2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 3348 of 5267

3.4C CLUTCH CIRCUIT LEAKS IN THE VALVE BODY
Turn the ignition off to the lock position.
Remove the transmission oil pan per the Service Information.
Remove the valve body per the Service Information.
Check condition of the 4C accumulator springs.
Look for possible leak paths into the 4C clutch hydraulics circuit within the valve body.
Were any problems found?
Ye s>>
Repair as necessary.
Perform 45RFE/545RFE TRANSMISSION VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 21- TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 45RFE/545RFE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Go To 4
4.AIR CHECK 4C CLUTCH CIRCUIT
Perform an air check on the 4C Clutch circuit per the Service Information.
Listen for proper 4C Clutch piston movement.
Were any problems found?
Ye s>>
Repair Internal transmission as necessary. Pay attention to the mechanical components related to the
4th clutch. A broken or weak return spring or a dislocated snap ring could cause this problem.
Perform 45RFE/545RFE TRANSMISSION VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 21- TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 45RFE/545RFE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Replace the Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly per the service information. With the scan tool, per-
form Quick Learn.
Perform 45RFE/545RFE TRANSMISSION VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 21- TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 45RFE/545RFE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
5.VERIFY PCM OPERATION
Perform eight learnable starts. A learnable start is defined as follows: Start engine. From a standstill, accelerate
lightly to 50 MPH, then brake lightly to a stop. Turn off engine.
With the scan tool, record Transmission CL VOL INDEX (CVI) for all clutches.
With the scan tool, perform a BATTERY DISCONNECT.
With the scan tool, read the CVI’s and compare them to the reading recorded before the BATTERY DISCONNECT.
Are any of the CVI’s less than 5 or are they different than before the batterydisconnect?
Ye s>>
Using the schematics as a guide, check the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)terminals for corrosion,
damage, or terminal push out. Pay particular attention to all power and ground circuits. If no problems
are found, replace the PCM per the Service Information. With the scan tool,perform QUICK LEARN.
Perform 45RFE/545RFE TRANSMISSION VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 21- TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 45RFE/545RFE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Te s t C o m p l e t e .
Page 3350 of 5267

When Monitored:
Initially at power-up, then every 10 seconds thereafter. The solenoid circuits will also be tested immediately
after a gear ratio or pressure switch error is detected.
Set Condition:
After three consecutive solenoid continuity test failures, or one failure if test is run in response to a gear ratio
or pressure switch error.Note: This DTC is strictly an electrical fault and does not apply to any internal
transmission failures.
Possible Causes
RELATED TCM POWER INPUT DTCS PRESENT
(T118) MS SOLENOID CONTROL CIRCUIT SHORT TO OTHER CIRCUITS
(T118) MS SOLENOID CONTROL CIRCUIT OPEN
(T118) MS SOLENOID CONTROL CIRCUIT SHORT TO GROUND
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
Always perform the 45RFE/545RFE Pre-Diagnostic Troubleshooting Procedure before proceeding. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 45RFE/545RFE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Theory of Operation
The Transmission Control System uses six electronically controlled solenoids that allow hydraulic fluid to be applied
to various friction elements (clutches), which enables the gear requested. The continuity of each solenoid circuit is
periodically tested. Each inactive solenoid is turned on for a few milliseconds, then off. Each active solenoid is
turned off for a few milliseconds, then on. This pulsing of voltage to the solenoid causes an inductive spike which
can be sensed by the Transmission Control System. If an inductive spike is not sensed by the Transmission Control
System during the continuity check, it is tested again. If the test fails three consecutive times, the appropriate Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) is set. If the solenoid test is run in response to agear ratio or pressure switch error, one
failure will result in setting the appropriate DTC.Note: This DTC is strictly an electrical fault and does not apply
to any internal transmission failures.
Diagnostic Test
1.RELATED TCM POWER INPUT DTCS PRESENT
With the scan tool, check for other transmission DTCs.
