downshift safeguard to prevent over-revving the
engine. The system offers the additional advantage of
21 - 4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1748 of 2305

flexible adaptation to different vehicle and engine
variants.
EMERGENCY RUNNING FUNCTION
In order to ensure a safe driving state and to pre-
vent damage to the automatic transmission, the TCM
control module switches to limp-home mode in the
event of critical faults. A diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) assigned to the fault is stored in memory. All
solenoid and regulating valves are thus de-energized.
The net effect is:
²The last engaged gear remains engaged.
²The modulating pressure and shift pressures
rise to the maximum levels.
²The torque converter lockup clutch is deacti-
vated.
In order to preserve the operability of the vehicle
to some extent, the hydraulic control can be used to
engage 2nd gear or reverse using the following pro-
cedure:²Stop the vehicle.
²Move selector lever to ªPº.
²Switch off engine.
²Wait at least 10 seconds.
²Start engine.
²Move selector lever to D: 2nd gear.
²Move selector lever to R: Reverse gear.
The limp-home function remains active until the
DTC is rectified or the stored DTC is erased with the
appropriate scan tool. Sporadic faults can be reset
via ignition OFF/ON.
CLUTCH APPLICATION
Refer to CLUTCH APPLICATION for which shift
elements are applied in each gear position.
CLUTCH APPLICATION
GEAR RATIO B1 B2 B3 K1 K2 K3 F1 F2
1 3.59 X* X X* X X
2 2.19 X X X* X
3 1.41 X X X
4 1.00 X X X
5 0.83 X X X X*
N N/A X X
R 3.16 X* X X X
R - Limp
In1.93 X X X
* = The shift components required during coast.
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21 - 5
Page 1749 of 2305

FIRST GEAR POWERFLOW
Fig. 2 First Gear Powerflow
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER LOCK-UP CLUTCH 14 - CENTER PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER TURBINE 15 - REAR PLANETARY CARRIER
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER IMPELLER 16 - TORQUE CONVERTER STATOR
4 - HOLDING CLUTCH B1 17 - FRONT PLANETARY PINION GEARS
5 - HOLDING CLUTCH B3 18 - CENTER PLANETARY PINION GEARS
6 - HOLDING CLUTCH B2 19 - REAR PLANETARY PINION GEARS
7 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 20 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F1
8 - FRONT PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 21 - FRONT PLANETARY SUN GEAR
9 - DRIVING CLUTCH K2 22 - CENTER PLANETARY SUN GEAR
10 - CENTER PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 23 - REAR PLANETARY SUN GEAR
11 - REAR PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 24 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F2
12 - DRIVING CLUTCH K3 25 - INPUT SHAFT
13 - FRONT PLANETARY CARRIER 26 - OUTPUT SHAFT
A - ENGINE SPEED D - SECOND GEAR RATIO
B - TRANSMISSION INPUT SPEED E - THIRD GEAR RATIO
C - FIRST GEAR RATIO F - FIXED PARTS
21 - 6 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1750 of 2305

Torque from the torque converter is increased via
the input shaft (25) and all three planetary gearsets
and transferred to the output shaft (26). (Fig. 2) (Fig.
3)
Front Planetary Gear Set
The annulus gear (8) is driven by the input shaft
(25). The sun gear (21) is held against the housing by
the locked freewheel F1 (20) during acceleration and
via the engaged multiple-disc holding clutch B1 (4)
during deceleration. The planetary pinion gears (17)
turn on the fixed sun gear (21) and increase the
torque from the annulus gear (8) to the planetary
carrier (13). The planetary carrier (13) moves at a
reduced speed in the running direction of the engine.Rear Planetary Gear Set
The annulus gear (11) turns at a reduced speed
due to the mechanical connection to the front plane-
tary carrier (15). The sun gear (23) is held against
the housing by the engaged multiple-disc holding
clutch B2 (6), by the locked freewheel F2 (24) during
acceleration and by the engaged multiple-disc clutch
K3 (12) during deceleration. The planetary gears (19)
turn on the fixed sun gear (23) and increase the
torque from the annulus gear (11) to the planetary
carrier (15). The planetary carrier (15) moves at a
reduced speed in the running direction of the engine.
