2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1788 of 2305

(12) Remove the torque converter bolts.
(a) Remove the steering gear (1) (Fig. 34) from
the chassis crossmember.
(b) Lower the steering gear (1) (Fig. 34) down-
wards.
(c) Remove the plastic torque converter access
cover (1) (Fig. 35) at back of engine flange.
(d) Rotate engine by hand until bolts (2) (Fig.
35) are in front of opening. Rotate engine forwards
at crankshaft.
(e) To remove bolts, position a ratchet with long
extension and joint nut as shown (Fig. 36).
(f) Remove the two bolts (2) (Fig. 35) at each of
the three locations at circumference of driving
plate.
(13) Remove torque converter drain plug and drain
automatic transmission oil into a clean container. Re-
install the drain plug and torque the plug to 14 N´m
(130 in.lbs.).
(14) Support engine. Insert wooden block between
oil pan and front chassis crossmember beam.
(15) Remove vent hose bracket and tie back to one
side.
Fig. 33 Shift Cable at Transmission
1 - SHIFT CABLE
2 - TRANSMISSION SHIFT LEVER
Fig. 34 Steering Gear
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - BRACKET
Fig. 35 Torque Converter Access Cover
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER ACCESS COVER
2 - BOLT
Fig. 36 Torque Converter Bolts Access
1 - BOLT
2 - STABILIZER BAR
3 - REINFORCEMENT PLATE
4 - OPENING
5 - CHASSIS CROSSMEMBER
6 - STEERING GEAR
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21 - 45
Page 1805 of 2305