Are there any TCM Power Input DTCs present?
Ye s>>
Refer to the Transmission category and perform the appropriate symptom.
No>>
Go To 2
2.TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
Turn the ignition off to the lock position.
Remove the Ignition Switch Feed fuse from the TIPM.
CAUTION: Removal of the Ignition Switch Feed fuse from the TIPM will prevent the vehicle from being
startedingear.
WARNING: The Ignition Switch Feed fuse must be removed from the TIPM. Failure to do so can result in
personal injury or death.
Install Transmission Simulator, Miller tool #8333.
Ignition on, engine not running.
With the scan tool, actuate the MS Solenoid.
Page 3361 of 5267

45RFE/545RFE PRE-DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURE
For a complete wiring diagramRefer to Section 8W.
1.
Perform the following before attempting any diagnostic procedures:
Check the transmission fluid level. Ifthe fluid level is low, locate and repair any leaks and fill the transmission
to the proper level. Refer to the appropriate Service Information for procedures. Many transmission symptoms
can be caused by a low fluid level.
Check the battery. To avoid false diagnosis, testing should only be performed with the battery fully charged.
With the scan tool, read Engine (PCM) DTCs. If DTCs are present, refer to theDriveability Category and per-
form to the appropriate diagnostic procedure(s) before proceeding.
With the scan tool, read Transmission (TCM) DTCs. Record all Stored, Active, and Pending DTC information.
Diagnose any Pending DTC as a matured DTC.
With the scan tool, read DTC EVENT DATA.Use this data to identify the conditions in which the DTC was set.
Performing a Battery Disconnect will clear all DTC EVENT DATA and reset alllearned Transmission values to
the default values, which may temporarily result in erratic shift schedules.
With the scan tool, perform the Shift Lever Position Test. If the test does not pass, refer to the diagnostic
procedure for P0706 Transmission Range Sensor Rationality.
For Gear Ratio Error DTCs, use the scan tool to view CVI Monitor data. Read and record the Clutch Volume
Index information.
Use the wiring diagram as a guide. Inspect the wiring and connectors related to this circuit. Repair as neces-
sary.
Refer to the When Monitored and Set Conditions for this DTC. DTCs can set at ignition on, at start up, after
driving under specific conditions and after diagnostic monitors have beenrun.
Refer to applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) for controller software update information. Some condi-
tions can be corrected by upgrading the Engine (PCM) or Transmission (TCM)controller software.
Refer to any Service Information Tune Ups or Technical Service Bulletins that apply.
Were there any repairs made that fixed the vehicle?
Ye s>>
Testing complete.
Perform 45RFE/545RFE TRANSMISSION VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 21- TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 45RFE/545RFE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Refer to the Transmission category and perform the appropriate diagnostic procedure(s).
Page 3363 of 5267

page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE -
SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION ............................... 844
OPERATION ................................. 845
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ............... 845
PRELIMINARY ............................. 846
ROAD TESTING ........................... 846
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST............. 847
AIR CHECKING TRANSMISSION CLUTCH
OPERATION............................... 850
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAK ....... 850
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR .......................... 851
REMOVAL ................................... 851
DISASSEMBLY .............................. 854
CLEANING .................................. 860
INSPECTION ................................ 861
ASSEMBLY .................................. 861
INSTALLATION .............................. 871
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS ................. 874
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION ........................... 896
SPECIAL TOOLS
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - RFE ......... 898
RETAINER/BULKHEAD-4C
DISASSEMBLY .............................. 901
ASSEMBLY .................................. 903
SEAL-ADAPTER HOUSING
REMOVAL ................................... 906
INSTALLATION .............................. 906
SYSTEM-BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK
DESCRIPTION ............................... 907