Center Planetary Gear Set
The annulus gear (10) is driven at the same speed
as the rear planetary carrier (15) as a result of a
Fig. 3 First Gear Powerflow
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER LOCK-UP CLUTCH 14 - CENTER PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER TURBINE 15 - REAR PLANETARY CARRIER
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER IMPELLER 16 - TORQUE CONVERTER STATOR
4 - HOLDING CLUTCH B1 17 - FRONT PLANETARY PINION GEARS
5 - HOLDING CLUTCH B3 18 - CENTER PLANETARY PINION GEARS
6 - HOLDING CLUTCH B2 19 - REAR PLANETARY PINION GEARS
7 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 20 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F1
8 - FRONT PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 21 - FRONT PLANETARY SUN GEAR
9 - DRIVING CLUTCH K2 22 - CENTER PLANETARY SUN GEAR
10 - CENTER PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 23 - REAR PLANETARY SUN GEAR
11 - REAR PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 24 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F2
12 - DRIVING CLUTCH K3 25 - INPUT SHAFT
13 - FRONT PLANETARY CARRIER 26 - OUTPUT SHAFT
A - ENGINE SPEED D - SECOND GEAR RATIO
B - TRANSMISSION INPUT SPEED E - THIRD GEAR RATIO
C - FIRST GEAR RATIO F - FIXED PARTS
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21 - 7
Page 1752 of 2305
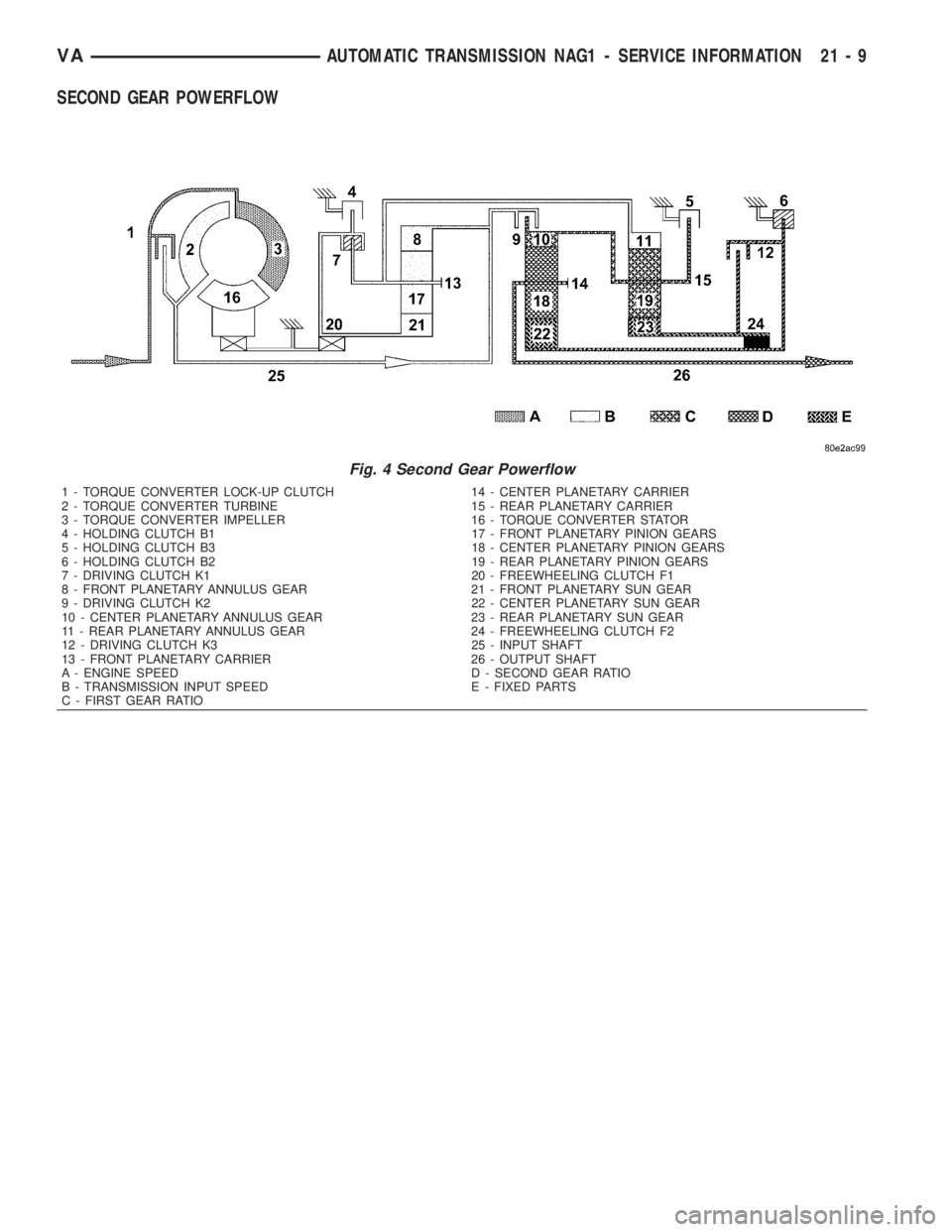
SECOND GEAR POWERFLOW
Fig. 4 Second Gear Powerflow
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER LOCK-UP CLUTCH 14 - CENTER PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER TURBINE 15 - REAR PLANETARY CARRIER
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER IMPELLER 16 - TORQUE CONVERTER STATOR
4 - HOLDING CLUTCH B1 17 - FRONT PLANETARY PINION GEARS
5 - HOLDING CLUTCH B3 18 - CENTER PLANETARY PINION GEARS