(14) Install the transmission electrical connector
(2) (Fig. 71) from transmission and hang to the side.
Turn sealing ring (3) clockwise and connect plug con-
nection (2).
(15) Install the shift cable (Fig. 72) to the trans-
mission.
(a) Push shift cable onto the transmission shift
lever ball socket.
(b) Latch ball socket latch of cable.
(c) Clip shift cable retainer into retainer
bracket.(16) Install the cooler lines to the transmission.
(a) Install the brackets for the oil cooler feed and
return lines (1) (Fig. 73) onto the engine oil pan
flange. Detail shows right side of motor. Position is
mirrored for the left side of engine.
(b) Attach the bracket for the cable retainer (4)
(Fig. 74) to the threaded shank of a engine oil pan
bolt (5).
(c) Install the bolts to hold the oil cooler lines (6)
to the left (Fig. 75) and right sides of transmission.
Torque the bolts to 34 N´m (25 ft.lbs.).
Fig. 70 Install Steering Gear
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - BRACKET
Fig. 71 Transmission Electrical Connector and
Cooler Line
1 - COOLER LINE
2 - TRANSMISSION ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - SEALING RING
Fig. 72 Shift Cable at Transmission
1 - SHIFT CABLE
2 - TRANSMISSION SHIFT LEVER
Fig. 73 Cooler Line Supports
1 - COOLER LINES
21 - 62 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1830 of 2305
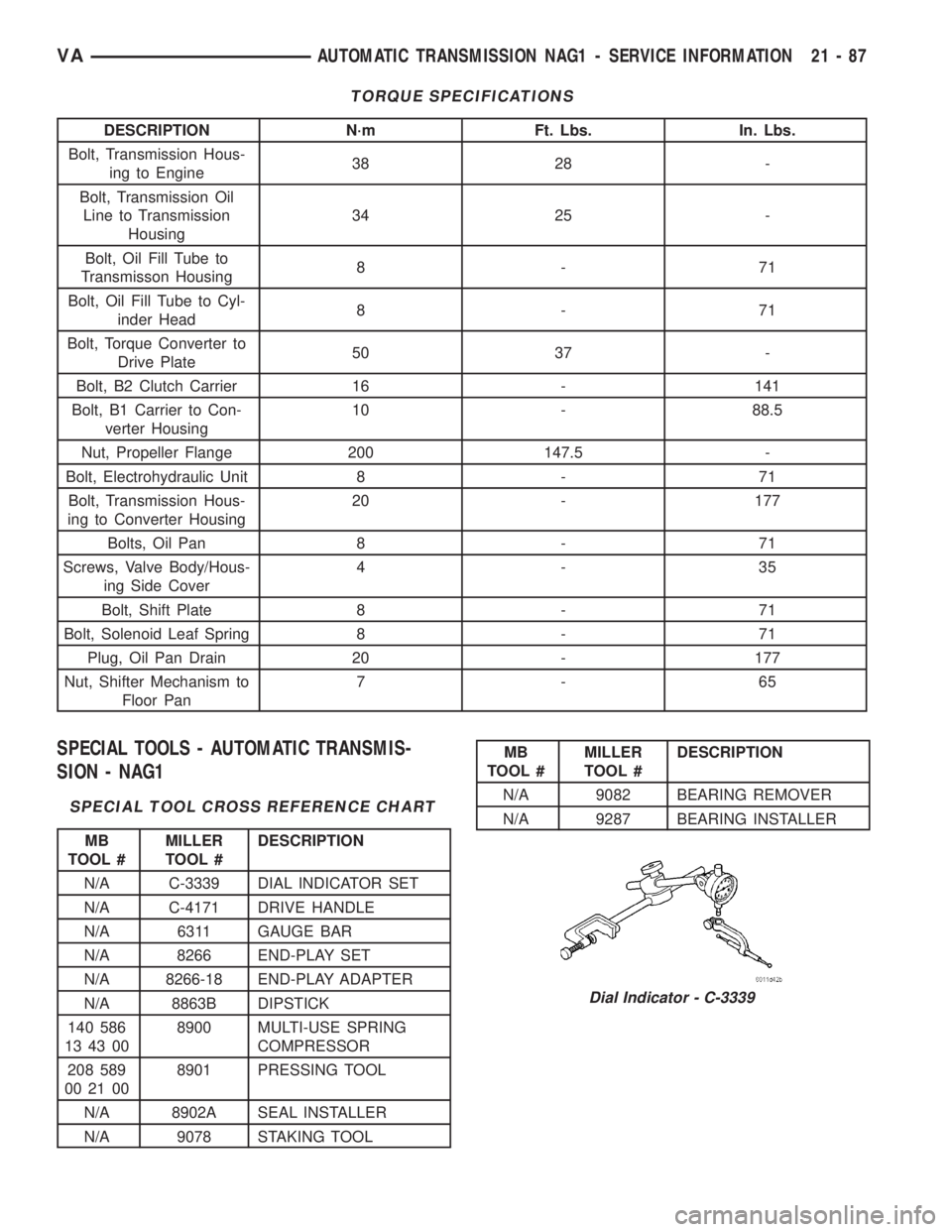
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, Transmission Hous-
ing to Engine38 28 -
Bolt, Transmission Oil
Line to Transmission
Housing34 25 -
Bolt, Oil Fill Tube to
Transmisson Housing8-71
Bolt, Oil Fill Tube to Cyl-
inder Head8-71
Bolt, Torque Converter to
Drive Plate50 37 -
Bolt, B2 Clutch Carrier 16 - 141
Bolt, B1 Carrier to Con-
verter Housing10 - 88.5
Nut, Propeller Flange 200 147.5 -
Bolt, Electrohydraulic Unit 8 - 71
Bolt, Transmission Hous-
ing to Converter Housing20 - 177
Bolts, Oil Pan 8 - 71
Screws, Valve Body/Hous-
ing Side Cover4-35
Bolt, Shift Plate 8 - 71
Bolt, Solenoid Leaf Spring 8 - 71
Plug, Oil Pan Drain 20 - 177
Nut, Shifter Mechanism to
Floor Pan7-65
SPECIAL TOOLS - AUTOMATIC TRANSMIS-
SION - NAG1
SPECIAL TOOL CROSS REFERENCE CHART
MB
TOOL #MILLER
TOOL #DESCRIPTION
N/A C-3339 DIAL INDICATOR SET
N/A C-4171 DRIVE HANDLE
N/A 6311 GAUGE BAR
N/A 8266 END-PLAY SET
N/A 8266-18 END-PLAY ADAPTER
N/A 8863B DIPSTICK
140 586
13 43 008900 MULTI-USE SPRING
COMPRESSOR
208 589
00 21 008901 PRESSING TOOL
N/A 8902A SEAL INSTALLER
N/A 9078 STAKING TOOL
MB
TOOL #MILLER
TOOL #DESCRIPTION
N/A 9082 BEARING REMOVER
N/A 9287 BEARING INSTALLER
Dial Indicator - C-3339
VAAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21 - 87
Page 1849 of 2305