OPERATION ................................. 907
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK ......... 907
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK ......................... 907
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.... 909
CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID ................. 909
FLUID CONTAMINATION ................... 909
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL CHECK . ..................... 909
FLUID AND FILTER REPLACEMENT ......... 911
TRANSMISSION FILL ...................... 912CABLE-GEARSHIFT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE .................................... 913
REMOVAL ................................... 913
INSTALLATION .............................. 914
ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT CABLE ......... 915
CLUTCHES-HOLDING
DESCRIPTION ............................... 916
OPERATION ................................. 917
ASSEMBLY-INPUT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION ............................... 918
OPERATION ................................. 920
DISASSEMBLY .............................. 920
ASSEMBLY .................................. 925
SENSOR-INPUT SPEED
DESCRIPTION ............................... 932
OPERATION ................................. 932
REMOVAL ................................... 932
INSTALLATION .............................. 933
SENSOR-LINE PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION ............................... 934
OPERATION ................................. 934
REMOVAL ................................... 934
INSTALLATION .............................. 935
CLUTCH-LOW/REVERSE
DISASSEMBLY .............................. 936
CLEANING .................................. 937
INSPECTION . . .............................. 937
ASSEMBLY .................................. 938
PUMP-OIL
DESCRIPTION ............................... 940
OPERATION ................................. 942
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK .......................... 942
DISASSEMBLY .............................. 943
CLEANING .................................. 945
INSPECTION . . .............................. 946
ASSEMBLY .................................. 946
SEAL-OIL PUMP FRONT
REMOVAL ................................... 950
INSTALLATION .............................. 950
SENSOR-OUTPUT SPEED
DESCRIPTION ............................... 951
OPERATION ................................. 951
REMOVAL ................................... 951
INSTALLATION .............................. 952
SWITCH-TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE
DESCRIPTION ............................... 953
OPERATION ................................. 953
REMOVAL ................................... 953
Page 3365 of 5267

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE-SERVICEINFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
The 45RFE/545RFE automatic transmissions is a sophisticated, multi-range, electronically controlled transmission
which combines optimized gear ratios for responsive performance, state of the art efficiency features and low NVH.
Other features include driver adaptive shifting and three planetary gearsets to provide wide ratio capability with
precise ratio steps for optimum driveability. The three planetary gear sets also make available a unique alternate
second gear ratio. The primary 2nd gear ratio fits between 1st and 3rd gearsfor normal through-gear accelerations.
The alternate second gear ratio (2prime) allows smoother 4-2 kickdowns athigh speeds to provide 2nd gear pass-
ing performance over a wider highway cruising range.
The hydraulic portion of the transmission consists of the transmission fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and
various line pressure control components.
The primary mechanical components of the transmission consist of the following:
Three multiple disc input clutches
Three multiple disc holding clutches
Five hydraulic accumulators
Three planetary gear sets
Dual Stage Hydraulic oil pump
Valve body
Solenoid pack
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is the “heart” or “brain” of the electronic control system and relies on infor-
mation from various direct and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.)to determine driver demand and vehicle oper-
ating conditions. Depending on the vehicle configuration, the TCM may be astandalone module or it it may be
housed along with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in a single module. With this information, the TCM can
calculate and perform timely and quality shifts through various output orcontrol devices (solenoid pack, transmission
control relay, etc.).