6 - HOLDING CLUTCH B2 19 - REAR PLANETARY PINION GEARS
7 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 20 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F1
8 - FRONT PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 21 - FRONT PLANETARY SUN GEAR
9 - DRIVING CLUTCH K2 22 - CENTER PLANETARY SUN GEAR
10 - CENTER PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 23 - REAR PLANETARY SUN GEAR
11 - REAR PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 24 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F2
12 - DRIVING CLUTCH K3 25 - INPUT SHAFT
13 - FRONT PLANETARY CARRIER 26 - OUTPUT SHAFT
A - ENGINE SPEED D - SECOND GEAR RATIO
B - TRANSMISSION INPUT SPEED E - FIXED PARTS
C - FIRST GEAR RATIO
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21 - 9
Page 1753 of 2305

Torque from the torque converter is increased via
the input shaft (25) and the center and rear plane-
tary gearset and transferred to the output shaft (26).
(Fig. 4) (Fig. 5)
Front Planetary Gear Set
The planetary carrier (13) and sun gear (21) are
connected via the engaged multiple-disc clutch K1
(7). The planetary gearset is therefore blocked and
turns as a closed unit at the input speed due to the
mechanical connection of the annulus gear (8) and
input shaft.
Rear Planetary Gear Set
The annulus gear (11) turns at the input speed as
a result of the mechanical connection to the front
planetary carrier (13). The sun gear (23) is heldagainst the housing by the engaged multiple-disc
holding clutch B2 (6), by the locked freewheel F2 (24)
during acceleration and by the engaged multiple-disc
clutch K3 (12) during deceleration. The planetary
pinion gears (19) turn on the fixed sun gear (23) and
increase the torque from the annulus gear (11) to the
planetary carrier (15). The planetary carrier (15)
moves at a reduced speed in the running direction of
the engine.
Center Planetary Gear Set
The annulus gear (10) is driven at the same speed
as the rear planetary carrier (15) as a result of a
mechanical connection. The sun gear (22) is held
against the housing by the multiple-disc holding
clutch B2 (6). The planetary pinion gears (18) turn
on the fixed sun gear (22) and increase the torque
Fig. 5 Second Gear Powerflow
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER LOCK-UP CLUTCH 14 - CENTER PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER TURBINE 15 - REAR PLANETARY CARRIER
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER IMPELLER 16 - TORQUE CONVERTER STATOR
4 - HOLDING CLUTCH B1 17 - FRONT PLANETARY PINION GEARS
5 - HOLDING CLUTCH B3 18 - CENTER PLANETARY PINION GEARS
6 - HOLDING CLUTCH B2 19 - REAR PLANETARY PINION GEARS
7 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 20 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F1
8 - FRONT PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 21 - FRONT PLANETARY SUN GEAR
9 - DRIVING CLUTCH K2 22 - CENTER PLANETARY SUN GEAR
10 - CENTER PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 23 - REAR PLANETARY SUN GEAR
11 - REAR PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 24 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F2
12 - DRIVING CLUTCH K3 25 - INPUT SHAFT
13 - FRONT PLANETARY CARRIER 26 - OUTPUT SHAFT
A - ENGINE SPEED D - SECOND GEAR RATIO
B - TRANSMISSION INPUT SPEED E - FIXED PARTS
C - FIRST GEAR RATIO
21 - 10 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1755 of 2305

THIRD GEAR POWERFLOW
Fig. 6 Third Gear Powerflow
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER LOCK-UP CLUTCH 14 - CENTER PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER TURBINE 15 - REAR PLANETARY CARRIER
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER IMPELLER 16 - TORQUE CONVERTER STATOR
4 - HOLDING CLUTCH B1 17 - FRONT PLANETARY PINION GEARS
5 - HOLDING CLUTCH B3 18 - CENTER PLANETARY PINION GEARS
6 - HOLDING CLUTCH B2 19 - REAR PLANETARY PINION GEARS
7 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 20 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F1
8 - FRONT PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 21 - FRONT PLANETARY SUN GEAR
9 - DRIVING CLUTCH K2 22 - CENTER PLANETARY SUN GEAR
10 - CENTER PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 23 - REAR PLANETARY SUN GEAR
11 - REAR PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 24 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F2
12 - DRIVING CLUTCH K3 25 - INPUT SHAFT
13 - FRONT PLANETARY CARRIER 26 - OUTPUT SHAFT
A - ENGINE SPEED C - FIRST GEAR RATIO
B - TRANSMISSION INPUT SPEED D - FIXED PARTS
21 - 12 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1756 of 2305

Torque from the torque converter is increased via
the input shaft (25) and the center planetary gearset
and transferred to the output shaft (26). (Fig. 6) (Fig.
7)
Front Planetary Gear Set
The planetary carrier (13) and sun gear (21) are
connected via the engaged multiple-disc clutch K1
(7). The planetary gearset is therefore locked and
turns as a closed unit at the input speed due to the
mechanical connection of the annulus gear (8) and
input shaft (25).
Rear Planetary Gear Set
The multiple-disc clutch K2 (9) is engaged and
transfers the input speed of the input shaft (25) to
the planetary carrier (15) via the annulus gear (10).The annulus gear (11) turns in the same way as the
planetary carrier (15) due to the mechanical connec-
tion with the locked front planetary gearset. This
planetary gearset is therefore locked and turns as a
closed unit.
Center Planetary Gear Set
The annulus gear (10) turns at the input speed as
a result of the engaged multiple-disc clutch K2 (9).
The sun gear (22) is held against the housing by the
multiple-disc holding clutch B2 (6). The planetary
pinion gears (18) turn on the fixed sun gear (22) and
increase the torque from the annulus gear (10) to the
planetary carrier (14). The output shaft (26) con-
nected to the planetary carrier (14) turns at a
reduced speed in the running direction of the engine.
Fig. 7 Third Gear Powerflow
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER LOCK-UP CLUTCH 14 - CENTER PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER TURBINE 15 - REAR PLANETARY CARRIER
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER IMPELLER 16 - TORQUE CONVERTER STATOR
4 - HOLDING CLUTCH B1 17 - FRONT PLANETARY PINION GEARS
5 - HOLDING CLUTCH B3 18 - CENTER PLANETARY PINION GEARS
6 - HOLDING CLUTCH B2 19 - REAR PLANETARY PINION GEARS
7 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 20 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F1
8 - FRONT PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 21 - FRONT PLANETARY SUN GEAR
9 - DRIVING CLUTCH K2 22 - CENTER PLANETARY SUN GEAR
10 - CENTER PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 23 - REAR PLANETARY SUN GEAR
11 - REAR PLANETARY ANNULUS GEAR 24 - FREEWHEELING CLUTCH F2
12 - DRIVING CLUTCH K3 25 - INPUT SHAFT
13 - FRONT PLANETARY CARRIER 26 - OUTPUT SHAFT
A - ENGINE SPEED C - FIRST GEAR RATIO
B - TRANSMISSION INPUT SPEED D - FIXED PARTS
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21 - 13