relation to the load and gear. All other pressures
required for the transmission control are derived
from the working pressure.
Lubrication Pressure (p - Sm)
At the working pressure regulating valve surplus
oil is diverted to the lubrication pressure regulating
valve, from where it is used in regulated amounts to
lubricate and cool the mechanical transmission com-
ponents and the torque converter. Furthermore, the
lubrication pressure (p-Sm) is also used to limit the
pressure in the torque converter.
Shift Pressure (p - S)
The shift pressure is determined by the shift pres-
sure regulating solenoid valve and the shift pressure
regulating valve. The shift pressure:
²Regulates the pressure in the activating shift
element during the shift phase.
²Determines together with the modulating pres-
sure the pressure reduction at the deactivating shift
element as regulated by the overlap regulating valve.
²Initializes 2nd gear in limp-home mode.
Modulating Pressure (p - Mod)
The modulating pressure influences the size of the
working pressure and determines together with the
shift pressure the pressure regulated at the overlap
regulating valve. The modulating pressure is regu-
lated at the modulating pressure regulating solenoid
valve, which is under regulating valve pressure. The
modulating pressure is variable and relative to the
engine load.
Regulating Valve / Control Valve Pressure (p - RV)
The regulating valve pressure is regulated at the
regulating valve pressure regulating valve in relation
to the working pressure (p-A) up to a maximum pres-
sure of 8 bar (116 psi). It supplies the modulating
pressure regulating solenoid valve, the shift pressure
regulating solenoid valve and the shift valve pressure
regulating valve.
Shift Valve Pressure (p - SV)
The shift valve pressure (p-SV) is derived from the
regulating valve pressure (p-RV), is regulated at the
shift valve pressure regulating valve and is then
present at the:
²1-2 and 4-5 shift solenoid valve.
²3-4 shift solenoid valve.
²2-3 shift solenoid valve.
²Torque converter lockup solenoid valve.
²3-4 and 2-3 shift pressure shift valve.
The shift valve pressure (p-SV) controls the com-
mand valves via the upshift/downshift solenoid
valves.Overlap Pressure (p - š)
The overlap pressure controls the shift component
pressure reduction during a shift phase. The pres-
sure in a shift element as it disengages is controlled
during the shift phase depending on engine load
(modulating pressure) and the pressure in the shift
element as it engages. The adjusted pressure is
inversely proportional to the transmission capability
of the shift element being engaged (controlled over-
lap).
Working Pressure Regulating Valve (Operating Pressure)
The working pressure regulating valve (4) (Fig.
101) is located in the valve housing of the shift plate.
It regulates the primary pressure of the hydraulic
system.
Fig. 101 Working Pressure Regulating Valve
1 - PRESSURE FROM K1/K2
2 - END FACE
3 - TO TORQUE CONVERTER REGULATING VALVE
4 - WORKING PRESSURE REGULATING VALVE
21 - 106 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1875 of 2305

CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
1. Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
2. A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged oil cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
3. Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
FLUID CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should be replaced whenever
a failure generates sludge and debris. This is neces-
sary because normal converter flushing procedures
will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
CHECK OIL LEVEL
(1) Verify that the vehicle is parked on a level sur-
face.
(2) Remove locking pin (1) (Fig. 149). Remove the
plate of the locking pin with a suitable tool and press
out the pin remaining in the cap downwards.
(3) Remove cap (2).
WARNING: Risk of accident from vehicle starting off
by itself when engine running. Risk of injury from
contusions and burns if you insert your hands into
the engine when it is started or when it is running.
Secure vehicle to prevent it from moving off by
itself. Wear properly fastened and close-fitting work
clothes. Do not touch hot or rotating parts.
(4) Actuate the service brake. Start engine and let
it run at idle speed in selector lever position ªPº.
(5) Shift through the transmission modes several
times with the vehicle stationary and the engine
idling
(6) Warm up the transmission, wait at least 2 min-
utes and check the oil level with the engine running.
Push the Oil Dipstick 8863A in up to the stop on the
electrohydraulic unit and pull out again, read off oil
level, repeat if necessary.
NOTE: The dipstick will protrude from the fill tube
approximately 75mm (3 inches) when installed.
Fig. 149 Remove Dipstick Tube Cap Lock
1 - LOCKING PIN
2 - TUBE CAP
3 - DIPSTICK TUBE
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1877 of 2305