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped (1)
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan seal-
ing surface. Refer to this information when ordering
replacement parts. A label is attached to the transmis-
sion case above the stamped numbers. The label
gives additional information which may also be neces-
sary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS
The 45RFE gear ratios are:
Page 3366 of 5267

GEAR RATIOS
The 545RFE gear ratios are:
OPERATION
The 45RFE/545RFE offers full electronic control of all automatic up and downshifts, and features real-time adaptive
closed-loop shift and pressure control. Electronic shift and torque converter clutch controls help protect the trans-
mission from damage due to high temperatures, which can occur under severeoperating conditions. By altering shift
schedules, line pressure, and converter clutch control, these controls reduce heat generation and increase trans-
mission cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses, the transmissions includes a dual-stage transmission fluid pump
with electronic output pressure control. Under most driving conditions,pump output capacity greatly exceeds that
which is needed to keep the clutches applied. The 45RFE/545RFE pump-pressure control system monitors input
torque and adjusts the pump pressure accordingly. The primary stage of thepump works continuously; the second
stage is bypassed when demand is low. The control system also monitors input and output speed and, if incipient
clutch slip is observed, the pressure control solenoid duty cycle is varied, increasing pressure in proportion to
demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to reduce slip-
page. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce internal friction. The 45RFE/545RFE is packaged in a one-piece die-cast
aluminum case. To reduce NVH, the case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiffness. It is also designed to
maximize the benefit of the structural dust cover that connects the bottomof the bell housing to the engine bed-
plate, enhancing overall power train stiffness. Dual filters protect thepump and other components. A cooler return
filter is added to the customary main sump filter. Independent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample pressure
for normal transmission operation even if the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due to extremely low
temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without electronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK, REVERSE,
NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears, based solely on driver shift lever selection. This design allows the vehicle
to be driven (in “limp-in” mode) in the event of a electronic control systemfailure, or a situation that the Transmis-
sion Control Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic functions and provides comprehensive information (sensor data,
DTC’s, etc.) which is helpful in proper diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed with the DRB
scan
tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a RFE automatic transmission, check for Diagnostic Trouble
Codes with the scan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these general conditions:
Poor engine performance
Page 3367 of 5267

Improper adjustments
Hydraulic malfunctions
Mechanical malfunctions
Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level and con-
dition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then perform a road test to determineif the problem has been corrected or if
more diagnosis is necessary. If the problem persists after the preliminary tests and corrections are completed,
hydraulic pressure checks should be performed.
PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate procedure for
disabled vehicles (will not back up or move forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
1. Check for transmission fault codes using scan tool.
2. Check fluid level and condition.
3. Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
4. Road test and note how transmission upshifts, downshifts, and engages.
5. Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift problems were noted during roadtest.
6. Perform air-pressure test to check clutch operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
1. Check fluid level and condition.
2. Check for broken or disconnected gearshift cable.
3. Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose or missing pressure-port plugs.
4. Raise and support vehicle on safety stands, start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note following:
a. If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not, problem is with differentialor axle shafts.
b. If propeller shaft does not turn and transmission is noisy, stop engine.Remove oil pan, and check for debris.
If pan is clear, remove transmission and check for damaged driveplate, converter, oil pump, or input shaft.
c. If propeller shaft does not turn and transmission is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to determine if
problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and control cable adjustmentshave been checked and adjusted if nec-
essary. Verify that all diagnostic trouble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test. A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analysis of trans-
mission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check for shift variations and engine flare which indicates slippage.
Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed, early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means clutch, overrunning clutch, or line pressure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by comparing which internal units are applied in the various gear ranges.
The Clutch Application charts provide a basis for analyzing road test results.
45RFE CLUTCH APPLICATION CHART
Page 3368 of 5267
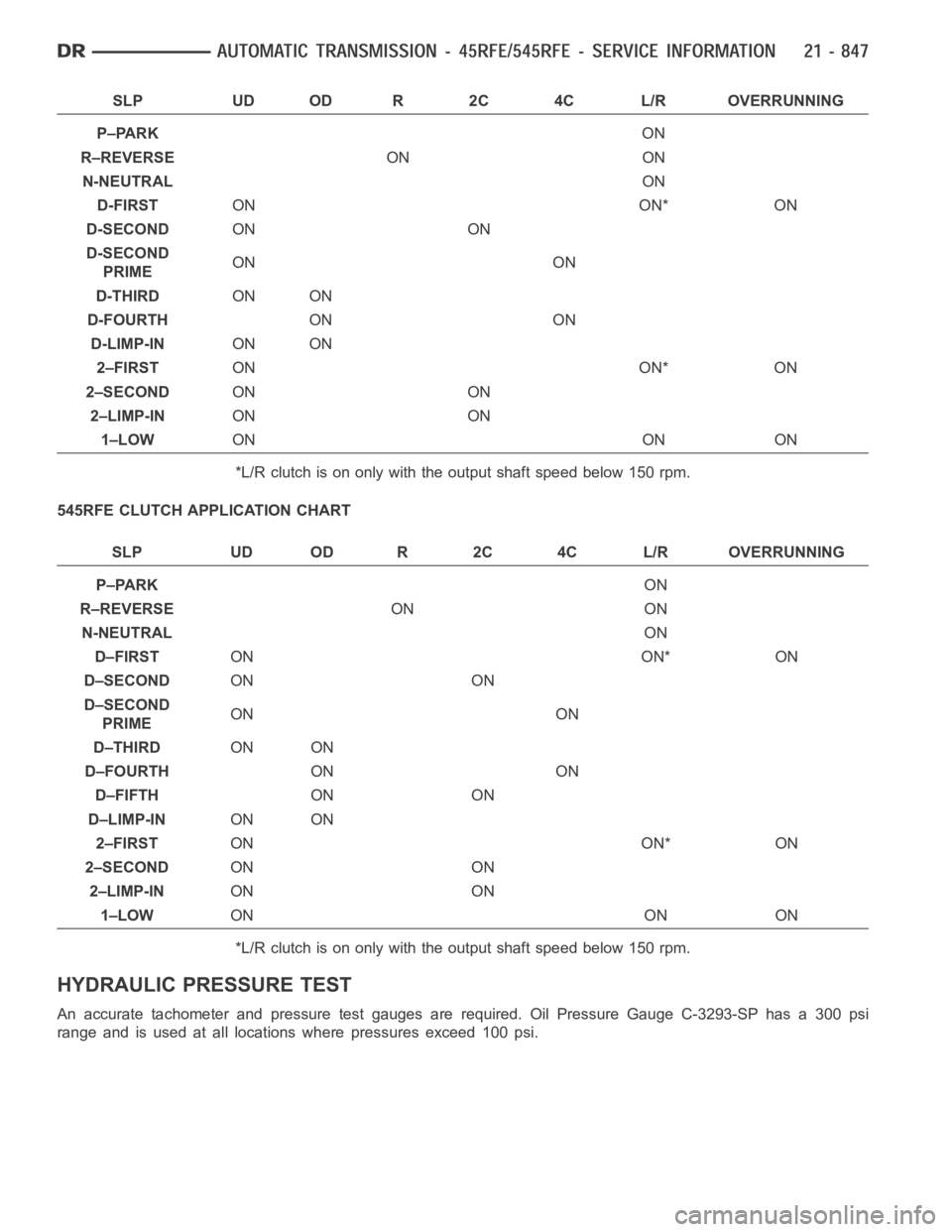
SLP UD OD R 2C 4C L/R OVERRUNNING
P–PARKON
R–REVERSEON ON
N-NEUTRALON
D-FIRSTON ON* ON
D-SECONDON ON
D-SECOND
PRIMEON ON
D-THIRDON ON
D-FOURTHON ON
D-LIMP-INON ON
2–FIRSTON ON* ON
2–SECONDON ON
2–LIMP-INON ON
1–LOWON ON ON
*L/R clutch is on only with the output shaft speed below 150 rpm.
545RFE CLUTCH APPLICATION CHART
SLP UD OD R 2C 4C L/R OVERRUNNING
P–PARKON
R–REVERSEON ON
N-NEUTRALON
D–FIRSTON ON* ON
D–SECONDON ON
D–SECOND
PRIMEON ON
D–THIRDON ON
D–FOURTHON ON
D–FIFTHON ON
D–LIMP-INON ON
2–FIRSTON ON* ON
2–SECONDON ON
2–LIMP-INON ON
1–LOWON ON ON
*L/R clutch is on only with the output shaft speed below 150 rpm.
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges are required. Oil Pressure Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at all locations where pressures exceed 100 psi.