To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Verify that the vehicle is parked on a level sur-
face.
(2) Remove locking pin (1) (Fig. 152). Remove the
plate of the locking pin with a suitable tool and press
out the pin remaining in the cap downwards.
(3) Remove cap (2).
(4) Add following initial quantity of required fluid
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID
TYPES - DESCRIPTION) to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add7.4
L (14.8 pts.)of transmission fluid to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add7.7 L (16.3 pts.)of trans-
mission fluid to transmission.
(5) Check the transmission fluid (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC - NAG1/FLUID AND
FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECK OIL
LEVEL) and adjust as required.
FLUID / FILTER SERVICE
(1) Run the engine until the transmission oil
reaches operating temperature.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Remove the torque converter drain plug access
plug from the bottom of the torque converter hous-
ing.
(4) Rotate the engine clockwise until the torque
converter drain plug (8) (Fig. 153) is aligned with the
access hole.
NOTE: Clean the area around the drain plug to pre-
vent dirt from entering the torque converter.
(5) Using a suitable drain pan to catch the fluid,
remove the torque converter drain plug (8) and allow
the torque converter to drain completely.
(6) Inspect the torque converter drain plug seal (9)
(Fig. 153). Replace the seal if necessary.
(7) Install the torque converter drain plug (8).
Tighten the drain plug to 14 N´m (10 ft.lbs.).
(8) Install the torque converter drain plug access
plug into the bottom of the torque converter housing.
(9) Using a suitable drain pan to catch the fluid,
remove the transmission oil pan drain plug (6) (Fig.
153) and allow the oil pan to drain completely.
(10) Inspect the transmission oil pan drain plug
seal (7). Replace the seal if necessary.
(11) Install the transmission oil pan drain plug (6).
Tighten the drain plug to 20 N´m (15 ft.lbs.).
(12) Remove the bolts (5) and retainers (4) (Fig.
153) holding the oil pan to the transmission.
(13) Remove the transmission oil pan (3) and gas-
ket (2) from the transmission.
Fig. 152 Remove Dipstick Tube Cap Lock
1 - LOCKING PIN
2 - TUBE CAP
3 - DIPSTICK TUBE
Fig. 153 Fluid/Filter Service Points
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - OIL PAN GASKET
3 - OIL PAN
4 - RETAINER
5 - BOLT
6 - OIL PAN DRAIN PLUG
7 - SEAL
8 - TORQUE CONVERTER DRAIN PLUG
9 - SEAL
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1897 of 2305

OPERATION
Signals from the input speed sensors (6, 8) (Fig.
183) are recorded in the transmission control module
(TCM) together with the wheel and engine speeds
and other information and are processed into an
input signal for electronic control.
Input speed sensor N2 (6) records the speed of the
front sun gear via the externally toothed disc carrier
of the multiple-disc clutch K1 (10) and input speed
sensor N3 (8) records the speed of the front planet
carrier via the internally toothed disc carrier of mul-
tiple-disc clutch K1 (3).
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump (2) (Fig. 184) (crescent-type pump) is
installed in the bellhousing behind the torque con-
verter and is driven by the drive flange of the torque
converter. The pump creates the oil pressure required
for the hydraulic procedures.
OPERATION
When the engine is running, the oil (Fig. 185) is
pumped through the inlet chamber (5) along the
Fig. 183 Input Speed Sensors
1 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1
2 - TRANSMISSION HOUSING
3 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 INTERNALLY TOOTHED DISC
4 - EXCITER RING
5 - VALVE HOUSING OF SHIFT PLATE
6 - N2 INPUT SPEED SENSOR
7 - SPRING
8 - N3 INPUT SPEED SENSOR
9 - EXCITER RING
10 - DRIVING CLUTCH K1 EXTERNALLY TOOTHED DISC
Fig. 184 Oil Pump
1 - CRESCENT
2 - OIL PUMP
3 - EXTERNAL GEAR
4 - INTERNAL GEAR
5 - INLET CHAMBER
6 - PRESSURE CHAMBER
Fig. 185 Oil Pump
1 - CRESCENT
2 - OIL PUMP
3 - EXTERNAL GEAR
4 - INTERNAL GEAR
5 - INLET CHAMBER
6 - PRESSURE CHAMBER
21 - 154 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA
Page 1921 of 2305

Refer to the Transmission Temperature Sensor
Specifications table (Fig. 241) for the relationship
between transmission temperature, sensor voltage,
and sensor resistance.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid.
The torque converter (Fig. 242) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine (1), a stator (3),
an overrunning clutch, an impeller (2), and an elec-
tronically applied converter clutch. The converter
clutch provides reduced engine speed and greater
fuel economy when engaged. Clutch engagement also
provides reduced transmission fluid temperatures.
The converter clutch engages in third through fifth
gears. The torque converter hub drives the transmis-
sion oil (fluid) pump.
A turbine damper (6) has been added for some
applications to help improve vehicle noise, vibration,
and harshness (NVH) characteristics.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 241 Transmission Temperature Sensor
Specifications
Fig. 242 Torque Converter
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3-STATOR
4 - INPUT SHAFT
5 - STATOR SHAFT
6 - TURBINE DAMPER
21 - 178 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATIONVA